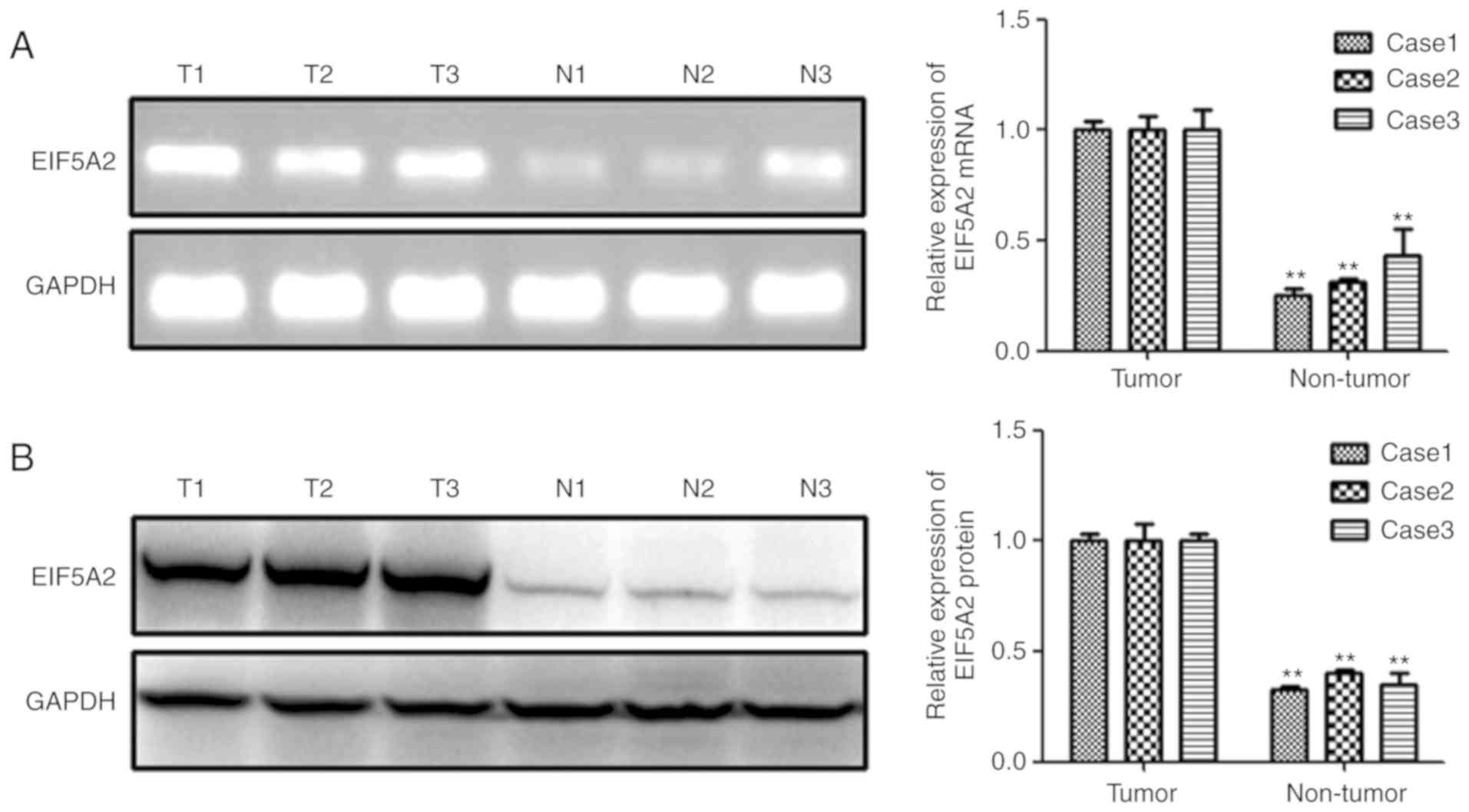
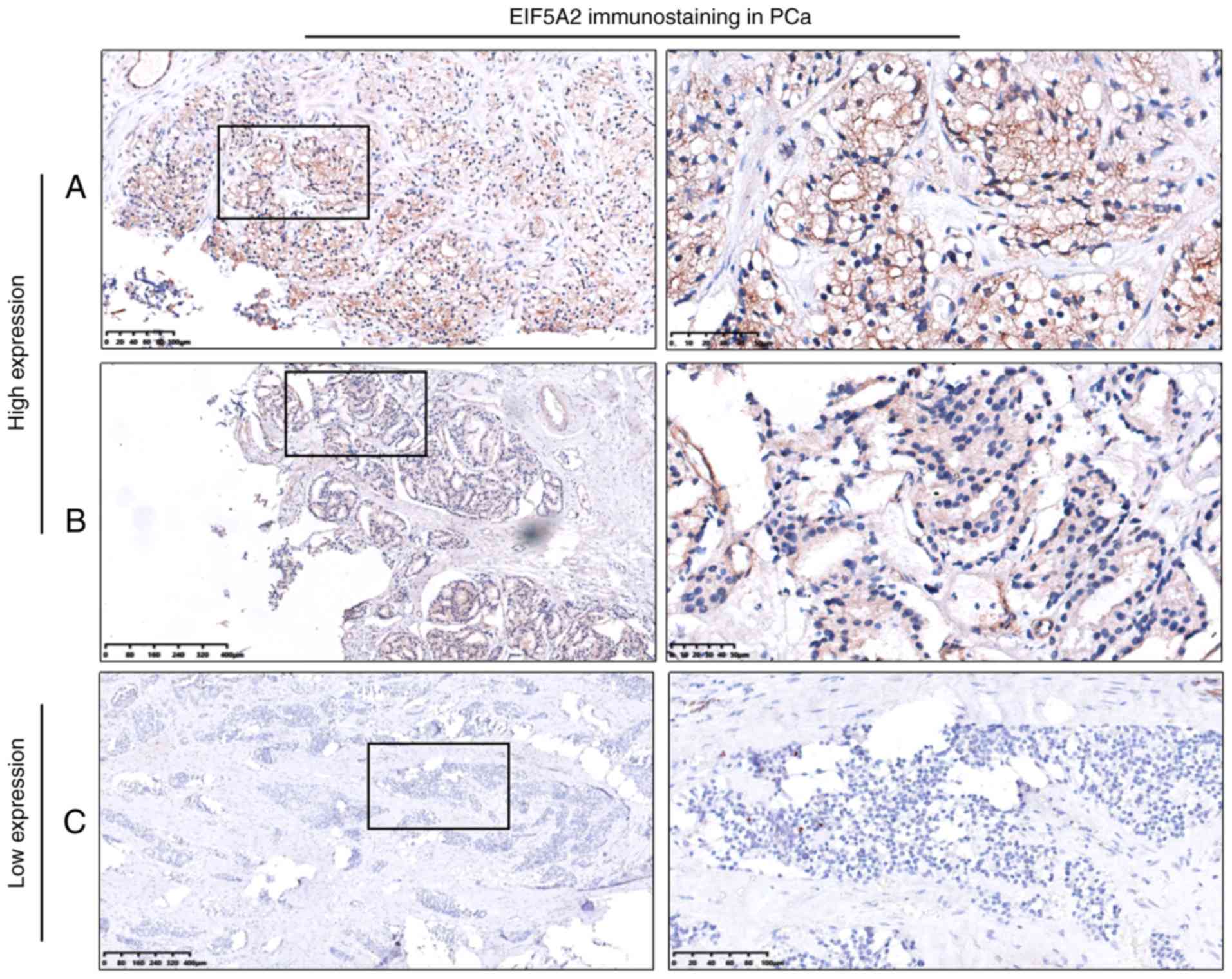
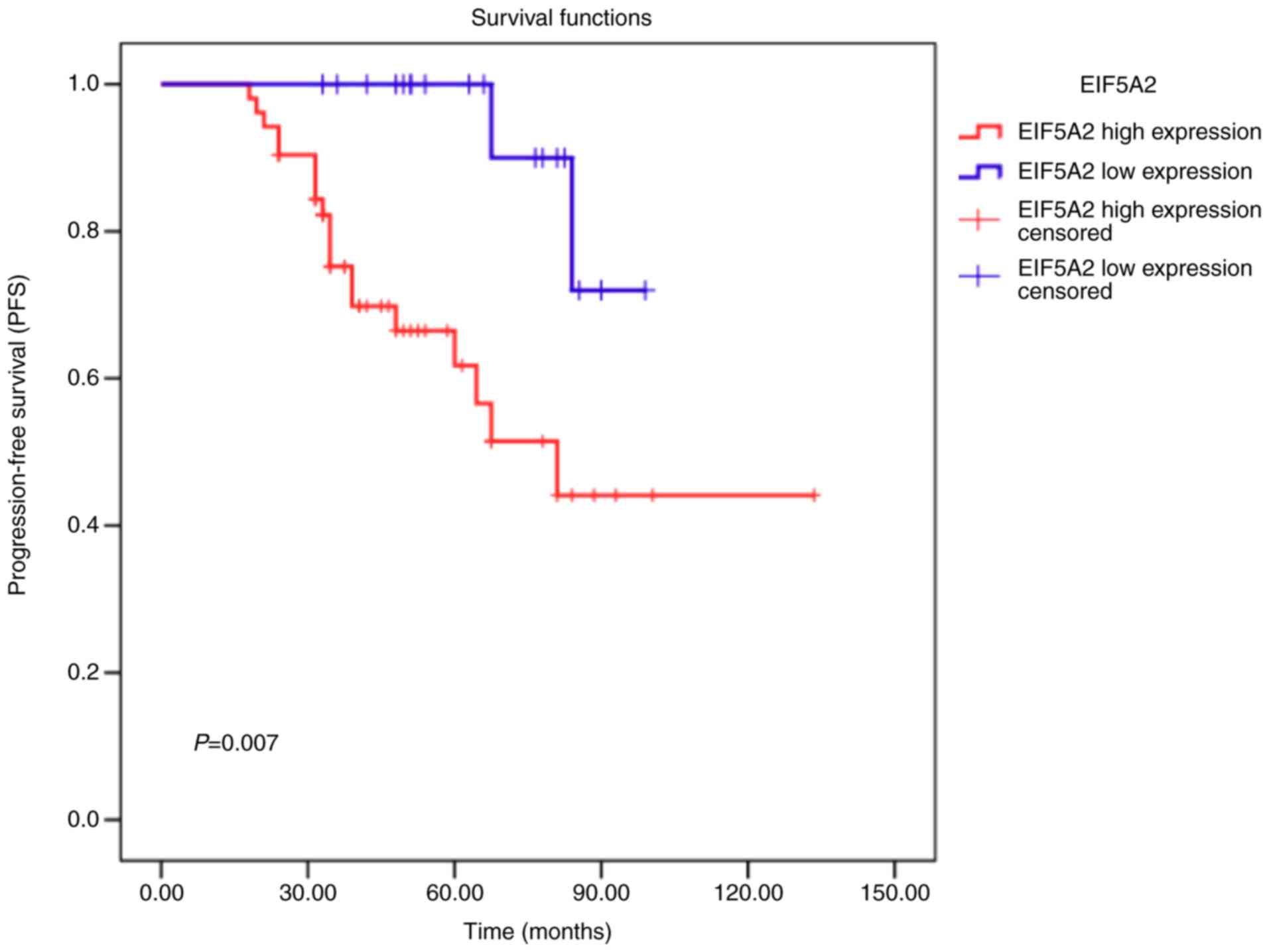
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Miller KD, Siegel RL, Lin CC, Mariotto AB,
Kramer JL, Rowland JH, Stein KD, Alteri R and Jemal A: Cancer
treatment and survivorship statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin.
66:271–289. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Epstein JI, Egevad L, Amin MB, Delahunt B,
Srigley JR, Humphrey PA and Grading Committee: The 2014
international society of urological pathology (ISUP) consensus
conference on gleason grading of prostatic carcinoma: Definition of
grading patterns and proposal for a new grading system. Am J Surg
Pathol. 40:244–252. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Benne R, Brown-Luedi ML and Hershey JW:
Purification and characterization of protein synthesis initiation
factors eIF-1, eIF-4C, eIF-4D, and eIF-5 from rabbit reticulocytes.
J Biol Chem. 253:3070–3077. 1978.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang Z, McGlynn KA, Rajpert-De ME, Bishop
DT, Chung CC, Dalgaard MD, Greene MH, Gupta R, Grotmol T, Haugen
TB, et al: Meta-analysis of five genome-wide association studies
identifies multiple new loci associated with testicular germ cell
tumor. Nat Genet. 49:1141–1147. 2017. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Davidson MA and Shanks EJ: 3q26-29
Amplification in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A review of
established and prospective oncogenes. FEBS J. 284:2705–2731. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jenkins ZA, Haag PG and Johansson HE:
Human eIF5A2 on chromosome 3q25-q27 is a phylogenetically conserved
vertebrate variant of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A
with tissue-specific expression. Genomics. 71:101–109. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang FW, Guan XY and Xie D: Roles of
eukaryotic initiation factor 5A2 in human cancer. Int J Biol Sci.
9:1013–1020. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mathews MB and Hershey JW: The translation
factor eIF5A and human cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1849:836–844.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wei JH, Cao JZ, Zhang D, Liao B, Zhong WM,
Lu J, Zhao HW, Zhang JX, Tong ZT, Fan S, et al: EIF5A2 predicts
outcome in localised invasive bladder cancer and promotes bladder
cancer cell aggressiveness in vitro and in vivo. Br J Cancer.
110:1767–1777. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lou B, Fan J, Wang K, Chen W, Zhou X,
Zhang J, Lin S, Lv F and Chen Y: N1-guanyl-1,7-diaminoheptane (GC7)
enhances the therapeutic efficacy of doxorubicin by inhibiting
activation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2 (eIF5A2)
and preventing the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Exp Cell Res. 319:2708–2717. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu Y, Liu R, Fu P, Du F, Hong Y, Yao M,
Zhang X and Zheng S: N1-Guanyl-1,7-diaminoheptane sensitizes
estrogen receptor negative breast cancer cells to doxorubicin by
preventing epithelial-mesenchymal transition through inhibition of
eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2 activation. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 36:2494–2503. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Edge SB, Byrd DR, Compton CC, Fritz AG,
Greene FL and Trotti A: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 7th edition.
Springer. (New York, NY). 2010.
|
|
15
|
Yang GF, Xie D, Liu JH, Luo JH, Li LJ, Hua
WF, Wu HM, Kung HF, Zeng YX and Guan XY: Expression and
amplification of eIF-5A2 in human epithelial ovarian tumors and
overexpression of EIF-5A2 is a new independent predictor of outcome
in patients with ovarian carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol. 112:314–318.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huang PY, Zeng TT, Ban X, Li MQ, Zhang BZ,
Zhu YH, Hua WF, Mai HQ, Zhang L, Guan XY and Li Y: Expression of
EIF5A2 associates with poor survival of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
patients treated with induction chemotherapy. BMC Cancer.
16:6692016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhu W, Cai MY, Tong ZT, Dong SS, Mai SJ,
Liao YJ, Bian XW, Lin MC, Kung HF, Zeng YX, et al: Overexpression
of EIF5A2 promotes colorectal carcinoma cell aggressiveness by
upregulating MTA1 through C-myc to induce
epithelial-mesenchymaltransition. Gut. 61:562–575. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tang DJ, Dong SS, Ma NF, Xie D, Chen L, Fu
L, Lau SH, Li Y, Li Y and Guan XY: Overexpression of eukaryotic
initiation factor 5A2 enhances cell motility and promotes tumor
metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 51:1255–1263.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Meng QB, Kang WM, Yu JC, Liu YQ, Ma ZQ,
Zhou L, Cui QC and Zhou WX: Overexpression of eukaryotic
translation initiation factor 5A2 (EIF5A2) correlates with cell
aggressiveness and poor survival in gastric cancer. PLoS One.
10:e1192292015.
|
|
20
|
He LR, Zhao HY, Li BK, Liu YH, Liu MZ,
Guan XY, Bian XW, Zeng YX and Xie D: Overexpression of eIF5A-2 is
an adverse prognostic marker of survival in stage I non-small cell
lung cancer patients. Int J Cancer. 129:143–150. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li S, Ma Y, Xie C, Wu Z, Kang Z, Fang Z,
Su B and Guan M: EphA6 promotes angiogenesis and prostate cancer
metastasis and is associated with human prostate cancer
progression. Oncotarget. 6:22587–22597. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang SS, Gao Y, Wang DY, Xia BR, Liu YD,
Qin Y, Ning XM, Li GY, Hao LX, Xiao M and Zhang YY: Overexpression
of eukaryotic initiation factor 5A2 (EIF5A2) is associated with
cancer progression and poor prognosis in patients with early-stage
cervical cancer. Histopathology. 69:276–287. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cao TT, Lin SH, Fu L, Tang Z, Che CM,
Zhang LY, Ming XY, Liu TF, Tang XM, Tan BB, et al: Eukaryotic
translation initiation factor 5A2 promotes metabolic reprogramming
in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Carcinogenesis. 38:94–104. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang FW, Cai MY, Mai SJ, Chen JW, Bai HY,
Li Y, Liao YJ, Li CP, Tian XP, Kung HF, et al: Ablation of EIF5A2
induces tumor vasculature remodeling and improves tumor response to
chemotherapy via regulation of matrix metalloproteinase 2
expression. Oncotarget. 5:6716–6733. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bai HY, Liao YJ, Cai MY, Ma NF, Zhang Q,
Chen JW, Zhang JX, Wang FW, Wang CY, Chen WH, et al: Eukaryotic
initiation factor 5A2 contributes to the maintenance of CD133(+)
hepatocellular carcinoma cells via the c-Myc/microRNA-29b axis.
Stem Cells. 36:180–191. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yang H, Li XD, Zhou Y, Ban X, Zeng TT, Li
L, Zhang BZ, Yun J, Xie D, Guan XY and Li Y: Stemness and
chemotherapeutic drug resistance induced by EIF5A2 overexpression
in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 6:26079–26089.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li Y, Fu L, Li JB, Qin Y, Zeng TT, Zhou J,
Zeng ZL, Chen J, Cao TT, Ban X, et al: Increased expression of
EIF5A2, via hypoxia or gene amplification, contributes to
metastasis and angiogenesis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Gastroenterology. 146:1701–1713. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang X, Jiang R, Cui EH, Feng WM, Guo HH,
Gu DH, Tang CW, Xue T and Bao Y: N1-guanyl-1,7-diaminoheptane
enhances the chemosensitivity of NSCLC cells to cetuximab through
inhibition of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2
activation. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 20:1244–1250.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xu G, Shao G, Pan Q, Sun L, Zheng D, Li M,
Li N, Shi H and Ni Y: MicroRNA-9 regulates non-small cell lung
cancer cell invasion and migration by targeting eukaryotic
translation initiation factor 5A2. Am J Transl Res. 9:478–488.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bao Y, Lu Y, Wang X, Feng W, Sun X, Guo H,
Tang C, Zhang X, Shi Q and Yu H: Eukaryotic translation initiation
factor 5A2 (eIF5A2) regulates chemoresistance in colorectal cancer
through epithelial mesenchymal transition. Cancer Cell Int.
15:1092015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|