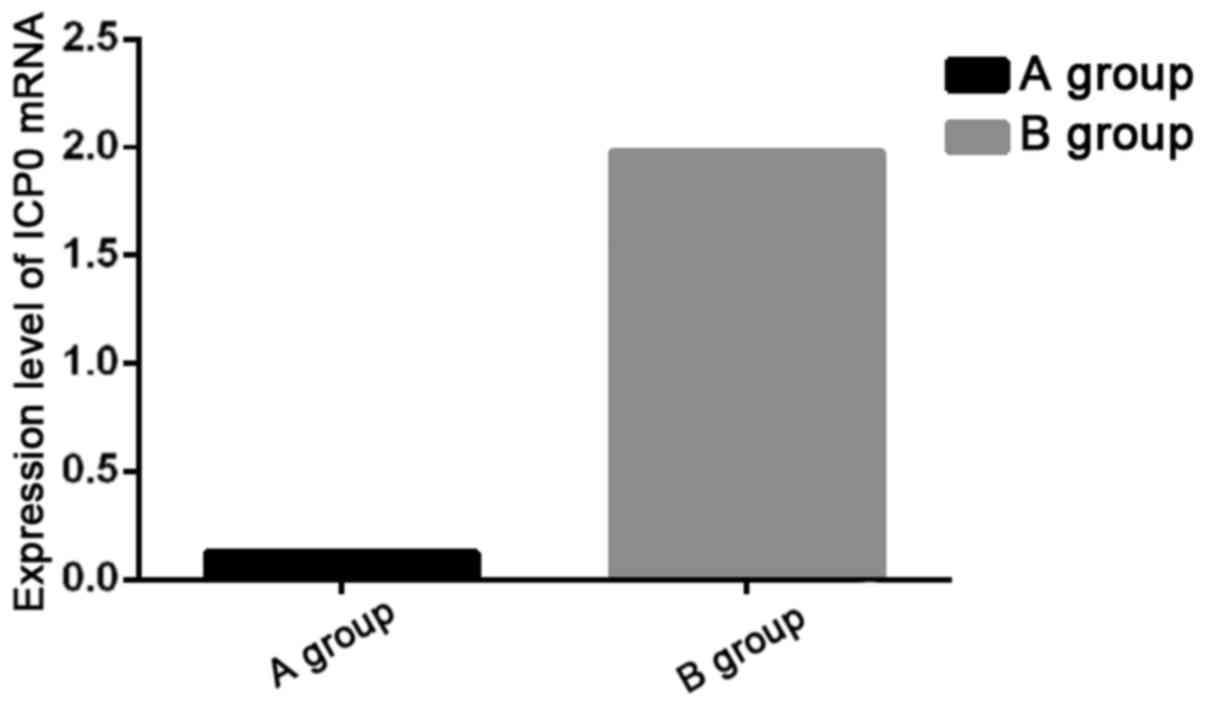
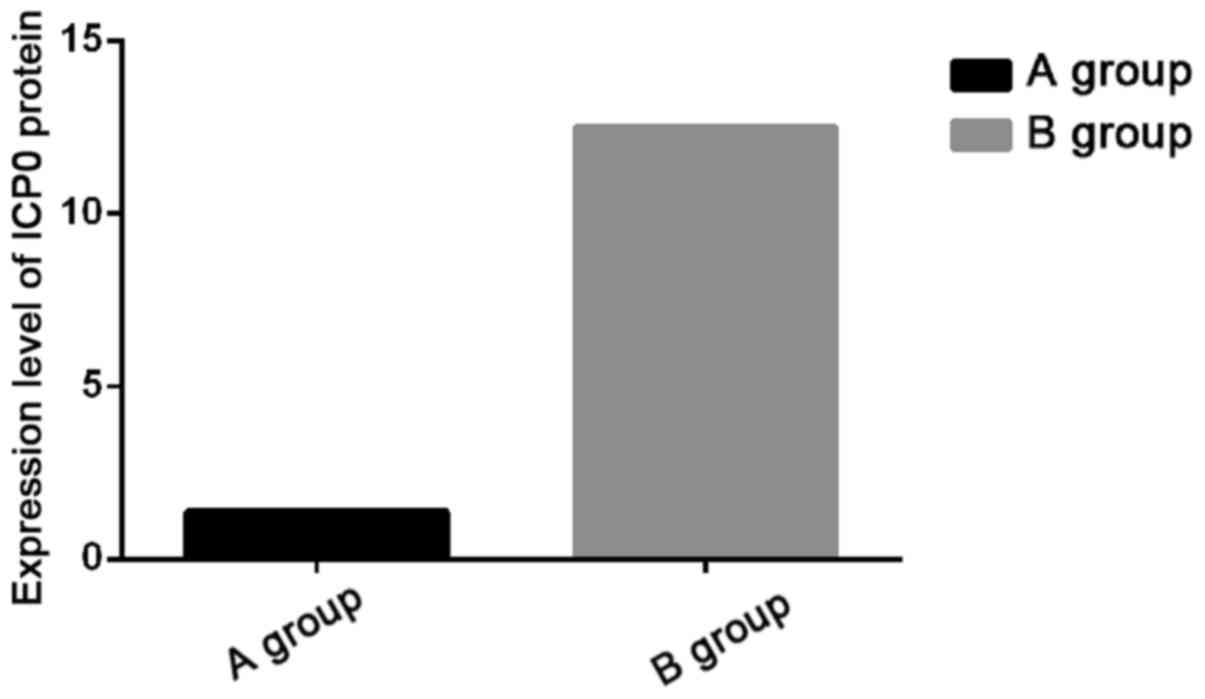
|
1
|
Armangue T, Leypoldt F, Málaga I,
Raspall-Chaure M, Marti I, Nichter C, Pugh J, Vicente-Rasoamalala
M, Lafuente-Hidalgo M, Macaya A, et al: Herpes simplex virus
encephalitis is a trigger of brain autoimmunity. Ann Neurol.
75:317–323. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cockle JV, Ilett E, Brüningrichardson A,
Scott K, Picton S, Short S and Melcher A: OP03 oncolytic herpes
simplex virus inhibits paediatric high grade glioma and diffuse
intrinsic pontine glioma migration and invasion; Mechanism and
potential for clinical application. Neuro-Oncology.
17:viii16.3–viii16. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Looker KJ, Magaret AS, Turner KM,
Vickerman P, Gottlieb SL and Newman LM: Correction: Global
estimates of prevalent and incident herpes simplex virus type 2
infections in 2012. PLoS One. 10:e01286152015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pan D, Flores O, Umbach JL, Pesola JM,
Bentley P, Rosato PC, Leib DA, Cullen BR and Coen DM: A
neuron-specific host microRNA targets herpes simplex virus-1 ICP0
expression and promotes latency. Cell Host Microbe. 15:446–456.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ha M and Kim VN: Regulation of microRNA
biogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:509–524. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lingam S, Beta M, Dendukuri D and
Krishnakumar S: A focus on microfluidics and nanotechnology
approaches for the ultra sensitive detection of microRNA. MicroRNA.
3:18–28. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Coleman JR, Papamichail D, Skiena S,
Futcher B, Wimmer E and Mueller S: Virus attenuation by
genome-scale changes in codon pair bias. Science. 320:1784–1787.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sharma S, Hussain S, Soni K, Singhal P,
Tripathi R, Ramachandran VG, Sharma S, Das S, Pillai B and
Bharadwaj M: Novel MicroRNA signatures in HPV-mediated cervical
carcinogenesis in Indian women. Tumour Biol. 37:4585–4595. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Boutell C and Everett RD: Regulation of
alphaherpesvirus infections by the ICP0 family of proteins. J Gen
Virol. 94:465–481. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Orzalli MH, Broekema NM and Knipe DM:
Relative contributions of herpes simplex virus 1 ICP0 and VHS to
loss of cellular IFI16 vary in different human cell types. J Virol.
90:8351–8359. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Heiligenhaus A, Li HF, Yang Y, Wasmuth S,
Steuhl KP and Bauer D: Transplantation of amniotic membrane in
murine herpes stromal keratitis modulates matrix metalloproteinases
in the cornea. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 46:4079–4085. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hacohen Y, Deiva K, Pettingill P, Waters
P, Siddiqui A, Chretien P, Menson E, Lin JP, Tardieu M, Vincent A,
et al: N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antibodies in post-herpes
simplex virus encephalitis neurological relapse. Mov Disord.
29:90–96. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bradley H, Markowitz LE, Gibson T and
McQuillan GM: Seroprevalence of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2
- United States, 1999-2010. J Infect Dis. 209:325–333. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mohammad SS, Sinclair K, Pillai S, Merheb
V, Aumann TD, Gill D, Dale RC and Brilot F: Herpes simplex
encephalitis relapse with chorea is associated with autoantibodies
to N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor or dopamine-2 receptor. Mov
Disord. 29:117–122. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Orzalli MH, Broekema NM, Diner BA, Hancks
DC, Elde NC, Cristea IM and Knipe DM: cGAS-mediated stabilization
of IFI16 promotes innate signaling during herpes simplex virus
infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:E1773–E1781. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pare JM and Sullivan CS: A host MicroRNA
brokers truce with HSV-1. Cell Host Microbe. 15:395–397. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Guo YE and Steitz JA: Virus meets host
microRNA: The destroyer, the booster, the hijacker. Mol Cell Biol.
34:3780–3787. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|