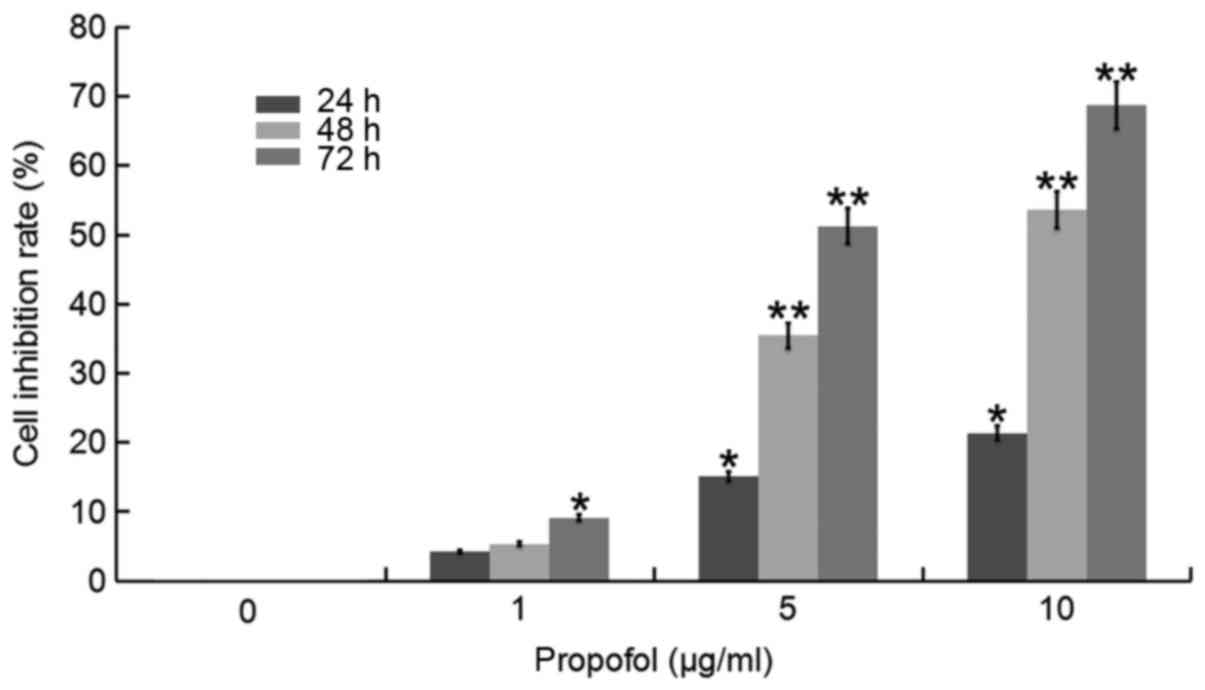
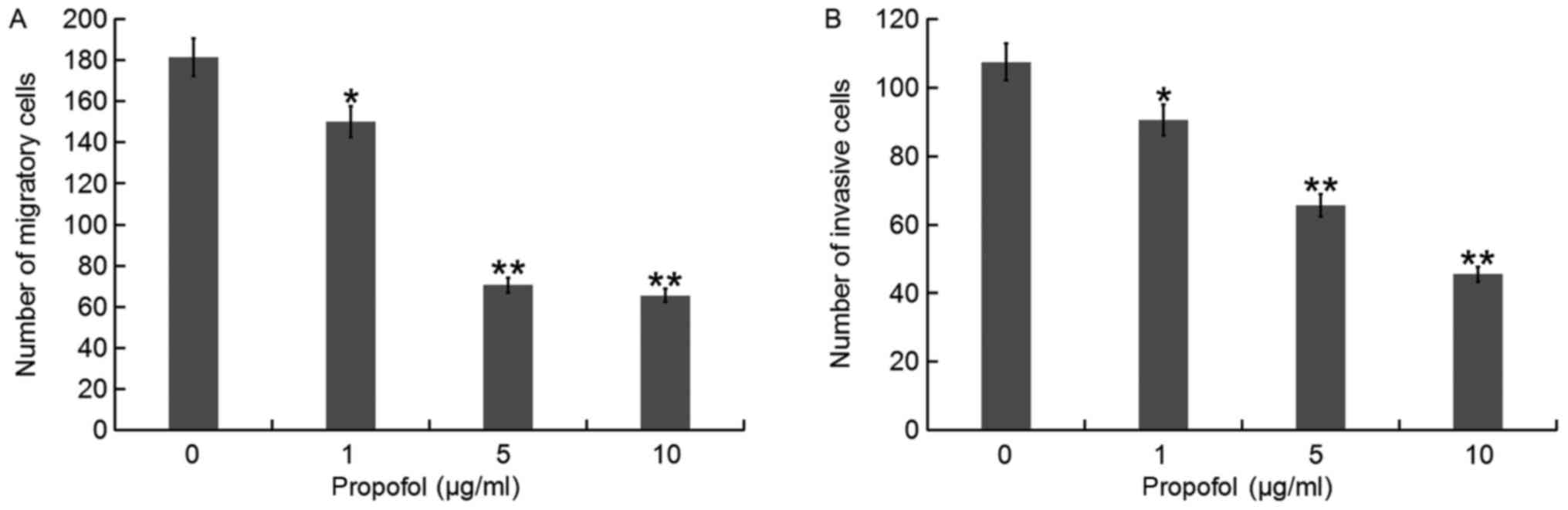
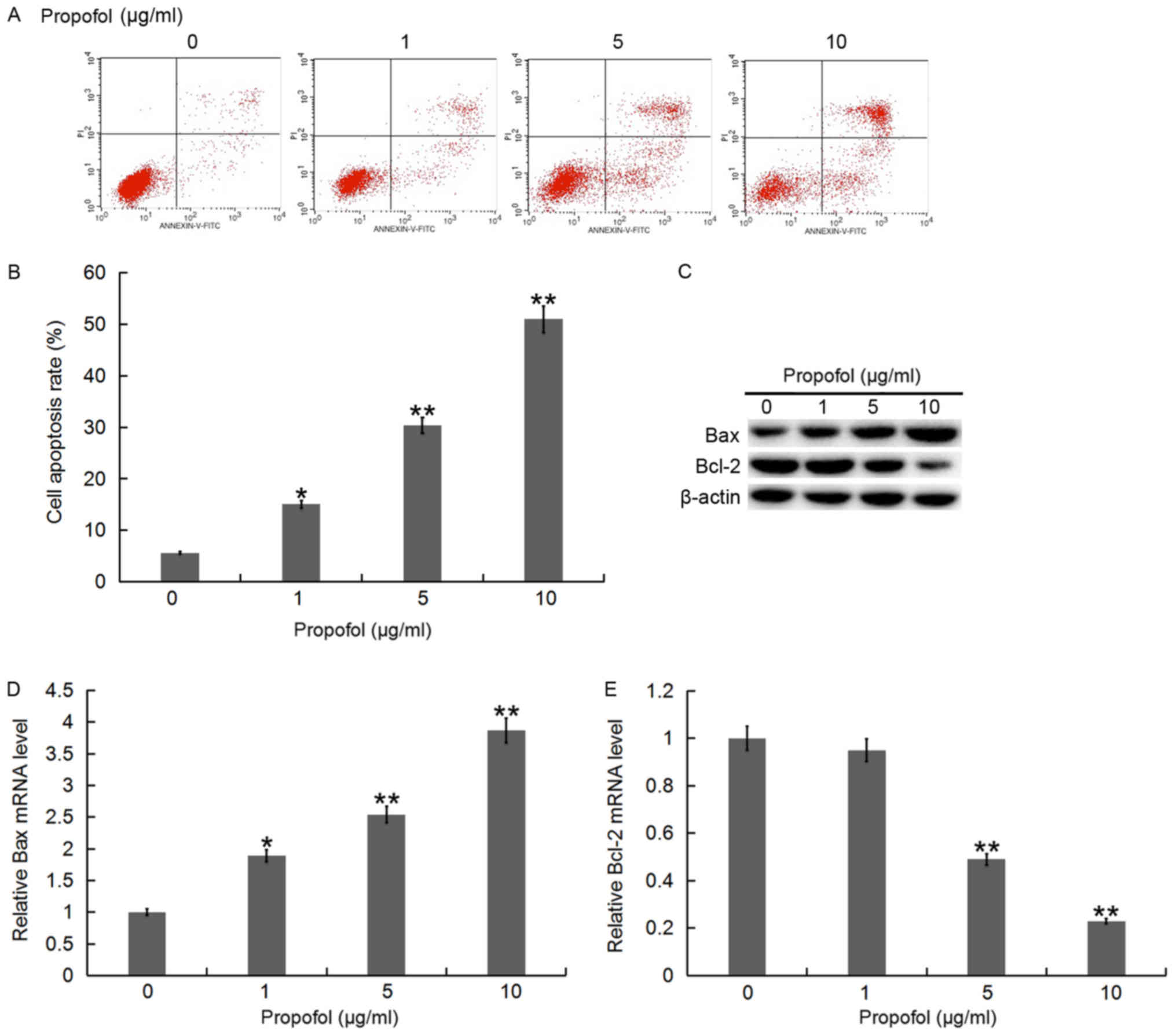
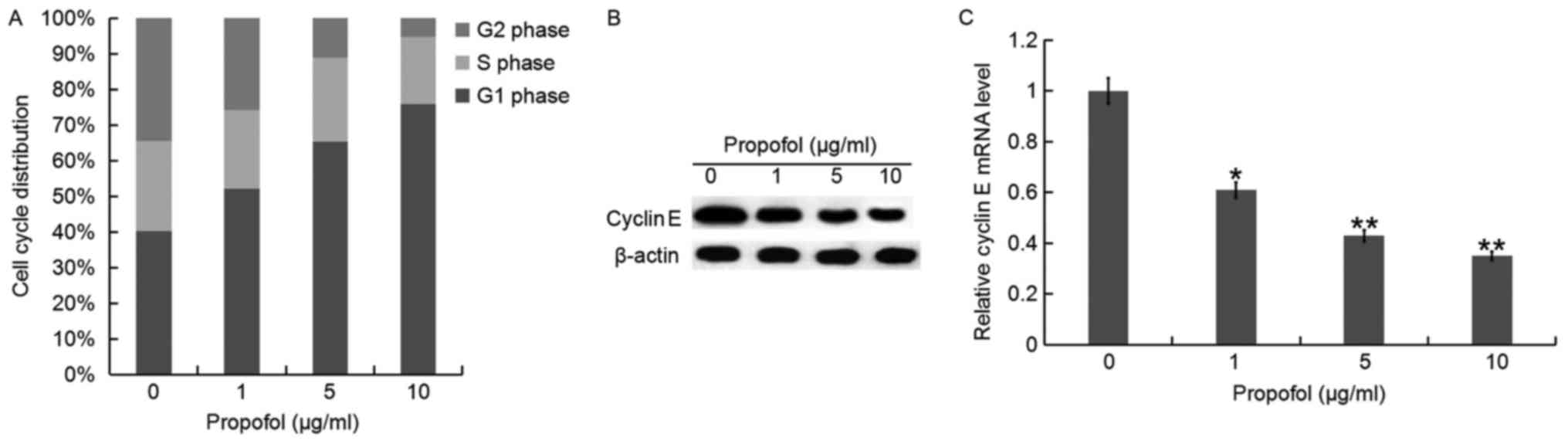
|
1
|
Khan SA, Davidson BR, Goldin RD, Heaton N,
Karani J, Pereira SP, Rosenberg WM, Tait P, Taylor-Robinson SD,
Thillainayagam AV, et al: Guidelines for the diagnosis and
treatment of cholangiocarcinoma: An update. Gut. 61:1657–1669.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Blechacz B and Gores GJ:
Cholangiocarcinoma: Advances in pathogenesis, diagnosis, and
treatment. Hepatology. 48:308–321. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shaib YH, Davila JA, Mcglynn K and
El-Serag HB: Rising incidence of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in
the United States: A true increase? J Hepatol. 40:472–477. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Landis SH, Murray T, Bolden S and Wingo
PA: Cancer statistics, 1998. Ca Cancer J Clin. 48:6–29. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Wang Q, Du T and Lu C: Perioperative blood
transfusion and the clinical outcomes of patients undergoing
cholangiocarcinoma surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 28:1233–1240. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yuan D, Huang S, Berger E, Liu L, Gross N,
Heinzmann F, Ringelhan M, Connor TO, Stadler M, Meister M, et al:
Kupffer cell-derived Tnf triggers cholangiocellular tumorigenesis
through JNK due to chronic mitochondrial dysfunction and ROS.
Cancer Cell. 31:771–789. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rahnemai-Azar AA, Weisbrod AB, Dillhoff M,
Schmidt C and Pawlik TM: Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: Current
management and emerging therapies. Expert Rev Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 11:439–449. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen X, Wu Q, Sun P, Zhao Y, Zhu M and
Miao C: Propofol disrupts aerobic glycolysis in colorectal cancer
cells via inactivation of the NMDAR-CAMKII-ERK Pathway. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 46:492–504. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cockshott ID, Briggs LP, Douglas EJ and
White M: Pharmacokinetics of propofol in female patients. Studies
using single bolus injections. Br J Anaesth. 59:1103–1110. 1987.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Buckley A, McQuaid S, Johnson P and Buggy
DJ: Effect of anaesthetic technique on the natural killer cell
anti-tumour activity of serum from women undergoing breast cancer
surgery: A pilot study. Br J Anaesth. 113:56–62. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zhang T, Fan Y, Liu K and Wang Y: Effects
of different general anaesthetic techniques on immune responses in
patients undergoing surgery for tongue cancer. Anaesth Intensive
Care. 42:220–227. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jaura AI, Flood G, Gallagher HC and Buggy
DJ: Differential effects of serum from patients administered
distinct anaesthetic techniques on apoptosis in breast cancer cells
in vitro: A pilot study. Br J Anaesth. 113:63–67. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ecimovic P, McHugh B, Murray D, Doran P
and Buggy DJ: Effects of sevoflurane on breast cancer cell function
in vitro. Anticancer Res. 33:4255–4260. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kurosawa S and Kato M: Anesthetics, immune
cells, and immune responses. J Anesth. 22:263–277. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Siddiqui RA, Zerouga M, Wu M, Wu M,
Castillo A, Harvey K, Zaloga GP and Stillwell W: Anticancer
properties of propofol-docosahexaenoate and
propofol-eicosapentaenoate on breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer
Res. 7:R645–R654. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wu KC, Yang ST, Hsia TC, Yang JS, Chiou
SM, Lu CC, Wu RS and Chung JG: Suppression of cell invasion and
migration by propofol are involved in down-regulating matrix
metalloproteinase-2 and p38 MAPK signaling in A549 human lung
adenocarcinoma epithelial cells. Anticancer Res. 32:4833–4842.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Qian J, Shen S, Chen W and Chen N:
Propofol reversed Hypoxia-induced docetaxel resistance in prostate
cancer cells by preventing epithelial-Mesenchymal transition by
inhibiting hypoxia-Inducible factor 1α. Biomed Res Int.
2018:41742322018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li Q, Zhang L, Han Y, Jiang Z and Wang Q:
Propofol reduces MMPs expression by inhibiting NF-kB activity in
human MDA-MB-231 cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 66:52–56. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Meng C, Song L, Wang J, Li D, Liu Y and
Cui X: Propofol induces proliferation partially via downregulation
of p53 protein and promotes migration via activation of the Nrf2
pathway in human breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231. Oncol Rep.
37:841–848. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Huang X, Teng Y, Yang H and Ma J: Propofol
inhibits invasion and growth of ovarian cancer cells via regulating
miR-9/NF-κB signal. Braz J Med Biol Res. 49:e57172016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Liu XF, Tang K, Sui LL and Xu G:
Cholangiocarcinoma: Present status and molecular aspects of
diagnosis. Onco Res. 22:177–183. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
El Chafic AH, Dewitt J, Leblanc JK, El
Hajj II, Cote G, House MG, Sherman S, McHenry L, Pitt HA, Johnson
C, et al: Impact of preoperative endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine
needle aspiration on postoperative recurrence and survival in
cholangiocarcinoma patients. Endoscopy. 45:883–889. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jeong S, Zheng B, Wang J, Chi J, Tong Y,
Xia L, Xu N, Zhang J, Kong X, Gu J and Xia Q: Transarterial
chemoembolization: A favorable postoperative management to improve
prognosis of hepatitis B virus-associated intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma after surgical resection. Int J Biol Sci.
13:1234–1241. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kovalenko YA, Vishnevsky VA, Chzhao AV and
Zharikov YO: New criteria of radical surgery and long-term outcomes
of hilar cholangiocarcinomamanagement (Russian). Khirurgiia (Mosk).
4–11. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yao D, Kunam VK and Li X: A review of the
clinical diagnosis and therapy of cholangiocarcinoma. J Int Med
Res. 42:3–16. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Deng F, Ouyang M, Wang X, Yao X, Chen Y,
Tao T, Sun X, Xu L, Tang J and Zhao L: Differential role of
intravenous anesthetics in colorectal cancer progression:
Implications for clinical application. Oncotarget. 7:77087–77095.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ecimovic P, Murray D, Doran P and Buggy
DJ: Propofol and bupivacaine in breast cancer cell function in
vitro-role of the NET1 gene. Anticancer Res. 34:1321–1331.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Peng Z and Zhang Y: Propofol inhibits
proliferation and accelerates apoptosis of human gastric cancer
cells by regulation of microRNA-451 and MMP-2 expression. Genet Mol
Res. 15:2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Mammoto T, Mukai M, Mammoto A, Yamanaka Y,
Hayashi Y, Mashimo T, Kishi Y and Nakamura H: Intravenous
anaesthetic, propofol inhibits invasion of cancer cells. Cancer
Lett. 184:165–170. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen X, Wu Q, You L, Chen S, Zhu M and
Miao C: Propofol attenuates pancreatic cancer malignant potential
via inhibition of NMDA receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 795:150–159.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen X, Lu P, Chen L, Yang SJ, Shen HY, Yu
DD, Zhang XH, Zhong SL, Zhao JH and Tang JH: Perioperative
propofol-paravertebral anesthesia decreases the metastasis and
progression of breast cancer. Tumour Biol. 36:8259–8266. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Xu YJ, Li SY, Cheng Q, Chen WK, Wang SL,
Ren Y and Miao CH: Effects of anaesthesia on proliferation,
invasion and apoptosis of LoVo colon cancer cells in vitro.
Anaesthesia. 71:147–154. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang ZT, Gong hY, Zheng F, Liu DJ and Yue
XQ: Propofol suppresses proliferation and invasion of gastric
cancer cells via downregulation of microRNA-221 expression. Genet
Mol Res. 14:8117–8124. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang D, Zhou XH, Zhang J, Zhou YX, Ying
J, Wu GQ and Qian JH: Propofol promotes cell apoptosis via
inhibiting HOTAIR mediated mTOR pathway in cervical cancer. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 468:561–567. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang L, Wang N, Zhou S, Ye W, Jing G and
Zshang M: Propofol induces proliferation and invasion of
gallbladder cancer cells through activation of Nrf2. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 31:662012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu Z, Zhang J, Hong G, Quan J, Zhang L
and Yu M: Propofol inhibits growth and invasion of pancreatic
cancer cells through regulation of the miR-21/Slug signaling
pathway. Am J Transl Res. 8:4120–4133. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Guo Q, Shen S, Liao M, Lian P and Wang X:
NGX6 inhibits cell invasion and adhesion through suppression of
Wnt/β-catenin signal pathway in colon cancer. Acta Biochim Biophys
Sin (Shanghai). 42:450–456. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Mohammed MK, Shao C, Wang J, Wei Q, Wang
X, Collier Z, Tang S, Liu H, Zhang F, Huang J, et al: Wnt/β-catenin
signaling plays an ever-expanding role in stem cell self-renewal,
tumorigenesis and cancer chemoresistance. Genes Dis. 3:11–40. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|