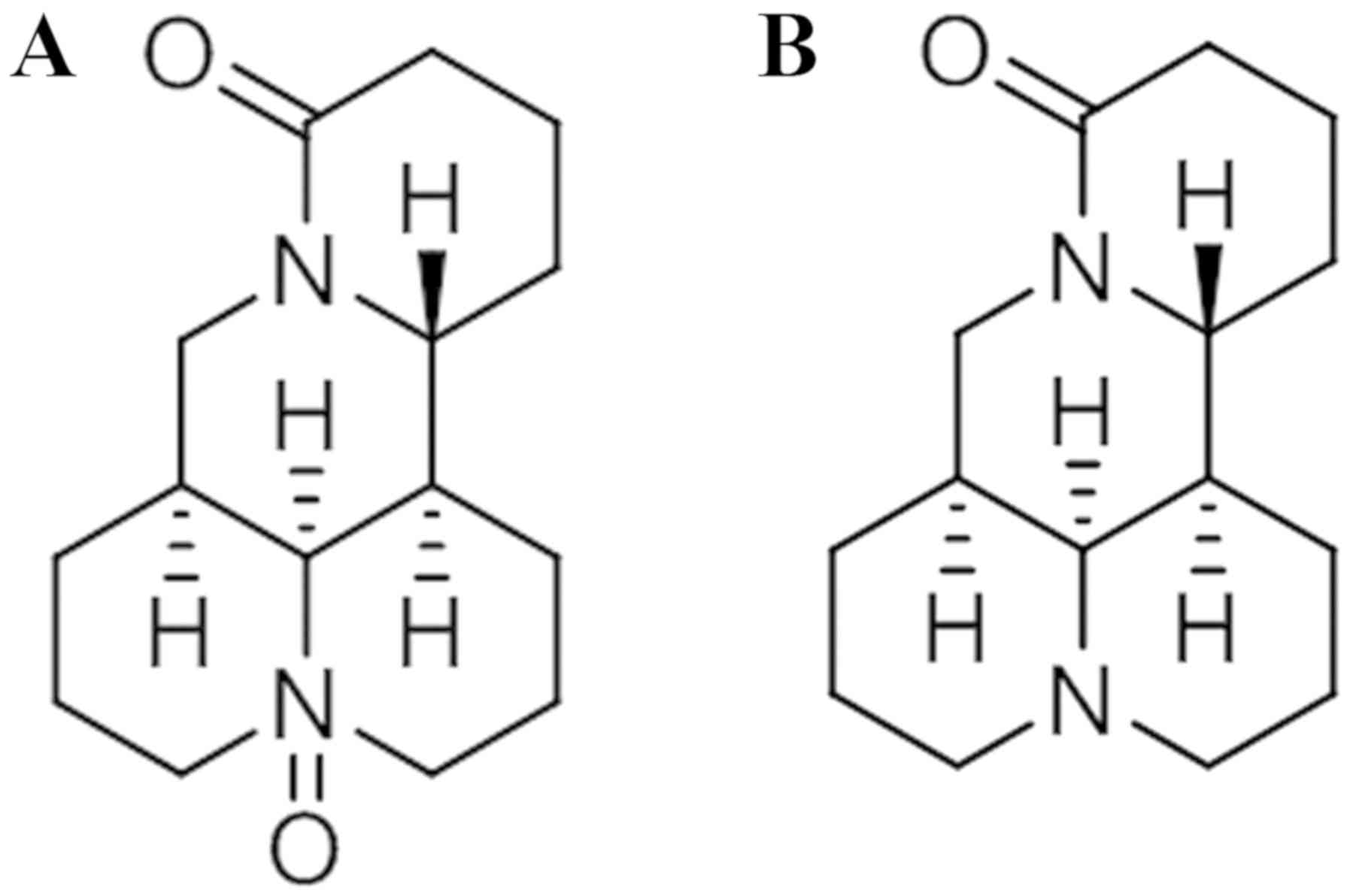
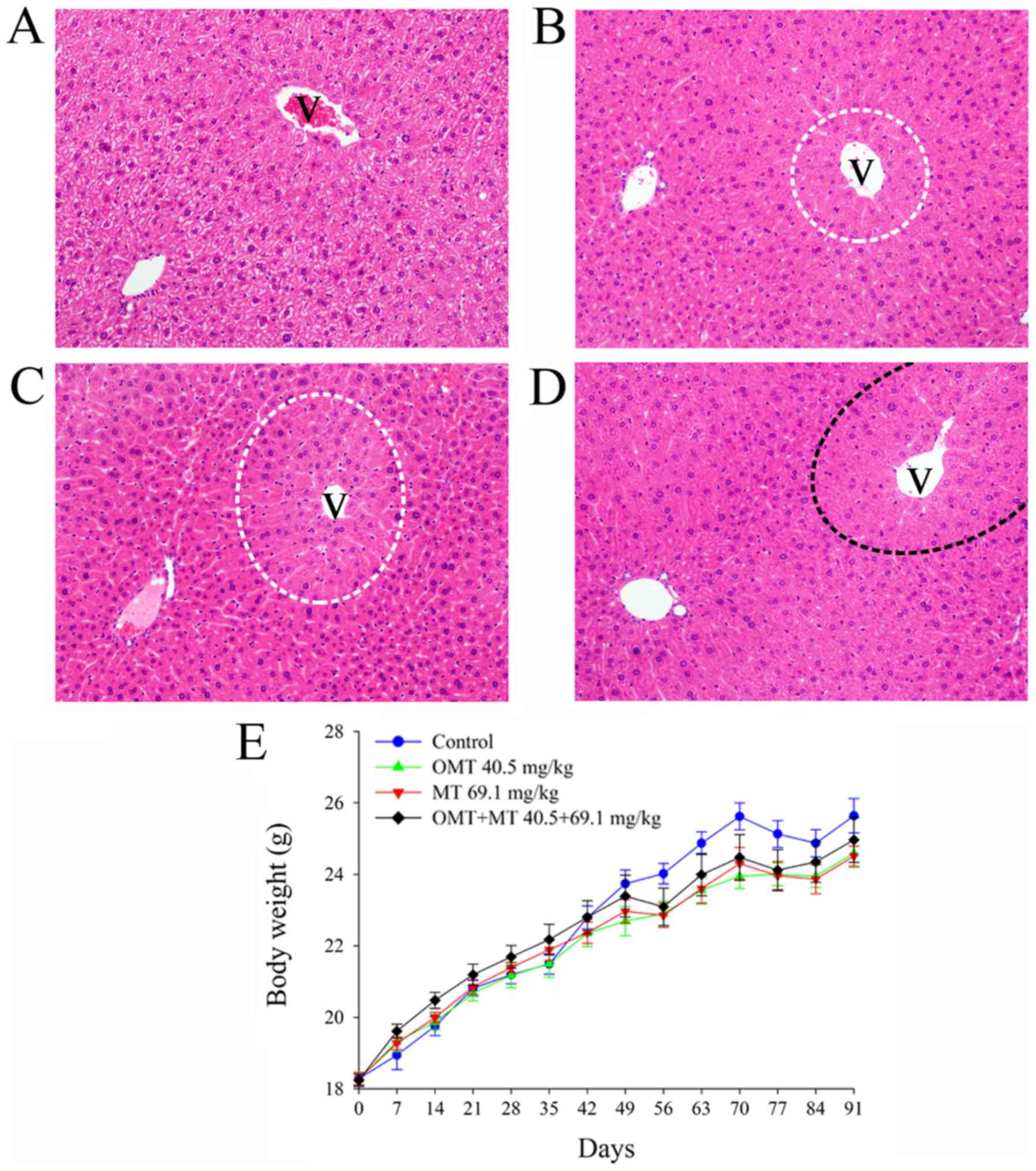
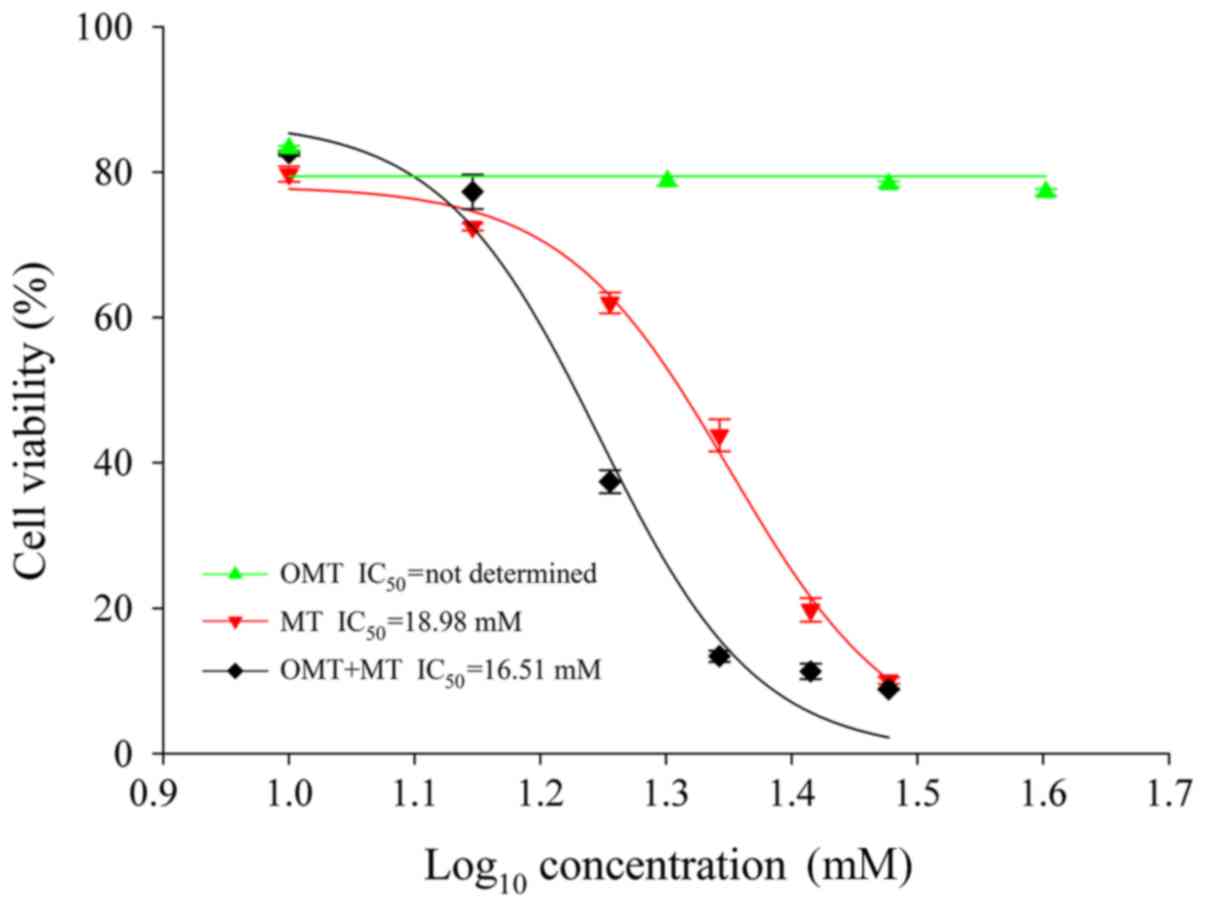
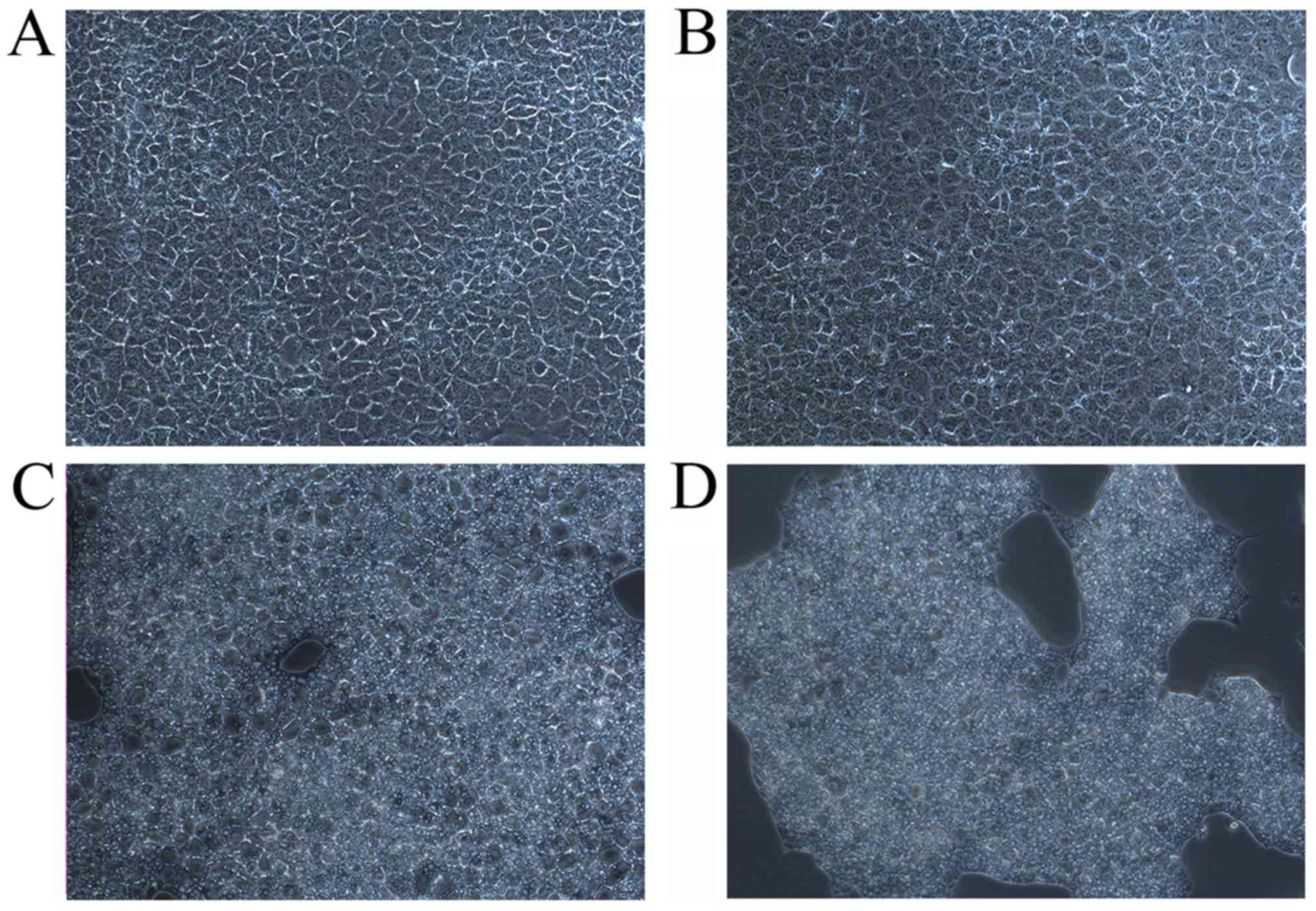
|
1
|
The State pharmacopoeia commission of P.R.
China. Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China. Chin Med
Sci Press. (Beijing). pp272015.(In Chinese).
|
|
2
|
Tian XS: Research progress on toxicity of
alkaloids in sophorae tonkinensis radix et rhizoma. Zhongguo Shi
Yan Fang Ji Xue Za Zhie. 22:230–234. 2016.(In Chinese).
|
|
3
|
Wang XP and Yang RM: Movement disorders
possibly induced by traditional Chinese herbs. Eur Neurol.
50:153–159. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li X, Luan Y, Li X and Sun R: Study on
anti-inflammatory efficacy accompanied by side effects of different
components of Sophorae Tonkinensis Radix et Rhizoma. Zhongguo Zhong
Yao Za Zhi. 37:2232–2237. 2012.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang L, Lu J, Sun W, Gu Y, Zhang C, Jin R,
Li L, Zhang Z and Tian X: Hepatotoxicity induced by radix Sophorae
tonkinensis in mice and increased serum cholinesterase as a
potential supplemental biomarker for liver injury. Exp Toxicol
Pathol. 69:193–202. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lee JW, Lee JH, Lee C, Jin Q, Lee D, Kim
Y, Hong JT, Lee MK and Hwang BY: Inhibitory constituents of Sophora
tonkinensis on nitric oxide production in RAW 264.7 macrophages.
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 25:960–962. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lu ML, Xiang XH and Xia SH: Potential
signaling pathways involved in the clinical application of
oxymatrine. Phytother Res. 30:1104–1112. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Huang J and Xu H: Matrine: Bioactivities
and structural modifications. Curr Top Med Chem. 16:3365–3378.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lu H, Zhang L, Gu LL, Hou BY and Du GH:
Oxymatrine induces liver injury through JNK signalling pathway
mediated by TNF-α in vivo. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol.
119:405–411. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gao ZW, Zhang RQ and Liao XH: Two cases of
aggravating liver damage caused by oxymatrine injection in the
patients with chronic hepatitis B. Yao Wu Bu Liang Fan Ying Za Zhi.
2002:120–121. 2002.(In Chinese).
|
|
11
|
Guo QP and Jin RM: Comparison of liver
toxicity of matrine and oxymatrine in mice. Zhongguo Yao Li Yu Du
Li Xue Za Zhi. 30:736–740. 2016.(In Chinese).
|
|
12
|
Chen Y, Zhang Q, Han SX, Han FM, Chen LM,
Tong Y and You Y: Study on toxicity of different extractions of
Sophorae tonkinensis. Zhongguo Yao Wu Jing Jie. 14:582–586.
2017.(In Chinese).
|
|
13
|
Miners JO, Knights KM, Houston JB and
Mackenzie PI: In vitro-in vivo correlation for drugs and other
compounds eliminated by glucuronidation in humans: Pitfalls and
promises. Biochem Pharmacol. 71:1531–1539. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen P, Zhang X, Huang T, Yu Q and Cheng
N: Metabolism of the hepatotoxic compound Sophoraflavanone G in rat
liver microsomes. J Food Sci. 79:T1462–T1468. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xie MZ, Zhou WZ and Zhang YD: The
metabolic fate of oxymatrine. Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao. 16:481–487.
1981.(In Chinese).
|
|
16
|
Wang ML, Zhou QL and Wang BX: Studies on
metabolism of oxymatrine by human intestinal bacteria. Zhongguo
Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 26:272–274. 2001.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu XL, Hang TJ, Shen JP and Zhang YD:
Determination and pharmacokinetic study of oxymatrine and its
metabolite matrine in human plasma by liquid chromatography tandem
mass spectrometry. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 41:918–924. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
National Research Council (US) committee
for the update of the guide for the care use of laboratory animals.
Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals. (8th). National
Academies Press (US). (Washington, DC). 2011.
|
|
19
|
Anon: The guidelines of test technology
for long-term toxicity of chemical drugs. http://www.sfda.gov.cn/directory/web/WS01/images/u6Rp9Kpzu+zpMbatr7Q1MrU0em8vMr11ri1vNSt1PIucGRm.pdf(In
Chinese).
|
|
20
|
Hou G, Xue L, Lu Z, Fan T, Tian F and Xue
Y: An activated mTOR/p70S6K signaling pathway in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma cell lines and inhibition of the pathway by
rapamycin and siRNA against mTOR. Cancer Lett. 253:236–248. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Amenya HZ, Gathumbi PK, Mbaria JM, Thaiyah
AG and Thoithi GN: Sub-acute toxicity of the chloroformic extract
of Rapanea melanophloeos (L.) Mez in rats. J Ethnopharmacol.
154:593–599. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Akanda MR, Kim IS, Ahn D, Tae HJ, Tian W,
Nam HH, Choo BK and Park BY: In vivo and in vitro hepatoprotective
effects of Geranium koreanum methanolic extract via downregulation
of MAPK/Caspase-3 pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2017:81376272017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Serfilippi LM, Pallman DR and Russell B:
Serum clinical chemistry and hematology reference values in outbred
stocks of albino mice from three commonly used vendors and two
inbred strains of albino mice. Contemp Top Lab Anim Sci. 42:46–52.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tse DY, Chung I and Wu SM: Pharmacological
inhibitions of glutamate transporters EAAT1 and EAAT2 compromise
glutamate transport in photoreceptor to ON-bipolar cell synapses.
Vision Res. 103:49–62. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shi C, Chen X, Liu Z, Meng R, Zhao X, Liu
Z and Guo N: Oleuropein protects L-02 cells against
H2O2-induced oxidative stress by increasing
SOD1, GPx1 and CAT expression. Biomed Pharmacother. 85:740–748.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sofi MS, Sateesh MK and Bashir M:
Screening of the Ethnobotanicals against MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7
breast cancer cell lines. Int J of Phytopharm. 4:140–147. 2014.
|
|
27
|
Mani S, Mondal D, Sarma K and Singh K:
Experimentally induced liver cirrhosis with ascites by carbon
tetrachloride and phenobarbital sodium in wistar rats. Adv Anim Vet
Sci. 2:159–163. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Gowda S, Desai PB, Hull VV, Math AA,
Vernekar SN and Kulkarni SS: A review on laboratory liver function
tests. Pan Afr Med J. 3:172009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Acton QA: Drugs-advances in research and
application: 2012 edition. Scholarly Editions; Atlanta, GA: pp.
6452012
|
|
30
|
Kleiner DE, Chalasani NP, Lee WM, Fontana
RJ, Bonkovsky HL, Watkins PB, Hayashi PH, Davern TJ, Navarro V,
Reddy R, et al: Hepatic histological findings in suspected
drug-induced liver injury: Systematic evaluation and clinical
associations. Hepatology. 59:661–670. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kirisci O, Paksoy T, Caliskan A, Analan A,
Ozkaya E, Kirmaci B, Tumer S, Citil R, Cikim G, Agirbas S, et al:
The relationship between serum DNA levels and serological markers,
Alt and Ast with liver histology in chronic hepatitis B patients.
Acta Medica Mediterr. 32:1805–1811. 2016.
|
|
32
|
Senoh H, Katagiri T, Arito H, Nishizawa T,
Nagano K, Yamamoto S and Matsushima T: Toxicity due to 2- and 13-wk
inhalation exposures of rats and mice to N, N-dimethylformamide. J
Occup Health. 45:365–375. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ennulat D, Walker D, Clemo F, Magid-Slav
M, Ledieu D, Graham M, Botts S and Boone L: Effects of hepatic
drug-metabolizing enzyme induction on clinical pathology parameters
in animals and man. Toxicol Pathol. 38:810–828. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Williams GM and Iatropoulos MJ: Alteration
of liver cell function and proliferation: Differentiation between
adaptation and toxicity. Toxicol Pathol. 30:41–53. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cataudella E, Malaguarnera G, Gagliano C,
Condorelli G, Antic T, Rampello L, Erdogan O, Rampello L and
Malaguarnera M: Pesticides exposure and the management of acute
hepatic injury. Acta Medica Mediterr. 28:245–252. 2012.
|
|
36
|
He X, Fang J, Huang L, Wang J and Huang X:
Sophora flavescens Ait: Traditional usage, phytochemistry and
pharmacology of an important traditional Chinese medicine. J
Ethnopharmacol. 172:10–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yang J, Zhang L, Zhu G and Li L:
Separation and enrichment of major quinolizidine type alkaloids
from Sophora alopecuroides using macroporous resins. J Chromatogr B
945–946. 17–22. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Firenzuoli F and Gori L: Herbal medicine
today: Clinical and research issues. Evid Based Complement Alternat
Med. 4 (Suppl 1):S37–S40. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Welz AN, Emberger-Klein A and Menrad K:
Why people use herbal medicine: Insights from a focus-group study
in Germany. Bmc Complem Altern Med. 18:922018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Wu JC, Merlino G and Fausto N:
Establishment and characterization of differentiated,
nontransformed hepatocyte cell lines derived from mice transgenic
for transforming growth factor alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
91:674–678. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hassoun E and Mettling C: Dichloroacetate
and trichloroacetate toxicity in AML12 cells: Role of oxidative
stress. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 29:508–512. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Fan R, Liu R, Ma R, Bi K and Li Q:
Determination of oxymatrine and its active metabolite matrine in
human plasma after administration of oxymatrine oral solution by
high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with mass
spectrometry. Fitoterapia. 89:271–277. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Song B, Han CX and Zhang HL: Toxicity of
three Sophora flavescens Ait alkaloids to mice. Xi Bei Zhi Wu Xue
Bao. 29:818–823. 2009.(In Chinese).
|
|
44
|
Sakamoto Y, Yoshida M, Tamura K, Takahashi
M, Kodama Y and Inoue K: Dose-dependent difference of nuclear
receptors involved in murine liver hypertrophy by piperonyl
butoxide. J Toxicol Sci. 40:787–796. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Deguchi Y, Yamada T, Hirose Y, Nagahori H,
Kushida M, Sumida K, Sukata T, Tomigahara Y, Nishioka K, Uwagawa S,
et al: Mode of action analysis for the synthetic pyrethroid
metofluthrin-induced rat liver tumors: Evidence for hepatic CYP2B
induction and hepatocyte proliferation. Toxicol Sci. 108:69–80.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
van der Ven LT, van de Kuil T, Verhoef A,
Leonards PE, Slob W, Cantón RF, Germer S, Hamers T, Visser TJ,
Litens S, et al: A 28-day oral dose toxicity study enhanced to
detect endocrine effects of a purified technical pentabromodiphenyl
ether (pentaBDE) mixture in Wistar rats. Toxicology. 245:109–122.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Nebert DW and Dalton TP: The role of
cytochrome P450 enzymes in endogenous signalling pathways and
environmental carcinogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:947–960. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhang X, Zong C, Zhang L, Garner E, Sugie
S, Huang C, Wu W, Chang J, Sakurai T, Kato M, et al: Exposure of
mice to 1,2-dichloropropane induces CYP450-dependent proliferation
and apoptosis of cholangiocytes. Toxicol Sci. 162:559–569. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|