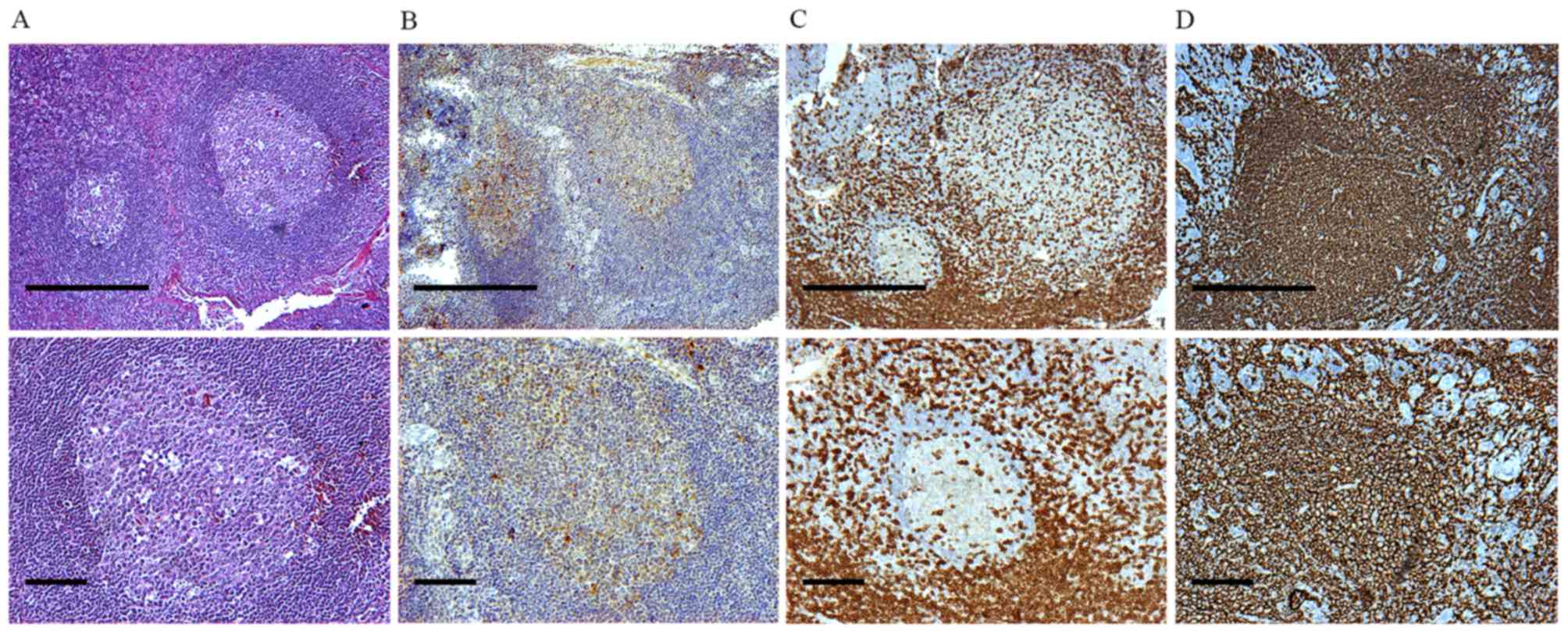
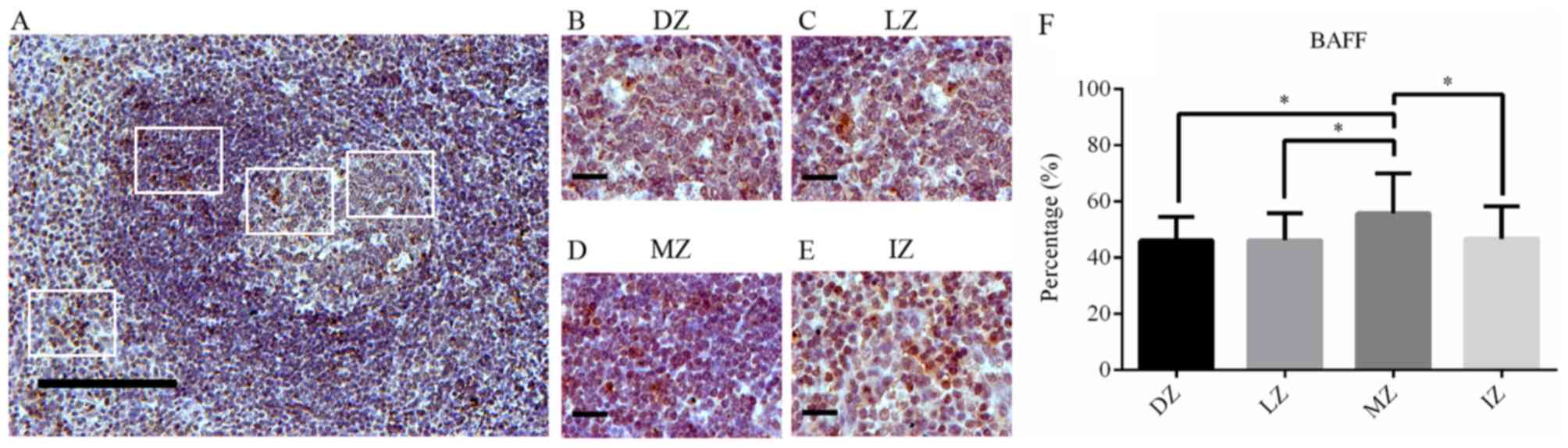
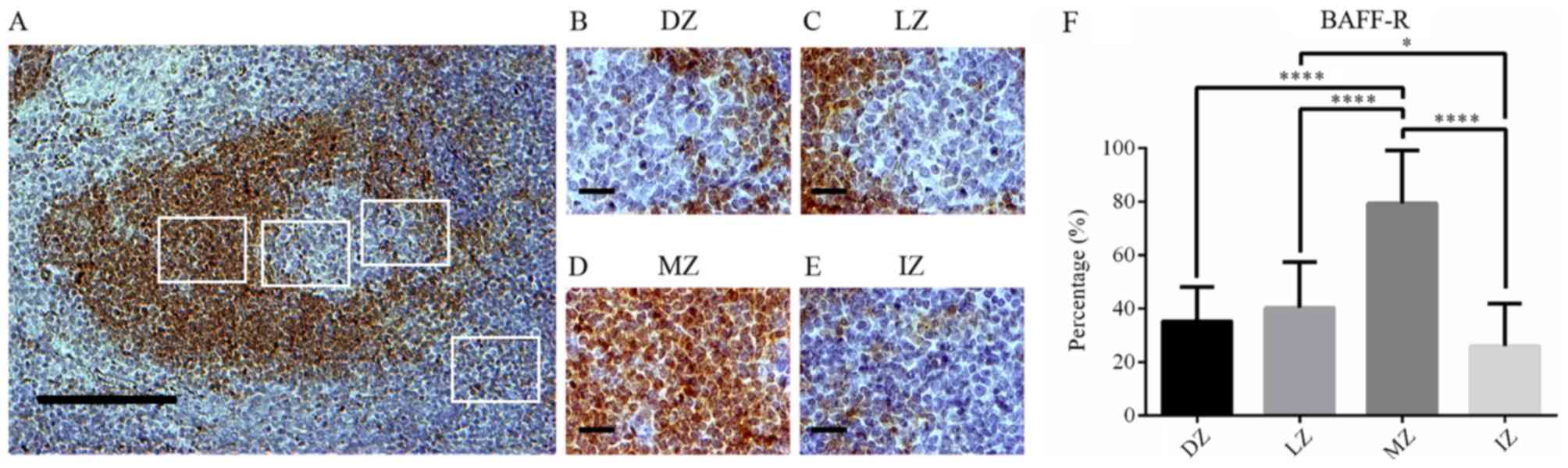
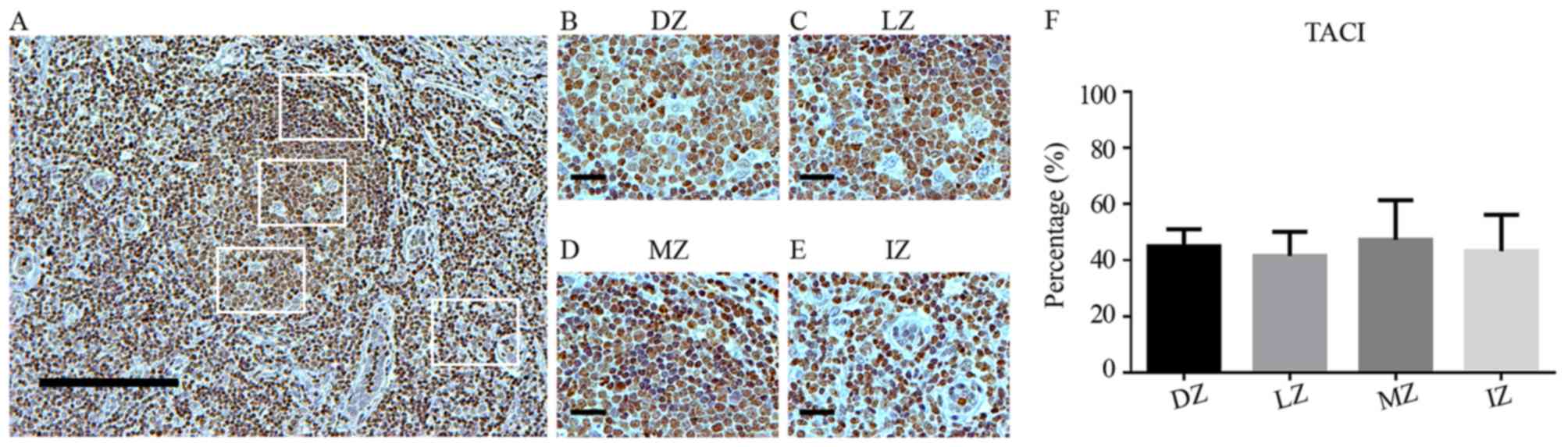
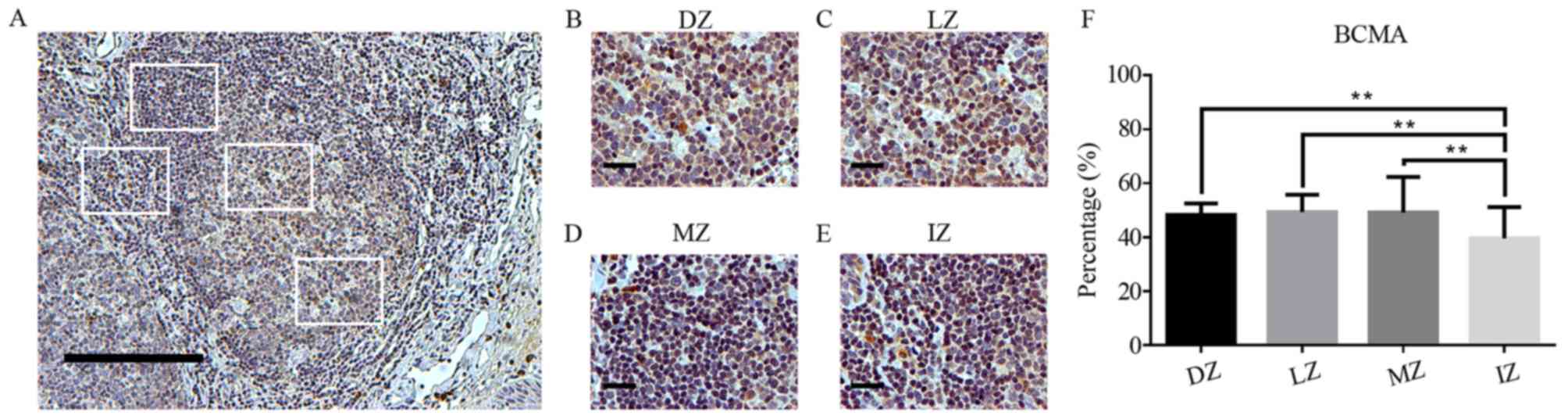
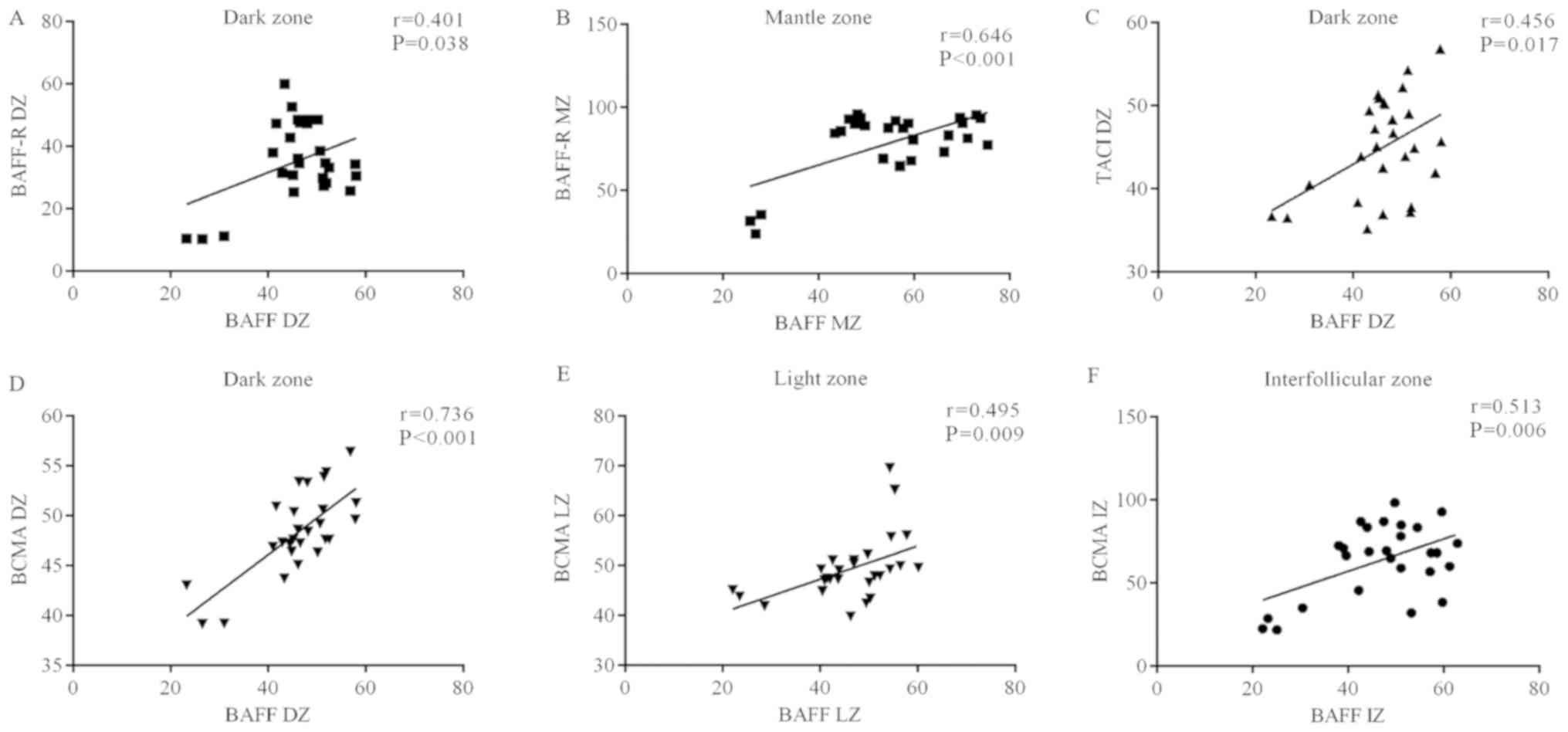
|
1
|
Vincent FB, Saulep-Easton D, Figgett WA,
Fairfax KA and Mackay F: The BAFF/APRIL system: Emerging functions
beyond B cell biology and autoimmunity. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.
24:203–215. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bossen C and Schneider P: BAFF, APRIL and
their receptors: Structure, function and signaling. Semin Immunol.
18:263–275. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Craxton A, Magaletti D, Ryan EJ and Clark
EA: Macrophage- and dendritic cell-dependent regulation of human
B-cell proliferation requires the TNF family ligand BAFF. Blood.
101:4464–4471. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Scapini P, Bazzoni F and Cassatella MA:
Regulation of B-cell-activating factor (BAFF)/B lymphocyte
stimulator (BLyS) expression in human neutrophils. Immunol Lett.
116:1–6. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
MacLennan I and Vinuesa C: Dendritic
cells, BAFF, and APRIL: Innate players in adaptive antibody
responses. Immunity. 17:235–238. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ogden CA, Pound JD, Batth BK, Owens S,
Johannessen I, Wood K and Gregory CD: Enhanced apoptotic cell
clearance capacity and B cell survival factor production by
IL-10-activated macrophages: Implications for burkitt's lymphoma. J
Immunol. 174:3015–3023. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Scapini P, Nardelli B, Nadali G, Calzetti
F, Pizzolo G, Montecucco C and Cassatella MA: G-CSF-stimulated
neutrophils are a prominent source of functional blys. J Exp Med.
197:297–302. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ohata J, Zvaifler NJ, Nishio M, Boyle DL,
Kalled SL, Carson DA and Kipps TJ: Fibroblast-like synoviocytes of
mesenchymal origin express functional B cell-activating factor of
the TNF family in response to proinflammatory cytokines. J Immunol.
174:864–870. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Krumbholz M, Theil D, Derfuss T, Rosenwald
A, Schrader F, Monoranu CM, Kalled SL, Hess DM, Serafini B, Aloisi
F, et al: BAFF is produced by astrocytes and up-regulated in
multiple sclerosis lesions and primary central nervous system
lymphoma. J Exp Med. 201:195–200. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chu VT, Enghard P, Riemekasten G and Berek
C: In vitro and in vivo activation induces BAFF and APRIL
expression in B cells. J Immunol. 179:5947–5957. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Suzuki K, Setoyama Y, Yoshimoto K, Tsuzaka
K, Abe T and Takeuchi T: Effect of interleukin-2 on synthesis of B
cell activating factor belonging to the tumor necrosis factor
family (BAFF) in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells.
Cytokine. 44:44–48. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pers JO, Daridon C, Devauchelle V, Jousse
S, Saraux A, Jamin C and Youinou P: BAFF overexpression is
associated with autoantibody production in autoimmune diseases. Ann
N Y Acad Sci. 1050:34–39. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Vincent FB, Morand EF and Mackay F: BAFF
and innate immunity: New therapeutic targets for systemic lupus
erythematosus. Immunol Cell Biol. 90:293–303. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Daridon C, Devauchelle V, Hutin P, Le
Berre R, Martins-Carvalho C, Bendaoud B, Dueymes M, Saraux A,
Youinou P and Pers JO: Aberrant expression of BAFF by B lymphocytes
infiltrating the salivary glands of patients with primary Sjögren's
syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 56:1134–1144. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bosello S, Pers JO, Rochas C, Devauchelle
V, De Santis M, Daridon C, Saraux A, Ferraccioli GF and Youinou P:
BAFF and rheumatic autoimmune disorders: Implications for disease
management and therapy. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 20:1–8. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pan J, Sun Y, Zhang N, Li J, Ta F, Wei W,
Yu S and Ai L: Characteristics of BAFF and APRIL factor expression
in multiple myeloma and clinical significance. Oncol Lett.
14:2657–2662. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Novak AJ, Grote DM, Stenson M, Ziesmer SC,
Witzig TE, Habermann TM, Harder B, Ristow KM, Bram RJ, Jelinek DF,
et al: Expression of BLyS and its receptors in B-cell non-Hodgkin
lymphoma: Correlation with disease activity and patient outcome.
Blood. 104:2247–2253. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Vaskua BJ, Bienerta P, Kodytkovab D,
Zlamala F, Tomandld J, Tomandlovad M, Vaskua A and Sterbab J: BAFF
levels are elevated in paediatric patients with acute lymphoblastic
leukaemia compared to other B-lineage neoplasms. J Hematol.
1:20–22. 2012.
|
|
19
|
Oki Y, Georgakis GV, Migone TS, Kwak LW
and Younes A: Prognostic significance of serum B-lymphocyte
stimulator in hodgkin's lymphoma. Haematologica. 92:269–270. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rowland SL, Leahy KF, Halverson R, Torres
RM and Pelanda R: BAFF receptor signaling aids the differentiation
of immature B cells into transitional B cells following tonic BCR
signaling. J Immunol. 185:4570–4581. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mackay F and Schneider P: TACI, an
enigmatic BAFF/APRIL receptor, with new unappreciated biochemical
and biological properties. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 19:263–276.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
von B, ülow GU, van Deursen JM and Bram
RJ: Regulation of the T-independent humoral response by TACI.
Immunity. 14:573–582. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yan M, Wang H, Chan B, Roose-Girma M,
Erickson S, Baker T, Tumas D, Grewal IS and Dixit VM: Activation
and accumulation of B cells in TACI-deficient mice. Nat Immunol.
2:638–643. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
O'Connor BP, Raman VS, Erickson LD, Cook
WJ, Weaver LK, Ahonen C, Lin LL, Mantchev GT, Bram RJ and Noelle
RJ: BCMA is essential for the survival of long-lived bone marrow
plasma cells. J Exp Med. 199:91–98. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Coquery CM, Loo WM, Wade NS, Bederman AG,
Tung KS, Lewis JE, Hess H and Erickson LD: BAFF regulates
follicular helper T cells and affects their accumulation and
interferon-γ production in autoimmunity: BAFF regulates follicular
helper T cells. Arthritis Rheumatol. 67:773–784. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rahman ZS, Rao SP, Kalled SL and Manser T:
Normal induction but attenuated progression of germinal center
responses in BAFF and BAFF-R signaling-deficient mice. J Exp Med.
198:1157–1169. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Vora KA, Wang LC, Rao SP, Liu ZY, Majeau
GR, Cutler AH, Hochman PS, Scott ML and Kalled SL: Cutting edge:
Germinal centers formed in the absence of B cell-activating factor
belonging to the TNF family exhibit impaired maturation and
function. J Immunol. 171:547–551. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ciccia F, Rizzo A, Maugeri R, Alessandro
R, Croci S, Guggino G, Cavazza A, Raimondo S, Cannizzaro A,
Iacopino DG, et al: Ectopic expression of CXCL13, BAFF, APRIL and
LT-β is associated with artery tertiary lymphoid organs in giant
cell arteritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 76:235–243. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kang S, Fedoriw Y, Brenneman EK, Truong
YK, Kikly K and Vilen BJ: BAFF induces tertiary lymphoid structures
and positions T cells within the glomeruli during lupus nephritis.
J Immunol. 198:2602–2611. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chiu A, Xu W, He B, Dillon SR, Gross JA,
Sievers E, Qiao X, Santini P, Hyjek E, Lee JW, et al: Hodgkin
lymphoma cells express TACI and BCMA receptors and generate
survival and proliferation signals in response to BAFF and APRIL.
Blood. 109:729–739. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yang S, Li JY and Xu W: Role of
BAFF/BAFF-R axis in B-cell non-hodgkin lymphoma. Crit Rev Oncol
Hematol. 91:113–122. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nocturne G and Mariette X: Sjögren
syndrome-associated lymphomas: An update on pathogenesis and
management. Br J Haematol. 168:317–327. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nakamura N, Hase H, Sakurai D, Yoshida S,
Abe M, Tsukada N, Takizawa J, Aoki S, Kojima M, Nakamura S and
Kobata T: Expression of BAFF-R (BR3) in normal and neoplastic
lymphoid tissues characterized with a newly developed monoclonal
antibody. Virchows Arch. 447:53–60. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang X, Park CS, Yoon SO, Li L, Hsu YM,
Ambrose C and Choi YS: BAFF supports human B cell differentiation
in the lymphoid follicles through distinct receptors. Int Immunol.
17:779–788. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chatterjee S, Malhotra R, Varghese F,
Bukhari AB, Patil A, Budrukkar A, Parmar V, Gupta S and De A:
Quantitative immunohistochemical analysis reveals association
between sodium iodide symporter and estrogen receptor expression in
breast cancer. PLoS One. 8:e540552013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Allen CD, Okada T and Cyster JG:
Germinal-center organization and cellular dynamics. Immunity.
27:190–202. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Corcoran LM and Tarlinton DM: Regulation
of germinal center responses, memory B cells and plasma cell
formation-an update. Curr Opin Immunol. 39:59–67. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Victora GD and Nussenzweig MC: Germinal
centers. Annu Rev Immunol. 30:429–457. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hase H, Kanno Y, Kojima M, Hasegawa K,
Sakurai D, Kojima H, Tsuchiya N, Tokunaga K, Masawa N, Azuma M, et
al: BAFF/BLyS can potentiate B-cell selection with the B-cell
coreceptor complex. Blood. 103:2257–2265. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Suzuki K, Maruya M, Kawamoto S, Sitnik K,
Kitamura H, Agace WW and Fagarasan S: The sensing of environmental
stimuli by follicular dendritic cells promotes immunoglobulin a
generation in the gut. Immunity. 33:71–83. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Treml LS, Carlesso G, Hoek KL, Stadanlick
JE, Kambayashi T, Bram RJ, Cancro MP and Khan WN: TLR stimulation
modifies BLyS receptor expression in follicular and marginal zone B
cells. J Immunol. 178:7531–7539. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Schneider P: The role of APRIL and BAFF in
lymphocyte activation. Curr Opin Immunol. 17:282–289. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Thien M, Phan TG, Gardam S, Amesbury M,
Basten A, Mackay F and Brink R: Excess BAFF rescues self-reactive B
cells from peripheral deletion and allows them to enter forbidden
follicular and marginal zone niches. Immunity. 20:785–798. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sharma A, Kiripolsky J, Klimatcheva E,
Howell A, Fereidouni F, Levenson R, Rothstein TL and Kramer JM:
Early BAFF receptor blockade mitigates murine Sjögren's syndrome:
Concomitant targeting of CXCL13 and the BAFF receptor prevents
salivary hypofunction. Clin Immunol. 164:85–94. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Bräuninger A, Yang W, Wacker HH, Rajewsky
K, Küppers R and Hansmann ML: B-cell development in progressively
transformed germinal centers: Similarities and differences compared
with classical germinal centers and lymphocyte-predominant hodgkin
disease. Blood. 97:714–719. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Le Pottier L, Devauchelle V, Fautrel A,
Daridon C, Saraux A, Youinou P and Pers JO: Ectopic germinal
centers are rare in sjogren's syndrome salivary glands and do not
exclude autoreactive B cells. J Immunol. 182:3540–3547. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Tussiwand R, Rauch M, Flück LA and Rolink
AG: BAFF-R expression correlates with positive selection of
immature B cells: Leukocyte signaling. Eur J Immunol. 42:206–216.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Smulski CR, Kury P, Seidel LM, Staiger HS,
Edinger AK, Willen L, Seidl M, Hess H, Salzer U, Rolink AG, et al:
BAFF- and TACI-dependent processing of BAFFR by ADAM proteases
regulates the survival of B cells. Cell Rep. 18:2189–2202. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ng LG, Sutherland AP, Newton R, Qian F,
Cachero TG, Scott ML, Thompson JS, Wheway J, Chtanova T, Groom J,
et al: B cell-activating factor belonging to the TNF family
(BAFF)-R is the principal BAFF receptor facilitating BAFF
costimulation of circulating T and B cells. J Immunol. 173:807–817.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ou X, Xu S and Lam KP: Deficiency in
TNFRSF13B (TACI) expands T-follicular helper and germinal center B
cells via increased ICOS-ligand expression but impairs plasma cell
survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:15401–15406. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Tran NL, Schneider P and Santiago-Raber
ML: TACI-dependent APRIL signaling maintains autoreactive B cells
in a mouse model of systemic lupus erythematosus. Eur J Immunol.
47:713–723. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Novak AJ, Darce JR, Arendt BK, Harder B,
Henderson K, Kindsvogel W, Gross JA, Greipp PR and Jelinek DF:
Expression of BCMA, TACI, and BAFF-R in multiple myeloma: A
mechanism for growth and survival. Blood. 103:689–694. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Jiang C, Loo WM, Greenley EJ, Tung KS and
Erickson LD: B cell maturation antigen deficiency exacerbates
lymphoproliferation and autoimmunity in murine lupus. J Immunol.
186:6136–6147. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|