Introduction
Liver ischemia/reperfusion (IR) is a major cause of
liver damage (1,2). IR occurs following tissue resection,
hemorrhagic shock or transplantation surgery, when tissue damage
occurs due to transient hypoxia and subsequent restoration of blood
flow (3,4). Managing IR is an important factor in
hepatobiliary surgery (5). IR
affects liver function and creates postoperative complications in
the cardiovascular system (6).
Molecular mechanisms underlying IR have been
extensively explored (7). Various
studies have indicated that IR is associated with lactate
accumulation, acidosis, depletion of ATP, reactive oxygen species
generation and resulting oxidative stress, neutrophil activation
and calcium overload (8–11). However, the full pathophysiological
process of IR is not completely known.
Interestingly, use of volatile anesthetics can
prevent tissue damage by regulating hepatic blood flow following
liver ischemia (12–14). Sevoflurane, an inhalation anesthetic,
functions as a bronchodilator via regulating calcium homeostasis
(15). Sevoflurane renders
protection form reperfusion injury during thoracic surgery
(16). In fact, sevoflurane has been
demonstrated to have a protective effect against liver IR in mouse
models (17,18).
IR induces the activation of the nuclear factor
(NF)-κB signaling pathway, which mediates IR-associated tissue
injury and sevoflurane ameliorates this NF-κB activation (18). It was suggested that sevoflurane
exerts its effects by downregulating miR-200c expression (17). However, it remains unknown how
sevoflurane regulates the activation of the NF-κB signaling
pathway. The objective of the current study was to establish an IR
rat model and to verify the mechanism by which sevoflurane
regulates the activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway. The
results suggested that sevoflurane induced microRNA (miRNA or
miR)-9-5p, which targets NFKB3, encoding for transcription
factor p65, and mitigated the effects of IR.
Materials and methods
Animals, surgery and experimental
intervention
The study was approved by the Institutional Animal
Care and Use Committee of Wuxi People's Hospital Affiliated to
Nanjing Medical University (Wuxi, China). A total of 36 male
Sprague-Dawley rats (Beijing Vital River Laboratory Animal
Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) aged 8 weeks and weighing
285±30 g were housed at 22±1°C with 50±10% relative humidity at
12-h light/dark cycles and with free access to water and food. The
animals were randomly assigned to six groups (n=6 rats/group):
Control (sham), IR, IR+sevoflurane, IR+miR-9-5p mimic group,
IR+miR-9-5p antagomir group, IR+sevoflurane+miR-9-5p antagomir
group. All rats were anesthetized using an intraperitoneal
injection of sodium pentobarbital (1%; 40 mg/kg body weight) and
rats in sevoflurane groups were then treated with sevoflurane (3%;
AbbVie Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) at a controlled flow rate (2 l/min)
for the full duration of the surgical intervention. Midline
laparotomy was performed to reveal the hepatic artery and portal
vein for subsequent occlusion. Liver ischemia was induced by
ligating the hepatic artery, portal vein and bile duct for 1 h and
reperfusion was performed by removing the clamping for 2 h.
Post-surgery liver tissue samples were collected and snap frozen in
liquid nitrogen or fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 24 h at 25°C.
Fixed tissues were used for immunohistochemistry analysis and were
stained with hematoxylin/eosin (H&E), including staining with
0.5% hematoxylin for 5 min followed by 0.5% eosin for 1 min at
25°C. The Suzuki score (criteria, 0–4) assesses liver damage and
was used for grading of hepatic IR injury based of the fixed
tissues (19). Venous blood samples
(5 ml) were collected at 4 h post reperfusion, centrifuged (5 min;
4,000 × g; 4°C) and serum was stored at −80°C.
Where indicated, miR-9-5p mimic (100 µl; 50 mg/kg;
5′-GGUUAUCUAGCUGUAUGA-3′; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Waltham,
MA, USA) or antagomir (100 µl; 50 mg/kg;
5′-AUACAGCUAGAUAACCAAAG-3′; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) was
injected in the liver at 1 h before performing the IR (n=6/group)
without anesthesia of rats.
Quantification of cytokines
ELISA kits (MyBiosource; Thermo Fisher Scientific,
Inc.) were used to quantify liver function markers, including
alanine aminotransferase (ALT; cat. no. MBS1601726), aspartate
aminotransferase (AST; cat. no. MBS778086), lactate dehydrogenase
(LDH; cat. no. MBS778339) (20), and
inflammatory cytokines, including interleukin (IL)-1 (cat. no.
MA5-23,736), −6 (cat. no. M620) and −10 (cat. no. AHC0103) and
tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α (cat. no. P300A), in serum following
the manufacturer's protocols. Data are presented as the mean ±
standard error of mean and experiments were performed three times
in triplicate.
Immunoblot analysis
To extract the proteins, liver tissue cells and
Hep3B cells were lysed in radioimmunoprecipitation assay buffer
(Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) supplemented with Mini protease
inhibitor cocktail (Roche Diagnostics, Indianapolis, IN, USA). The
protein concentration was determined using bicinchoninic acid kit
(Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.). Whole cell lysate (50 µg) was
separated on 10% SDS-PAGE gels and transferred to polyvinylidene
difluoride membranes. Membranes were blocked for 1 h at 25°C using
4% non-fat milk (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) and probed with
anti-GAPDH antibody (cat. no. ab9458; 1:1,000); anti-phosphorylated
(p)-p65 antibody (cat. no. ab76302; 1:500); anti-total p65 antibody
(cat. no. ab207297; 1:500); anti-IκBα antibody (cat. no. ab55341;
1:500; all Abcam, Cambridge, UK) at 4°C for 12 h. Membranes were
then incubated with goat anti-rat IgG horseradish
peroxidase-conjugated antibody (cat. no. ab205720; 1:2,000; Abcam)
for 1 h at 25°C. Blots were visualized using enhanced
chemiluminescence reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.). GAPDH
was used to confirm equal loading.
RNA and miRNA extraction and reverse
transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR)
TRIzol reagent (Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA,
Darmstadt, Germany) was used to isolate total RNA and miRNA from
tumor tissues. The SuperScript III First Strand cDNA synthesis kit
(Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) was to obtain first strand cDNA
using the following protocol: 30°C for 10 min, 42°C for 30 min,
99°C for 5 min followed by 5°C for 5 min. TaqMan Gene Expression
probes (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) were used for subsequent
RT-qPCR assays. TATA-box binding protein was used as normalization
control for assessing NFKB3 transcription levels. Primers sequences
were as follows: NFKB3 forward, 5′-GACGACTGTTCCCCCTC-3′ and
reverse, 5′-CCTCGCACTTGTAGCGG-3′ (21); miR-9-5p forward,
5′-GTGCAGGGTCCGAGGT-3′ and reverse, 5′-GCGCTCTTTGGTTATCTAGC-3′
(22); TBP forward,
5′-CCCGAAACGCCGAATATAATCC-3′ and reverse,
5′-AATCAGTGCCGTGGTTCGTG-3′ (23);
and RNU6B forward, 5′-CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA-3′ and reverse,
5′-AACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGT-3′ (24).
Thermocycling conditions were as follows: 95°C for 2 min followed
by 45 cycles of 94°C for 15 sec, 55°C for 15 sec and 68°C for 30
sec and final elongation at 72°C for 5 min. Data was analyzed using
the 2−ΔΔCq method (25).
TaqMan probe based quantification was done for RNU6B and miR-9-5p,
where RNU6B was the normalization control. TBP was used as control
for mRNA.
Gene construction, transfection of
plasmid constructs and in vitro luciferase reporter assays
The NFKB3 3′-untranslated region (UTR) was
constructed by amplifying the endogenous NFKB3 3′-UTR from the
pMirTarget plasmid (OriGene Technologies, Inc., Rockville, MD, USA)
and cloning into the pCXCR4 6X Renilla luciferase vector (OriGene
Technologies, Inc.). The NFKB3 3′-UTR miR-9-5p binding mutant
(deleted region, 29–35) construct was generated by site-directed
mutagenesis. Hep3B cells (2×106) were transiently transfected with
the reporter construct (4 µg) and a control luciferase vector (4
µg) using Lipofectamine 2000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.)
according to the manufacturer's instructions. Cells were
co-transfected with anti-miR-9-5p antagomir
(5′-AUACAGCUAGAUAACCAAAG-3′; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) or
antagomir control (cat. no. miR03201-1-10; Guangzhou RiboBio Co.,
Ltd., Guangzhou, China). Transfection efficiency was determined by
RT-qPCR and luciferase activity. Luciferase activities were
determined using the Dual-luciferase reporter assay system (Promega
Corporation, Madison, WI, USA) and normalized to Renilla. Data are
presented as the mean in relative fluorescence units ± standard
error of mean.
Regulation of p65 using miR-9-5p
In order to explore regulatory effects of miR-9-5p
on p65, miR-9-5p antagomir (5′-AUACAGCUAGAUAACCAAAG-3′), antagomir
control, miR-9-5p mimic (5′-GGUUAUCUAGCUGUAUGA-3′) and mimic
control (cat. no. miR01201-1-5; Guangzhou RiboBio Co., Ltd.) were
designed. miRs (100 nmol/l) were transfected into Hep3B cells
(2×106) using Lipofectamine 2000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.)
according to the manufacture's protocols. Following 6 h, cell
culture medium was changed and cells were cultured for further 48
h. Transfection efficiency was determined by RT-qPCR. Subsequently,
western blot assays detecting p65 were performed.
Apoptosis quantification by flow
cytometry
Liver tissues of the IR+sevoflurane, the IR and the
control groups were collected. Tissues were homogenated into single
cell suspension using the mechanical trituration method. Cell
viability was determined by Annexin-V/propidium iodide (PI)
staining (BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA), with
Annexin-V-/PI- as viable, Annexin-V+/PI as early apoptotic and
Annexin-V+/PI+ as late apoptotic cells. Samples were analyzed using
a BD Accuri C6 flow cytometer with C6 software (version 1.0.264; BD
Biosciences). Data are presented as the means ± standard error of
mean representative of three experiments and each performed in
triplicate.
TUNEL staining assay
Liver tissues of the IR+sevoflurane, the IR and the
control groups were collected, fixed using 4% paraformaldehyde for
24 h at 25°C and 5 µm frozen sections were prepared. TUNEL
immunohistochemistry analysis was performed using the TUNEL
Apoptosis Assay kit (Shanghai Yeasen Biotech Co., Ltd., Shanghai,
China). First, tissue slides were deparaffinized twice for 10 min
at room temperature using xylene and treated with proteinase K (20
µg/ml; Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA) for 20 min at 25°C. Tissue
sections were equilibrated in the kit's equilibration buffer (100
µl) for 5 min at 25°C. FITC-12-dUTP Labeling mix containing
recombinant terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (100 µl) was
added to the sections and samples were incubated at 37°C in a
humidity chamber (plastic box with PBS) for 1 h. Sections were
incubated with DAPI at 25°C for 5 min. Samples were imaged using a
fluorescence microscope (magnification, ×400) and five random
fields were selected for each sample.
Statistical analyses
Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 20.0
(IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). Differences between groups were
determined by one-way analysis of variance followed by least
significant difference post-hoc tests. Student's t-test or
Mann-Whitney U tests were used for the comparison of two groups.
P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant
difference.
Results
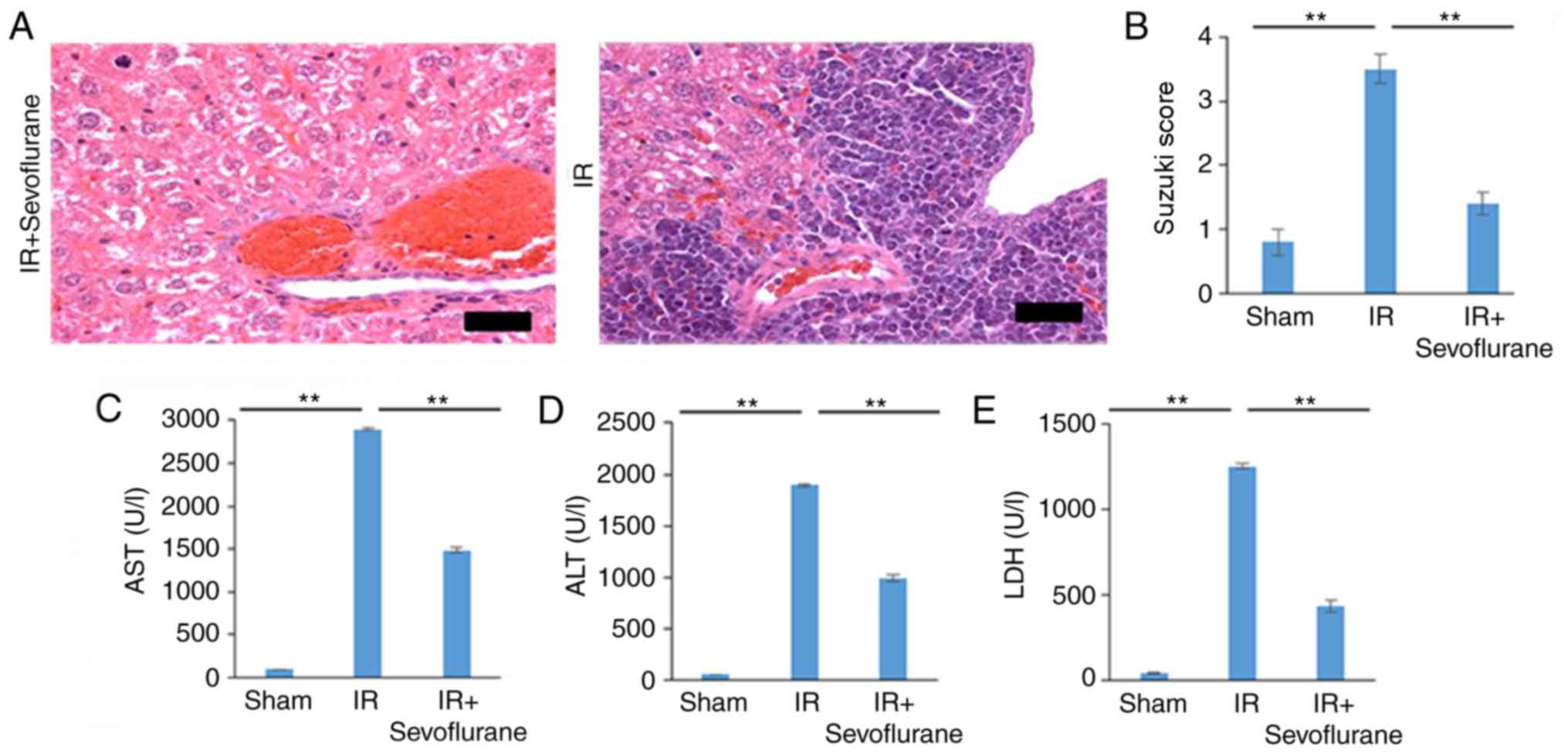
Sevoflurane reverses IR-induced liver
damage in tissues
Liver damage induced by IR was visualized using
H&E staining and was graded using the Suzuki score.
Pathological changes evident in the IR group indicated severe liver
damage and were validated by high Suzuki scores (Fig. 1A and B). Sevoflurane administration
significantly attenuated liver damage compared with the IR group
(P<0.01; Fig. 1A and B). High
serum levels of AST, ALT and LDH, indicative of severe liver
damage, were observed in the IR group and levels were significantly
decreased in the IR+sevoflurane compared with the IR group
(P<0.01; Fig. 1C-E).
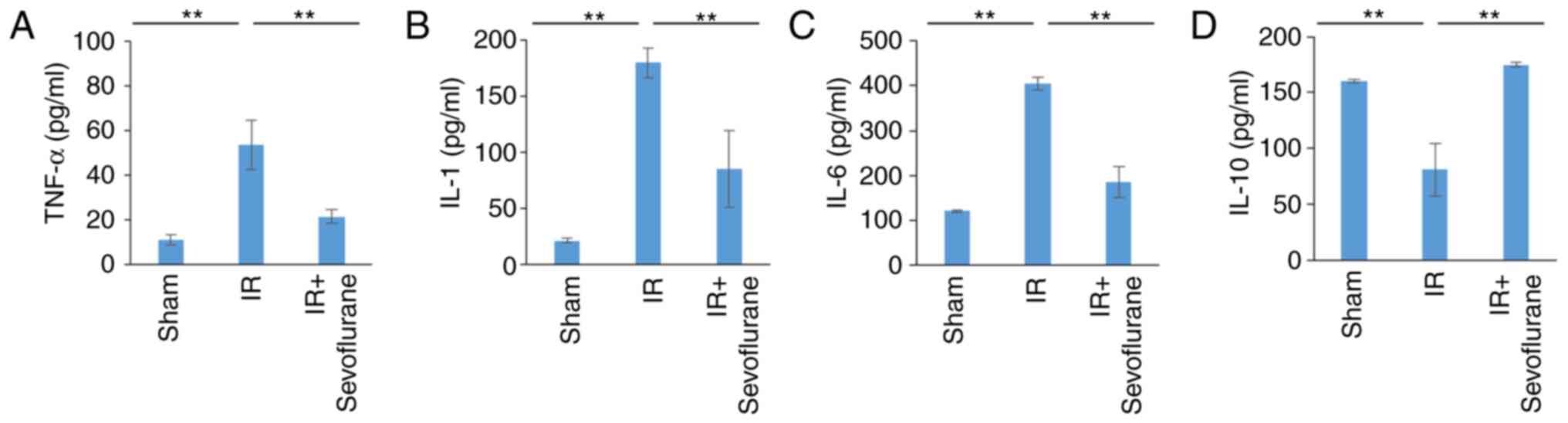
Sevoflurane administration attenuates
IR-associated cytokine storms and apoptosis
Levels of inflammatory cytokines were determined in
the various experimental groups to evaluate if sevoflurane
attenuates IR-associated cytokine storms. Compared with the sham
group, TNF-α, IL-1 and −6 levels were significantly increased in
the IR group (P<0.01; Fig. 2A-C).
Sevoflurane administration significantly decreased cytokine levels
compared with the IR group (P<0.01; Fig. 2A-C). IL-10 levels were significantly
reduced in the IR compared with the sham group and this decrease
was significantly reversed in the IR+sevoflurane group (P<0.01
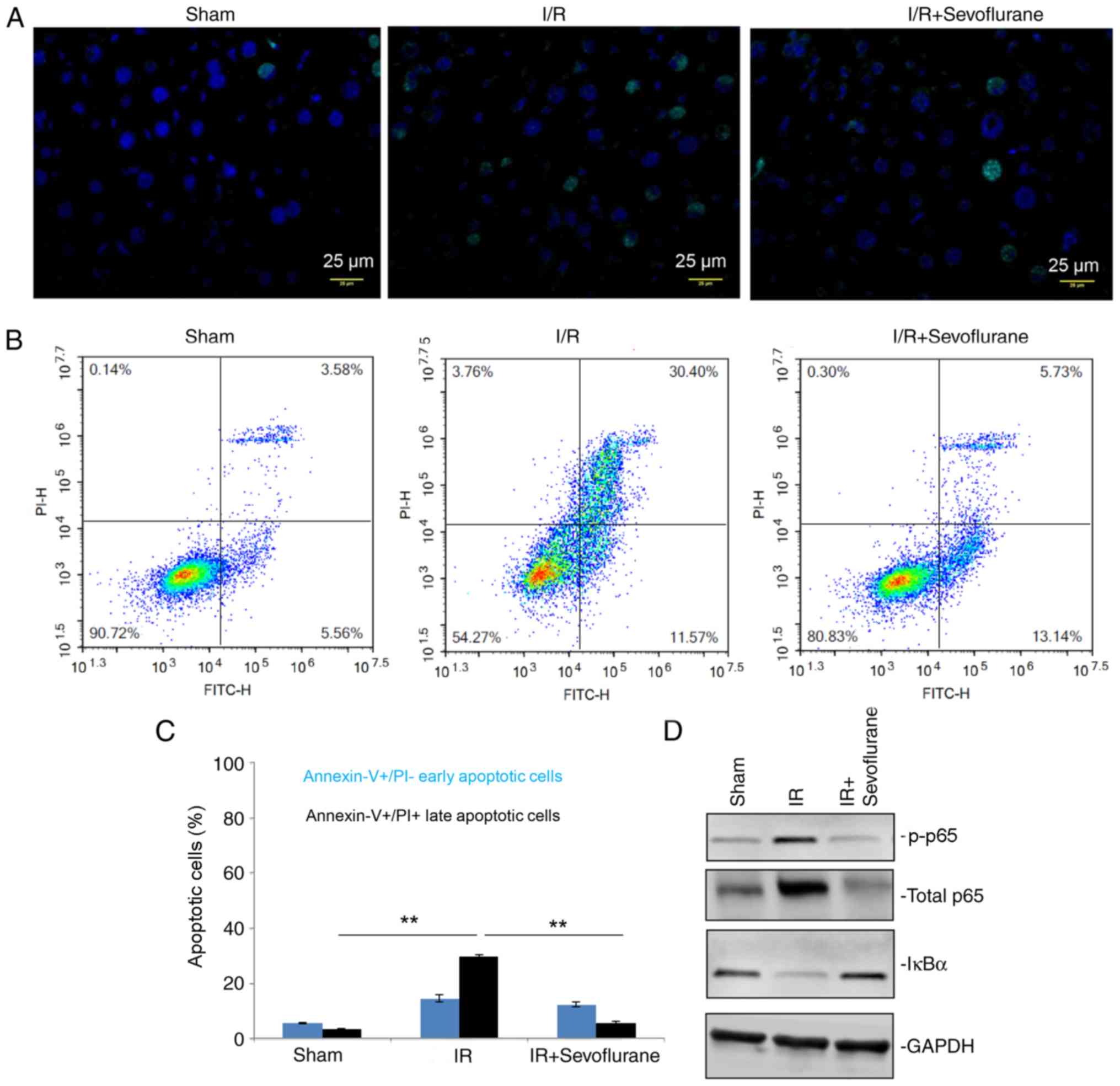
Fig. 2D). Additionally, TUNEL
staining assays and flow cytometry suggested that the late
apoptotic rate in the IR group was significantly increased compared
with the sham group and sevoflurane significantly attenuated
IR-induced late apoptotic rates (P<0.01; Fig. 3A-C).
Sevoflurane administration attenuates
IR-associated injury via the NF-κB signaling pathway
Activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway was
investigated to evaluate if cytokine levels were mediated by this
pathway. Levels of total p65 and p-p65 were increased in the IR
group compared with the sham group and IκBα, an inhibitor of NF-κB
signaling, levels were downregulated (Fig. 3D). Sevoflurane administration
increased IκBα expression and decreased total and phosphorylated
p65 levels compared with the IR group (Fig. 3D). The results indicated a successful
attenuation of NF-κB signaling was detrimental in the protective
role of sevoflurane against IR-associated injury and tissue
damage.
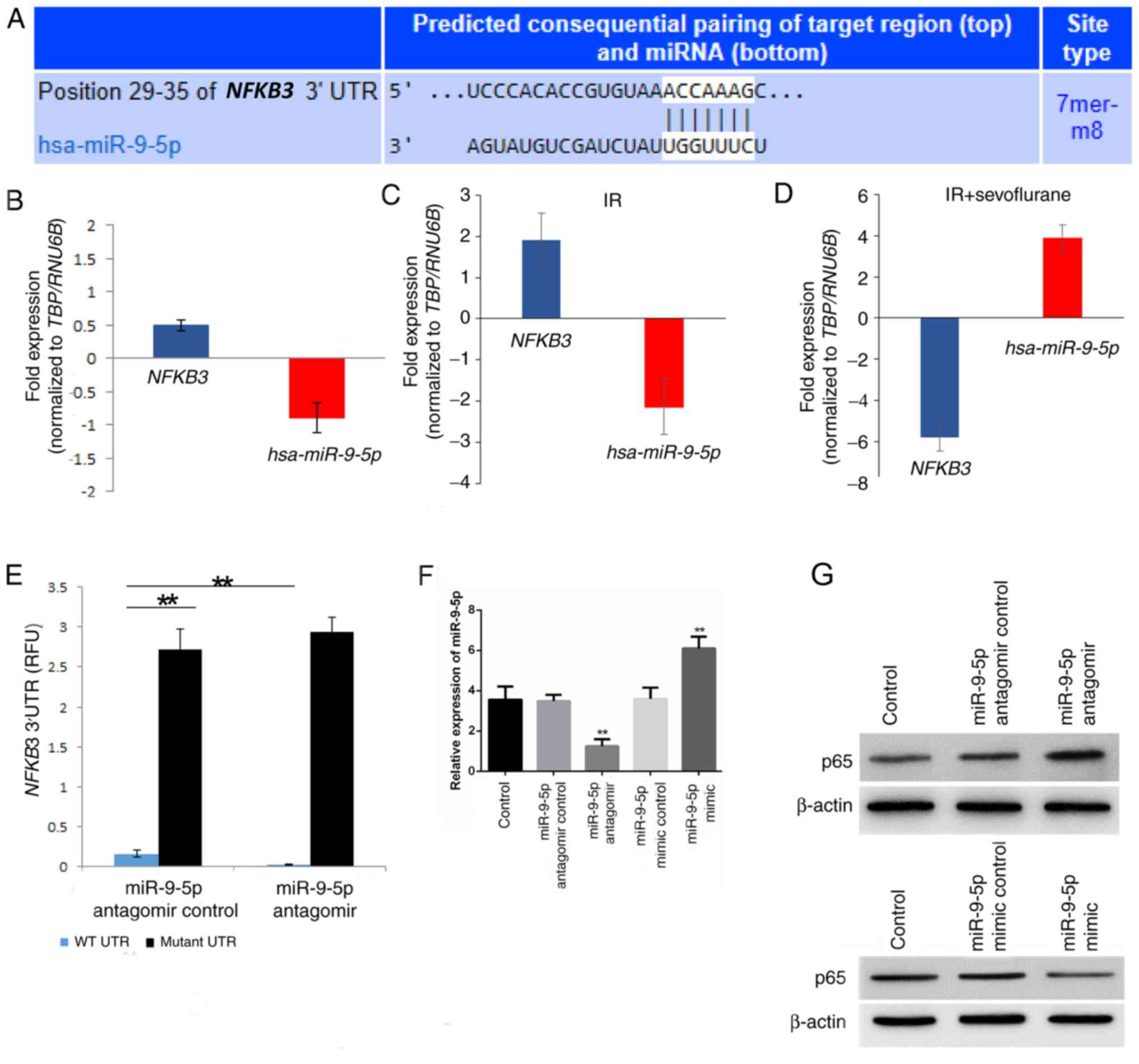
miR-9-5p affects p65 levels by
targeting NFKB3
To explore the mechanism by which p65 levels
decreased following IR, miRNA targets were investigated, as no
obvious changes in mRNA expression were detected (data not shown).
miR-9-5p was predicted as a putative miRNA targeting NFKB3,
encoding for p65, by TargetScan (Fig.
4A). NFKB3 mRNA expression was significantly upregulated
following IR and miR-9-5p was downregulated in IR tissues compared
with the sham control (Fig. 4B and
C). Following sevoflurane treatment, NFKB3 mRNA expression was
downregulated while miR-9-5p expression was upregulated in hepatic
tissue specimens compared to the IR specimen (Fig. 4D).
To evaluate if NFKB3 is a direct target of
miR-9-5p luciferase reporter assays were performed. Various hepatic
cell lines including AML12, HepG2, Hep3B, MIHA, BNL CL.2 and Huh7
were screened for miR-9-5p and NFKB3 expression and Hep3B
exhibited high miR-9-5p and increased NFKB3 expression
compared with these other hepatic cell lines (data not shown).
Hep3B cells have previously been used to mimic IR by
hypoxia/reoxygenation treatment (26). Hence, Hep3B was selected for
subsequent in vitro assays. Luciferase reporter constructs
containing the wild type NFKB3 3′-UTR were transfected with
or without the antagomir targeting miR-9-5p. The relative activity
in wild type NFKB3 3′-UTR containing cells was increased
3.09±0.03 fold (P=0.0073; Fig. 4E)
in the presence of antagomir compared with the antagomir control
cells. The specificity of this interaction was confirmed using a
miR-9-5p binding mutant of the NFKB3 3′-UTR. No significant
difference was determined between the anti-miR-9-5p antagomir and
the antagomir control cells (Fig.
4E).
Relative miR-9-5p levels were detected in cells
transfected with miR-9-5p antagomir, mimic or controls to determine
transfection efficiency. miR-9-5p antagomir significantly decreased
miR-9-5p levels compared with the antagomir control (P=0.0097) and
the miR-9-5p mimic significantly increased miR-9-5p levels compared
with the mimic control (P=0.0074; Fig.
4F). Furthermore, p65 expression was increased in the miR-9-5p
antagomir compared to control group and decreased in the miR-9-5p
mimic compared with the control group (Fig. 4G).
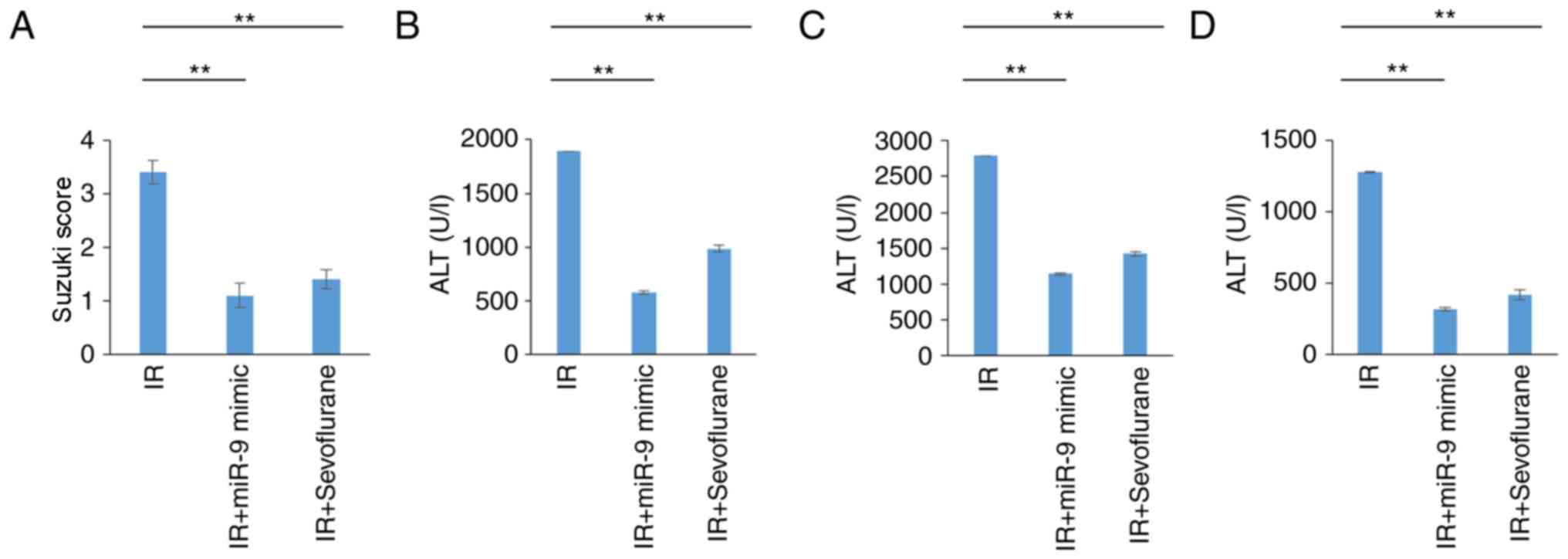
miR-9-5p treatment in rats attenuates
IR-induced liver injury
It was further evaluated if protective effects of
sevoflurane were mediated by miR-9-5p. Rats of the IR group were
injected with miR-9-5p mimic prior to IR induction. Sevoflurane
administration and treatment with miR-9-5p mimic significantly
attenuated IR-associated liver damage as indicated by the Suzuki
score (P<0.01; Fig. 5A).
Additionally, decreased AST, ALT and LDH serum levels were observed
in the IR+miR-9-5p mimic and the IR+sevoflurane groups compared
with the IR group (P<0.01; Fig.
5B-D). Cumulatively, this indicated that protective effect of
sevoflurane on IR-associated injury may be mediated miR-9-5p
expression.
Sevoflurane alters the NF-κB signaling
pathway through miR-9-5p upregulation
To verify whether sevoflurane inhibited NF-κB by
upregulating miR-9-5p, western blot analysis investigating p65
phosphorylation and IκBα was performed in the following groups:
Sham, IR, IR+sevoflurane, IR+miR-9-5p mimic, IR+miR-9-5p antagomir
and IR+sevoflurane+miR-9-5p antagomir. miR-9-5p levels were
detected to determine transfection efficiency; IR significantly
decreased miR-9-5p levels compared with the sham group (P=0.029)
and miR-9-5p levels were significantly increased in IR+sevoflurane
group and IR+miR-9-5p mimic group compared with the IR group
(P=0.022 and P=0.013, respectively; Fig.
6A). In the IR+miR-9-5p antagomir and the
IR+sevoflurane+miR-9-5p antagomir groups, miR-9-5p levels were not
significantly different compared with the IR group (P>0.05;
Fig. 6A). Western blot analysis
revealed that p65 phosphorylation was increased in the IR compared
with the sham group (P<0.01; Fig. 6B
and C). Treatment with sevoflurane and miR-9-5p mimic decreased
phosphorylation levels of p65 compared with the IR group
(P<0.01; Fig. 6B and C). In the
IR+miR-9-5p antagomir and the IR+sevoflurane+miR-9-5p antagomir
groups, p65 phosphorylation was not significantly different
compared with the IR group (Fig. 6B and
C). IκBα expression decreased in the IR compared with the sham
group and sevoflurane and miR-9-5p mimic treatment significantly
reversed the IR-induced change (Fig. 6B
and D). The results indicated that sevoflurane inhibited the
NF-κB signaling pathway by miR-9-5p upregulation.
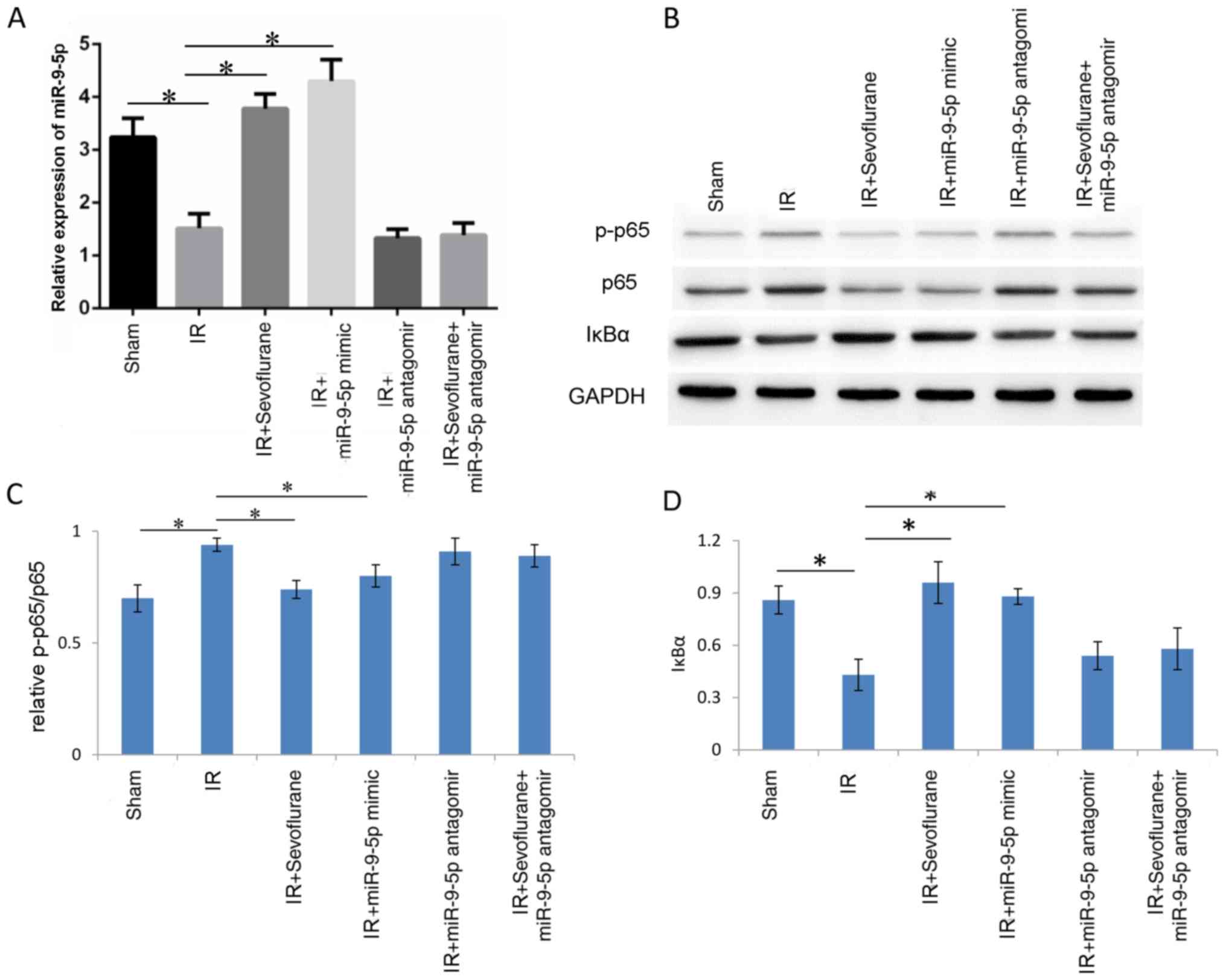 | Figure 6.Sevoflurane inhibits the NF-κB
signaling pathway through miR-9-5p upregulation. Rats were randomly
divided into sham, IR, IR+sevoflurane, IR+miR-9-5p mimic,
IR+miR-9-5p antagomir group, IR+sevoflurane+miR-9-5p antagomir
groups (n=6/group). The IR+miR-9-5p mimic, IR+miR-9-5p antagomir
and IR+sevoflurane+miR-9-5p antagomir groups were injected with
miR-9-5p mimic or antagomir in the liver at 1 h prior to IR. (A)
Relative miR-9-5p expression. (B) Western blot images for p-p65,
p65 and IκBα and quantitative evaluation of (C) p65 phosphorylation
and (D) IκBα expression. Results are presented as the mean ±
standard error of mean of three independent experiments.
*P<0.01. IR, ischemia/reperfusion; miR, microRNA; p-,
phosphorylated; NF, nuclear factor; IκBα, inhibitor of κBα. |
Discussion
miRs are 21–23 nucleotide-long noncoding RNAs that
regulate gene expression by inhibiting translation, in case of
imperfect complementarity between miR seed the target, or by
degrading the target mRNA, in cases of perfect complementarity
between the target and miR seed (27,28).
miRs are involved in various important physiological processes and
in disease pathogenesis (29–34).
Sevoflurane is an inhalational anesthetics that is widely used in
clinic and has little toxic effects on the liver (35). Low blood pressure and blood loss can
lead to organ ischemia during surgery, including of the liver, and
IR liver injury is a known side effect (36). Whether sevoflurane exerts protective
effects on IR liver injury has not been determined so far.
The current study explored the protective effects of
sevoflurane on the IR liver injury in rats and cell models. H&E
staining of tissues from various experimental animal groups was
performed and Suzuki scores were determined, allowing for the
evaluation of the liver injury level. The results demonstrated that
sevoflurane protected the structural integrity of the liver in the
IR group. Serum markers of liver function, including AST, ALT and
LDH, were further determined and supported the conclusion that
sevoflurane protected against IR injury. Apoptosis is a result of
IR injury. To measure apoptosis in liver tissues, flow cytometry
and TUNEL staining assays were performed. The results suggested
that sevoflurane inhibited apoptosis rates compared with the IR
group. It was presented that sevoflurane protected the function and
structural integrity of liver from IR injury.
Inflammation is an important mechanism in IR injury.
To explore the protective mechanism of sevoflurane, key
inflammation factors were determined in serum samples. TNF-α, IL-1
and IL-6 serve important roles in innate immunological response and
IL-10 exhibits negative immunological regulation effects (37). The current study described that IR
significantly increased the serum levels of TNF-α, IL-1 and IL-6,
and IL-10 was decreased. Following sevoflurane treatment,
proinflammatory factors, TNF-α, IL-1 and IL-6, were all decreased
and the anti-inflammatory factor IL-10 was increased compared with
the IR group. This suggested that sevoflurane inhibited
inflammatory effects induced by IR and contributed to the
protection against liver injury.
The NF-κB signaling pathway serves an important role
in inflammation activation (38).
p65 phosphorylation and IκBα levels were determined, which are key
proteins of the NF-κB signaling pathway. It was observed that
sevoflurane decreased the p65 phosphorylation and increased IκBα
expression compared with the IR group. p65 phosphorylation
initiates the transcription of various inflammation factors and
promotes inflammation activation (38). IκBα inhibits the NF-κB signaling
pathway by masking nuclear localization signals of NF-κB-associated
proteins and keeping them sequestered in an inactive state in the
cytoplasm (39). These results
suggested that sevoflurane inhibited the NF-κB signaling
pathway.
miRs paricipate in the regulation of various cell
signaling pathways. Utilizing bioinformatic, miR-9-5p was
identified to target NFKB3, the gene coding for p65. A
previous study suggested that miR-9-5p regulated NF-κB in ovarian
cancer by targeting to NFKB1 (40); however, there was no evidence that
NF-κB was regulated by miR-9-5p in IR as miRs can have various
targets in different cells. Monocyte chemotactic protein-induced
protein-1 is a target of miR-9-5p in microglia (41). To determine miR-9-5p expression,
RT-qPCR was performed. The results suggested that sevoflurane
potentiated protective effects by inducing miR-9-5p expression.
Hep3B cell treatment with miR-9-5p antagomir increased p65
expression and miR-9-5p mimic significantly decreased p65
expression compared with the respective controls. Furthermore,
miR-9-5p mimic exhibited similar protective effects on IR injury as
sevoflurane. Results suggested that the volatile anesthetic
protected from IR injury by increasing miR-9-5p expression, which
in turn directly targeted the proinflammatory NF-κB signaling
pathway.
Whether the induction and suppression of miR are
direct effects of sevoflurane treatment remains to be investigated.
It is imperative that promoter analyses of induced and suppressed
miRs are performed to determine which factors are directly
regulating expression and how these are manipulated by sevoflurane
administration. In addition, the involvement of additional miRs in
IR injury and subsequent protection by sevoflurane require to be
investigated. There is evidence for the miR-133-5p-mediated
regulation of MAPK6 (42),
the miR-182-5p-mediated regulation of TLR4 (43), the miR-148a-mediated regulation of
CamKIIα (44) and the
miR-370-mediated regulation of the NF-κB signaling pathway
(45) in different aspects of IR
injury and amelioration using volatile anesthetics. This indicates
that miRs may serve a more important role in IR-associated injury
and subsequent remediation by volatile anesthetics.
In conclusion, sevoflurane protected the liver from
IR injury by increasing miR-9-5p expression. Increased miR-9-5p
expression inhibited NF-κB signaling pathway activation, a cytokine
storm and apoptotic cell death. Further research using other models
and patients may further the potential clinical administration of
sevoflurane to managing IR injury of the liver.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
No funding was received.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current
study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable
request.
Authors' contributions
XL, JZ and ZW contributed to the study design, data
acquisition, analysis, statistical analysis and manuscript
preparation. SZ contributed to analysis and interpretation of data,
and revised the manuscript critically for important intellectual
content. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
The present study was approved by the Institutional
Animal Care and Use Committee of Wuxi People's Hospital Affiliated
to Nanjing Medical University.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Hochhauser E, Lahat E, Sultan M, Pappo O,
Waldman M, Sarne Y, Shainberg A, Gutman M, Safran M and Ben Ari Z:
Ultra low dose delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol protects mouse liver
from ischemia reperfusion injury. Cell Physiol Biochem.
36:1971–1981. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang X, Tan Z, Wang Y, Tang J, Jiang R,
Hou J, Zhuo H, Wang X, Ji J, Qin X and Sun B: PTPRO-associated
hepatic stellate cell activation plays a critical role in liver
fibrosis. Cell Physiol Biochem. 35:885–898. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li C and Jackson RM: Reactive species
mechanisms of cellular hypoxia-reoxygenation injury. Am J Physiol
Cell Physiol. 282:C227–C241. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jaeschke H: Molecular mechanisms of
hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury and preconditioning. Am J
Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 284:G15–G26. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Montalvo-Jave EE, Piña E, Montalvo-Arenas
C, Urrutia R, Benavente-Chenhalls L, Peña-Sanchez J and Geller DA:
Role of ischemic preconditioning in liver surgery and hepatic
transplantation. J Gastrointest Surg. 13:2074–2083. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang Y, Shen J, Xiong X, Xu Y, Zhang H,
Huang C, Tian Y, Jiao C, Wang X and Li X: Remote ischemic
preconditioning protects against liver ischemia-reperfusion injury
via heme oxygenase-1-induced autophagy. PLoS One. 9:e988342014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kang JW, Cho HI and Lee SM: Melatonin
inhibits mTOR-dependent autophagy during liver
ischemia/reperfusion. Cell Physiol Biochem. 33:23–36. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Grossini E, Pollesello P, Bellofatto K,
Sigaudo L, Farruggio S, Origlia V, Mombello C, Mary DA, Valente G
and Vacca G: Protective effects elicited by levosimendan against
liver ischemia/reperfusion injury in anesthetized rats. Liver
Transpl. 20:361–375. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Schulz R, Kelm M and Heusch G: Nitric
oxide in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc Res.
61:402–413. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ren G, Dewald O and Frangogiannis NG:
Inflammatory mechanisms in myocardial infarction. Curr Drug Targets
Inflamm Allergy. 2:242–256. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kihara F, Inoue Y, Arima I, Ono M and
Masumoto H: Case of Recklinghausen's disease presenting as acute
porphyria in the terminal stage. Naika. 18:381–387. 1966.(In
Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dikmen Y, Eminoglu E, Salihoglu Z and
Demiroluk S: Pulmonary mechanics during isoflurane, sevoflurane and
desflurane anaesthesia. Anaesthesia. 58:745–748. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Goff MJ, Arain SR, Ficke DJ, Uhrich TD and
Ebert TJ: Absence of bronchodilation during desflurane anesthesia:
A comparison to sevoflurane and thiopental. Anesthesiology.
93:404–408. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Puglisi F, Crovace A, Staffieri F, Capuano
P, Carravetta G, De Fazio M, Lograno G, Lacitignola L, Troilo VL,
Martines G, et al: Comparison of hemodynamic and respiratory
effects of propofol and sevoflurane during carbon dioxide
pneumoperitoneum in a swine model. Chir Ital. 59:105–111.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kim JW, Kim JD, Yu SB and Ryu SJ:
Comparison of hepatic and renal function between inhalation
anesthesia with sevoflurane and remifentanil and total intravenous
anesthesia with propofol and remifentanil for thyroidectomy. Korean
J Anesthesiol. 64:112–116. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Erturk E, Topaloglu S, Dohman D, Kutanis
D, Beşir A, Demirci Y, Kayir S and Mentese A: The comparison of the
effects of sevoflurane inhalation anesthesia and intravenous
propofol anesthesia on oxidative stress in one lung ventilation.
Biomed Res Int. 2014:3609362014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu Y, Gu C and Huang X: Sevoflurane
protects against hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury by modulating
microRNA-200c regulation in mice. Biomed Pharmacother.
84:1126–1136. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xu Z, Yu J, Wu J, Qi F, Wang H and Wang Z
and Wang Z: The effects of two anesthetics, propofol and
sevoflurane, on liver ischemia/reperfusion injury. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 38:1631–1642. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Suzuki S, Toledo-Pereyra LH, Rodrigyez FJ
and Cejalvo D: Neutrophil infiltration as an important factor in
liver ischemia and reperfusion injury. Modulating effects of FK506
and cyclosporine. Transplantation. 55:1265–1272. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Veldhuis GJ, Willemse PH, Sleijfer DT, van
der Graaf WT, Groen HJ, Limburg PC, Mulder NH and de Vries EG:
Toxicity and efficacy of escalating dosages of recombinant human
interleukin-6 after chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer or
non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 13:2585–2593. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sun S, Guo M, Zhang JB, Ha A, Yokoyama KK
and Chiu RH: Cyclophilin A (CypA) interacts with NF-κB subunit,
p65/RelA, and contributes to NF-κB activation signaling. PLoS One.
9:e962112014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li G, Wu F, Yang H, Deng X and Yuan Y:
MiR-9-5p promotes cell growth and metastasis in non-small cell lung
cancer through the repression of TGFBR2. Biomed Pharmacother.
96:1170–1178. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
He A, Chen Z, Mei H and Liu Y: Decreased
expression of LncRNA MIR31HG in human bladder cancer. Cancer
Biomark. 17:231–236. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jiang JJ, Liu CM, Zhang BY, Wang XW, Zhang
M, Saijilafu, Zhang SR, Hall P, Hu YW and Zhou FQ: MicroRNA-26a
supports mammalian axon regeneration in vivo by suppressing GSK3β
expression. Cell Death Dis. 6:e18652015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Teng H, Wu B, Zhao K, Yang G, Wu L and
Wang R: Oxygen-sensitive mitochondrial accumulation of
cystathionine β-synthase mediated by Lon protease. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 110:12679–12684. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ:
Oncomirs-microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
6:259–269. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Aleckovic M and Kang Y: Regulation of
cancer metastasis by cell-free miRNAs. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1855:24–42. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gaur A, Jewell DA, Liang Y, Ridzon D,
Moore JH, Chen C, Ambros VR and Israel MA: Characterization of
microRNA expression levels and their biological correlates in human
cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 67:2456–2468. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kumar MS, Lu J, Mercer KL, Golub TR and
Jacks T: Impaired microRNA processing enhances cellular
transformation and tumorigenesis. Nat Genet. 39:673–677. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra
E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA,
et al: MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature.
435:834–838. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Guo L, Qiu Z, Wei L, Yu X, Gao X, Jiang S,
Tian H, Jiang C and Zhu D: The microRNA-328 regulates hypoxic
pulmonary hypertension by targeting at insulin growth factor 1
receptor and L-type calcium channel-alpha1C. Hypertension.
59:1006–1013. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Marques FZ, Campain AE, Tomaszewski M,
Zukowska-Szczechowska E, Yang YH, Charchar FJ and Morris BJ: Gene
expression profiling reveals renin mRNA overexpression in human
hypertensive kidneys and a role for microRNAs. Hypertension.
58:1093–1098. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Safari S, Motavaf M, Seyed Siamdoust SA
and Alavian SM: Hepatotoxicity of halogenated inhalational
anesthetics. Iran Red Crescent Med J. 16:e201532014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kwan I, Bunn F, Chinnock P and Roberts I:
Timing and volume of fluid administration for patients with
bleeding. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. CD002245. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Lin RK, Zhang CH, Mu N, Yao QY, Dong SL,
Ai QB and Wang QX: Effects of astilbin on the expression of TNF
alpha and IL-10 in liver warm ischemia-reperfusion injury. Zhonghua
Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 18:463–466. 2010.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu T, Zhang L, Joo D and Sun SC: NF-κB
signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2(pii):
170232017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Christian F, Smith EJ and Carmody RJ: The
regulation of NF-κB subunits by phosphorylation. Cells. 5(pii):
E122016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Guo LM, Pu Y, Han Z, Liu T, Li YX, Liu M,
Li X and Tang H: MicroRNA-9 inhibits ovarian cancer cell growth
through regulation of NF-kappaB1. FEBS J. 276:5537–5546. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yao H, Ma R, Yang L, Hu G, Chen X, Duan M,
Kook Y, Niu F, Liao K, Fu M, et al: MiR-9 promotes microglial
activation by targeting MCPIP1. Nat Commun. 5:43862014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hao W, Zhao ZH, Meng QT, Tie ME, Lei SQ
and Xia ZY: Propofol protects against hepatic ischemia/reperfusion
injury via miR-133a-5p regulating the expression of MAPK6. Cell
Biol Int. 41:495–504. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Jiang W, Liu G and Tang W: MicroRNA-182-5p
ameliorates liver ischemia-reperfusion injury by suppressing
Toll-like receptor 4. Transplant Proc. 48:2809–2814. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zheng D, He D, Lu X, Sun C, Luo Q and Wu
Z: The miR-148a alleviates hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in
mice via targeting CaMKIIα. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi.
32:1202–1206. 2016.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhu J, Zhu F, Song W, Zhang B, Zhang X,
Jin X and Li H: Altered miR-370 expression in hepatic
ischemia-reperfusion injury correlates with the level of nuclear
kappa B (NF-κB) related factors. Gene. 607:23–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|