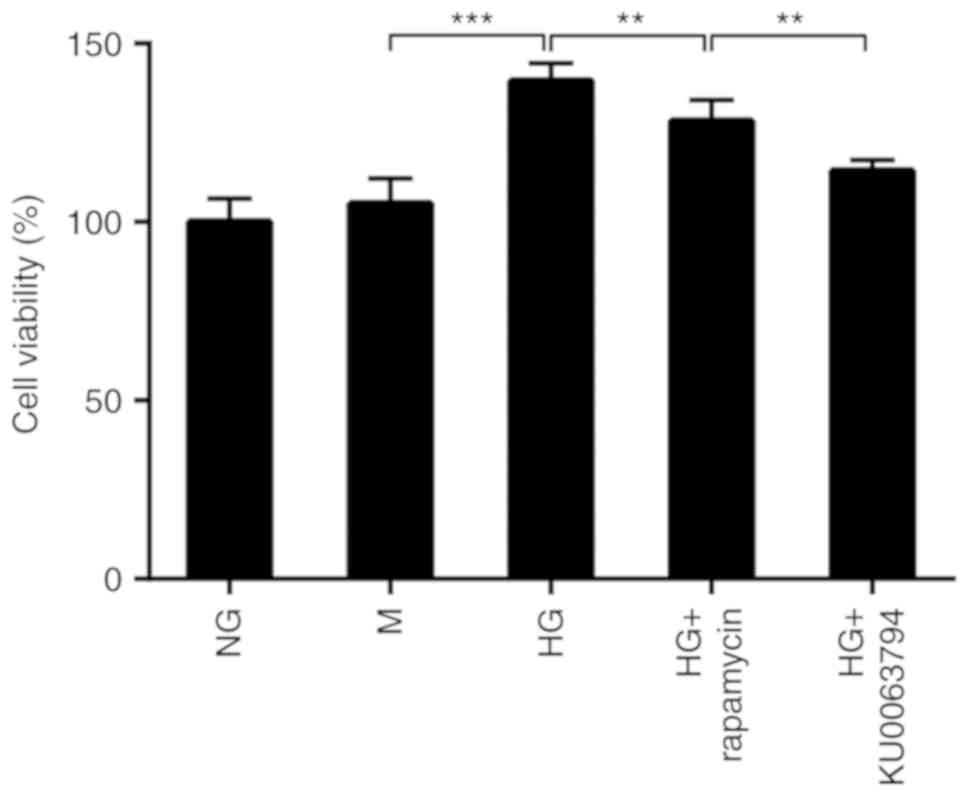
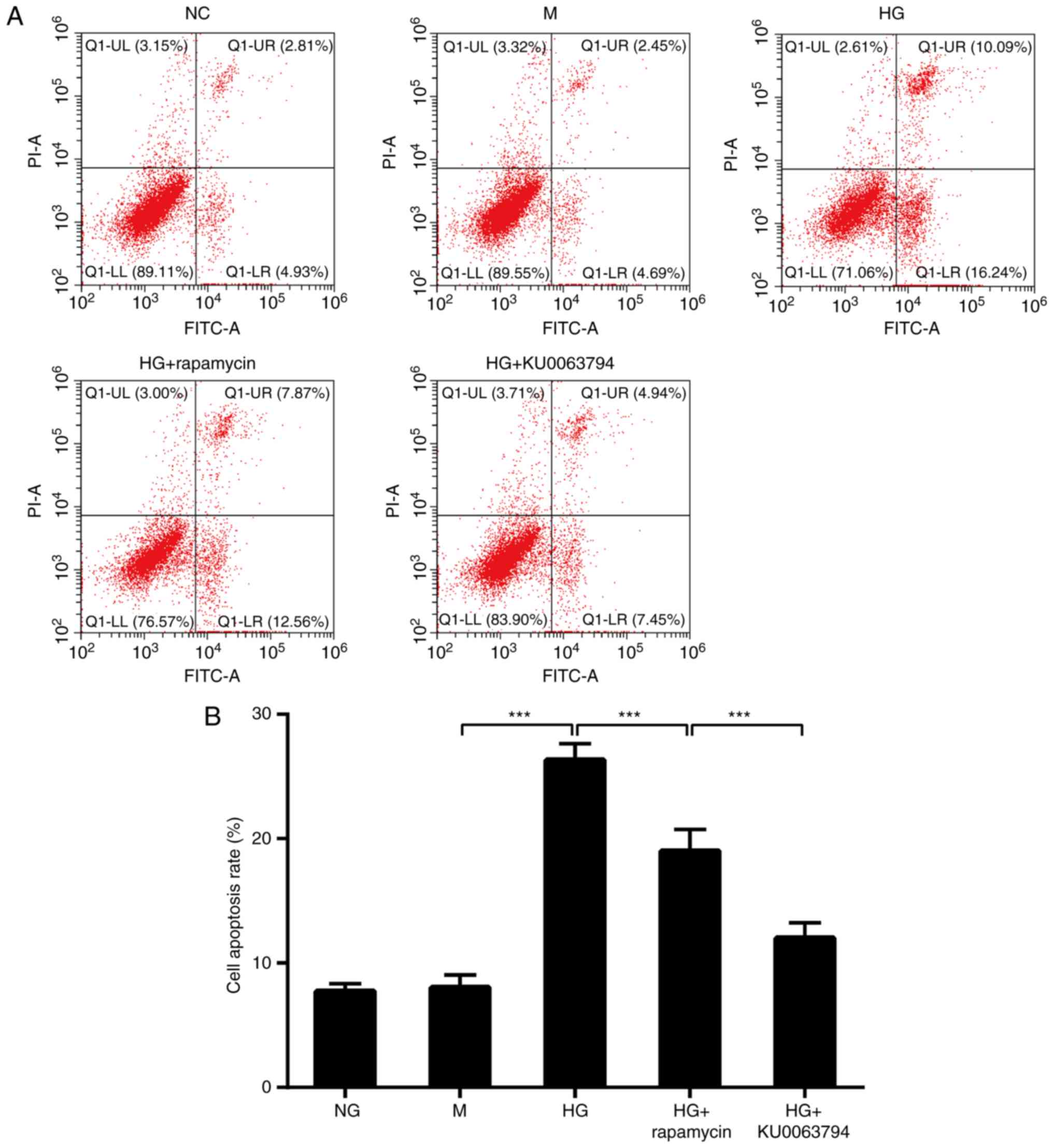
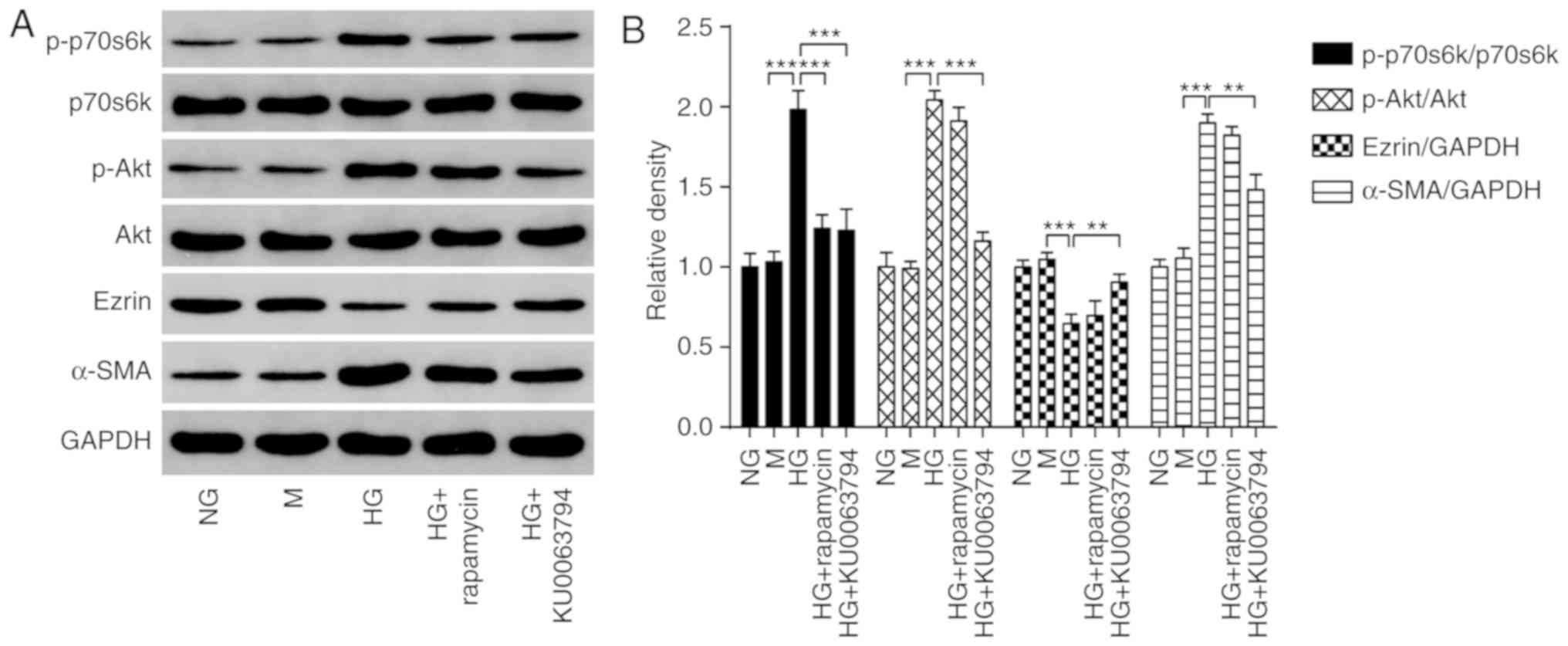
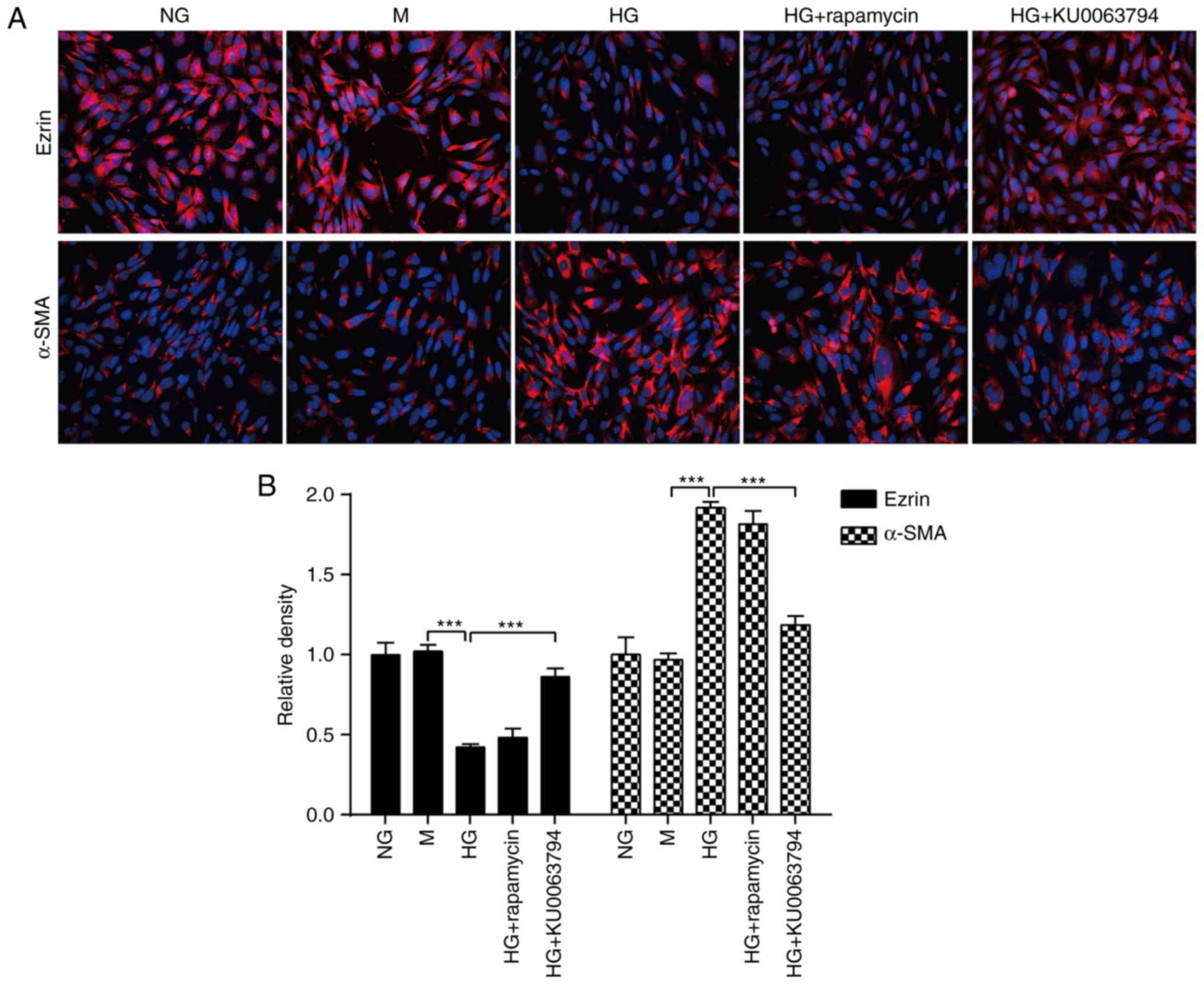
|
1
|
Lippert J, Ritz E, Schwarzbeck A and
Schneider P: The rising tide of endstage renal failure from
diabetic nephropathy type II-an epidemiological analysis. Nephrol
Dial Transplant. 10:462–467. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Graves DT and Kayal RA: Diabetic
complications and dysregulated innate immunity. Front Biosci.
13:1227–1239. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ziyadeh FN: Mediators of diabetic renal
disease: The case for tgf-Beta as the major mediator. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 15 (Suppl 1):S552004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yasuda-Yamahara M, Kume S, Tagawa A,
Maegawa H and Uzu T: Emerging role of podocyte autophagy in the
progression of diabetic nephropathy. Autophagy. 11:2385–2386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jefferson JA, Shankland SJ and Pichler RH:
Proteinuria in diabetic kidney disease: A mechanistic viewpoint.
Kidney Int. 74:22–36. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mathieson PW: The podocyte as a target for
therapies-new and old. Nat Rev Nephrol. 8:52–56. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Covington MD and Schnellmann RG: Chronic
high glucose downregulates mitochondrial calpain 10 and contributes
to renal cell death and diabetes-induced renal injury. Kidney Int.
81:391–400. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fox CS, Matsushita K, Woodward M, Bilo HJ,
Chalmers J, Heerspink HJ, Lee BJ, Perkins RM, Rossing P, Sairenchi
T, et al: Associations of kidney disease measures with mortality
and end-stage renal disease in individuals with and without
hypertension: A meta-analysis. Lancet. 380:1662–1673. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li C and Siragy HM: High glucose induces
podocyte injury via enhanced (pro)renin
receptor-Wnt-β-catenin-snail signaling pathway. PLoS One.
9:e892332014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tryggvason K, Patrakka J and Wartiovaara
J: Hereditary proteinuria syndromes and mechanisms of proteinuria.
N Engl J Med. 354:1387–1401. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Coimbra TM, Janssen U, Gröne HJ, Ostendorf
T, Kunter U, Schmidt H, Brabant G and Floege J: Early events
leading to renal injury in obese Zucker (fatty) rats with type II
diabetes. Kidney Int. 57:167–182. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Siu B, Saha J, Smoyer WE, Sullivan KA and
Brosius FC: Reduction in podocyte density as a pathologic feature
in early diabetic nephropathy in rodents: Prevention by lipoic acid
treatment. Bmc Nephrol. 7:62006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Torres VE, Boletta A, Chapman A, Gattone
V, Pei Y, Qian Q, Wallace DP, Weimbs T and Wüthrich RP: Prospects
for mTOR inhibitor use in patients with polycystic kidney disease
and hamartomatous diseases. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 5:1312–1329.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wullschleger S, Loewith R and Hall MN: TOR
signaling in growth and metabolism. Cell. 124:471–484. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sarbassov DD, Ali SM, Kim DH, Guertin DA,
Latek RR, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P and Sabatini DM: Rictor, a
novel binding partner of mTOR, defines a rapamycin-insensitive and
raptor-independent pathway that regulates the cytoskeleton. Curr
Biol. 14:1296–1302. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mori S, Nada S, Kimura H, Tajima S,
Takahashi Y, Kitamura A, Oneyama C and Okada M: The mTOR pathway
controls cell proliferation by regulating the FoxO3a transcription
factor via SGK1 kinase. PLoS One. 9:e888912014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tsai TF, Lin JF, Chou KY, Lin YC, Chen HE
and Hwang TI: miR-99a-5p acts as tumor suppressor via targeting to
mTOR and enhances RAD001-induced apoptosis in human urinary bladder
urothelial carcinoma cells. Onco Targets Ther. 11:239–252. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shortt J, Martin BP, Newbold A, Hannan KM,
Devlin JR, Baker AJ, Ralli R, Cullinane C, Schmitt CA, Reimann M,
et al: Combined inhibition of PI3K-related DNA damage response
kinases and mTORC1 induces apoptosis in MYC-driven B-cell
lymphomas. Blood. 121:2964–2974. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hagiwara A, Nishiyama M and Ishizaki S:
Branched-chain amino acids prevent insulin-induced hepatic tumor
cell proliferation by inducing apoptosis through mTORC1 and
mTORC2-dependent mechanisms. J Cell Physiol. 227:2097–2105. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gurusamy N, Lekli I, Mukherjee S, Ray D,
Ahsan MK, Gherghiceanu M, Popescu LM and Das DK: Cardioprotection
by resveratrol: A novel mechanism via autophagy involving the
mTORC2 pathway. Cardiovasc Res. 86:103–112. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang HT, Wang WW, Ren LH, Zhao XX, Wang
ZH, Zhuang DL and Bai YN: The mTORC2/Akt/NFκB pathway-mediated
activation of TRPC6 participates in adriamycin-induced podocyte
apoptosis. Cell Physiol Biochem. 40:1079–1093. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cao W, Li M, Wu T, Feng F, Feng T, Xu Y
and Sun C: αMSH prevents ROS-induced apoptosis by inhibiting
Foxo1/mTORC2 in mice adipose tissue. Oncotarget. 8:40872–40884.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lei J, Zhao L, Zhang Y, Wu Y and Liu Y:
High glucose-induced podocyte injury involves activation of
mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)-induced endoplasmic reticulum
(ER) stress. Cell Physiol Biochem. 45:2431–2443. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Altman JK, Szilard A, Goussetis DJ,
Sassano A, Colamonici M, Gounaris E, Frankfurt O, Giles FJ, Eklund
EA, Beauchamp EM and Platanias LC: Autophagy is a survival
mechanism of acute myelogenous leukemia precursors during dual
mTORC2/mTORC1 targeting. Clin Cancer Res. 20:2400–2409. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hettmer S, Liu J, Miller CM, Lindsay MC,
Sparks CA, Guertin DA, Bronson RT, Langenau DM and Wagers AJ:
Sarcomas induced in discrete subsets of prospectively isolated
skeletal muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:20002–20007.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang H, Berel D, Wang Y, Li P, Bhowmick
NA, Figlin RA and Kim HL: A comparison of Ku0063794, a dual mTORC1
and mTORC2 inhibitor, and temsirolimus in preclinical renal cell
carcinoma models. PLoS One. 8:e549182013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Laplante M and Sabatini DM: mTOR signaling
in growth control and disease. Cell. 149:274–293. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Boehlke C, Kotsis F, Patel V, Braeg S,
Voelker H, Bredt S, Beyer T, Janusch H, Hamann C, Gödel M, et al:
Primary cilia regulate mTORC1 activity and cell size through Lkb1.
Nat Cell Biol. 12:1115–1122. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lou JS, Xia YT, Wang HY, Kong XP, Yao P,
Dong TTX, Zhou ZY and Tsim KWK: The WT1/MVP-mediated stabilization
on mTOR/AKT axis enhances the effects of cisplatin in non-small
cell lung cancer by a reformulated yu ping feng san herbal
preparation. Front Pharmacol. 9:8532018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Arpin M, Chirivino D, Naba A and
Zwaenepoel I: Emerging role for ERM proteins in cell adhesion and
migration. Cell Adh Migr. 5:199–206. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhong L, Jin J, Zheng D, Guan W, Guo Y,
Chen A, Peng Y, Gao Q, Zheng Y and Huang H: Influence of
super-hydrophobic silicone rubber substrate on the growth and
differentiation of human lens epithelial cells. J Mater Sci Mater
Med. 29:1762018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dalla Vestra M, Masiero A, Roiter AM,
Saller A, Crepaldi G and Fioretto P: Is podocyte injury relevant in
diabetic nephropathy? Studies in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Diabetes. 52:1031–1035. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jauregui A, Mintz DH, Mundel P and Fornoni
A: Role of altered insulin signaling pathways in the pathogenesis
of podocyte malfunction and microalbuminuria. Curr Opin Nephrol
Hypertens. 18:539–545. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Meyer TW, Bennett PH and Nelson RG:
Podocyte number predicts long-term urinary albumin excretion in
Pima Indians with Type II diabetes and microalbuminuria.
Diabetologia. 42:1341–1344. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang C, Hou B, Yu S, Chen Q, Zhang N and
Li H: HGF alleviates high glucose-induced injury in podocytes by
GSK3β inhibition and autophagy restoration. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1863:2690–2699. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tung CW, Hsu YC, Shih YH, Chang PJ and Lin
CL: Glomerular mesangial cell and podocyte injuries in diabetic
nephropathy. Nephrology (Carlton). 23 (Suppl 4):S32–S37. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Xu L, Fan Q, Wang X, Li L, Lu X, Yue Y,
Cao X, Liu J, Zhao X and Wang L: Ursolic acid improves podocyte
injury caused by high glucose. Nephrol Dial Transplant.
32:1285–1293. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sun J, Li ZP, Zhang RQ and Zhang HM:
Repression of miR-217 protects against high glucose-induced
podocyte injury and insulin resistance by restoring PTEN-mediated
autophagy pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 483:318–324. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Miaomiao W, Chunhua L, Xiaochen Z,
Xiaoniao C, Hongli L and Zhuo Y: Autophagy is involved in
regulating VEGF during high-glucose-induced podocyte injury. Mol
Biosyst. 12:2202–2212. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wei M, Li Z, Xiao L and Yang Z: Effects of
ROS-relative NF-κB signaling on high glucose-induced TLR4 and MCP-1
expression in podocyte injury. Mol Immunol. 68:261–271. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Li J, Wang B, Zhou G, Yan X and Zhang Y:
Tetrahydroxy stilbene glucoside alleviates high glucose-induced
MPC5 podocytes injury through suppression of NLRP3 inflammasome. Am
J Med Sci. 355:588–596. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Shen ZN, Gan H, Du X and Wang X: Effect of
PFT-α on ubiquitin and apoptosis of podocyte injured by high
glucose. J Chongqing Med Univ. 4:412–415. 2011.
|
|
43
|
Huo HZ, Zhou ZY, Wang B, Qin J, Liu WY and
Gu Y: Dramatic suppression of colorectal cancer cell growth by the
dual mTORC1 and mTORC2 inhibitor AZD-2014. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 443:406–412. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Fantus D, Rogers NM, Grahammer F, Huber TB
and Thomson AW: Roles of mTOR complexes in the kidney: Implications
for renal disease and transplantation. Nat Rev Nephrol. 12:587–609.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Gödel M, Hartleben B, Herbach N, Liu S,
Zschiedrich S, Lu S, Debreczeni-Mór A, Lindenmeyer MT, Rastaldi MP,
Hartleben G, et al: Role of mTOR in podocyte function and diabetic
nephropathy in humans and mice. J Clin Invest. 121:2197–2209. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Inoki K, Mori H, Wang J, Suzuki T, Hong S,
Yoshida S, Blattner SM, Ikenoue T, Rüegg MA, Hall MN, et al: mTORC1
activation in podocytes is a critical step in the development of
diabetic nephropathy in mice. J Clin Invest. 121:2181–2196. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Gödel M, Hartleben B, Herbach N, Liu S,
Zschiedrich S, Lu S, Debreczeni-Mór A, Lindenmeyer MT, Rastaldi MP,
Hartleben G, et al: Role of mTOR in podocyte function and diabetic
nephropathy in humans and mice. J Clin Invest. 121:2197–2209. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Eid S, Boutary S, Braych K, Sabra R,
Massaad C, Hamdy A, Rashid A, Moodad S, Block K, Gorin Y, et al:
mTORC2 signaling regulates nox4-induced podocyte depletion in
diabetes. Antioxid Redox Signal. 25:703–719. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yang Z, Liu F, Qu H, Wang H, Xiao X and
Deng H: 1, 25(OH)2D3 protects β cell against high glucose-induced
apoptosis through mTOR suppressing. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
414:111–119. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ng T, Parsons M, Hughes WE, Monypenny J,
Zicha D, Gautreau A, Arpin M, Gschmeissner S, Verveer PJ, Bastiaens
PI and Parker PJ: Ezrin is a downstream effector of trafficking
PKC-integrin complexes involved in the control of cell motility.
EMBO J. 20:2723–2741. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Bretscher A, Edwards K and Fehon RG: ERM
proteins and merlin: Integrators at the cell cortex. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 3:586–599. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Shen ZY, Xu LY, Li EM, Li JT, Chen MH,
Shen J and Zeng Y: Ezrin, actin and cytoskeleton in apoptosis of
esophageal epithelial cells induced by arsenic trioxide. Int J Mol
Med. 12:341–347. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wasik AA, Koskelainen S, Hyvönen ME,
Musante L, Lehtonen E, Koskenniemi K, Tienari J, Vaheri A,
Kerjaschki D, Szalay C, et al: Ezrin is down-regulated in diabetic
kidney glomeruli and regulates actin reorganization and glucose
uptake via GLUT1 in cultured podocytes. Am J Pathol. 184:1727–1739.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Lu Q, Zuo WZ, Ji XJ, Zhou YX, Liu YQ, Yao
XQ, Zhou XY, Liu YW, Zhang F and Yin XX: Ethanolic Ginkgo biloba
leaf extract prevents renal fibrosis through Akt/mTOR signaling in
diabetic nephropathy. Phytomedicine. 22:1071–1078. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Kawasaki Y, Imaizumi T, Matsuura H, Ohara
S, Takano K, Suyama K, Hashimoto K, Nozawa R, Suzuki H and Hosoya
M: Renal expression of alpha-smooth muscle actin and c-Met in
children with Henoch-Schönlein purpura nephritis. Pediatr Nephrol.
23:913–919. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Ren X, Guan G and Liu G and Liu G:
Irbesartan ameliorates diabetic nephropathy by reducing the
expression of connective tissue growth factor and
alpha-smooth-muscle actin in the tubulointerstitium of diabetic
rats. Pharmacology. 83:80–87. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Huang Z, Zhang L, Chen Y, Zhang H, Yu C,
Zhou F, Zhang Z, Jiang L, Li R, Ma J, et al: RhoA deficiency
disrupts podocyte cytoskeleton and induces podocyte apoptosis by
inhibiting YAP/dendrin signal. BMC Nephrol. 17:662016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Yao Q, Pei Y, Zhang X and Xie B:
microRNA-96 acts as a tumor suppressor gene in human osteosarcoma
via target regulation of EZRIN. Life Sci. 203:1–11. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Yan SJ, Wang L, Li Z, Zhu DN, Guo SC, Xin
WF, Yang YF, Cong X, Ma T, Shen PP, et al: Inhibition of advanced
glycation end product formation by Pu-erh tea ameliorates
progression of experimental diabetic nephropathy. J Agric Food
Chem. 60:4102–4110. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Mcrobert EA, Gallicchio M, Jerums G,
Cooper ME and Bach LA: The amino-terminal domains of the ezrin,
radixin, and moesin (ERM) proteins bind advanced glycation end
products, an interaction that may play a role in the development of
diabetic complications. J Biol Chem. 278:25783–25789. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
McRobert EA and Bach LA: Ezrin contributes
to impaired podocyte migration and adhesion caused by advanced
glycation end products. Nephrology (Carlton). 21:13–20. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|