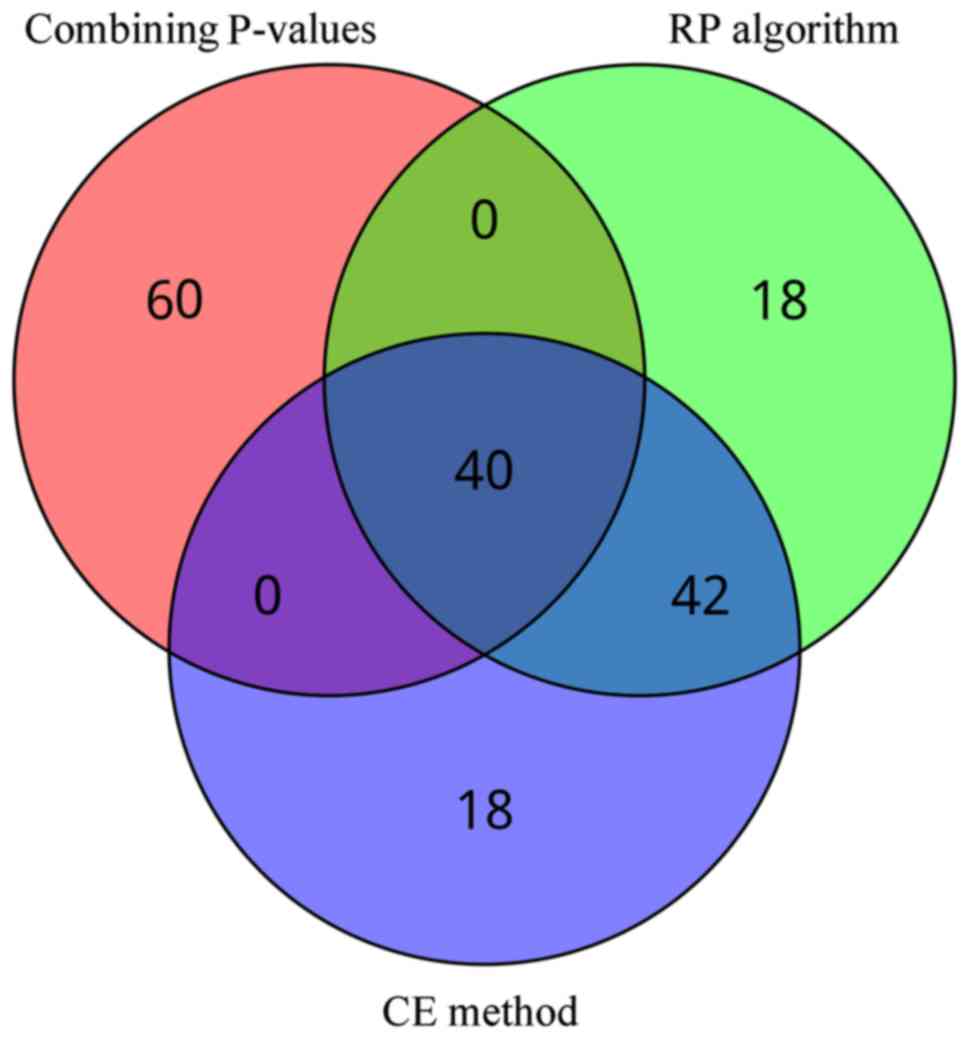
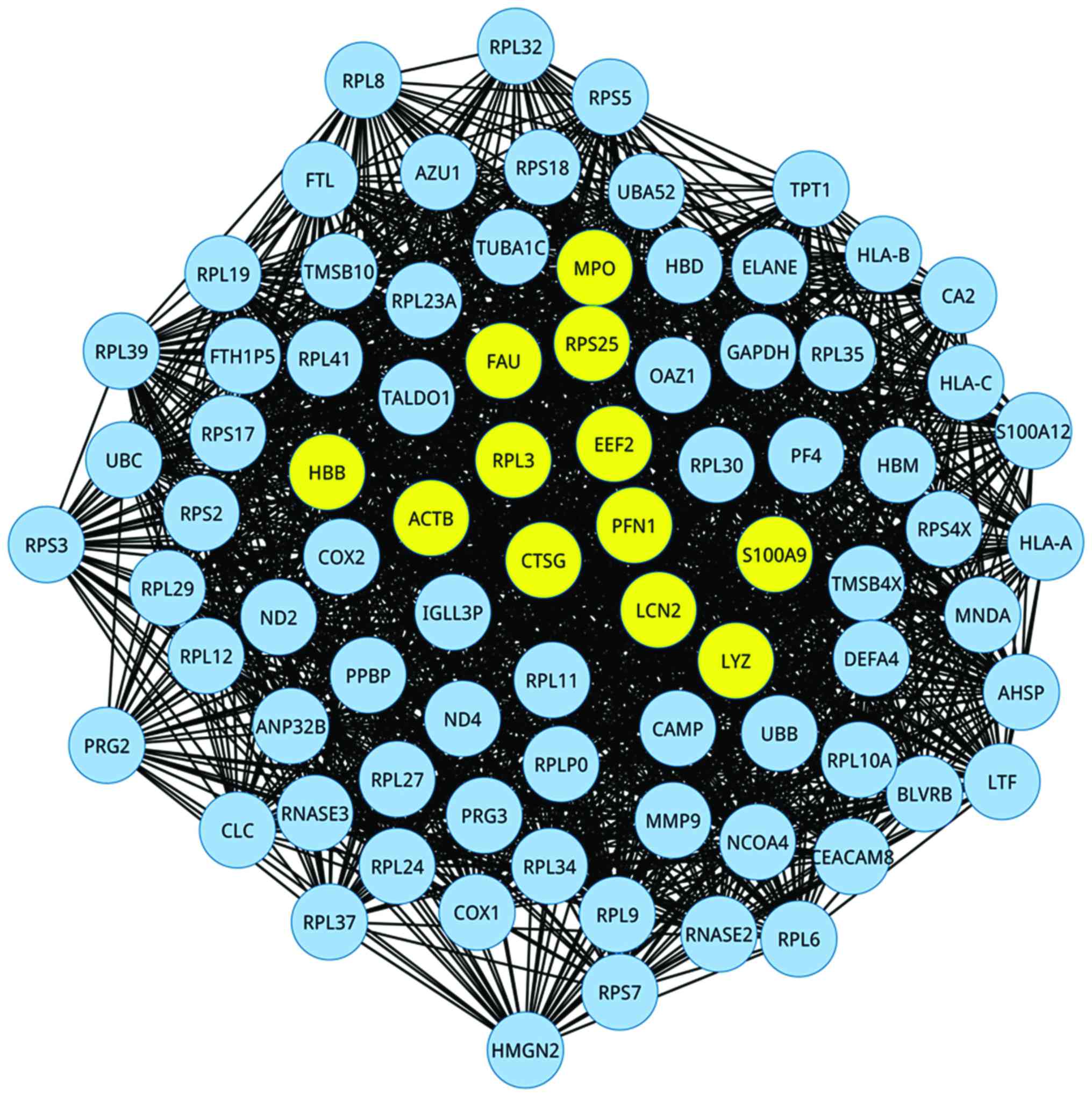
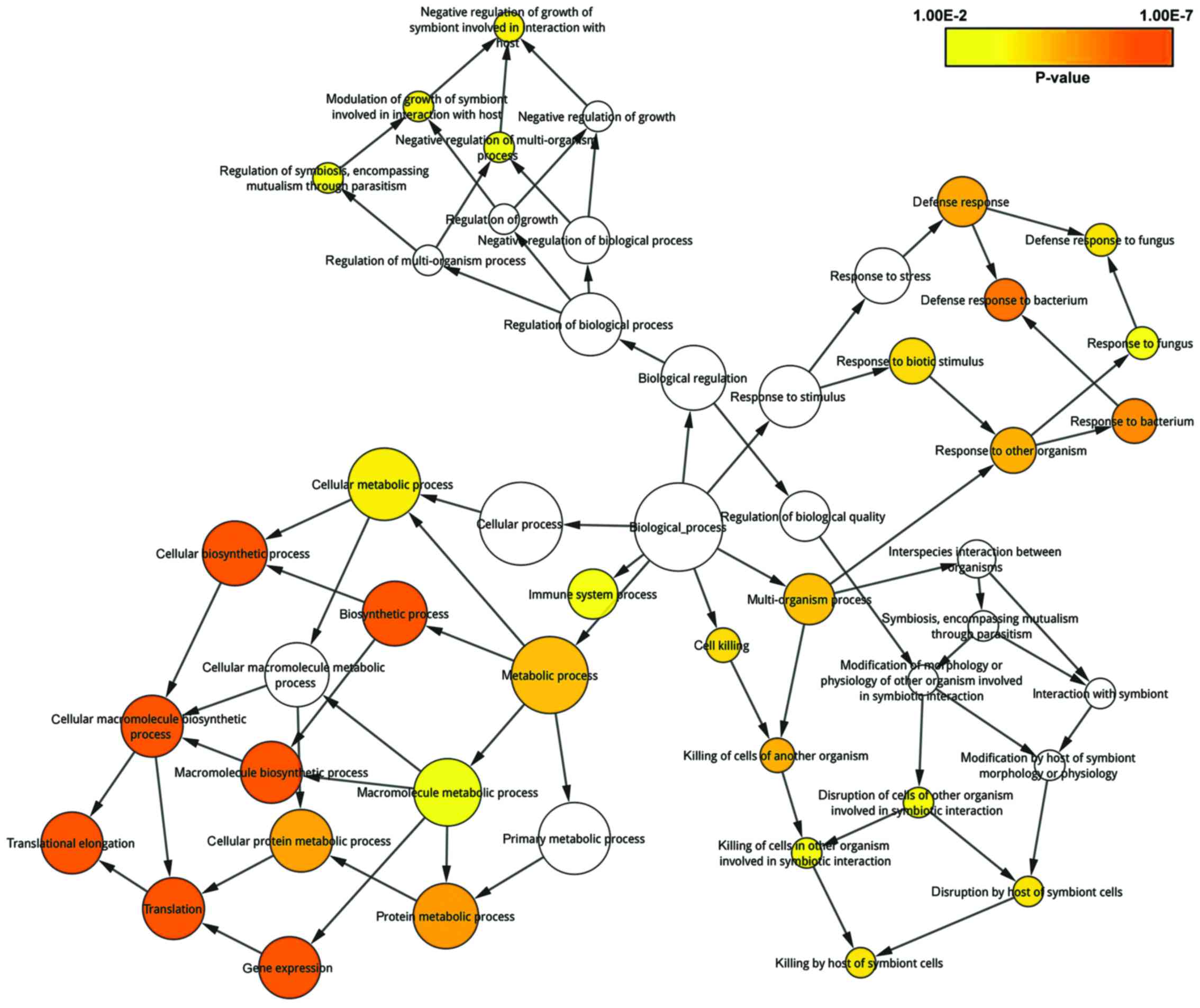
|
1
|
Kanis JA, Burlet N, Cooper C, Delmas PD,
Reginster JY, Borgstrom F and Rizzoli R: European Society for
Clinical and Economic Aspects of Osteoporosis and Osteoarthritis
(ESCEO): European guidance for the diagnosis and management of
osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. Osteoporos Int. 19:399–428.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Marcus R: Post-menopausal osteoporosis.
Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 16:309–327. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Unni S, Yao Y, Milne N, Gunning K, Curtis
JR and LaFleur J: An evaluation of clinical risk factors for
estimating fracture risk in postmenopausal osteoporosis using an
electronic medical record database. Osteoporos Int. 26:581–587.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cosman F, de Beur SJ, LeBoff MS, Lewiecki
EM, Tanner B, Randall S and Lindsay R: National Osteoporosis
Foundation: Clinician's guide to prevention and treatment of
osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int. 25:2359–2381. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Breitling R, Armengaud P, Amtmann A and
Herzyk P: Rank products: A simple, yet powerful, new method to
detect differentially regulated genes in replicated microarray
experiments. FEBS Lett. 573:83–92. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu Y, Koyutürk M, Barnholtz-Sloan JS and
Chance MR: Gene interaction enrichment and network analysis to
identify dysregulated pathways and their interactions in complex
diseases. BMC Syst Biol. 6:652012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li RH, Zhang AM, Li S, Li TY, Wang LJ,
Zhang HR, Li P, Jia XJ, Zhang T, Peng XY, et al: Multiple
differential expression networks identify key genes in rectal
cancer. Cancer Biomark. 16:435–444. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ein-Dor L, Kela I, Getz G, Givol D and
Domany E: Outcome signature genes in breast cancer: Is there a
unique set? Bioinformatics. 21:171–178. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tharmaratnam K, Sperrin M, Jaki T, Reppe S
and Frigessi A: Tilting the lasso by knowledge-based
post-processing. BMC Bioinformatics. 17:3442016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Reppe S, Refvem H, Gautvik VT, Olstad OK,
Høvring PI, Reinholt FP, Holden M, Frigessi A, Jemtland R and
Gautvik KM: Eight genes are highly associated with BMD variation in
postmenopausal Caucasian women. Bone. 46:604–612. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kanduri C and Jarvela I: GenRank: An
R/Bioconductor package for prioritization of candidate genes.
bioRxiv 048264. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/048264.
|
|
12
|
Morrison JL, Breitling R, Higham DJ and
Gilbert DR: GeneRank: Using search engine technology for the
analysis of microarray experiments. BMC Bioinformatics. 6:2332005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Oikkonen J, Onkamo P, Järvelä I and
Kanduri C: Convergent evidence for the molecular basis of musical
traits. Sci Rep. 6:397072016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang K, Cheng Y, Liao WK and Choudhary A:
Mining millions of reviews: a technique to rank products based on
importance of reviews. Proceedings of the 13th International
Conference on Electronic Commerce. ICEC'11 [2378116] doi:
10.1145/2378104.2378116.
|
|
15
|
Westfall PH: Combining P Values.
Encyclopedia of Biostatistics. Armitage P and Colton T: Jonh Wiley
& Sons, Ltd.; Chichester, UK: pp. 987–991. 2005
|
|
16
|
Fay MP: Confidence intervals that match
Fisher's exact or Blaker's exact tests. Biostatistics. 11:373–374.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Benjamini Y and Hochberg Y: Controlling
the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to
multiple testing. J R Stat Soc B. 57:289–300. 1995.
|
|
18
|
Cover TM and Thomas JA: Elements of
information theory. Jonh Wiley & Sons Ltd.; Chichester, UK:
2012
|
|
19
|
Meyer PE, Lafitte F and Bontempi G: minet:
A R/Bioconductor package for inferring large transcriptional
networks using mutual information. BMC Bioinformatics. 9:4612008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kohl M, Wiese S and Warscheid B:
Cytoscape: Software for visualization and analysis of biological
networks. Methods Mol Biol. 696:291–303. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Haythornthwaite C: Social network
analysis: An approach and technique for the study of information
exchange. Libr Inf Sci Res. 18:323–342. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Maere S, Heymans K and Kuiper M: BiNGO: A
Cytoscape plugin to assess overrepresentation of gene ontology
categories in biological networks. Bioinformatics. 21:3448–3449.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Busse RT, Elliott SN and Kratochwill TR:
Convergent evidence scaling for multiple assessment indicators:
Conceptual issues, applications, and technical challenges. J Appl
Sch Psychol. 26:149–161. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Ayalew M, Le-Niculescu H, Levey DF, Jain
N, Changala B, Patel SD, Winiger E, Breier A, Shekhar A, Amdur R,
et al: Convergent functional genomics of schizophrenia: From
comprehensive understanding to genetic risk prediction. Mol
Psychiatry. 17:887–905. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu ZP, Wang Y, Zhang XS and Chen L:
Network-based analysis of complex diseases. IET Systems Biology.
6:22–23. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen L, Wang RS and Zhang XS:
Reconstruction of gene regulatory networks. Biomolecular Networks.
John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; pp. 47–87. 2009, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Donato R, Cannon B, Sorci G, Riuzzi F, Hsu
K, Weber D and Geczy C: Functions of S100 Proteins. Curr Mol Med.
13:242013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Paschalis EP, Gamsjaeger S, Hassler N,
Fahrleitner-Pammer A, Dobnig H, Stepan JJ, Pavo I, Eriksen EF and
Klaushofer K: Vitamin D and calcium supplementation for three years
in postmenopausal osteoporosis significantly alters bone mineral
and organic matrix quality. Bone. 95:41–46. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pawar H, Srikanth SM, Kashyap MK, Sathe G,
Chavan S, Singal M, Manju HC, Kumar KV, Vijayakumar M, Sirdeshmukh
R, et al: Downregulation of S100 calcium binding protein A9 in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Sci World J. 2015:3257212015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Lee TH, Jang AS, Park JS, Kim TH, Choi YS,
Shin HR, Park SW, Uh ST, Choi JS, Kim YH, et al: Elevation of S100
calcium binding protein A9 in sputum of neutrophilic inflammation
in severe uncontrolled asthma. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol.
111:268–275.e1. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gebhardt C, Németh J, Angel P and Hess J:
S100A8 and S100A9 in inflammation and cancer. Biochem Pharmacol.
72:1622–1631. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mackiewicz M, Shockley KR, Romer MA,
Galante RJ, Zimmerman JE, Naidoo N, Baldwin DA, Jensen ST,
Churchill GA and Pack AI: Macromolecule biosynthesis: A key
function of sleep. Physiol Genomics. 31:441–457. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Miller WR, Larionov A, Renshaw L, Anderson
TJ, Walker JR, Krause A, Sing T, Evans DB and Dixon JM: Gene
expression profiles differentiating between breast cancers
clinically responsive or resistant to letrozole. J Clin Oncol.
27:1382–1387. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|