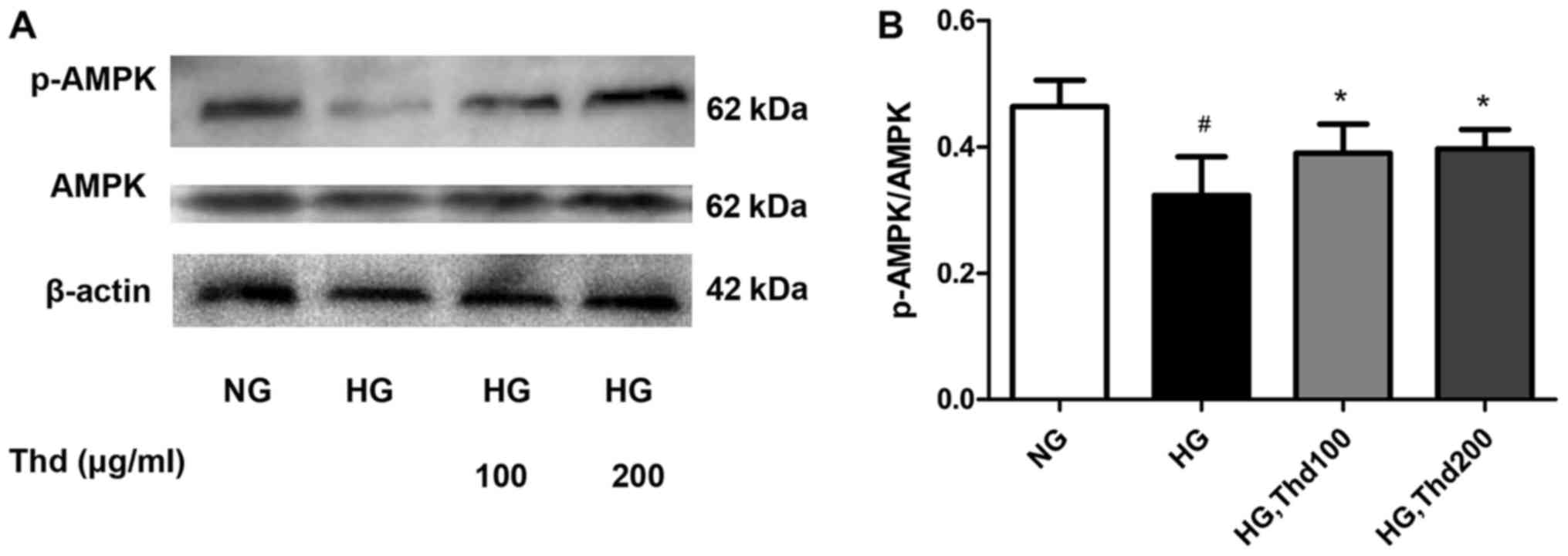
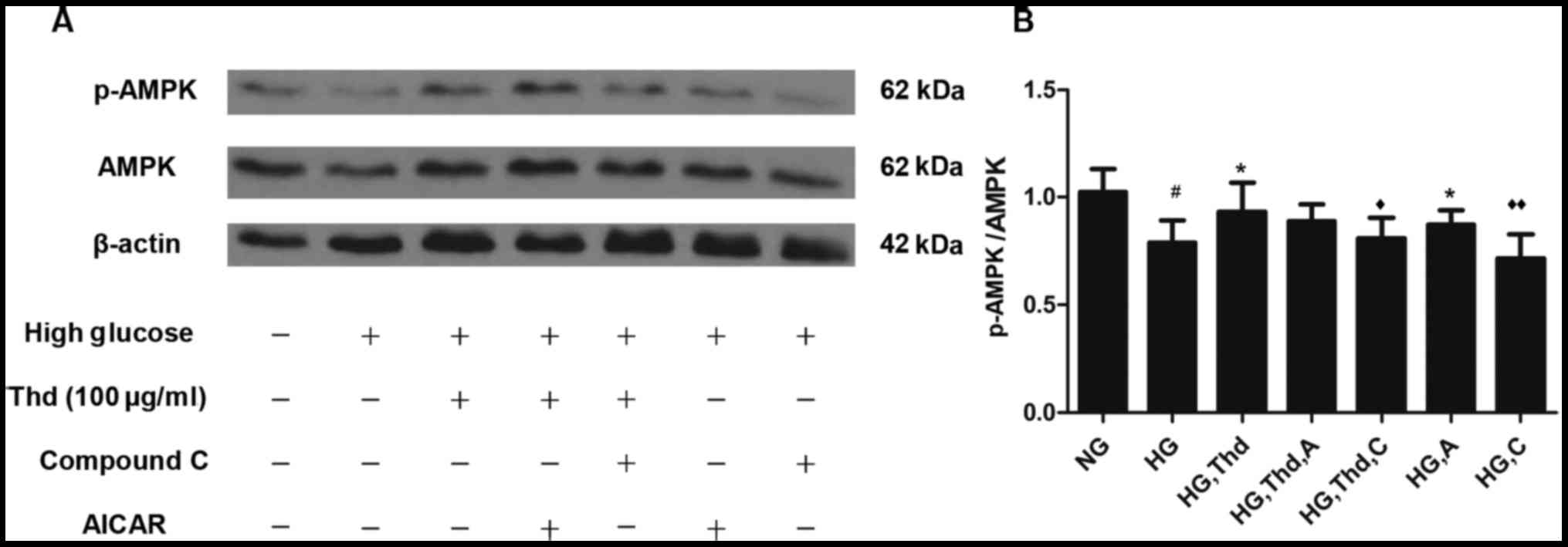
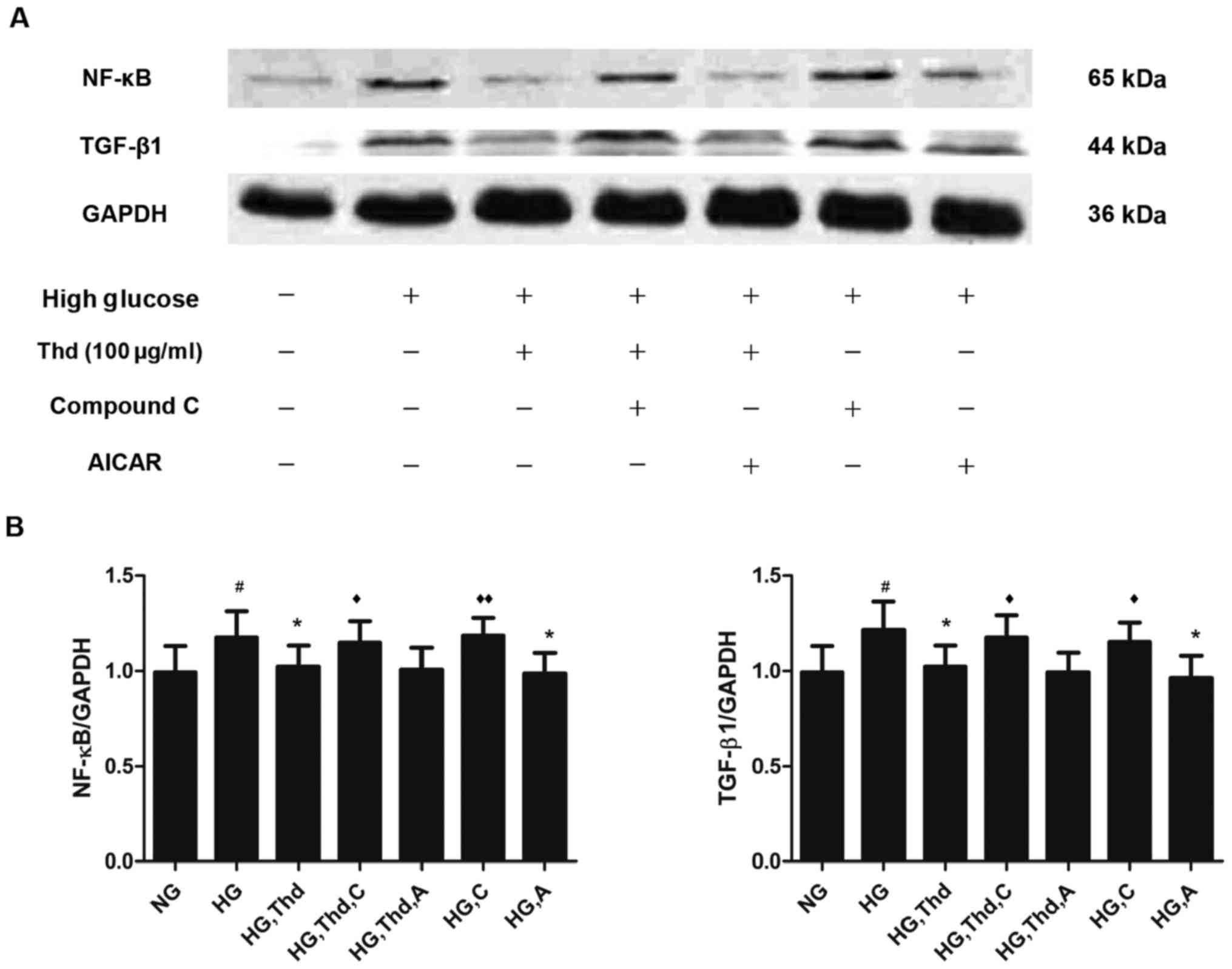
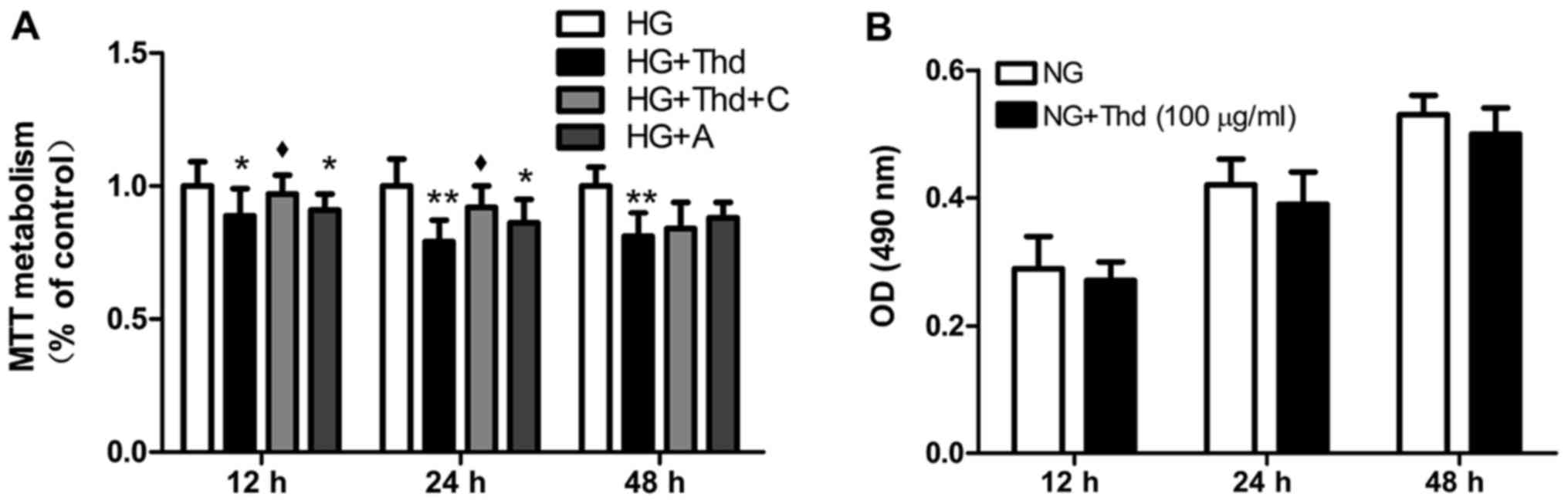
|
1
|
International Diabetes Federation: IDF
Diabetes Atlas 7th edition (2015). https://www.idf.org/e-library/epidemiology-research/diabetes-atlas/13-diabetes-atlas-seventh-edition.htmlAugust
14–2018
|
|
2
|
Kolset SO, Reinholt FP and Jenssen T:
Diabetic nephropathy and extracellular matrix. J Histochem
Cytochem. 60:976–986. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mason RM and Wahab NA: Extracellular
matrix metabolism in diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol.
14:1358–1373. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wada J and Makino H: Inflammation and the
pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Clin Sci (Lond). 124:139–152.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Navarro-González JF, Mora-Fernández C, de
Fuentes Morus M and García-Pérez J: Inflammatory molecules and
pathways in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Nat Rev
Nephrol. 7:327–340. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Min D, Lyons JG, Bonner J, Twigg SM, Yue
DK and McLennan SV: Mesangial cell-derived factors alter monocyte
activation and function through inflammatory pathways: Possible
pathogenic role in diabetic nephropathy. Am J Physiol Renal
Physiol. 297:F1229–F1237. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ingaramo PI, Ronco MT, Francés DE, Monti
JA, Pisani GB, Ceballos MP, Galleano M, Carrillo MC and Carnovale
CE: Tumor necrosis factor alpha pathways develops liver apoptosis
in type 1 diabetes Mellitus. Mol Immunol. 48:1397–1407. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Giunti S, Tesch GH, Pinach S, Burt DJ,
Cooper ME, Cavallo-Perin P, Camussi G and Gruden G: Monocyte
chemoattractant protein-1 has prosclerotic effects both in a mouse
model of experimental diabetes and in vitro in human mesangial
cells. Diabetologia. 51:198–207. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kemp BE, Stapleton D, Campbell DJ, Chen
ZP, Murthy S, Walter M, Gupta A, Adams JJ, Katsis F, van Denderen
B, et al: AMP-activated protein kinase, super metabolic regulator.
Biochem Soc Trans. 31:162–168. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Decleves AE, Mathew AV, Cunard R and
Sharma K: AMPK mediates the initiation of kidney disease induced by
a high-fat diet. J Am Soc Nephrol. 22:1846–1855. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hallows KR, Mount PF, Pastor-Soler NM and
Power DA: Role of the energy sensor AMP-activated protein kinase in
renal physiology and disease. Am JPhysiol Renal Physiol.
298:F1067–F1077. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Lv ZM, Liu Y, Zhang PJ, Xu J, Jia ZH, Wang
R and Wan Q: The role of AMPKα in high glucose-induced dysfunction
of cultured rat mesangial cells. Ren Fail. 34:616–621. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang S, Zhang M, Liang B, Xu J, Xie Z, Liu
C, Viollet B, Yan D and Zou MH: AMPKalpha2 deletion causes aberrant
expression and activation of NAD(P)H oxidase and consequent
endothelial dysfunction in vivo: Role of 26S proteasomes. Circ Res.
106:1117–1128. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim MY, Lim JH, Youn HH, Hong YA, Yang KS,
Park HS, Chung S, Ko SH, Shin SJ, Choi BS, et al: Resveratrol
prevents renal lipotoxicity and inhibits mesangial cell
glucotoxicity in a manner dependent on the AMPK-Sirt1-PGC1α axis in
db/db mice. Diabetologia. 56:204–217. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Salminen A, Hyttinen JM and Kaarniranta K:
AMP-activated protein kinase inhibits NF-κB signaling and
inflammation: Impact on healthspan and lifespan. J Mol Med (Berl).
89:667–676. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee JH, Kim JH, Kim JS, Chang JW, Kim SB,
Park JS and Lee SK: AMP-activated protein kinase inhibits TGF-β-,
angiotensin II-, aldosterone, high glucose-, and albumin-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
304:F686–F697. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Raje N and Anderson K: Thalidomide - a
revival story. N Engl J Med. 341:1606–1609. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Asher C and Furnish T: Lenalidomide and
thalidomide in the treatment of chronic pain. Expert Opin Drug Saf.
12:367–374. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Amirshahrokhi K and Ghazi-Khansari M:
Thalidomide attenuates multiple low-dose streptozotocin-induced
diabetes in mice by inhibition of proinflammatory cytokines.
Cytokine. 60:522–527. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhao J, Wang H, Song T, Yang Y, Gu K, Ma
P, Zhang Z, Shen L, Liu J and Wang W: Thalidomide promotes morphine
efficacy and prevents morphine-induced tolerance in rats with
diabetic neuropathy. Neurochem Res. 41:3171–3180. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Behl T, Kaur I, Goel H and Kotwani A:
Significance of the antiangiogenic mechanisms of thalidomide in the
therapy of diabetic retinopathy. Vascul Pharmacol. 92:6–15. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kim DH, Kim YJ, Chang SA, Lee HW, Kim HN,
Kim HK, Chang HJ, Sohn DW and Park YB: The protective effect of
thalidomide on left ventricular function in a rat model of diabetic
cardiomyopathy. Eur J Heart Fail. 12:1051–1060. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang H, Yang Y, Wang Y, Wang B and Li R:
Renal-protective effect of thalidomide in streptozotocin-induced
diabetic rats through anti-inflammatory pathway. Drug Des Devel
Ther. 12:89–98. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xu WW, Guan MP, Zheng ZJ, Gao F, Zeng YM,
Qin Y and Xue YM: Exendin-4 alleviateshigh glucose-induced rat
mesangial cell dysfunction throughthe AMPK pathway. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 33:423–432. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
García-García PM, Getino-Melián MA,
Domínguez-Pimentel V and Navarro-González JF: Inflammation in
diabetic kidney disease. World J Diabetes. 5:431–443. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Williams MD and Nadler JL: Inflammatory
mechanisms of diabetic complications. Curr Diab Rep. 7:242–248.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tesch GH: MCP-1/CCL2: A new diagnostic
marker and therapeutic target for progressive renal injury in
diabetic nephropathy. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 294:F697–F701.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Morii T, Fujita H, Narita T, Shimotomai T,
Fujishima H, Yoshioka N, Imai H, Kakei M and Ito S: Association of
monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 with renal tubular damage in
diabetic nephropathy. J Diabetes Complications. 17:11–15. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cheng J, Encarnacion Diaz MM, Warner GM,
Gray CE, Nath KA and Grande JP: TGF-beta1 stimulates monocyte
chemoattractant protein-1 expression in mesangial cells through a
phosphodiesterase isoenzyme 4-dependent process. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 289:C959–C970. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lee MJ, Feliers D, Mariappan MM,
Sataranatarajan K, Mahimainathan L, Musi N, Foretz M, Viollet B,
Weinberg JM, Choudhury GG and Kasinath BS: A role for AMP-activated
protein kinase in diabetes-induced renal hypertrophy. Am J Physiol
Renal Physiol. 292:F617–F627. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhao J, Miyamoto S, You YH and Sharma K:
AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activation inhibits nuclear
translocation of Smad4 in mesangial cells and diabetic kidneys. Am
J Physiol Renal Physiol. 308:F1167–F1177. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dugan LL, You YH, Ali SS, Diamond-Stanic
M, Miyamoto S, DeCleves AE, Andreyev A, Quach T, Ly S, Shekhtman G,
et al: AMPK dysregulation promotes diabetes-related reduction of
superoxide and mitochondrial function. J Clin Invest.
123:4888–4899. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|