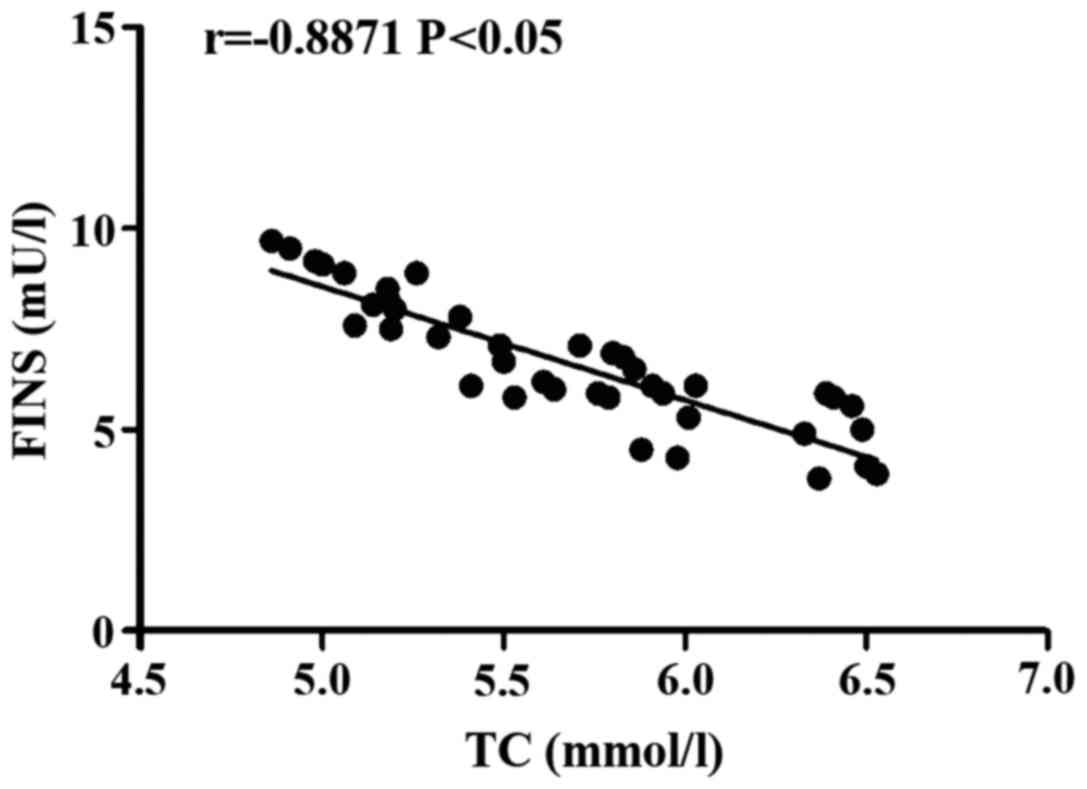
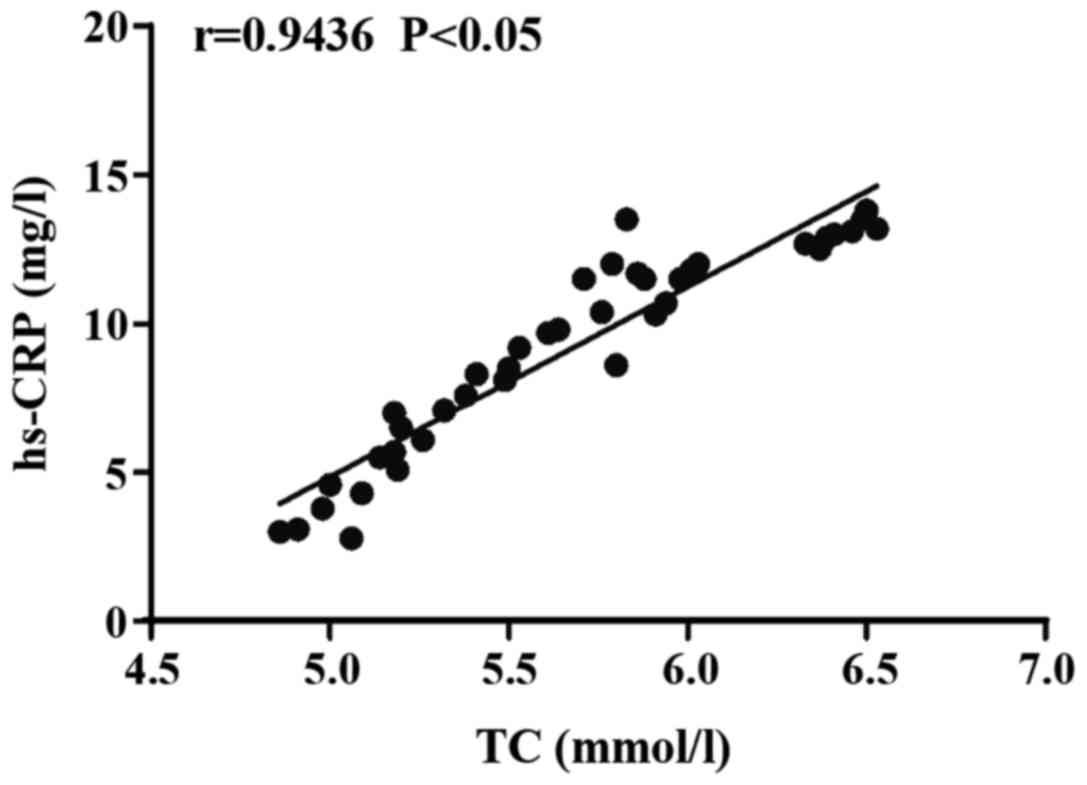
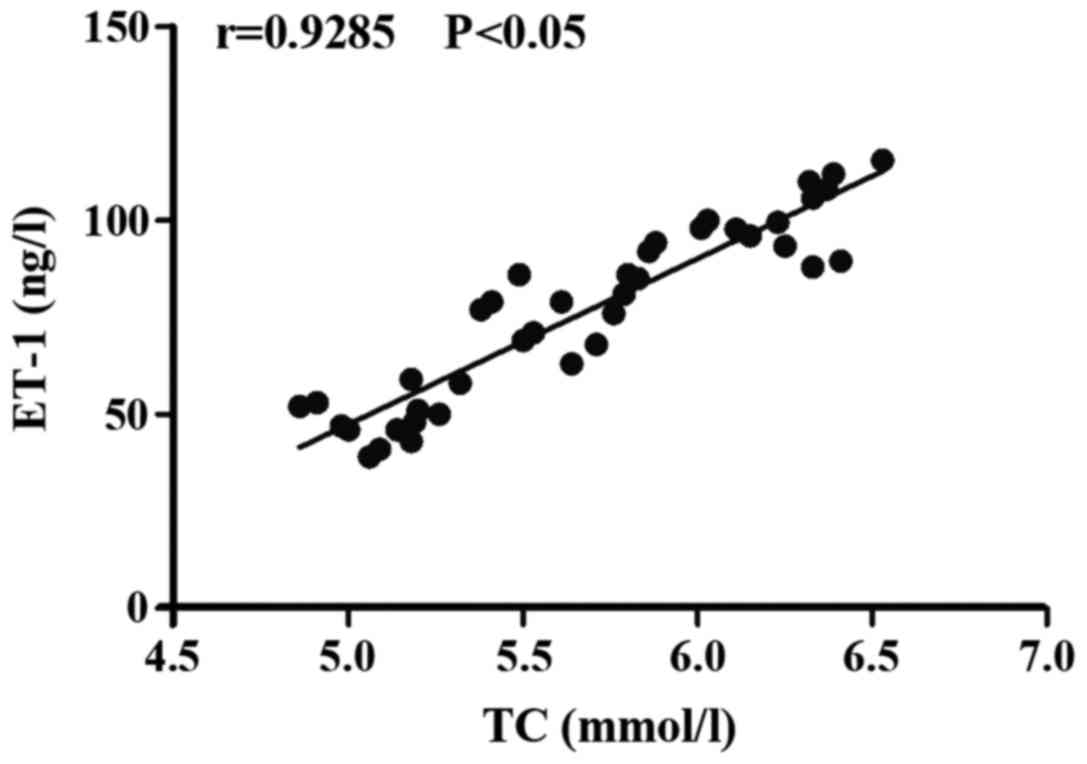
|
1
|
Foley TR, Singh GD, Kokkinidis DG, Choy
HK, Pham T, Amsterdam EA, Rutledge JC, Waldo SW, Armstrong EJ and
Laird JR: High-intensity statin therapy is associated with improved
survival in patients with peripheral artery disease. J Am Heart
Assoc. 6:e0056992017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liang M, Yang S and Fu N: Efficacy of
short-term moderate or high-dose rosuvastatin in preventing
contrast-induced nephropathy: A meta-analysis of 15 randomized
controlled trials. Medicine (Baltimore). 96:e73842017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kwon O, Kang SJ, Kang SH, Lee PH, Yun SC,
Ahn JM, Park DW, Lee SW, Kim YH, Lee CW, et al: Relationship
between serum inflammatory marker levels and the dynamic changes in
coronary plaque characteristics after statin therapy. Circ
Cardiovasc Imaging. 10:e0059342017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Roy S, Weinstock JL, Ishino AS, Benites
JF, Pop SR, Perez CD, Gumbs EA, Rosenbaum JA, Roccato MK, Shah H,
et al: Association of cognitive impairment in patients on
3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-CoA reductase inhibitors. J Clin Med
Res. 9:638–649. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ovrakh T, Serik S and Kochubiei O: Impact
of atorvastatin and rosuvastatin on residual on-clopidogrel
treatment platelet reactivity in patients with ischemic heart
disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus after acute coronary syndrome.
Georgian Med News. 4:7–14. 2017.(In Russian).
|
|
6
|
Jellinger PS, Handelsman Y, Rosenblit PD,
Bloomgarden ZT, Fonseca VA, Garber AJ, Grunberger G, Guerin CK,
Bell DSH, Mechanick JI, et al: American Association of Clinical
Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology guidelines
for management of dyslipidemia and prevention of cardiovascular
disease. Endocr Pract. 23 Suppl 2:1–87. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang W, Yi L, Jin C, Xu S, Bi X, Zhao Y,
Qiu F, Fu G and Min W: The impact of rosuvastatin on the density
score of coronary artery calcification in coronary artery disease
patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: Rationale and design of
RosCal Study. Clin Drug Investig. 36:1023–1029. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ullah F, Afridi AK, Rahim F, ur Rahman S
and Ashfaq M: Efficacy of 5 mg and 10 mg rosuvastatin in type-2
diabetes mellitus with hypercholesteroalemia. J Ayub Med Coll
Abbottabad. 27:564–568. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xiong X, Liu H, Hua L, Zhao H, Wang D and
Li Y: The association of HDL-apoCIII with coronary heart disease
and the effect of statin treatment on it. Lipids Health Dis.
14:1272015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gungoren F, Besli F, Caliskan S, Polat U,
Basar C and Serdar OA: Statin therapy may not effect NLR and MPV
levels in patients with hypercholesterolemia: A retrospective
study. Angiology. 67:536–540. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Koshelskaia OA, Vinnitskaia IV, Konko TI,
Kravchenko ES, Suslova TE and Karpov RS: Comparative randomized
study of the effects of long-term therapy with rosuvastatin and
combination of atorvastatin and ezetimibe on carbohydrate
metabolism and adipokines levels in patients with coronary artery
disease and diabetes mellitus. Kardiologiia. 55:67–74. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Terao Y, Satomi-Kobayashi S, Hirata K and
Rikitake Y: Involvement of Rho-associated protein kinase (ROCK) and
bone morphogenetic protein-binding endothelial cell
precursor-derived regulator (BMPER) in high glucose-increased
alkaline phosphatase expression and activity in human coronary
artery smooth muscle cells. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 14:1042015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Suthar KS, Vanikar AV and Trivedi HL:
Acute kidney injury and quadriparesis due to rosuvastatin induced
rhabdomyolysis - a case report. J Clin Diagn Res. 9:OD08–OD09.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Laires PA, Ejzykowicz F, Hsu TY,
Ambegaonkar B and Davies G: Cost-effectiveness of adding ezetimibe
to atorvastatin vs switching to rosuvastatin therapy in Portugal. J
Med Econ. 18:565–572. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Laufs U, Gertz K, Dirnagl U, Böhm M,
Nickenig G and Endres M: Rosuvastatin, a new HMG-CoA reductase
inhibitor, upregulates endothelial nitric oxide synthase and
protects from ischemic stroke in mice. Brain Res. 942:23–30. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Halcox JP, Tubach F, Lopez-Garcia E, De
Backer G, Borghi C, Dallongeville J, Guallar E, Medina J, Perk J,
Sazova O, et al: Low rates of both lipid-lowering therapy use and
achievement of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol targets in
individuals at high-risk for cardiovascular disease across Europe.
PLoS One. 10:e01152702015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ball T and McCullough PA: Statins for the
prevention of contrast-induced acute kidney injury. Nephron Clin
Pract. 127:165–171. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Puri R, Nissen SE, Shao M, Ballantyne CM,
Barter PJ, Chapman MJ, Erbel R, Libby P, Raichlen JS, Uno K, et al:
Sex-related differences of coronary atherosclerosis regression
following maximally intensive statin therapy: Insights from SATURN.
JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 7:1013–1022. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu YH, Liu Y, Duan CY, Tan N, Chen JY,
Zhou YL, Li LW and He PC: statins for the prevention of
contrast-induced nephropathy after coronary
angiography/percutaneous interventions: A meta-analysis of
randomized controlled trials. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther.
20:181–192. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Stegman B, Puri R, Cho L, Shao M,
Ballantyne CM, Barter PJ, Chapman MJ, Erbel R, Libby P, Raichlen
JS, et al: High-intensity statin therapy alters the natural history
of diabetic coronary atherosclerosis: Insights from SATURN.
Diabetes Care. 37:3114–3120. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|