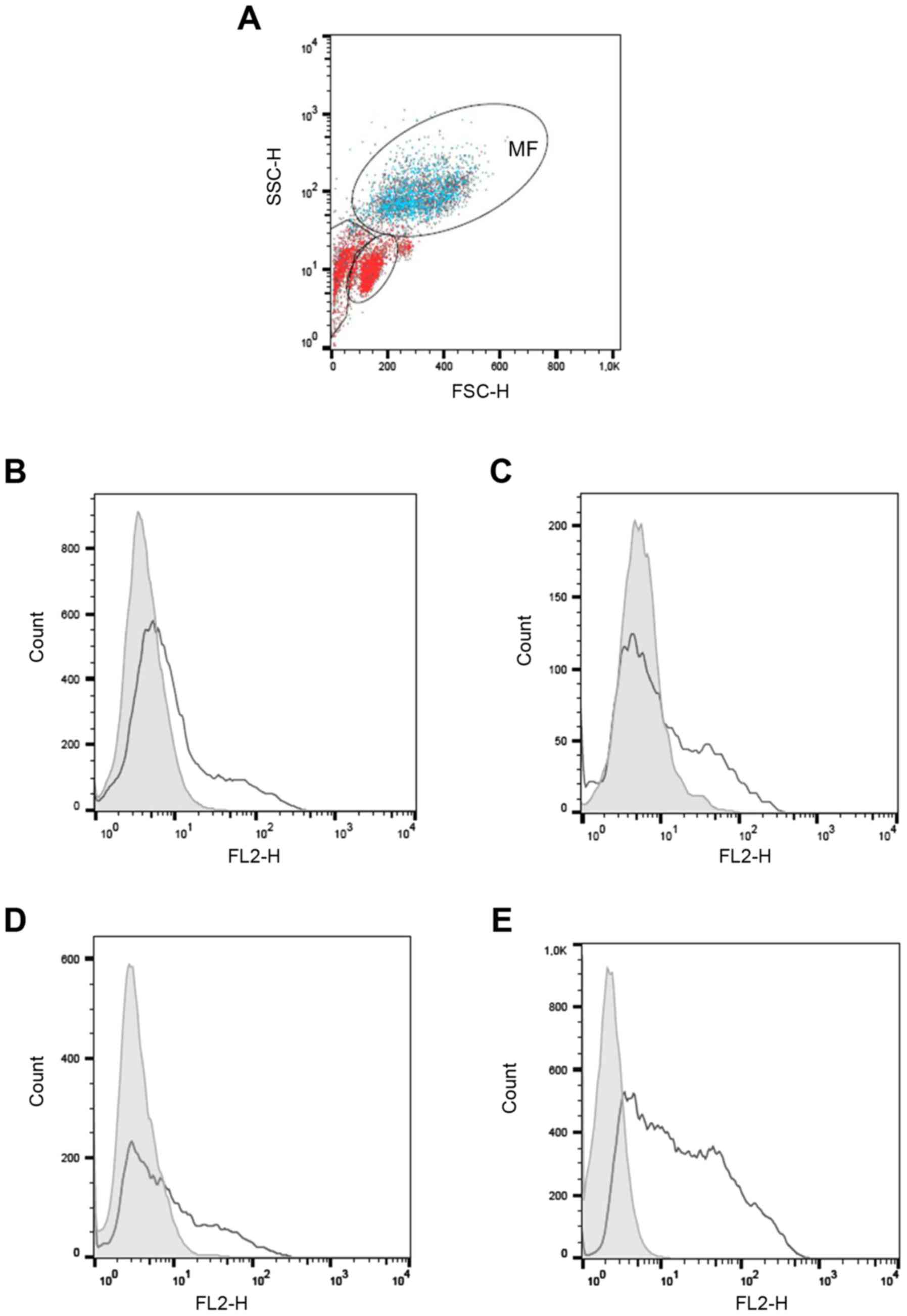
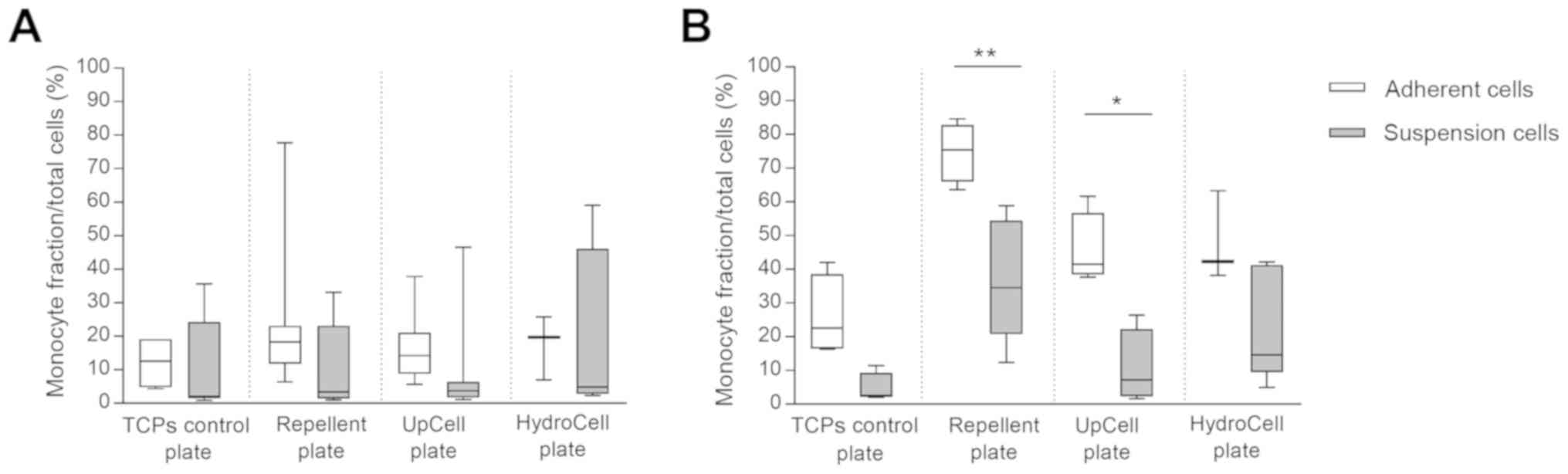
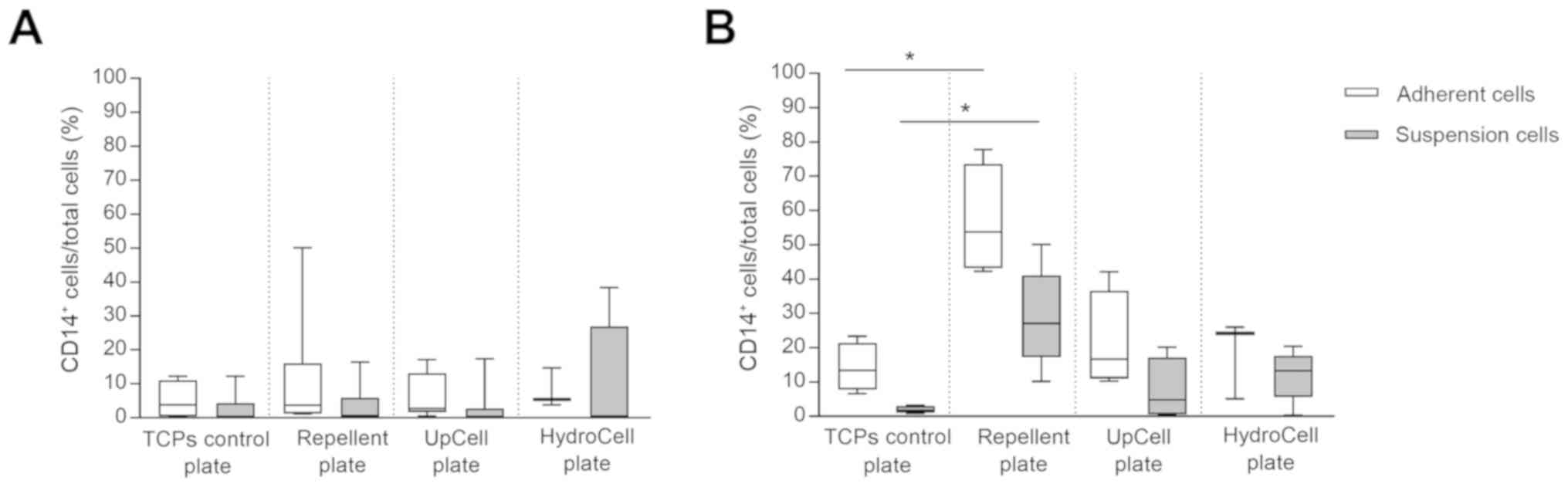
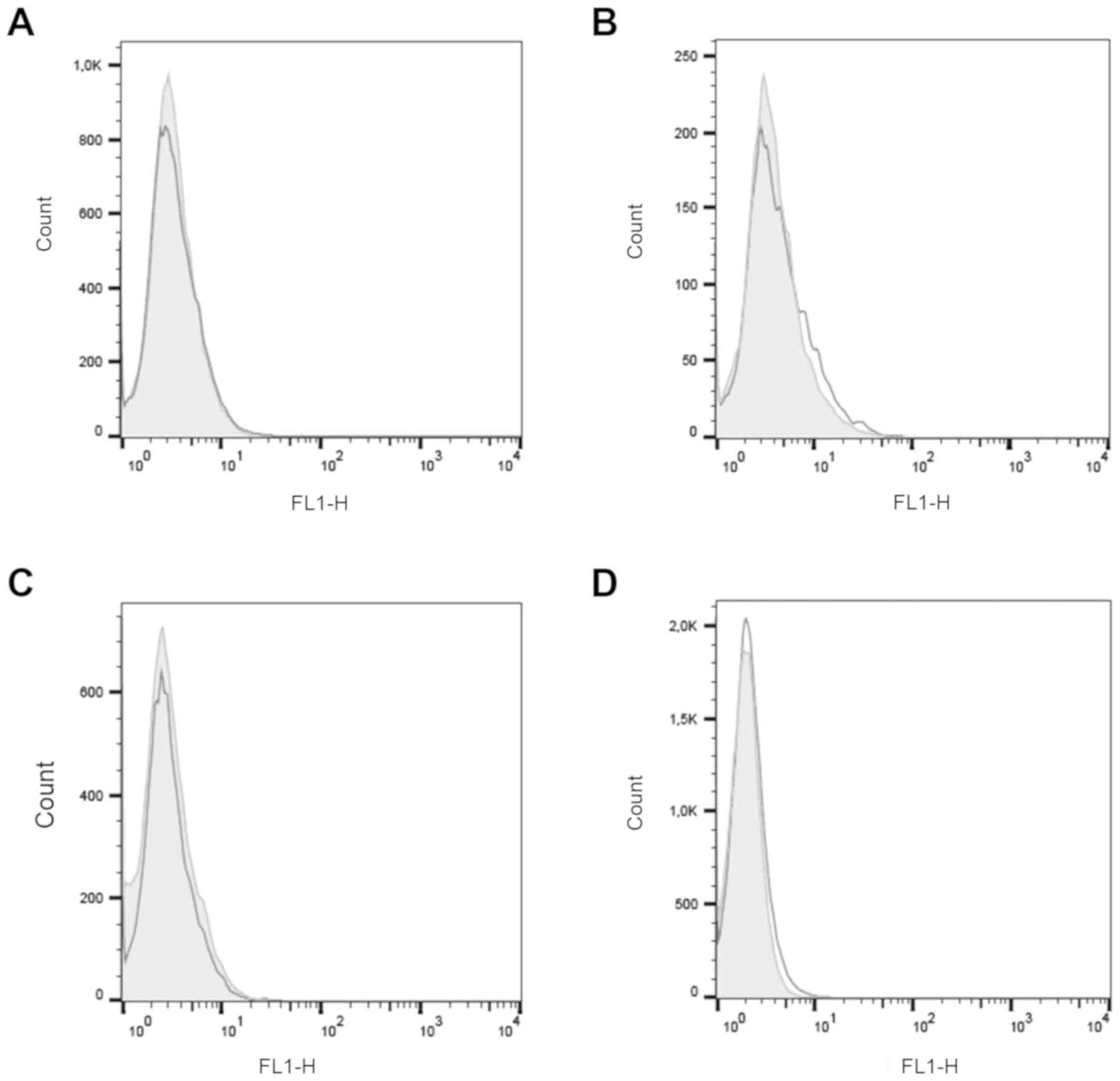
|
1
|
Ziegler-Heitbrock L, Ancuta P, Crowe S,
Dalod M, Grau V, Hart DN, Leenen PJ, Liu YJ, MacPherson G, Randolph
GJ, et al: Nomenclature of monocytes and dendritic cells in blood.
Blood. 116:e74–e80. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ginhoux F and Guilliams M: Tissue-resident
macrophage ontogeny and homeostasis. Immunity. 44:439–449. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yang J, Zhang L, Yu C, Yang XF and Wang H:
Monocyte and macrophage differentiation: Circulation inflammatory
monocyte as biomarker for inflammatory diseases. Biomark Res.
2:12014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Geissmann F, Manz MG, Jung S, Sieweke MH,
Merad M and Ley K: Development of monocytes, macrophages, and
dendritic cells. Science. 327:656–661. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mosser DM and Edwards JP: Exploring the
full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat Rev Immunol. 8:958–969.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Davies LC, Rosas M, Jenkins SJ, Liao CT,
Scurr MJ, Brombacher F, Fraser DJ, Allen JE, Jones SA and Taylor
PR: Distinct bone marrow-derived and tissue-resident macrophage
lineages proliferate at key stages during inflammation. Nat Commun.
4:18862015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Thomsen P and Gretzer C: Macrophage
interactions with modified material surfaces. Curr Opin Solid State
Mater Sci. 5:163–176. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Yao T and Asayama Y: Animal-cell culture
media: History, characteristics, and current issues. Reprod Med
Biol. 16:99–117. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tang Z, Akiyama Y and Okano T: Recent
development of temperature-responsive cell culture surface using
poly (N-isopropylacrylamide). J Polym Sci Part B. 52:917–926. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
France RM and Short RD: Plasma treatment
of polymers: The effects of energy transfer from an Argon plasma on
the surface chemistry of polystyrene, and polypropylene. A
high-energy resolution X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy study.
Langmuir. 14:4827–4835. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Guruvenket S, Mohan Rao G, Komath M and
Raichur AM: Plasma surface modification of polystyrene and
polyethylene. Appl Surf Sci. 236:278–284. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Kunisch E, Fuhrmann R, Roth A, Winter R,
Lungershausen W and Kinne RW: Macrophage specificity of three
anti-CD68 monoclonal antibodies (KP1, EBM11, and PGM1) widely used
for immunohistochemistry and flow cytometry. Ann Rheum Dis.
63:774–784. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hoffman RA, Kung PC, Hansen WP and
Goldstein G: Simple and rapid measurement of human T lymphocytes
and their subclasses in peripheral blood. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
77:4914–4917. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Terstappen LW, de Grooth BG, Visscher K,
van Kouterik FA and Greve J: Four-parameter white blood cell
differential counting based on light scattering measurements.
Cytometry. 9:39–43. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Williams JM, Abbud-Filho M, Kelley VE and
Strom TB: Interleukin-2 apparently upregulates its receptor and
induces proliferation of various resting mononuclear leukocytes in
the absence of antigen. Cell Immunol. 94:383–393. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bertolo A, Pavlicek D, Gemperli A, Baur M,
Pötzel T and Stoyanov J: Increased motility of mesenchymal stem
cells is correlated with inhibition of stimulated peripheral blood
mononuclear cells in vitro. J Stem Cells Regen Med. 13:62–74.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hodge G, Hodge S and Han P: Increased
levels of apoptosis of leukocyte subsets in cultured PBMCs compared
to whole blood as shown by Annexin V binding: Relevance to cytokine
production. Cytokine. 12:1763–1768. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jones JA, Chang DT, Meyerson H, Colton E,
Kwon IK, Matsuda T and Anderson JM: Proteomic analysis and
quantification of cytokines and chemokines from biomaterial
surface-adherent macrophages and foreign body giant cells. J Biomed
Mater Res A. 83:585–596. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Schildberger A, Rossmanith E, Eichhorn T,
Strassl K and Weber V: Monocytes, peripheral blood mononuclear
cells, and THP-1 cells exhibit different cytokine expression
patterns following stimulation with lipopolysaccharide. Mediators
Inflamm 2013. 6979722013.
|
|
20
|
Shen M and Horbett TA: The effects of
surface chemistry and adsorbed proteins on monocyte/macrophage
adhesion to chemically modified polystyrene surfaces. J Biomed
Mater Res. 57:336–345. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Anderson JM, Rodriguez A and Chang DT:
Foreign body reaction to biomaterials. Semin Immunol. 20:86–100.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Brodbeck WG, Shive MS, Colton E, Nakayama
Y, Matsuda T and Anderson JM: Influence of biomaterial surface
chemistry on the apoptosis of adherent cells. J Biomed Mater Res.
55:661–668. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dinnes DL, Santerre JP and Labow RS:
Influence of biodegradable and non-biodegradable material surfaces
on the differentiation of human monocyte-derived macrophages.
Differentiation. 76:232–244. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Thevenot P, Hu W and Tang L: Surface
chemistry influences implant biocompatibility. Curr Top Med Chem.
8:270–280. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sheikh Z, Brooks PJ, Barzilay O, Fine N
and Glogauer M: Macrophages, foreign body giant cells and their
response to implantable biomaterials. Materials (Basel).
8:5671–5701. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rostam HM, Singh S, Salazar F, Magennis P,
Hook A, Singh T, Vrana NE, Alexander MR and Ghaemmaghami AM: The
impact of surface chemistry modification on macrophage
polarisation. Immunobiology. 221:1237–1246. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tedesco S, Bolego C, Toniolo A, Nassi A,
Fadini GP, Locati M and Cignarella A: Phenotypic activation and
pharmacological outcomes of spontaneously differentiated human
monocyte-derived macrophages. Immunobiology. 220:545–554. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Brodbeck WG, Voskerician G, Ziats NP,
Nakayama Y, Matsuda T and Anderson JM: In vivo leukocyte cytokine
mRNA responses to biomaterials are dependent on surface chemistry.
J Biomed Mater Res A. 64:320–329. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Schutte RJ, Parisi-Amon A and Reichert WM:
Cytokine profiling using monocytes/macrophages cultured on common
biomaterials with a range of surface chemistries. J Biomed Mater
Res A. 88:128–139. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jenney CR and Anderson JM: Adsorbed serum
proteins responsible for surface dependent human macrophage
behavior. J Biomed Mater Res. 49:435–447. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ktari N, Poncet P, Sénéchal H, Malaquin L,
Kanoufi F and Combellas C: Patterning of polystyrene by scanning
electrochemical microscopy. Biological applications to cell
adhesion. Langmuir. 26:17348–17356. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bacakova L, Filova E, Parizek M, Ruml T
and Svorcik V: Modulation of cell adhesion, proliferation and
differentiation on materials designed for body implants. Biotechnol
Adv. 29:739–767. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Harris CA, Resau JH, Hudson EA, West RA,
Moon C, Black AD and McAllister JP II: Effects of surface
wettability, flow, and protein concentration on macrophage and
astrocyte adhesion in an in vitro model of central nervous system
catheter obstruction. J Biomed Mater Res A. 97:433–440. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Battiston KG, Labow RS and Santerre JP:
Protein binding mediation of biomaterial-dependent monocyte
activation on a degradable polar hydrophobic ionic polyurethane.
Biomaterials. 33:8316–8328. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Maciel J, Oliveira MI, Goncalves RM and
Barbosa MA: The effect of adsorbed fibronectin and osteopontin on
macrophage adhesion and morphology on hydrophilic and hydrophobic
model surfaces. Acta Biomater. 8:3669–3677. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
McBane JE, Matheson LA, Sharifpoor S,
Santerre JP and Labow RS: Effect of polyurethane chemistry and
protein coating on monocyte differentiation towards a wound healing
phenotype macrophage. Biomaterials. 30:5497–5504. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Collier TO, Anderson JM, Kikuchi A and
Okano T: Adhesion behavior of monocytes, macrophages, and foreign
body giant cells on poly (N-isopropylacrylamide)
temperature-responsive surfaces. J Biomed Mater Res. 59:136–143.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Brodbeck WG, Patel J, Voskerician G,
Christenson E, Shive MS, Nakayama Y, Matsuda T, Ziats NP and
Anderson JM: Biomaterial adherent macrophage apoptosis is increased
by hydrophilic and anionic substrates in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 99:10287–10292. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Jonitz-Heincke A, Tillmann J, Klinder A,
Krueger S, Kretzer JP, Høl PJ, Paulus AC and Bader R: The impact of
metal ion exposure on the cellular behavior of human osteoblasts
and PBMCs: In vitro analyses of osteolytic processes. Materials.
10(pii): E7342017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Klinder A, Seyfarth A, Hansmann D, Bader R
and Jonitz-Heincke A: Inflammatory response of human peripheral
blood mononuclear cells and osteoblasts incubated with metallic and
ceramic submicron particles. Front Immunol. 9:8312018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Markhoff J, Krogull M, Schulze C, Rotsch
C, Hunger S and Bader R: Biocompatibility and inflammatory
potential of titanium alloys cultivated with human osteoblasts,
fibroblasts and macrophages. Materials. 10(pii): E522017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|