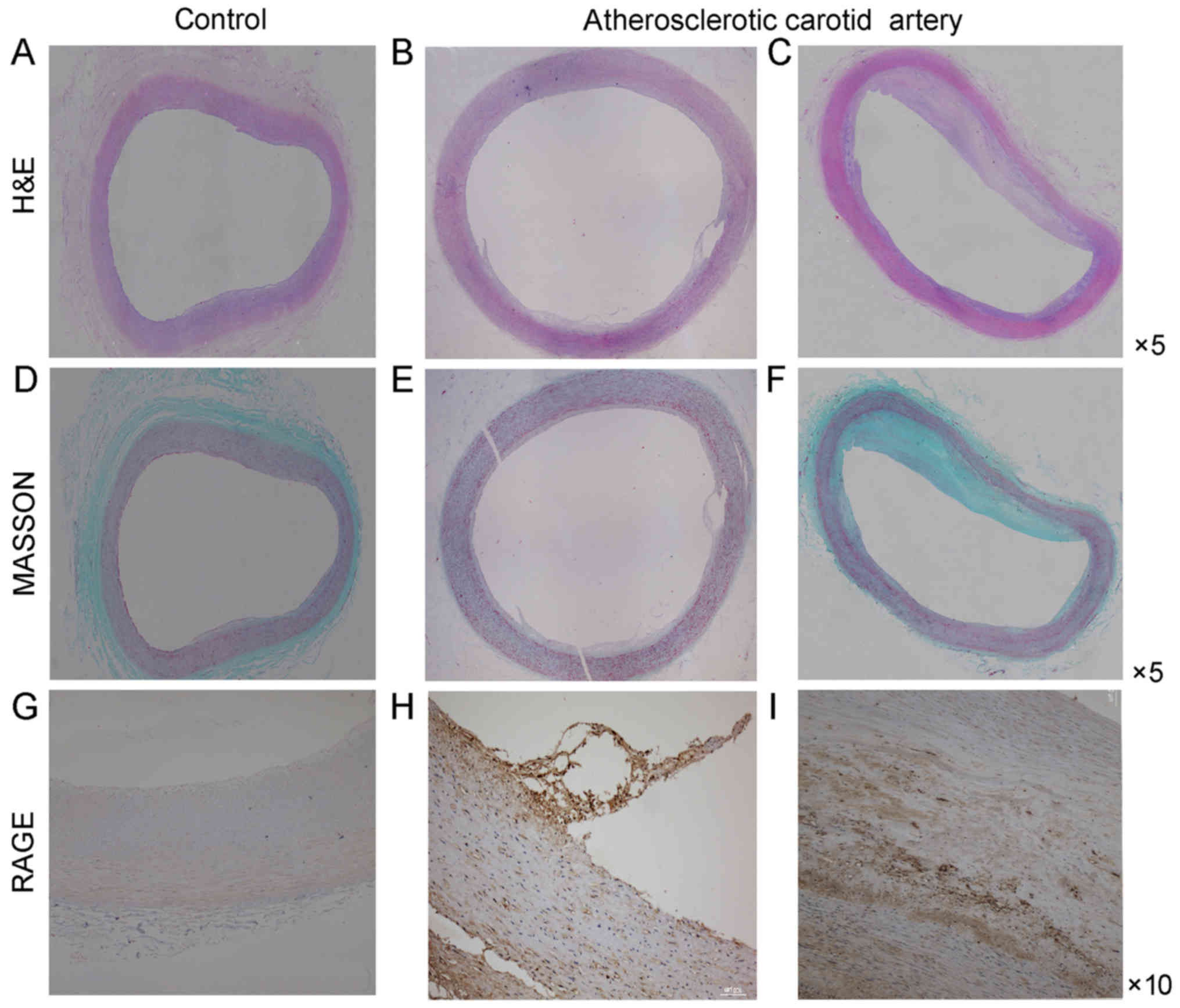
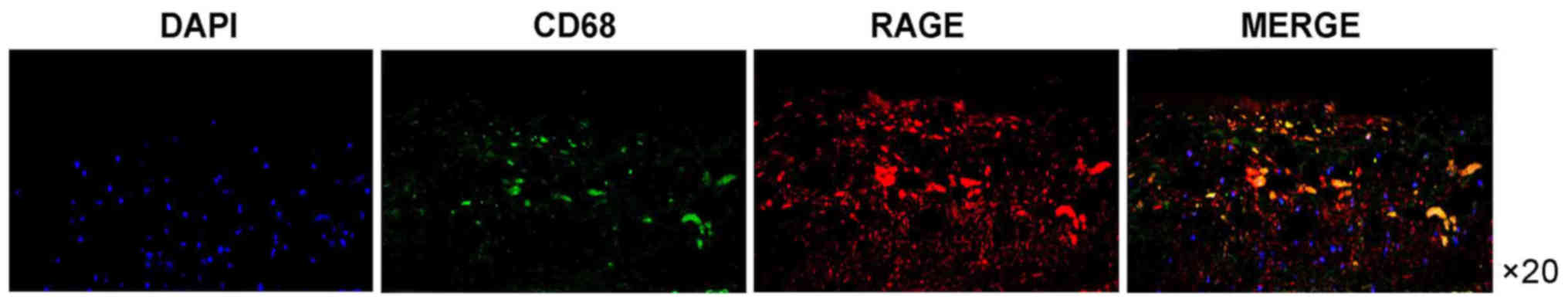
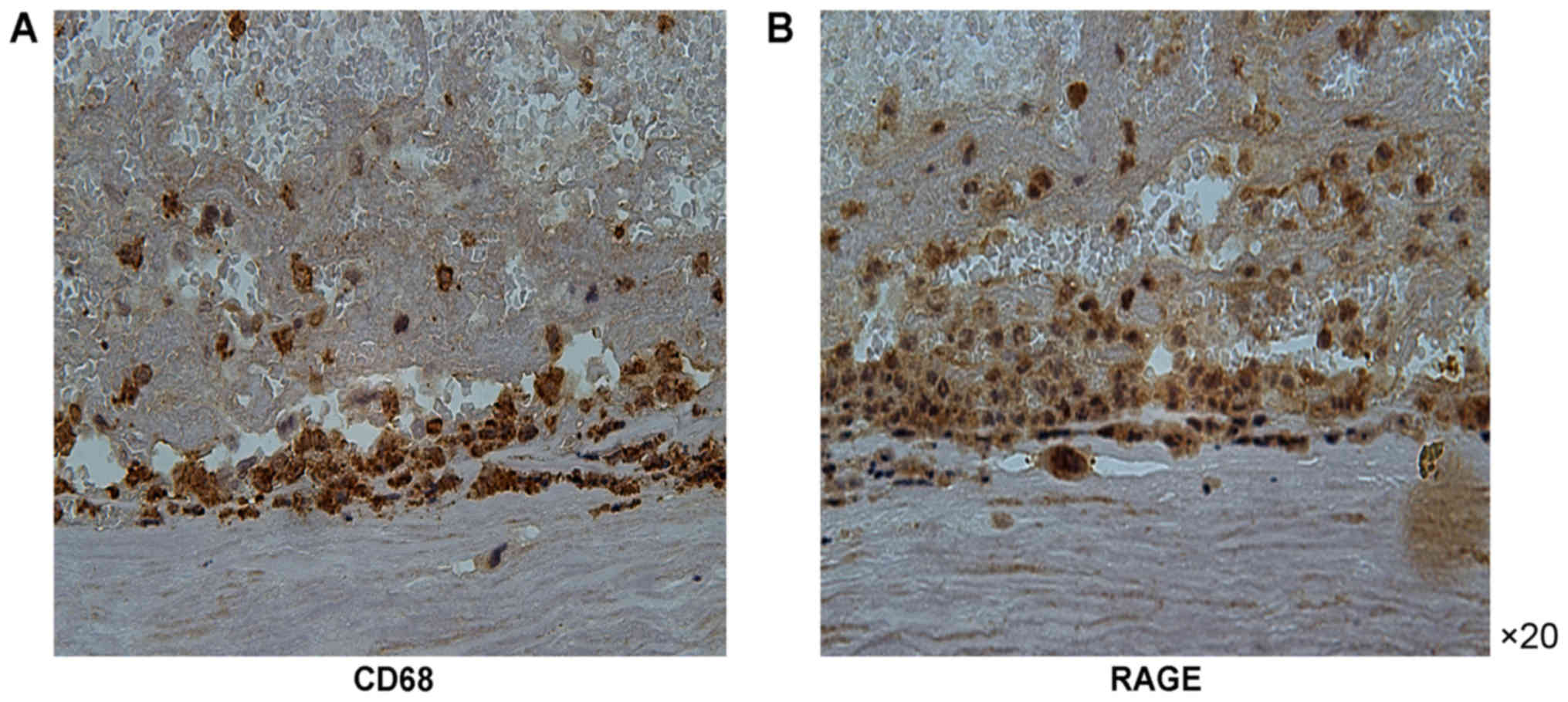
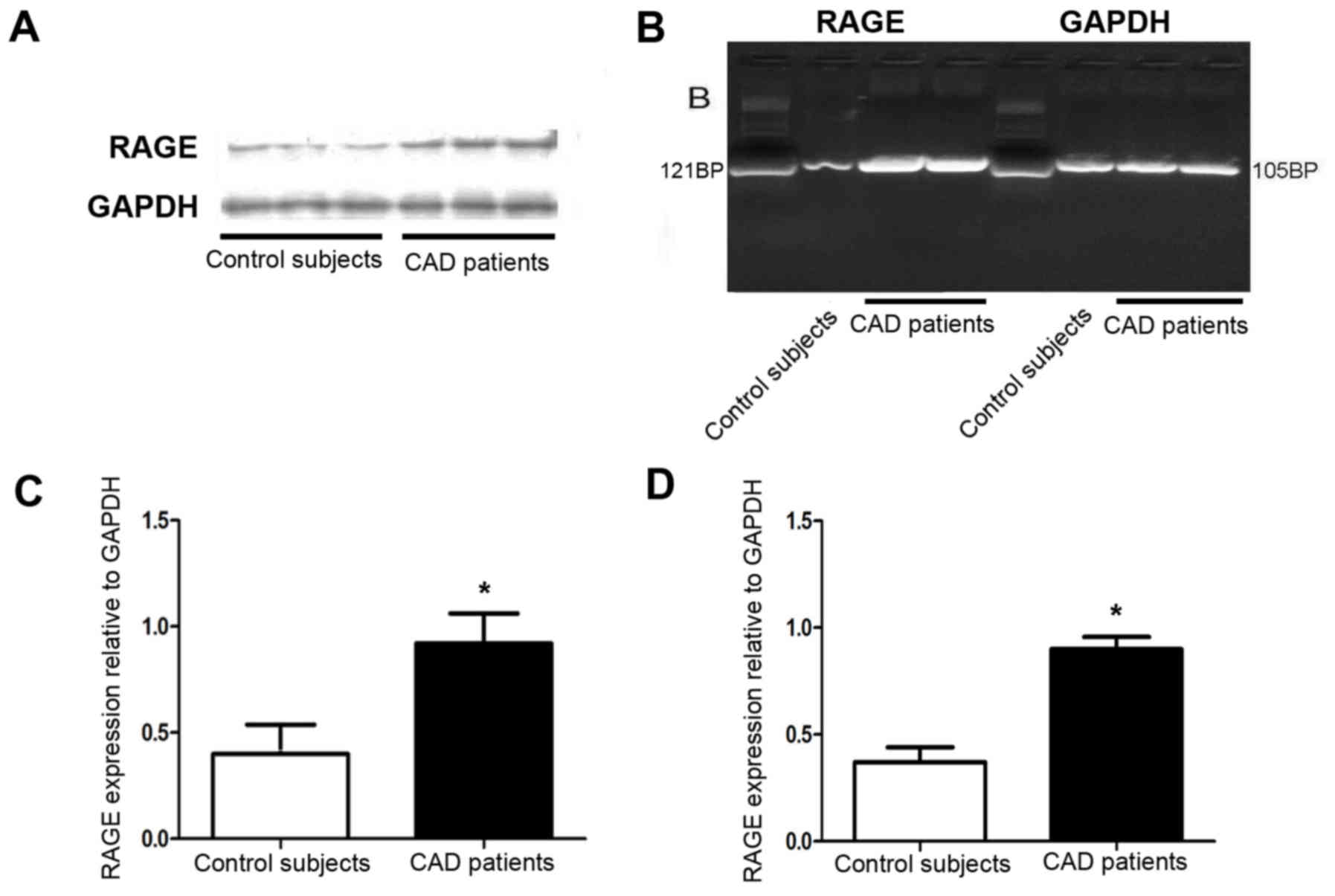
|
1
|
Kriszbacher I, Koppan M and Bodis J:
Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease. N Engl
J Med. 353:429–430. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Khera AV, Emdin CA, Drake I, Natarajan P,
Bick AG, Cook NR, Chasman DI, Baber U, Mehran R, Rader DJ, et al:
Genetic risk, adherence to a healthy lifestyle, and coronary
disease. N Engl J Med. 375:2349–2358. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Abaci A: Management of cardiovascular risk
factors for primary prevention: Evaluation of Turkey results of the
EURIKA study. Turk Kardiyol DernArs. 40:135–142. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Arbab-Zadeh A and Fuster V: The myth of
the ‘vulnerable plaque’: Transitioning from a focus on individual
lesions to atherosclerotic disease burden for coronary artery
disease risk assessment. J Am Coll Cardiol. 65:846–855. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bjorkegren JLM, Kovacic JC, Dudley JT and
Schadt EE: Genome-wide significant loci: How important are they?
Systems genetics to understand heritability of coronary artery
disease and other common complex disorders. J Am Coll Cardiol.
65:830–845. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gao J, Deng L, Wang Y, Shi Y, Xiao X,
Zheng X, Ren H and Xu D: Relationship between RAGE gene
polymorphisms and cardiovascular disease prognosis in the Chinese
Han population. Mol Genet Genomics. 292:1139–1149. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kajikawa M, Nakashima A, Fujimura N,
Maruhashi T, Iwamoto Y, Iwamoto A, Matsumoto T, Oda N, Hidaka T,
Kihara Y, et al: Ratio of serum levels of AGEs to soluble form of
RAGE is a predictor of endothelial function. Diabetes Care.
38:119–125. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Katakami N: Can soluble receptor for
advanced glycation end-product (sRAGE) levels in blood be used as a
predictor of cardiovascular diseases? Atherosclerosis. 266:223–225.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nam MH, Son WR, Lee YS and Lee KW:
Glycolaldehyde-derived advanced glycation end products
(glycol-AGEs)-induced vascular smooth muscle cell dysfunction is
regulated by the AGES-receptor (RAGE) axis in endothelium. Cell
Commun Adhes. 22:67–78. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Puri R, Nicholls SJ, Shao M, Kataoka Y,
Uno K, Kapadia SR, Tuzcu EM and Nissen SE: Impact of statins on
serial coronary calcification during atheroma progression and
regression. J Am Coll Cardiol. 65:1273–1282. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Reichert S, Triebert U, Santos AN, Hofmann
B, Schaller HG, Schlitt A and Schulz S: Soluble form of receptor
for advanced glycation end products and incidence of new
cardiovascular events among patients with cardiovascular disease.
Atherosclerosis. 266:234–239. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rowisha M, El-Batch M, El Shikh T, El
Melegy S and Aly H: Soluble receptor and gene polymorphism for AGE:
Relationship with obesity and cardiovascular risks. Pediatr Res.
80:67–71. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ligthart S, Sedaghat S, Ikram MA, Hofman
A, Franco OH and Dehghan A: EN-RAGE: A novel inflammatory marker
for incident coronary heart disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
34:2695–2699. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
American College of Cardiology
Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice
Guidelines; American Society of Echocardiography; American Society
of Nuclear Cardiology; Heart Rhythm Society; Society of
Cardiovascular Anesthesiologists; Society for Cardiovascular
Angiography and Interventions; Society for Vascular Medicine;
Society for Vascular Surgery, ; Fleisher LA, Beckman JA, et al:
2009 ACCF/AHA focused update on perioperative beta blockade
incorporated into the ACC/AHA 2007 guidelines on perioperative
cardiovascular evaluation and care for noncardiac surgery. J Am
Coll Cardiol. 54:e13–e118. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Elisaf M, Tzouvelekis E and Nikas N; Greek
EURIKA Investigators, : Primary prevention of cardiovascular
disease in Greece: Greek results of the EURIKA study. Hellenic J
Cardiol. 55:217–226. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ford TJ, Rocchiccioli P, Good R,
McEntegart M, Eteiba H, Watkins S, Shaukat A, Lindsay M, Robertson
K, Hood S, et al: Systemic microvascular dysfunction in
microvascular and vasospastic angina. Eur Heart J. 1–12.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ong P, Athanasiadis A and Sechtem U:
Treatment of angina pectoris associated with coronary microvascular
dysfunction. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 30:351–356. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Loffler AI and Bourque JM: Coronary
microvascular dysfunction, microvascular angina, and management.
Curr Cardiol Rep. 18:12016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ezhumalai B, Ananthakrishnapillai A,
Selvaraj RJ, Satheesh S and Jayaraman B: Cardiac syndrome X:
Clinical characteristics revisited. Indian Heart J. 67:328–331.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chhabra L and Kowlgi NG: Low incidence of
diabetes mellitus in coronary microvascular dysfunction: An
intriguing association. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 9:395–396. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Suzuki H: Different definition of
microvascular angina. Eur J Clin Invest. 45:1360–1366. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Morrison AC, Fu YP and O'Donnell CJ;
Cohorts for Heart and Aging Research in Genomic Epidemiology
(CHARGE) Consortium Subclinical Atherosclerosis and CHD Working
Working, : Working Group: Variants in ANGPTL4 and the risk of
coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med. 375:23032016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu Y, Tian X, Li Y, Liu D, Liu M, Zhang
X, Zhang Q, Yan C and Han Y: Up-Regulation of CREG expression by
the transcription factor GATA1 inhibits high glucose- and high
palmitate-induced apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial
cells. PLoS One. 11:e01548612016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cai W, Tao J, Zhang X, Tian X, Liu T, Feng
X, Bai J, Yan C and Han Y: Contribution of homeostatic chemokines
CCL19 and CCL21 and their receptor CCR7 to coronary artery disease.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 34:1933–1941. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Okon I, Ding Y and Zou MH: Ablation of
interferon regulatory factor 3 promotes the stability of
atherosclerotic plaques. Hypertension. 69:407–408. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Huang M, Han Y, Zhang X, Pei F, Deng J,
Kang J and Yan C: An intron polymorphism in the CXCL16 gene is
associated with increased risk of coronary artery disease in
Chinese Han population: A large angiography-based study.
Atherosclerosis. 210:160–165. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhao D, Tong L, Zhang L, Li H, Wan Y and
Zhang T: Tanshinone II A stabilizes vulnerable plaques by
suppressing RAGE signaling and NF-κB activation in
apolipoprotein-E-deficient mice. Mol Med Rep. 14:4983–4990. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yu Y, Wang L, Delguste F, Durand A,
Guilbaud A, Rousselin C, Schmidt AM, Tessier F, Boulanger E and
Neviere R: Advanced glycation end products receptor RAGE controls
myocardial dysfunction and oxidative stress in high-fat fed mice by
sustaining mitochondrial dynamics and autophagy-lysosome pathway.
Free Radic Biol Med. 112:397–410. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Muniyappa R and Srinivas PR: Dicarbonyl
stress and atherosclerosis: Is it all RAGE? Diabetes. 63:3587–3589.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ma WQ, Qu QR, Zhao Y and Liu NF:
Association of RAGE gene Gly82Ser polymorphism with coronary artery
disease and ischemic stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Medicine (Baltimore). 95:e55932016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Watson AM, Li J, Samijono D, Bierhaus A,
Thomas MC, Jandeleit-Dahm KA and Cooper ME: Quinapril treatment
abolishes diabetes-associated atherosclerosis in
RAGE/apolipoprotein E double knockout mice. Atherosclerosis.
235:444–448. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li Y, Zhu J, Chen L, Hu W, Wang M, Li S,
Gu X, Tao H, Zhao B, Ma G and Li K: Genetic predisposition to
ischaemic stroke by RAGE and HMGB1 gene variants in Chinese Han
population. Oncotarget. 8:100150–100164. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|