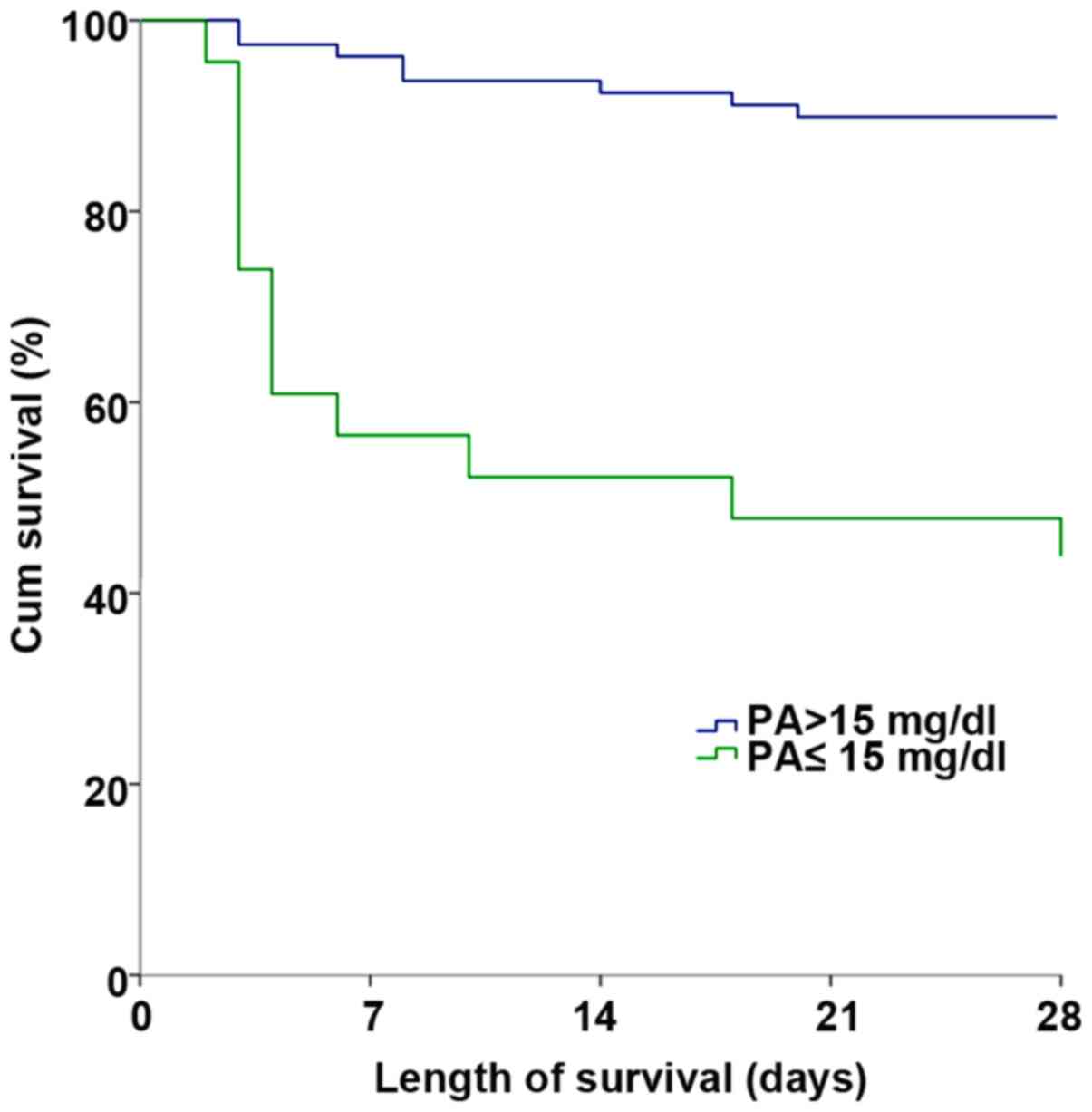
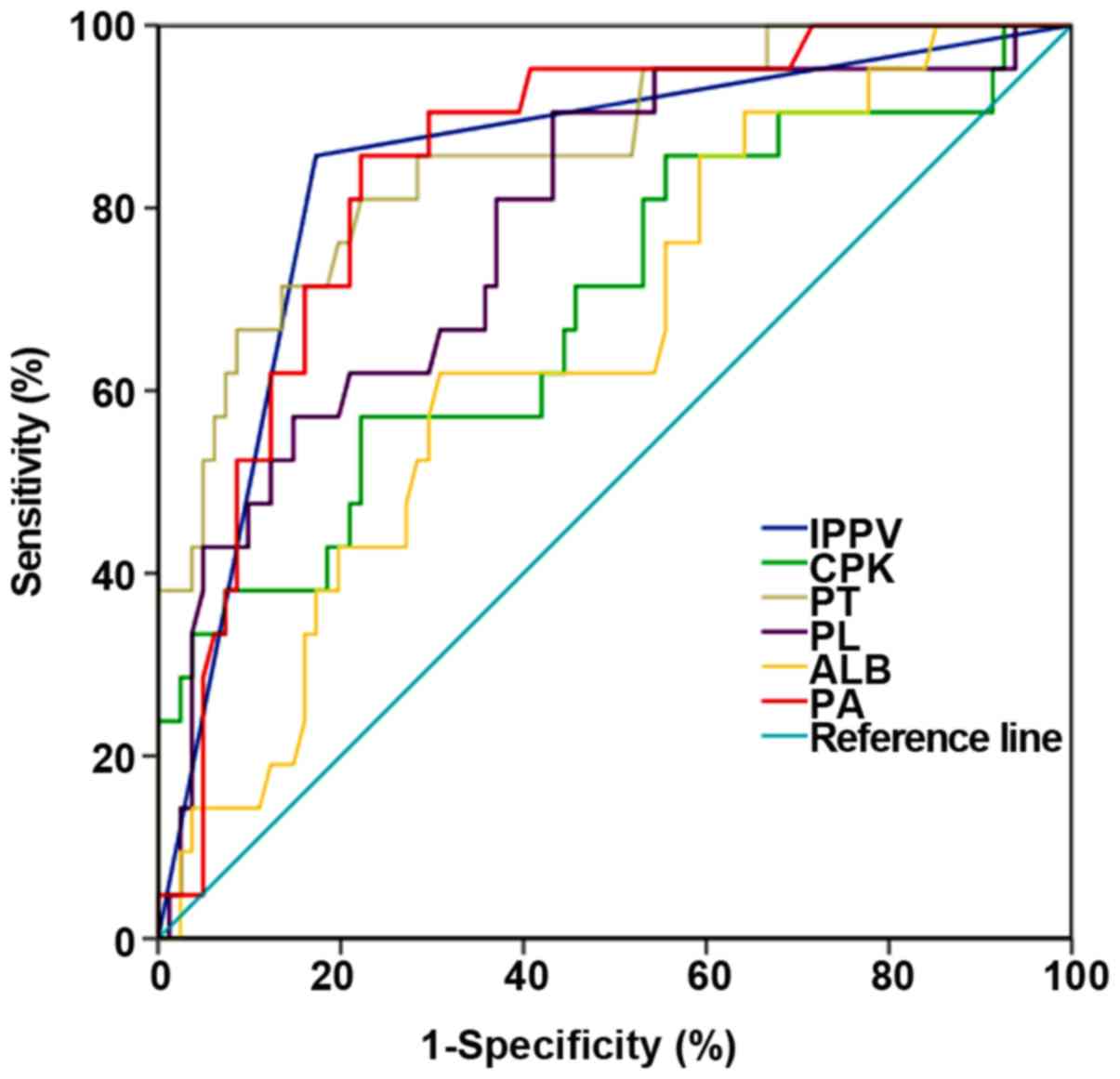
|
1
|
Glazer JL: Management of heatstroke and
heat exhaustion. Am Fam Physician. 71:2133–2140. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bouchama A and Knochel JP: Heat stroke. N
Engl J Med. 346:1978–1988. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hammami MM, Bouchama A, Al-Sedairy S,
Shail E, AlOhaly Y and Mohamed GE: Concentrations of soluble tumor
necrosis factor and interleukin-6 receptors in heatstroke and
heatstress. Crit Care Med. 25:1314–1319. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lee EJ, Lee SW, Park JS, Kim SJ and Hong
YS: Successful treatment of severe heat stroke with selective
therapeutic hypothermia using an automated surface cooling device.
Resuscitation. 84:e77–e78. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Leon LR: Heat stroke and cytokines. Prog
Brain Res. 162:481–524. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vandevyver S, Dejager L, Vandenbroucke RE
and Libert C: An acute phase protein ready to go therapeutic for
sepsis. EMBO Mol Med. 6:2–3. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Franco J, Formiga F, Trullas JC, Salamanca
Bautista P, Conde A, Manzano L, Quirós R, Franco ÁG, Ezquerro AM
and Montero-Pérez-Barquero M; RICA investigators group, : Impact of
prealbumin on mortality and hospital readmission in patients with
acute heart failure. Eur J Intern Med. 43:36–41. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xie Q, Zhou Y, Xu Z, Yang Y, Kuang D, You
H, Ma S, Hao C, Gu Y, Lin S, et al: The ratio of CRP to prealbumin
levels predict mortality in patients with hospital-acquired acute
kidney injury. BMC Nephrol. 12:302011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Berbel MN, Góes CR, Balbi AL and Ponce D:
Nutritional parameters are associated with mortality in acute
kidney injury. Clinics (São Paulo). 69:476–482. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Lee KH, Cho JH, Kwon O, Kim SU, Kim RH,
Cho YW, Jung HY, Choi JY, Kim CD, Kim YL, et al: Low prealbumin
levels are independently associated with higher mortality in
patients on peritoneal dialysis. Kidney Res Clin Pract. 35:169–175.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang HT, Yim H, Cho YS, Kim D, Hur J, Kim
JH, Lee BC, Seo DK, Kim HS and Chun W: Prediction of clinical
outcomes for massively-burned patients via serum transthyretin
levels in the early postburn period. J Trauma Acute Care Surg.
72:999–1005. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bae HJ, Lee HJ, Han DS, Suh YS, Lee YH,
Lee HS, Cho JJ, Kong SH and Yang HK: Prealbumin levels as a useful
marker for predicting infectious complications after gastric
surgery. J Gastrointest Surg. 15:2136–2144. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li L, Dai L, Wang X, Wang Y, Zhou L, Chen
M and Wang H: Predictive value of the C-reactive
protein-to-prealbumin ratio in medical ICU patients. Biomarkers
Med. 11:329–337. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Hausfater P, Hurtado M, Pease S, Juillien
G, Lvovschi VE, Salehabadi S, Lidove O, Wolff M, Bernard M,
Chollet-Martin S, et al: Is procalcitonin a marker of critical
illness in heatstroke? Intensive Care Med. 34:1377–1383. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bouchama A, Dehbi M, Mohamed G, Matthies
F, Shoukri M and Menne B: Prognostic factors in heat wave related
deaths: A meta-analysis. Arch Intern Med. 167:2170–2176. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Davis CJ, Sowa D, Keim KS, Kinnare K and
Peterson S: The use of prealbumin and C-reactive protein for
monitoring nutrition support in adult patients receiving enteral
nutrition in an urban medical center. J Parenter Enteral Nutr.
36:197–204. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Prealbumin in Nutritional Care Consensus
Group, : Measurement of visceral protein status in assessing
protein and energy malnutrition: Standard of care. Nutrition.
11:169–171. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang X, Yuan B, Dong W, Yang B, Yang Y,
Lin X and Gong G: Humid heat exposure induced oxidative stress and
apoptosis in cardiomyocytes through the angiotensin II signaling
pathway. Heart Vessels. 30:396–405. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Quinn CM, Duran RM, Audet GN, Charkoudian
N and Leon LR: Cardiovascular and thermoregulatory biomarkers of
heat stroke severity in a conscious rat model. J Appl Physiol
(1985). 117:971–978. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hausfater P, Doumenc B, Chopin S, Le
Manach Y, Santin A, Dautheville S, Patzak A, Hericord P, Mégarbane
B, Andronikof M, et al: Elevation of cardiac troponin I during
non-exertional heat-related illnesses in the context of a heatwave.
Crit Care. 14:R992010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ye J, Mo W, Chen Y and Yang A: An analysis
of laboratory results of parameters of organ function in patients
with heat stroke. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue.
27:658–661. 2015.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jilma B and Derhaschnig U: Disseminated
intravascular coagulation in heat stroke: A hot topic. Crit Care
Med. 40:1370–1372. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Leon LR and Helwig BG: Heat stroke: Role
of the systemic inflammatory response. J Appl Physiol (1985).
109:1980–1988. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhao JJ, Zhou JJ, Hu J, Zhou FH, Kang HJ,
Liu H, Pan L and Song Q: Analysis of risk factors affecting
prognosis of exertional heat stroke. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu
Yi Xue. 25:515–518. 2013.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pan ZG, Shao Y, Liu YN, Gu ZT, Zhang XQ,
Xu YQ and Su L: Relationship between early coagulability parameters
at admission and outcome in patients with severe heatstroke.
Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 25:725–728. 2013.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li Z, Wang Z, Tu X, Lu W, Fang Y, Gao J,
Yu S, He R, Shi K and Chu H: Analysis of indicators for clinical
prognosis of the patients with heat stroke. Zhonghua Jizhen Yixue
Zazhi. 25:1058–1061. 2016.(In Chinese).
|
|
27
|
Liu Z, Sun X, Tang J, Tang Y, Tong H, Wen
Q, Liu Y and Su L: Intestinal inflammation and tissue injury in
response to heat stress and cooling treatment in mice. Mol Med Rep.
4:437–443. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Leon LR, Blaha MD and DuBose DA: Time
course of cytokine, corticosterone, and tissue injury responses in
mice during heat strain recovery. J Appl Physiol (1985).
100:1400–1409. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lim CL and Mackinnon LT: The roles of
exercise-induced immune system disturbances in the pathology of
heat stroke: The dual pathway model of heat stroke. Sports Med.
36:39–64. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hsu CC, Niu CS and Lin MT: Decrease of
heatstroke-induced multiorgan dysfunction by whole body cooling in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Chin J Physiol. 52:47–55.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tong HS, Liu YS, Wen Q, Tang YQ, Yuan FF
and Su L: Serum procalcitonin predicting mortality in exertional
heatstroke. Emerg Med J. 29:113–117. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Danesh J, Wheeler JG, Hirschfield GM, Eda
S, Eiriksdottir G, Rumley A, Lowe GD, Pepys MB and Gudnason V:
C-reactive protein and other circulating markers of inflammation in
the prediction of coronary heart disease. N Engl J Med.
350:1387–1397. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Martin C, Boisson C, Haccoun M, Thomachot
L and Mege JL: Patterns of cytokine evolution (tumor necrosis
factor-alpha and interleukin-6) after septic shock, hemorrhagic
shock, and severe trauma. Crit Care Med. 25:1813–1819. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Pourakbari B, Mamishi S, Zafari J,
Khairkhah H, Ashtiani MH, Abedini M, Afsharpaiman S and Rad SS:
Evaluation of procalcitonin and neopterin level in serum of
patients with acute bacterial infection. Braz J Infect Dis.
14:252–255. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yousef AA, Amr YM and Suliman GA: The
diagnostic value of serum leptin monitoring and its correlation
with tumor necrosis factor-alpha in critically ill patients: A
prospective observational study. Crit Care. 14:R332010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|