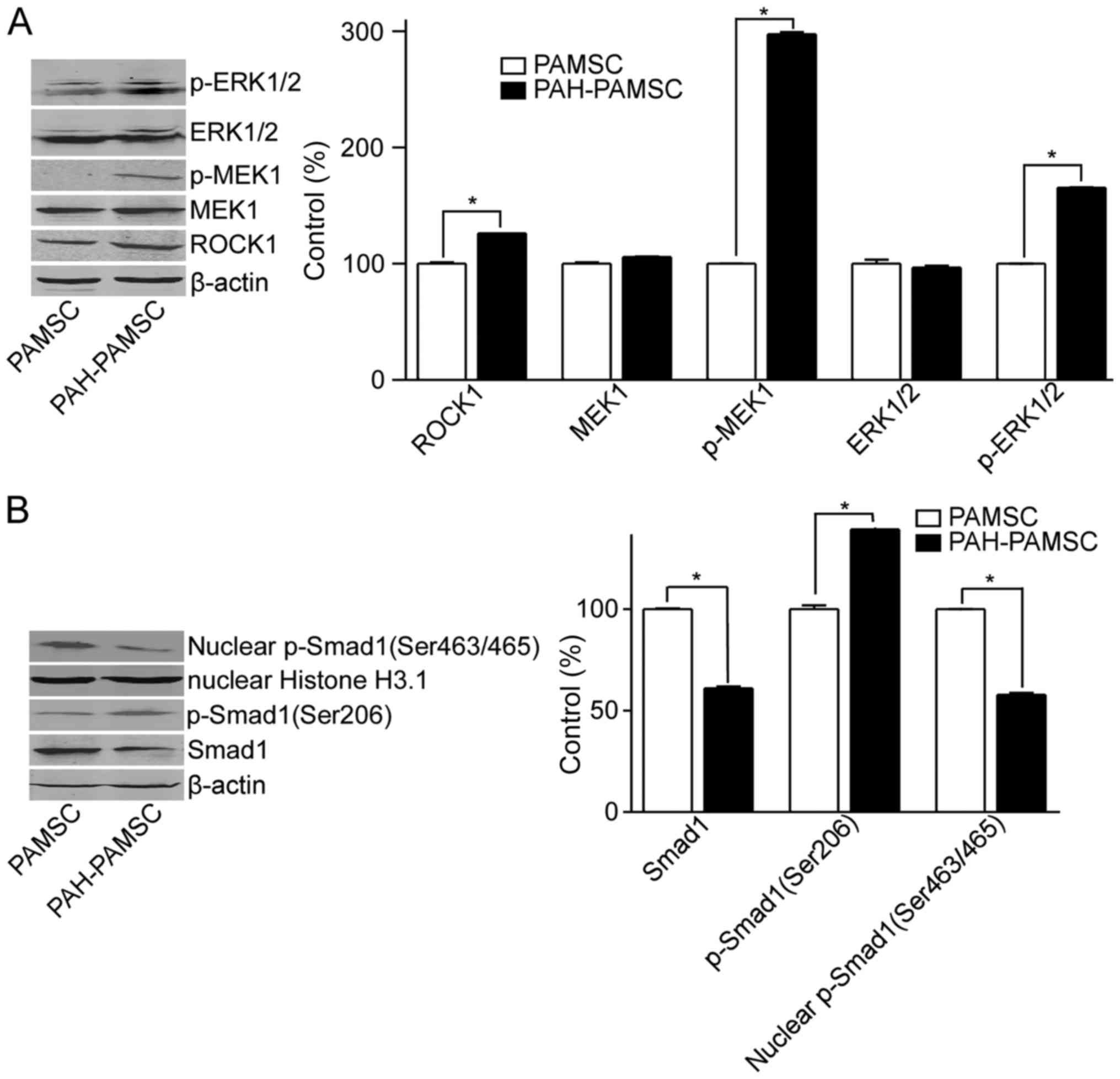
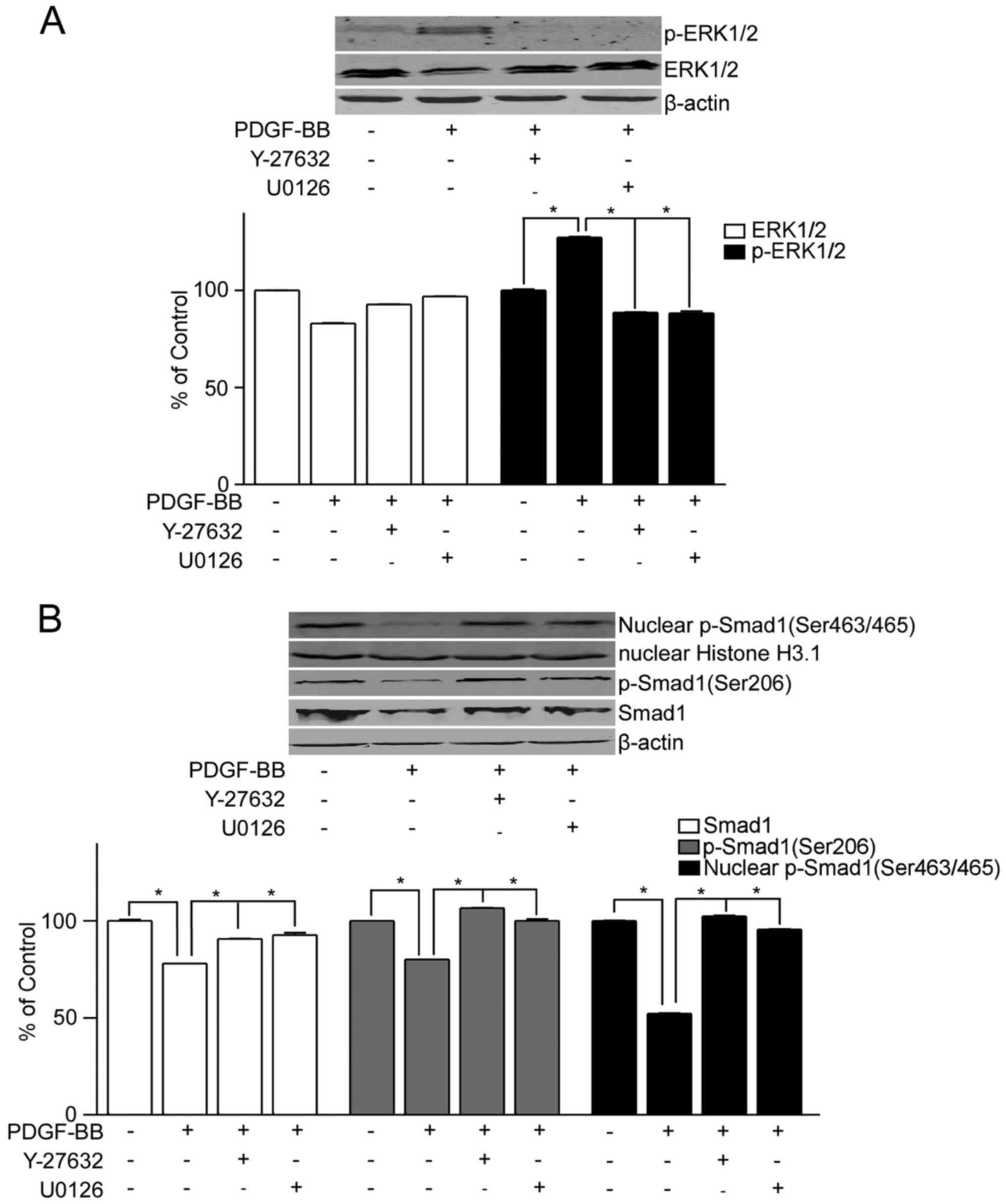
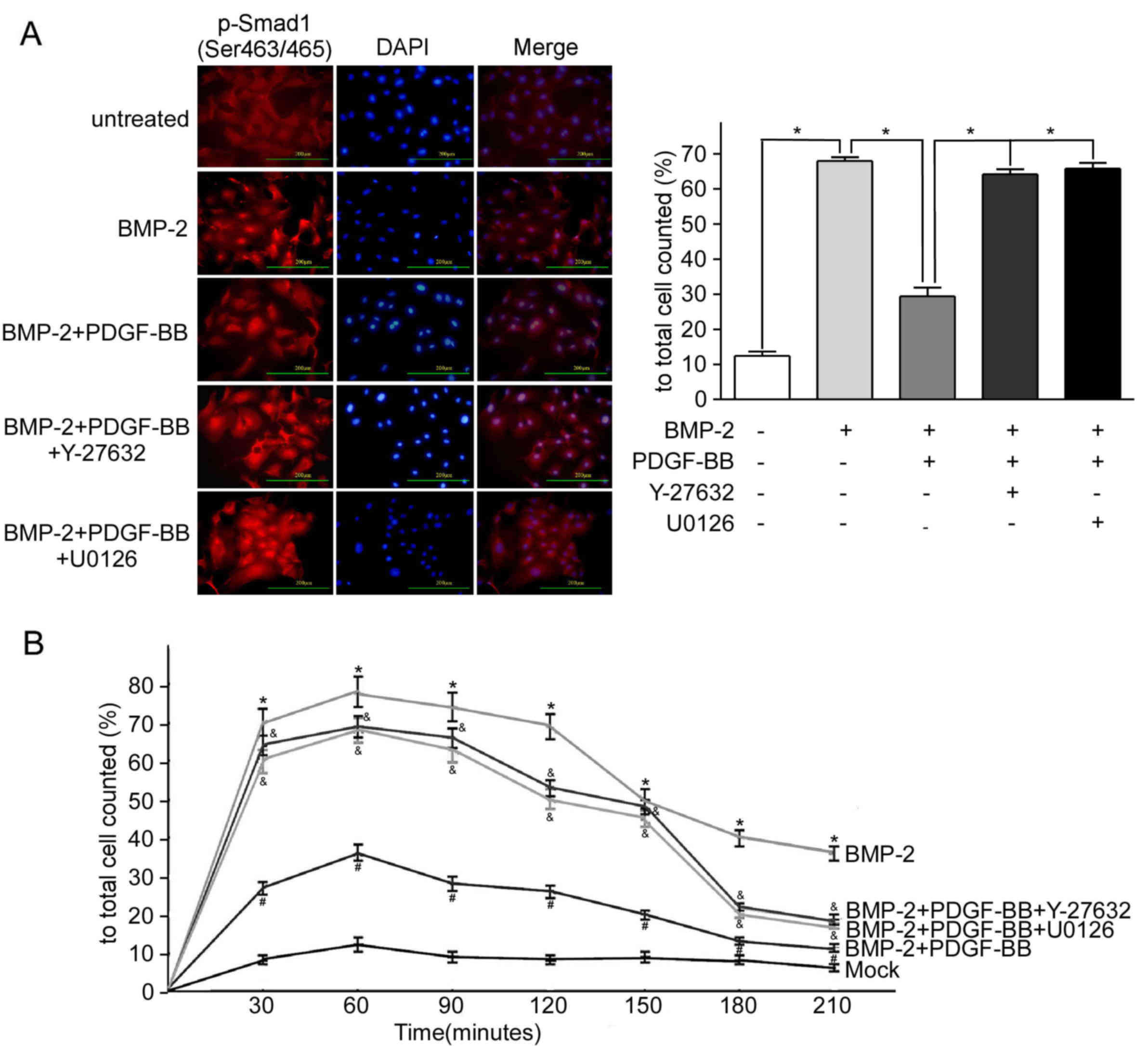
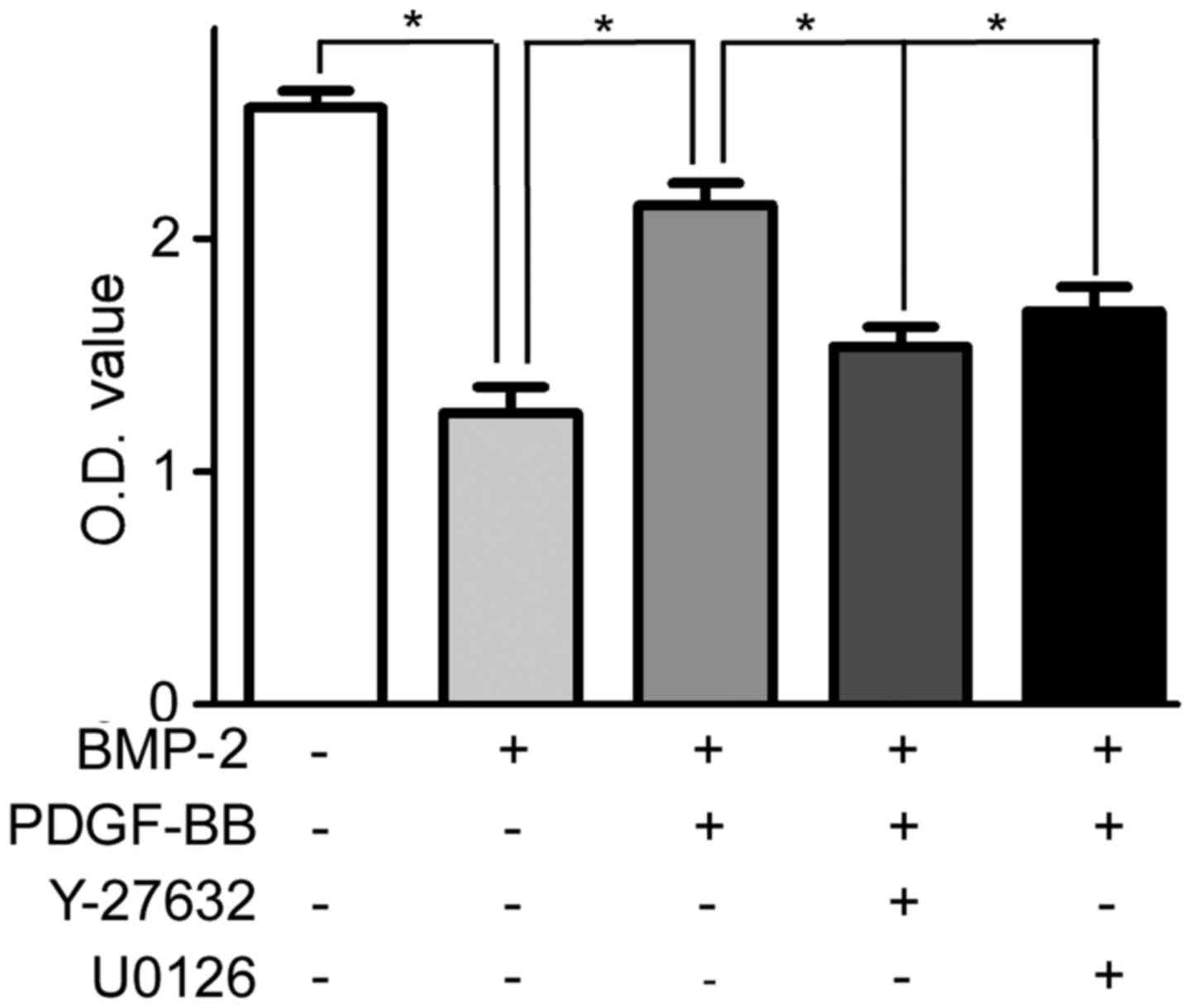
|
1
|
Miyazono K, Kamiya Y and Morikawa M: Bone
morphogenetic protein receptors and signal transduction. J Bio
chem. 147:35–51. 2010.
|
|
2
|
Sieber C, Kopf J, Hiepen C and Knaus P:
Recent advances in bmp receptor signaling. Cytokine Growth Factor
Rev. 20:343–355. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Awad KS, West JD, de Jesus Perez V and
MacLean M: Novel signaling pathways in pulmonary arterial
hypertension. Pulm Circ. 6:285–294. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
West J, Austin E, Fessel JP, Loyd J and
Hamid R: Rescuing the BMPR2 signaling axis in pulmonary arterial
hypertension. Drug Discov Today. 19:1241–1245. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Soubrier F, Chung WK, Machado R, Grünig E,
Aldred M, Geraci M, Loyd JE, Elliott CG, Trembath RC, Newman JH and
Humbert M: Genetics and genomics of pulmonary arterial
hypertension. J Am Coll Cardio. l62 25 Suppl:D13–D21. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ormiston ML, Upton PD, Li W and Morrell
NW: The promise of recombinant BMP ligands and other approaches
targeting BMPR-II in the treatment of pulmonary arterial
hypertension. Glob Cardiol Sci Pract. 2015:472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Long L, Ormiston ML, Yang X, Southwood M,
Gräf S, Machado RD, Mueller M, Kinzel B, Yung LM, Wilkinson JM, et
al: Selective enhancement of endothelial BMPR-II with BMP9 reverses
pulmonary arterial hypertension. Nat Med. 21:777–785. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yang J, Li X, Al-Lamki RS, Wu C, Weiss A,
Berk J, Schermuly RT and Morrell NW: Sildenafil potentiates bone
morphogenetic protein signaling in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle
cells and in experimental pulmonary hypertension. Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol. 33:34–42. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Price LC, Montani D, Tcherakian C,
Dorfmüller P, Souza R, Gambaryan N, Chaumais MC, Shao DM, Simonneau
G, Howard LS, et al: Dexamethasone reverses monocrotaline-induced
pulmonary arterial hypertension in rats. Eur Respir J. 37:813–822.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Machado RD, Southgate L, Eichstaedt CA,
Aldred MA, Austin ED, Best DH, Chung WK, Benjamin N, Elliott CG,
Eyries M, et al: Pulmonary arterial hypertension: A current
perspective on established and emerging molecular genetic defects.
Hum Mutat. 36:1113–1127. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Upton PD and Morrell NW: The transforming
growth factor-β-bone morphogenetic protein type signalling pathway
in pulmonary vascular homeostasis and disease. Exp Physiol.
98:1262–1266. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wrana JL: Regulation of smad activity.
Cell. 100:189–192. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sapkota G, Alarcón C, Spagnoli FM,
Brivanlou AH and Massagué J: Balancing BMP signaling through
integrated inputs into the Smad1 linker. Mol Cell. 25:441–454.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kretzschmar M, Doody J and Massague J:
Opposing bmp and egfsignalling pathways converge on the tgf-beta
family mediator smad1. Nature. 389:618–622. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wilson JL, Yu J, Taylor L and Polgar P:
Hyperplastic growth of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells from
subjects with pulmonary arterial hypertension is activated through
JNK and p38 MAPK. PLoS One. 10:e01236622015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jin C and Guo J, Qiu X, Ma K, Xiang M, Zhu
X and Guo J: IGF-1 induces iNOS expression via the p38 MAPK signal
pathway in the anti-apoptotic process in pulmonary artery smooth
muscle cells during PAH. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 34:325–331.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ziino AJ, Ivanovska J, Belcastro R,
Kantores C, Xu EZ, Lau M, McNamara PJ, Tanswell AK and Jankov RP:
Effects of rho-kinase inhibition on pulmonary hypertension, lung
growth, and structure in neonatal rats chronically exposed to
hypoxia. Pediatr Res. 67:177–182. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yasuda T, Tada Y, Tanabe N, Tatsumi K and
West J: Rho-kinase inhibition alleviates pulmonary hypertension in
transgenic mice expressing a dominant-negative type II bone
morphogenetic protein receptor gene. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 301:L667–L674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jasińska-Stroschein M, Owczarek J,
Sołtysiak U and Orszulak-Michalak D: Rosuvastatin intensifies the
beneficial effects of rho-kinase inhibitor in reversal of
monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension. Arch Med Sci.
12:898–905. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu Y, Ren W, Warburton R, Toksoz D and
Fanburg BL: Serotonin induces Rho/ROCK-dependent activation of
Smads 1/5/8 in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. FASEB J.
23:2299–2306. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen XY, Dun JN, Miao QF and Zhang YJ:
Fasudil hydrochloride hydrate, a rho-kinase inhibitor, suppresses
5-hydroxytryptamine-induced pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell
proliferation via jnk and erk1/2 pathway. Pharmacology. 83:67–79.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tanabe T, Furuya H, Kanemoto N, Goto Y and
Hata J: Experimental study on monocrotaline induced pulmonary
hypertensive rats. (1) Effect of long-term injection of
immunosuppressant. Tokai J Exp Clin Med. 6:41–48. 1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li F, Xia W, Li A, Zhao C and Sun R:
Long-term inhibition of Rho kinase with fasudil attenuates high
flow induced pulmonary artery remodeling in rats. Pharmacol Res.
55:64–71. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
The Ministry of Science and Technology of
the People's Republic of China: Guidance Suggestions for the Care
and Use of Laboratory Animals. 2006.http://www.most.gov.cn/fggw/zfwj/zfwj2006/200609/t20060930_54389.htmSeptember
30–2006
|
|
25
|
Amano M, Nakayama M and Kaibuchi K:
Rho-kinase/ROCK: A key regulator of the cytoskeleton and cell
polarity. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 67:545–554. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gupta V, Gupta N, Shaik IH, Mehvar R,
McMurtry IF, Oka M, Nozik-Grayck E, Komatsu M and Ahsan F:
Liposomal fasudil, a rho-kinase inhibitor, for prolonged pulmonary
preferential vasodilation in pulmonary arterial hypertension. J
Control Release. 167:189–199. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xiao JW, Zhu XY, Wang QG, Zhang DZ, Cui
CS, Zhang P, Chen HY and Meng LL: Acute effects of Rho-kinase
inhibitor fasudilon pulmonary arterial hypertension in patients
with congenital heart defects. Circ J. 79:1342–1348. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jiang X, Wang YF, Zhao QH, Jiang R, Wu Y,
Peng FH, Xu XQ, Wang L, He J and Jing ZC: Acute hemodynamic
response of infused fasudil in patients with pulmonary arterial
hypertension: A randomized, controlled, crossover study. Int J
Cardiol. 77:61–65. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Luo L, Zheng W, Lian G, Chen H, Li L, Xu C
and Xie L: Combination treatment of adipose-derived stem cells and
adiponectin attenuates pulmonary arterial hypertension in rats by
inhibiting pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cell proliferation and
regulating the AMPK/BMP/Smad pathway. Int J Mol Med. 41:51–60.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang Y, Lu W, Yang K, Xu L, Lai N, Tian
L, Jiang Q, Duan X, Chen M and Wang J: Bone morphogenetic protein 2
decreases TRPC expression, store-operated Ca(2+) entry, and basal
[Ca(2+)]i in rat distal pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells. Am
J Physiol Cell Physiol. 304:C833–C843. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Watanabe H: Rho-kinase activation in
patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Circ J.
73:1597–1598. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Morrell NW: Role of bone morphogenetic
protein receptors in the development of pulmonary arterial
hypertension. AdvExp Med Biol. 661:251–264. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Kamiyama M, Utsunomiya K, Taniguchi K,
Yokota T, Kurata H, Tajima N and Kondo K: Contribution of Rho A and
Rho kinase to platelet-derived growth factor-BB-induced
proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells. J Atheroscler
Thromb. 10:117–123. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nunes KP, Rigsby CS and Webb RC:
Rhoa/rho-kinase and vascular diseases: What is the link? Cell Mol
Life Sci. 67:3823–3836. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|