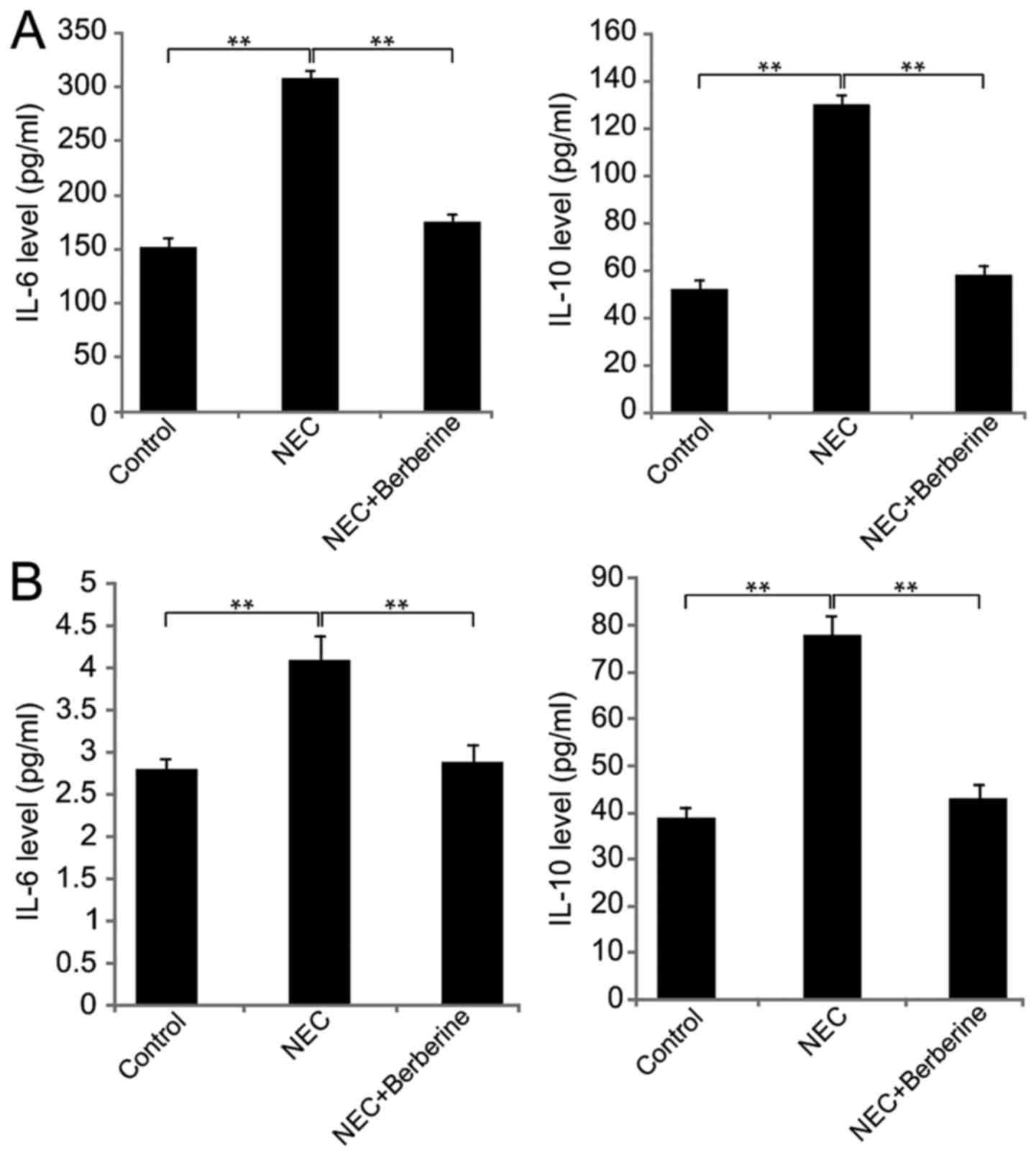
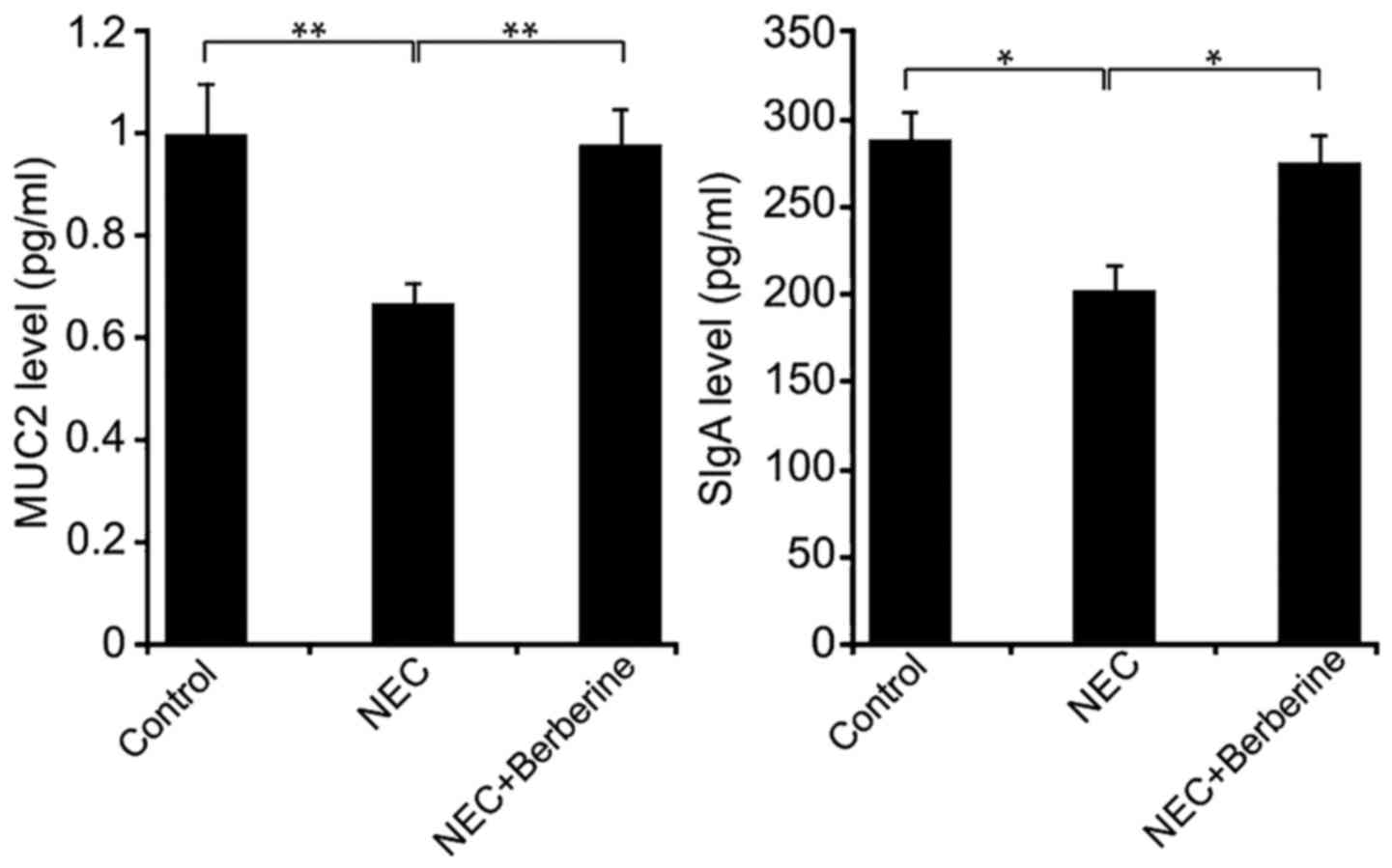
|
1
|
Hackam DJ and Sodhi CP: Toll-like
receptor-mediated intestinal inflammatory imbalance in the
pathogenesis of necrotizing enterocolitis. Cell Mol Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 6:229–238.e1. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Halpern MD and Denning PW: The role of
intestinal epithelial barrier function in the development of NEC.
Tissue Barriers. 3:e10007072015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dvorak B, Halpern MD, Holubec H, Williams
CS, McWilliam DL, Dominguez JA, Stepankova R, Payne CM and McCuskey
RS: Epidermal growth factor reduces the development of necrotizing
enterocolitis in a neonatal rat model. Am J Physiol Gastrointest
Liver Physiol. 282:G156–G164. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu T, Zhang L, Joo D and Sun SC: NF-κB
signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
2:2017.
|
|
6
|
Martin NA, Mount Patrick SK, Estrada TE,
Frisk HA, Rogan DT, Dvorak B and Halpern MD: Active transport of
bile acids decreases mucin 2 in neonatal ileum: Implications for
development of necrotizing enterocolitis. PLoS One. 6:e271912011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tian F, Liu GR, Li N and Yuan G: YUAN4
insulin-like growth factor I reduces the occurrence of necrotizing
enterocolitis by reducing inflammatory response and protecting
intestinal mucosal barrier in neonatal rats model. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 21:4711–4719. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Garg BD, Sharma D and Bansal A: Biomarkers
of necrotizing enterocolitis: A review of literature. J Matern
Fetal Neonatal Med. 31:3051–3064. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rai SE, Sidhu AK and Krishnan RJ:
Transfusion-associated necrotizing enterocolitis re-evaluated: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. J Perinat Med. 46:665–676.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
De Plaen IG: Inflammatory signaling in
necrotizing enterocolitis. Clin Perinatol. 40:109–124. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Frost BL, Jilling T and Caplan MS: The
importance of pro-inflammatory signaling in neonatal necrotizing
enterocolitis. Semin Perinatol. 32:100–106. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
MohanKumar K, Namachivayam K,
Chapalamadugu KC, Garzon SA, Premkumar MH, Tipparaju SM and
Maheshwari A: Smad7 interrupts TGF-β signaling in intestinal
macrophages and promotes inflammatory activation of these cells
during necrotizing enterocolitis. Pediatr Res. 79:951–961. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Claud EC: Neonatal necrotizing
enterocolitis-inflammation and intestinal immaturity. Antiinflamm
Antiallergy Agents Med Chem. 8:248–259. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zani A and Pierro A: Necrotizing
enterocolitis: Controversies and challenges. F1000Res. 4:F1000
Faculty Rev. –1373. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Maheshwari A, Schelonka RL, Dimmitt RA,
Carlo WA, Munoz-Hernandez B, Das A, McDonald SA, Thorsen P,
Skogstrand K, Hougaard DM, et al: Cytokines associated with
necrotizing enterocolitis in extremely-low-birth-weight infants.
Pediatr Res. 76:100–108. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Benkoe T, Baumann S, Weninger M, Pones M,
Reck C, Rebhandl W and Oehler R: Comprehensive evaluation of 11
cytokines in premature infants with surgical necrotizing
enterocolitis. PLoS One. 8:e587202013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Habtemariam S: Berberine and inflammatory
bowel disease: A concise review. Pharmacol Res. 113:592–599. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cicero AF and Baggioni A: Berberine and
its role in chronic disease. Adv Exp Med Biol. 928:27–45. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhou X, Ren F, Wei H, Liu L, Shen T, Xu S,
Wei J, Ren J and Ni H: Combination of berberine and evodiamine
inhibits intestinal cholesterol absorption in high fat diet induced
hyperlipidemic rats. Lipids Health Dis. 16:2392017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shinyama S, Kaji T, Mukai M, Nakame K,
Matsufuji H, Takamatsu H and Ieiri S: The novel preventive effect
of Daikenchuto (TJ-100), a Japanese herbal drug, against neonatal
necrotizing enterocolitis in rats. Pediatr Surg Int. 33:1109–1114.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Patel RM and Underwood MA: Probiotics and
necrotizing enterocolitis. Semin Pediatr Surg. 27:39–46. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Harpavat S, Pammi M and Gilger M: Novel
treatments for NEC: Keeping IBD in mind. Curr Gastroenterol Rep.
14:373–379. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jiang F, Meng D, Weng M, Zhu W, Wu W,
Kasper D and Walker WA: The symbiotic bacterial surface factor
polysaccharide A on Bacteroides fragilis inhibits IL-1beta-induced
inflammation in human fetal enterocytes via toll receptors 2 and 4.
PLoS One. 12:e01727382017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dolasia K, Bisht MK, Pradhan G, Udgata A
and Mukhopadhyay S: TLRs/NLRs: Shaping the landscape of host
immunity. Int Rev Immunol. 37:3–19. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mohammadi S, Seyedhoseini FS, Asadi J and
Yazdani Y: Effects of berberine on the secretion of cytokines and
expression of genes involved in cell cycle regulation in THP-1
monocytic cell line. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 20:530–537.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fang C, Xie L, Liu C, Fu C, Ye W, Liu H
and Zhang B: Berberine ameliorates neonatal necrotizing
enterocolitis by activating the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein
kinase B signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med. 15:3530–3536.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nanthakumar N, Meng D, Goldstein AM, Zhu
W, Lu L, Uauy R, Llanos A, Claud EC and Walker WA: The mechanism of
excessive intestinal inflammation in necrotizing enterocolitis: An
immature innate immune response. PLoS One. 6:e177762011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Dong XS, Xu XY, Sun YQ, Wei-Liu, Jiang ZH
and Liu Z: Toll-like receptor 4 is involved in myocardial damage
following paraquat poisoning in mice. Toxicology. 312:115–122.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hong JT: NF-kB as a mediator of brain
inflammation in AD. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2017.
|
|
30
|
Liu Q, Xu D, Jiang S, Huang J, Zhou F,
Yang Q, Jiang S and Yang L: Toll-receptor 9 gene in the black tiger
shrimp (Penaeus monodon) induced the activation of the
TLR-NF-κB signaling pathway. Gene. 639:27–33. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Qi W, Shen Q, Zhang L, Han LP and Wang S:
Study on the inflammatory intervention of erythropoietin on NEC.
Exp Ther Med. 11:2221–2224. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Satoh T, Izumi H, Iwabuchi N, Odamaki T,
Namba K, Abe F and Xiao JZ: Bifidobacterium breve prevents
necrotising enterocolitis by suppressing inflammatory responses in
a preterm rat model. Benef Microbes. 7:75–82. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sicard JF, Le Bihan G, Vogeleer P, Jacques
M and Harel J: Interactions of intestinal bacteria with components
of the intestinal mucus. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 7:3872017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Betge J, Schneider NI, Harbaum L,
Pollheimer MJ, Lindtner RA, Kornprat P, Ebert MP and Langner C:
MUC1, MUC2, MUC5AC, and MUC6 in colorectal cancer: Expression
profiles and clinical significance. Virchows Arch. 469:255–265.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chatterton DE, Nguyen DN, Bering SB and
Sangild PT: Anti-inflammatory mechanisms of bioactive milk proteins
in the intestine of newborns. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
45:1730–1747. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|