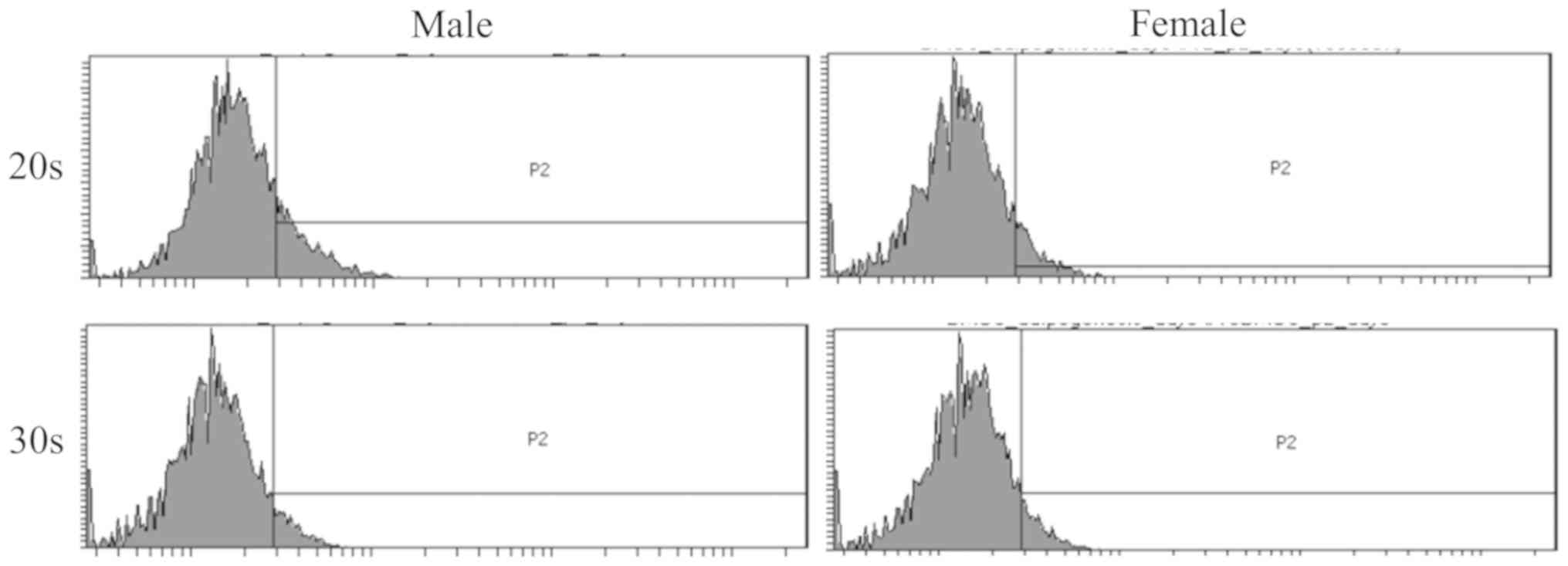
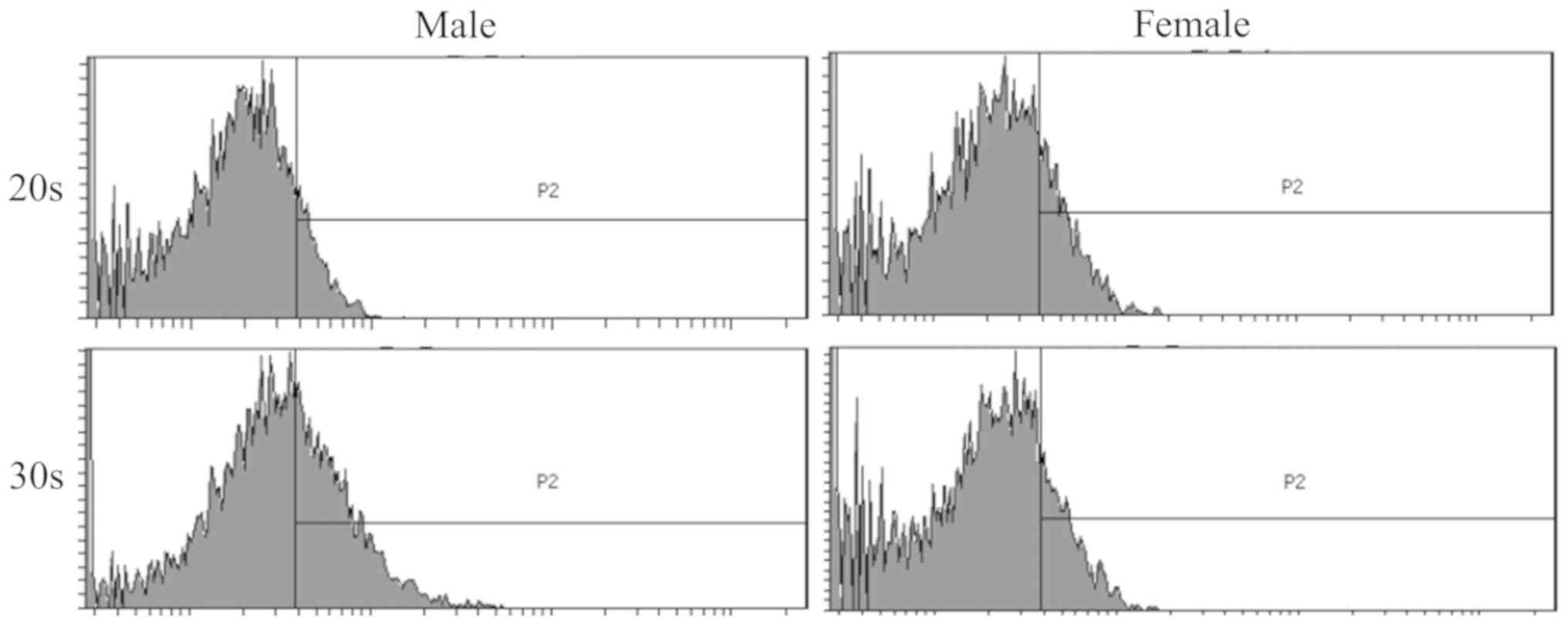
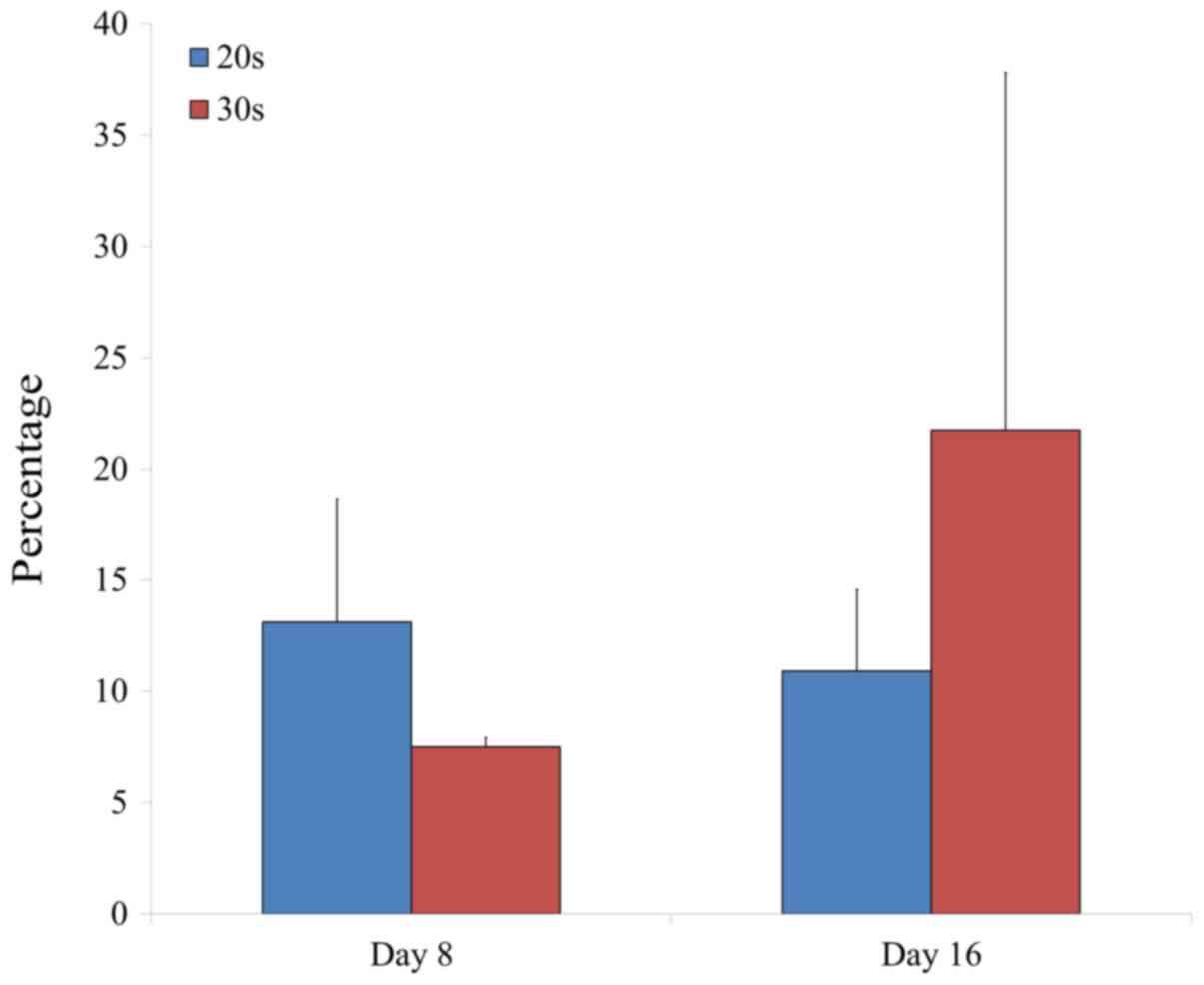
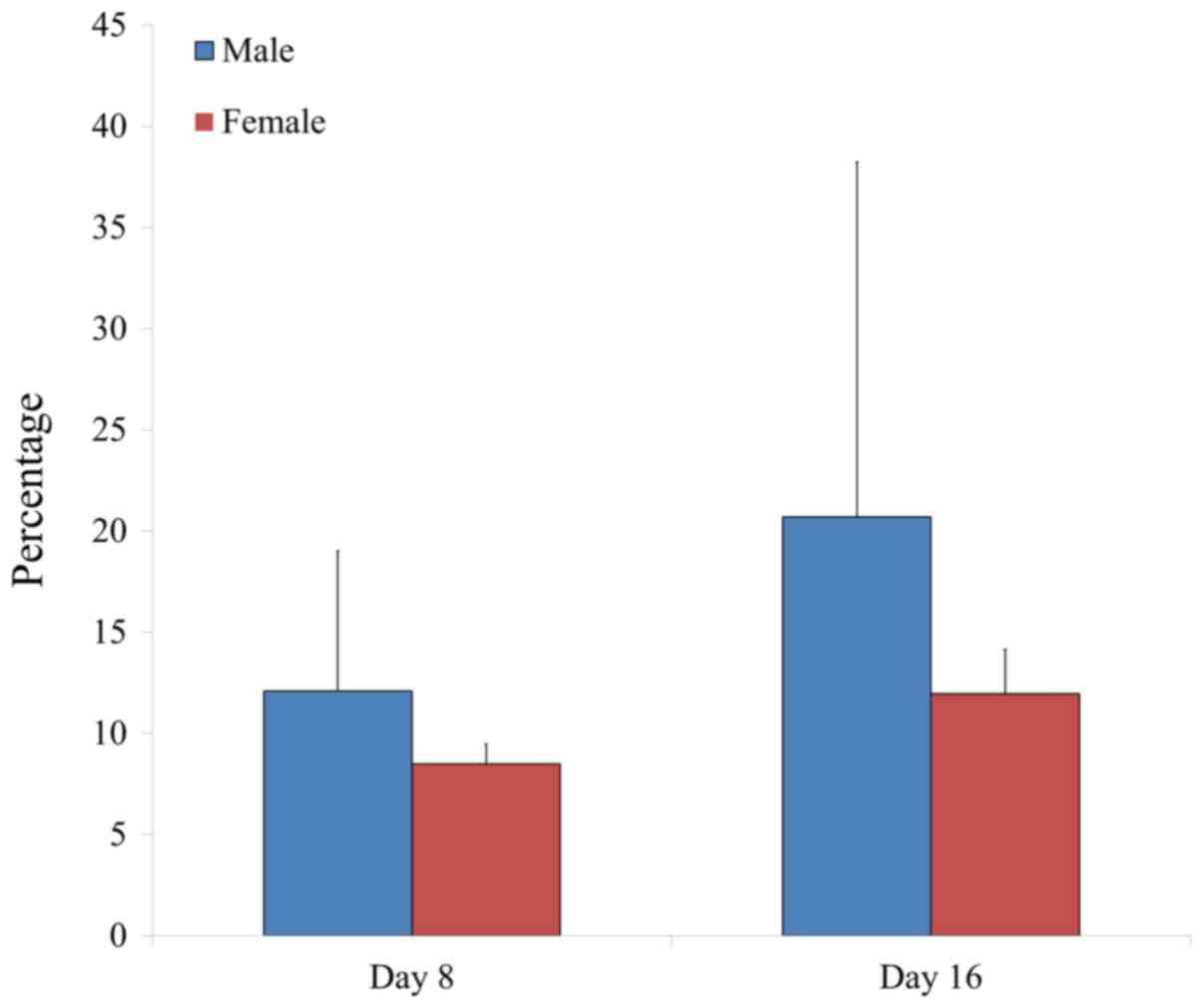
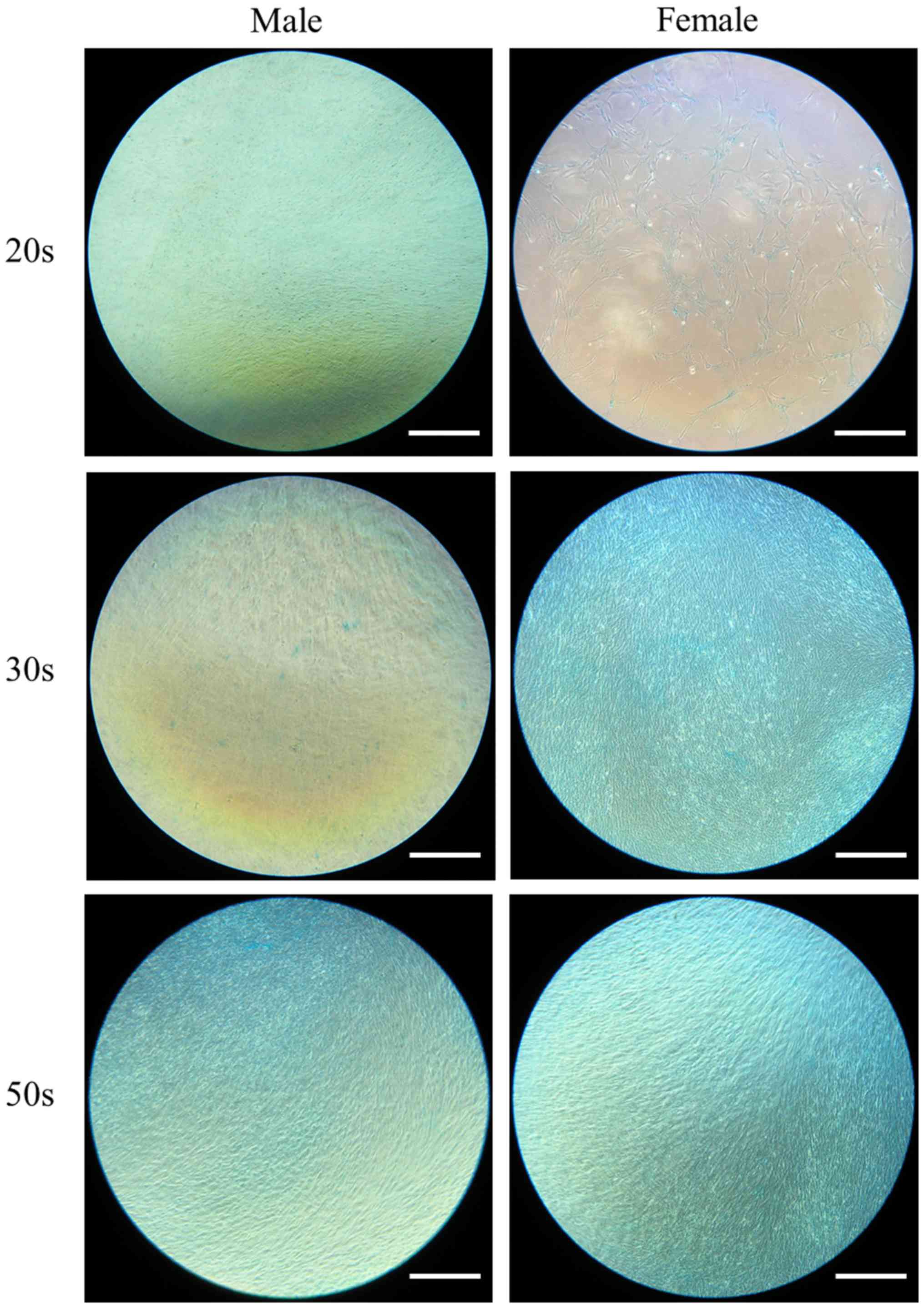
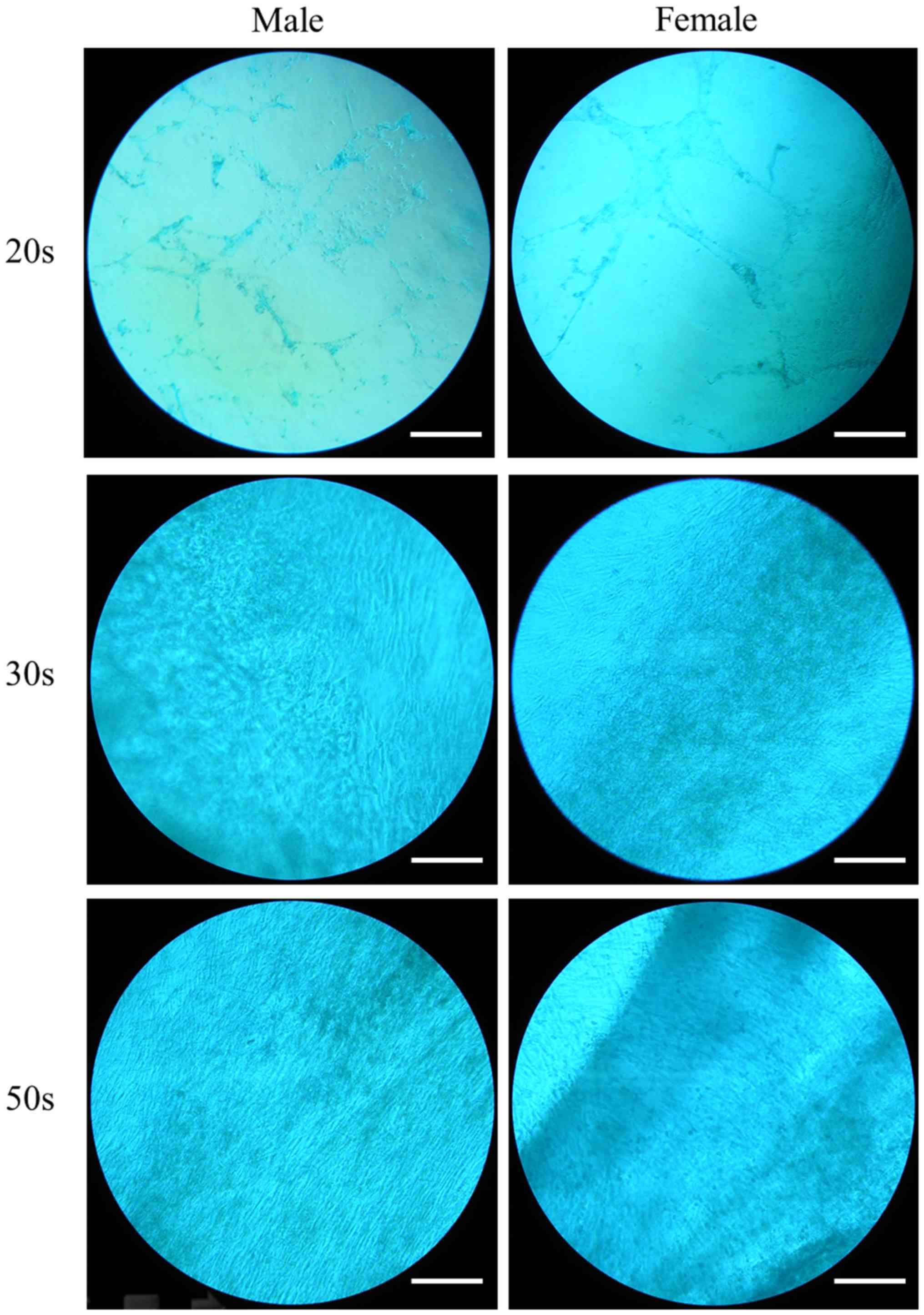
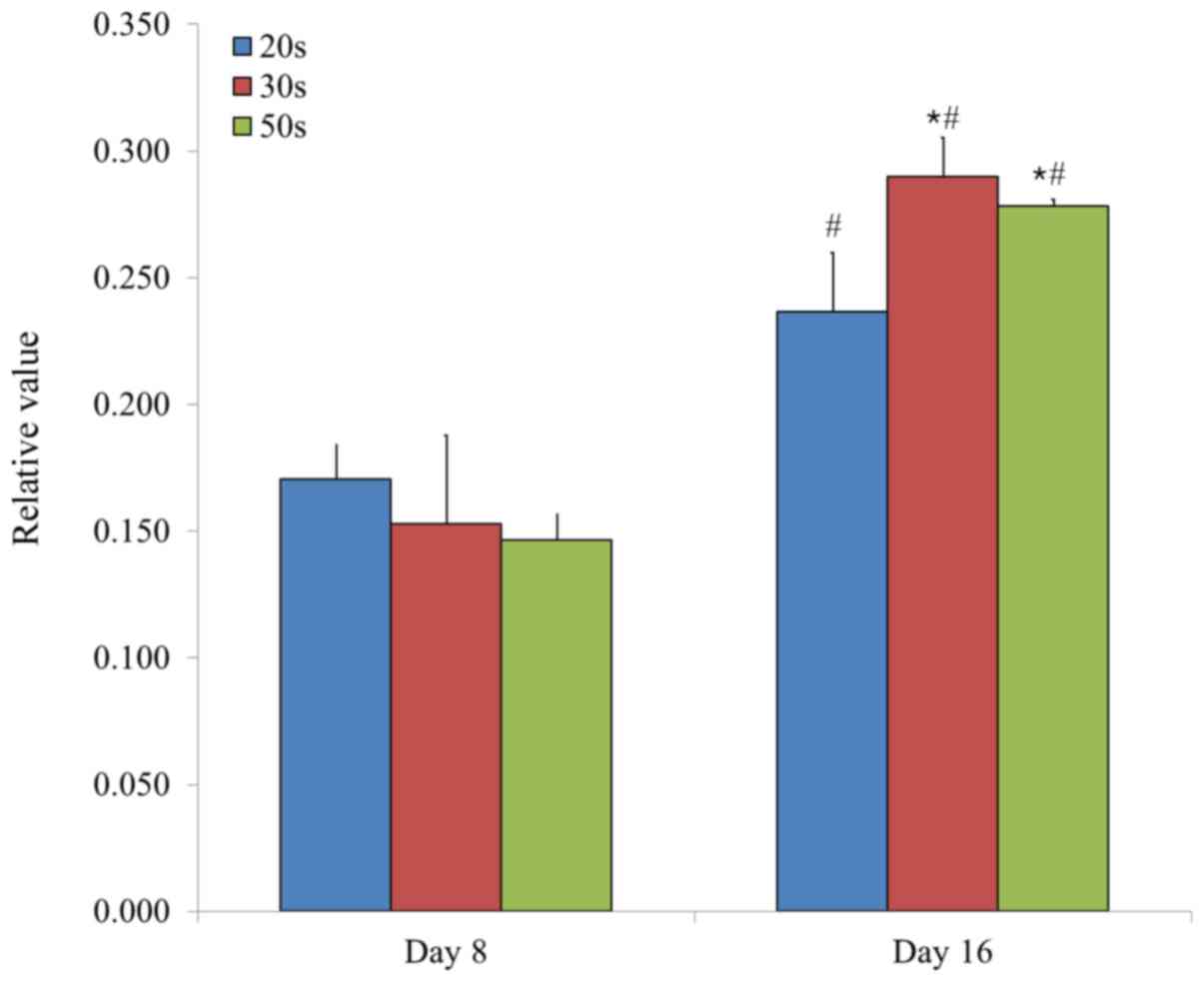
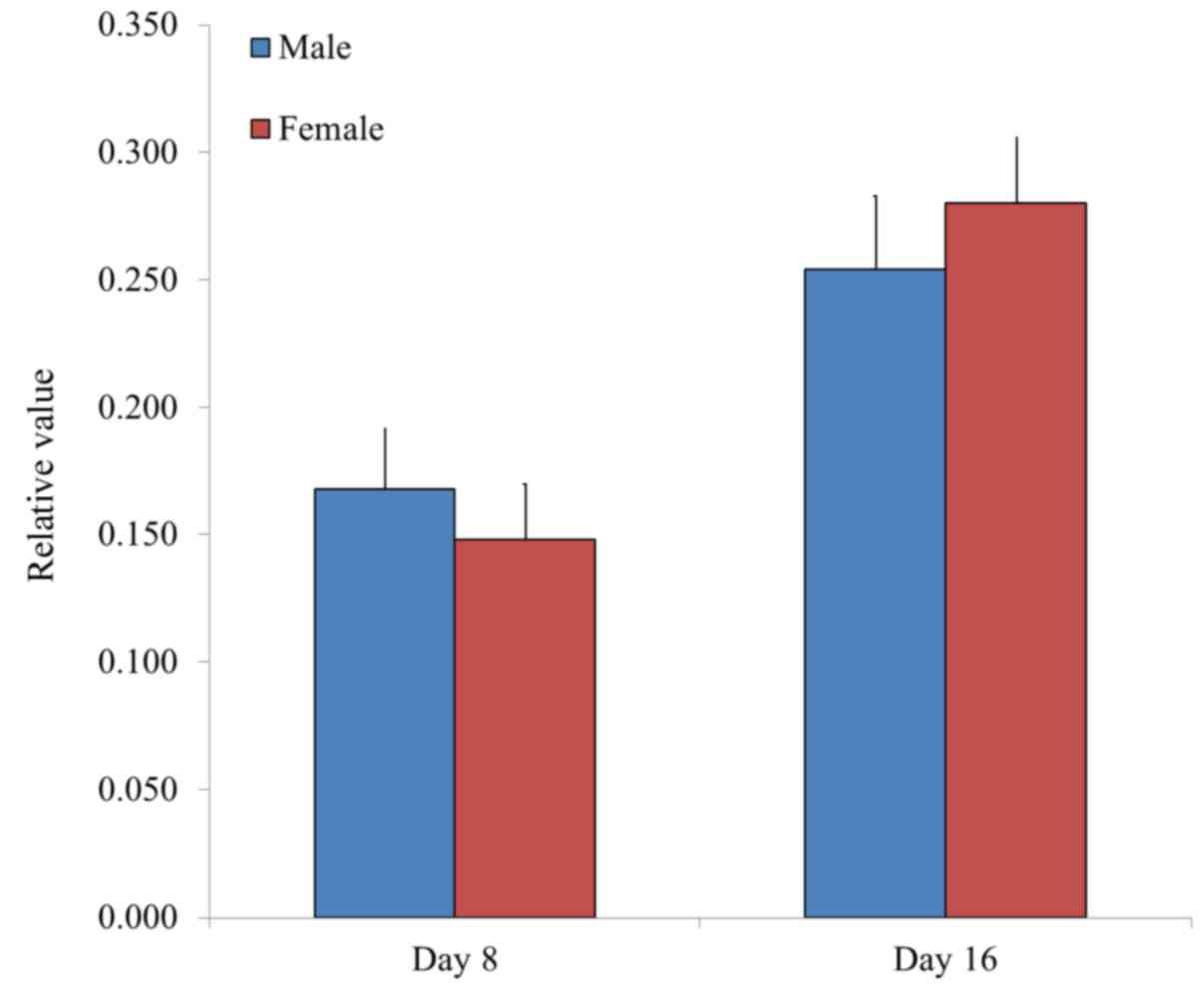
|
1
|
Tögel F and Westenfelder C: Adult bone
marrow-derived stem cells for organ regeneration and repair. Dev
Dyn. 236:3321–3331. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Totey S, Totey S and Pal R and Pal R:
Adult stem cells: A clinical update. J Stem Cells. 4:105–121.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Maria OM, Khosravi R, Mezey E and Tran SD:
Cells from bone marrow that evolve into oral tissues and their
clinical applications. Oral Dis. 13:11–16. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
D'Ippolito G, Schiller PC, Ricordi C, Roos
BA and Howard GA: Age-related osteogenic potential of mesenchymal
stromal stem cells from human vertebral bone marrow. J Bone Miner
Res. 14:1115–1122. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Justesen J, Stenderup K, Eriksen EF and
Kassem M: Maintenance of osteoblastic and adipocytic
differentiation potential with age and osteoporosis in human marrow
stromal cell cultures. Calcif Tissue Int. 71:36–44. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Stenderup K, Rosada C, Justesen J,
Al-Soubky T, Dagnaes-Hansen F and Kassem M: Aged human bone marrow
stromal cells maintaining bone forming capacity in vivo evaluated
using an improved method of visualization. Biogerontology.
5:107–118. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bragdon B, Burns R, Baker AH, Belkina AC,
Morgan EF, Denis GV, Gerstenfeld LC and Schlezinger JJ: Intrinsic
Sex-linked variations in osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation
potential of bone marrow multipotent stromal cells. J Cell Physiol.
230:296–307. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Muschler GF, Nitto H, Boehm CA and Easley
KA: Age- and gender-related changes in the cellularity of human
bone marrow and the prevalence of osteoblastic progenitors. J
Orthop Res. 19:117–125. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Murphy JM, Dixon K, Beck S, Fabian D,
Feldman A and Barry F: Reduced chondrogenic and adipogenic activity
of mesenchymal stem cells from patients with advanced
osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 46:704–713. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zheng YH, Xiong W, Su K, Kuang SJ and
Zhang ZG: Multilineage differentiation of human bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cells in vitro and in vivo. Exp Ther Med.
5:1576–1580. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jeong CH, Kim SM, Lim JY, Ryu CH, Jun JA
and Jeun SS: Mesenchymal stem cells expressing brain-derived
neurotrophic factor enhance endogenous neurogenesis in an ischemic
stroke model. Biomed Res Int. 2014:1291452014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee JE, Kim BB, Ko Y, Jeong SH and Park
JB: Effects of Cimicifugae Rhizoma on the osteogenic and adipogenic
differentiation of stem cells. Exp Ther Med. 13:443–448. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Park JB, Bae SS, Lee PW, Lee W, Park YH,
Kim H, Lee K and Kim I: Comparison of stem cells derived from
periosteum and bone marrow of jaw bone and long bone in rabbit
models. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 9:224–230. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Jiang Y, Mishima H, Sakai S, Liu YK,
Ohyabu Y and Uemura T: Gene expression analysis of major
lineage-defining factors in human bone marrow cells: Effect of
aging, gender and age-related disorders. J Orthop Res. 26:910–917.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bolt AM, Grant MP, Wu TH, Flores Molina M,
Plourde D, Kelly AD, Negro Silva LF, Lemaire M, Schlezinger JJ,
Mwale F and Mann KK: Tungsten promotes sex-specific adipogenesis in
the bone by altering differentiation of bone marrow-resident
mesenchymal stromal cells. Toxicol Sci. 150:333–346. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Johnstone B, Hering TM, Caplan AI,
Goldberg VM and Yoo JU: In vitro chondrogenesis of bone
marrow-derived mesenchymal progenitor cells. Exp Cell Res.
238:265–272. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yoo JU, Barthel TS, Nishimura K, Solchaga
L, Caplan AI, Goldberg VM and Johnstone B: The chondrogenic
potential of human bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal progenitor
cells. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 80:1745–1757. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Scharstuhl A, Schewe B, Benz K, Gaissmaier
C, Buhring HJ and Stoop R: Chondrogenic potential of human adult
mesenchymal stem cells is independent of age or osteoarthritis
etiology. Stem Cells. 25:3244–3251. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zheng H, Martin JA, Duwayri Y, Falcon G
and Buckwalter JA: Impact of aging on rat bone marrow-derived stem
cell chondrogenesis. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 62:136–148.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Barbero A, Grogan S, Schäfer D, Heberer M,
Mainil-Varlet P and Martin I: Age related changes in human
articular chondrocyte yield, proliferation and post-expansion
chondrogenic capacity. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 12:476–484. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gallay SH, Miura Y, Commisso CN,
Fitzsimmons JS and O'Driscoll SW: Relationship of donor site to
chondrogenic potential of periosteum in vitro. J Orthop Res.
12:515–525. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Stolzing A, Jones E, McGonagle D and Scutt
A: Age-related changes in human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal
stem cells: Consequences for cell therapies. Mech Ageing Dev.
129:163–173. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ock SA, Lee YM, Park JS, Shivakumar SB,
Moon SW, Sung NJ, Lee WJ, Jang SJ, Park JM, Lee SC, et al:
Evaluation of phenotypic, functional and molecular characteristics
of porcine mesenchymal stromal/stem cells depending on donor age,
gender and tissue source. J Vet Med Sci. 78:987–995. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Aksu AE, Rubin JP, Dudas JR and Marra KG:
Role of gender and anatomical region on induction of osteogenic
differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells. Ann Plast
Surg. 60:306–322. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Matsumoto T, Kubo S, Meszaros LB, Corsi
KA, Cooper GM, Li G, Usas A, Osawa A, Fu FH and Huard J: The
influence of sex on the chondrogenic potential of muscle-derived
stem cells: Implications for cartilage regeneration and repair.
Arthritis Rheum. 58:3809–3819. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
O'Driscoll SW, Saris DB, Ito Y and
Fitzimmons JS: The chondrogenic potential of periosteum decreases
with age. J Orthop Res. 19:95–103. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|