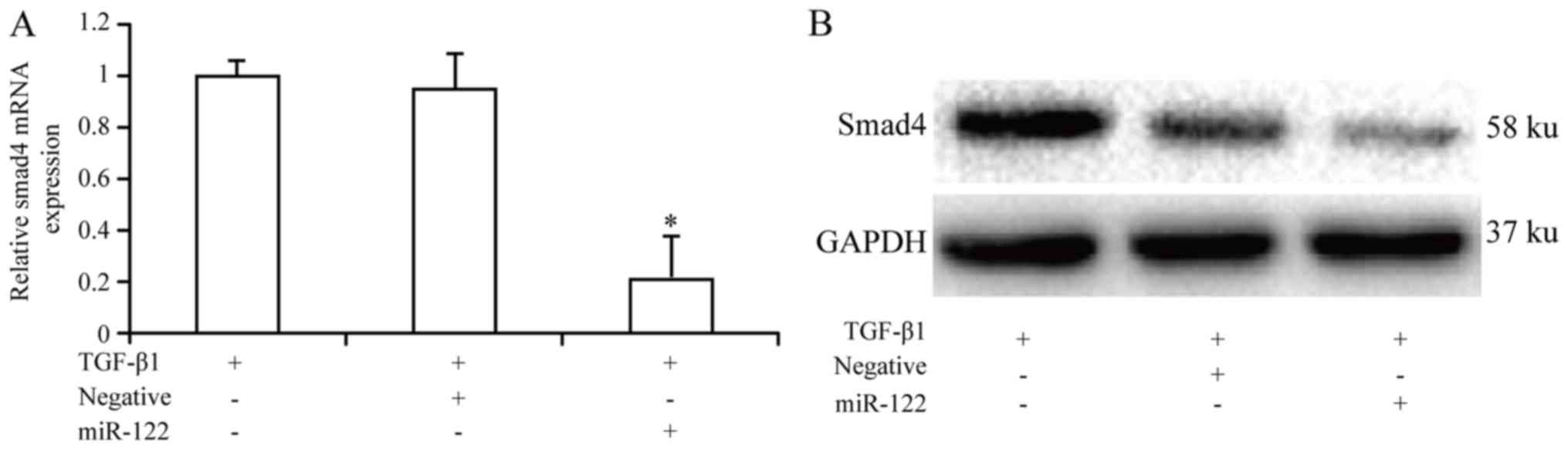
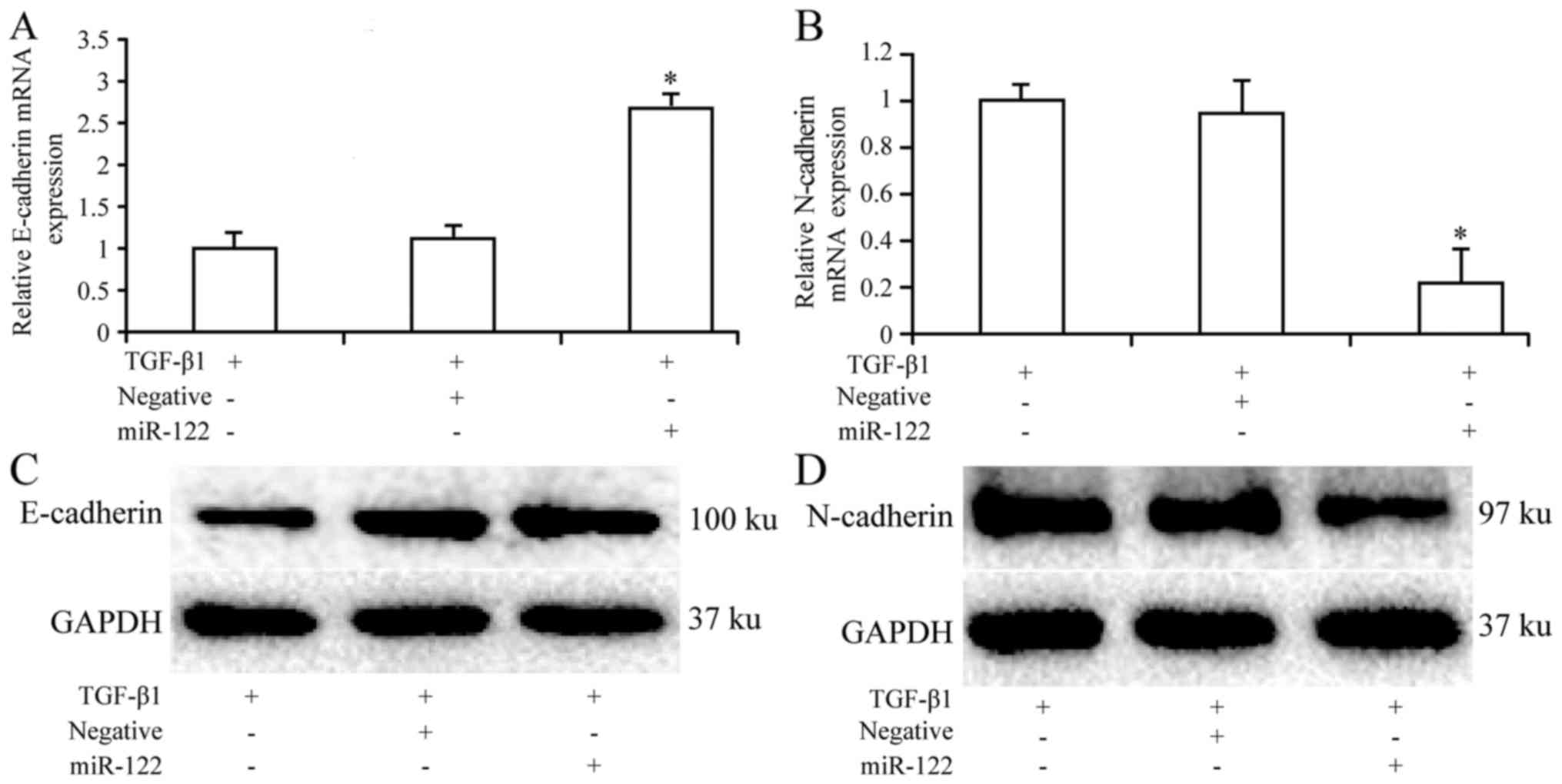
|
1
|
Tomita K, Teratani T, Suzuki T, Shimizu M,
Sato H, Narimatsu K, Usui S, Furuhashi H, Kimura A, Nishiyama K, et
al: Acyl-CoA: Cholesterol acyltransferase 1 mediates liver fibrosis
by regulating free cholesterol accumulation in hepatic stellate
cells. J Hepatol. 61:98–106. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Duval F, Moreno-Cuevas JE, González-Garza
MT, Rodríguez-Montalvo C and Cruz-Vega DE: Liver fibrosis and
protection mechanisms action of medicinal plants targeting
apoptosis of hepatocytes and hepatic stellate cells. Adv Pharmacol
Sci. 2014:3732952014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yang AT, Hu DD, Wang P, Cong M, Liu TH,
Zhang D, Sun YM, Zhao WS, Jia JD and You H: TGF-β1 induces the dual
regulation of hepatic progenitor cells with both anti- and proliver
fibrosis. Stem Cells Int. 2016:14926942016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li JH, Huang XR, Zhu HJ, Johnson R and Lan
HY: Role of TGF-beta signaling in extracellular matrix production
under high glucose conditions. Kidney Int. 63:2010–2019. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dropmann A, Dediulia T, Breitkopf-Heinlein
K, Korhonen H, Janicot M, Weber SN, Thomas M, Piiper A, Bertran E,
Fabregat I, et al: TGF-β1 and TGF-β2 abundance in liver diseases of
mice and men. Oncotarget. 7:19499–19518. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Duan L, Ye L, Zhuang L, Zou X, Liu S,
Zhang Y, Zhang L, Jin C and Huang Y: VEGFC/VEGFR3 axis mediates
TGFβ1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in non-small
cell lung cancer cells. PLoS One. 13:e02004522018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang QL, Tao YY, Yuan JL, Shen L and Liu
CH: Salvianolic acid B preventsepithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
through the TGF-beta1 signal transduction pathway in vivo and in
vitro. BMC Cell Biol. 11:312010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bi WR, Yang CQ and Shi Q: Transforming
growth factor-β1 induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
hepatic fibrosis. Hepatogastroenterology. 59:1960–1963.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Girard M, Jacquemin E, Munnich A, Lyonnet
S and Henrion-Caude A: miR-122, a paradigm for the role of
microRNAs in the liver. J Hepatol. 48:648–656. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang Y, Jia Y, Zheng R, Guo Y, Wang Y,
Guo H, Fei M and Sun S: Plasma microRNA-122 as a biomarker for
viral-, alcohol-, and chemical-related hepatic diseases. Clin Chem.
56:1830–1838. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lewis Starkey PJ, Dear J, Platt V, Simpson
KJ, Craig DG, Antoine DJ, French NS, Dhaun N, Webb DJ, Costello EM,
et al: Circulating microRNAs as potential markers of human
drug-induced liver injury. Hepatology. 54:1767–1776. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Su TH, Chen M, Liu CJ, Chen CL, Ting TT,
Tseng TC, Chen PJ, Kao JH and Chen DS: Serum microRNA-122 level
correlates with Virologic responses to pegylated interferon therapy
in chronic hepatitis C. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:7844–7849.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ding X, Ding J, Ning J, Yi F, Chen J, Zhao
D, Zheng J, Liang Z, Hu Z and Du Q: Circulating microRNA-122 as a
potential biomarker for liver injury. Mol Med Rep. 5:1428–1432.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Omran AA, Osman KS, Kamel HM, Abdel-Naem
EA and Hasan DE: MicroRNA-122 as a novel non-invasive marker of
liver fibrosis in hepatitis C virus patients. Clin Lab.
62:1329–1337. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nakamura M, Kanda T, Jiang X, Haga Y,
Takahashi K, Wu S, Yasui S, Nakamoto S and Yokosuka O: Serum
microRNA-122 and Wisteria floribunda agglutinin-positive Mac-2
binding protein are useful tools for liquid biopsy of the patients
with hepatitis B virus and advanced liver fibrosis. PLoS One.
12:e01773022017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Waidmann O, Köberle V, Brunner F, Zeuzem
S, Piiper A and Kronenberger B: Serum microRNA-122 predicts
survival in patients with liver cirrhosis. PLoS One. 7:e456522012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tsai WC, Hsu PW, Lai TC, Chau GY, Lin CW,
Chen CM, Lin CD, Liao YL, Wang JL, Chau YP, et al: MicroRNA-122, a
tumor suppressor microRNA that regulates intrahepatic metastasis of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 49:1571–1582. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Qiao DD, Yang J, Lei XF, Mi GL, Li SL, Li
K, Xu CQ and Yang HL: Expression of microRNA-122 and microRNA-22 in
HBV-related liver cancer and the correlation with clinical
features. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 21:742–747. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang N, Wang Q, Shen D, Sun X, Cao X and
Wu D: Downregulation of microRNA-122 promotes proliferation,
migration, and invasion of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by
activating epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Onco Targets Ther.
9:2035–2047. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xu J, Zhu X, Wu L, Yang R, Yang Z, Wang Q
and Wu F: MicroRNA-122 suppresses cell proliferation and induces
cell apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma by directly targeting
Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Liver Int. 32:752–760. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jin Y, Wang J, Han J, Luo D and Sun Z:
MiR-122 inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting Snail1 and Snail2 and
suppressing WNT/β-cadherin signaling pathway. Exp Cell Res.
360:210–217. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ma L, Yang X, Wei R, Ye T, Zhou JK, Wen M,
Wen RT, Li P, Dong B, Liu L, et al: MicroRNA-214 promotes hepatic
stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis by suppressing Sufu
expression. Cell Death Dis. 9:7182018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cui X, Zhang X, Yin Q, Meng A, Su S, Jing
X, Li H, Guan X, Li X, Liu S and Cheng M: F-actin cytoskeleton
reorganization is associated with hepatic stellate cell activation.
Mol Med Rep. 9:1641–1647. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yu F, Ji S, Su L, Wan L, Zhang S, Dai C,
Wang Y, Fu J and Zhang Q: Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells
inhibit activation of hepatic stellate cells in vitro and
ameliorate rat liver fibrosis in vivo. J Formos Med Assoc.
114:130–138. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yu H, Shen Y, Hong J, Xia Q, Zhou F and
Liu X: The contribution of TGF-β in Epithelial-Mesenchymal
Transition (EMT): Down-regulation of E-cadherin via snail.
Neoplasma. 62:1–15. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen T, Nie HY, Gao X, Yang J, Pu J, Chen
Z, Cui X, Wang Y, Wang H and Jia G: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition involved in pulmonary fibrosis induced by multi-walled
carbon nanotubes via TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathway. Toxicol Lett.
226:150–162. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Molè-Bajer J, Bajer AS and Inoué S:
Three-dimensional localization and redistribution of F-actin in
higher plant mitosis and cell plate formation. Cell Motil
Cytoskeleton. 10:217–228. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gong X, Fan Y, Zhang Y, Luo C, Duan X,
Yang L and Pan J: Inserted rest period resensitizes MC3T3-E1 cells
to fluid shear stress in a time-dependent manner via
F-actin-regulated mechanosensitive channel(s). Biosci Biotechnol
Biochem. 78:565–573. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lee UE and Friedman SL: Mechanisms of
hepatic fibrogenesis. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol.
25:195–206. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Boesch-Saadatmandi C, Wagner AE, Wolffram
S and Rimbach G: Effect of quercetin on inflammatory gene
expression in mice liver in vivo-role of redox factor 1, miRNA-122
and miRNA-125b. Pharmacol Res. 65:523–530. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bala S, Petrasek J, Ward J, Alao H, Levin
I and Szabo G: Serum microrna-122 and mir-155 as biomarkers of
liver injury and inflammation in models of acute and chronic liver
disease. Gastroenterology. 140:9062012. View Article : Google Scholar
|