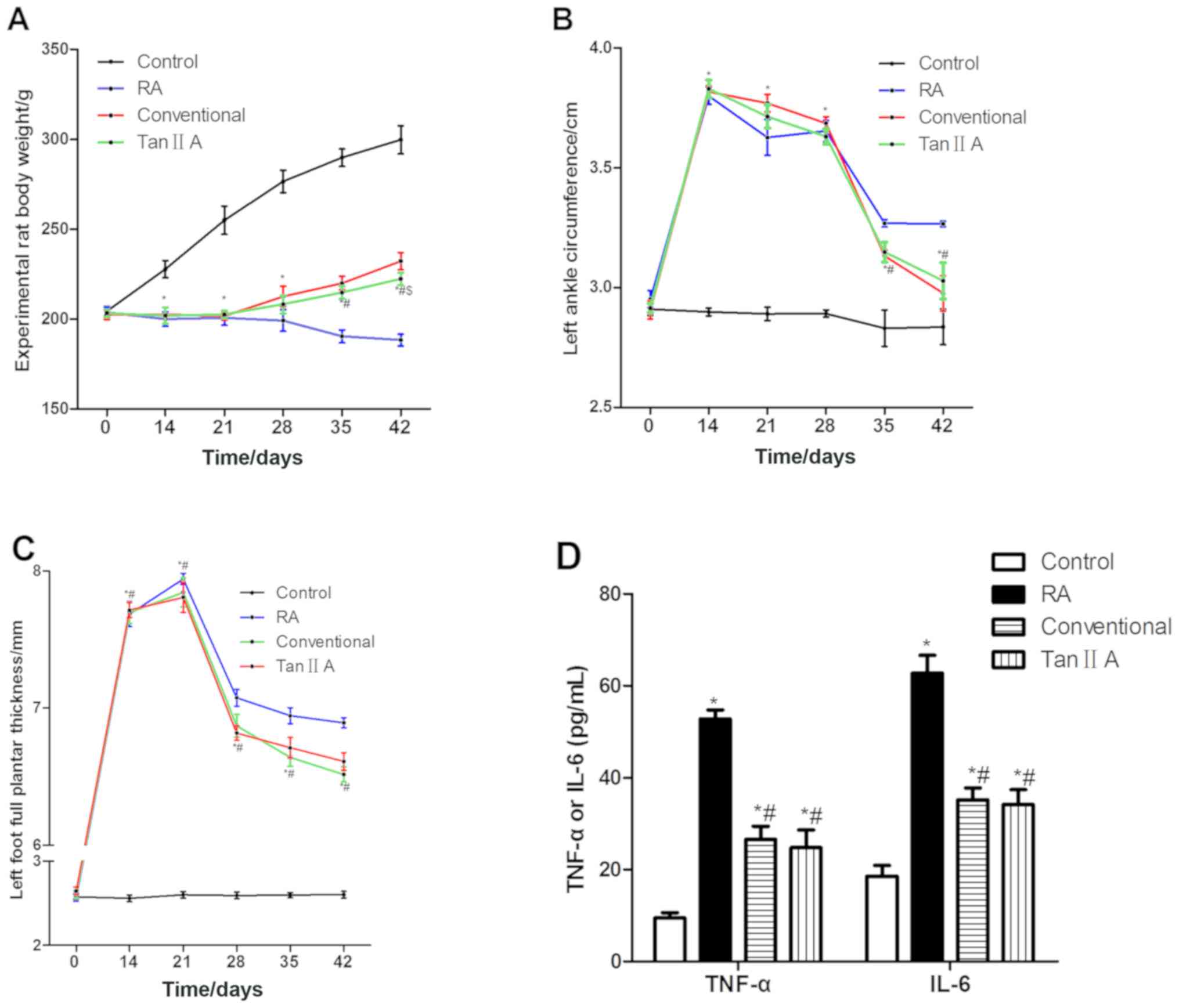
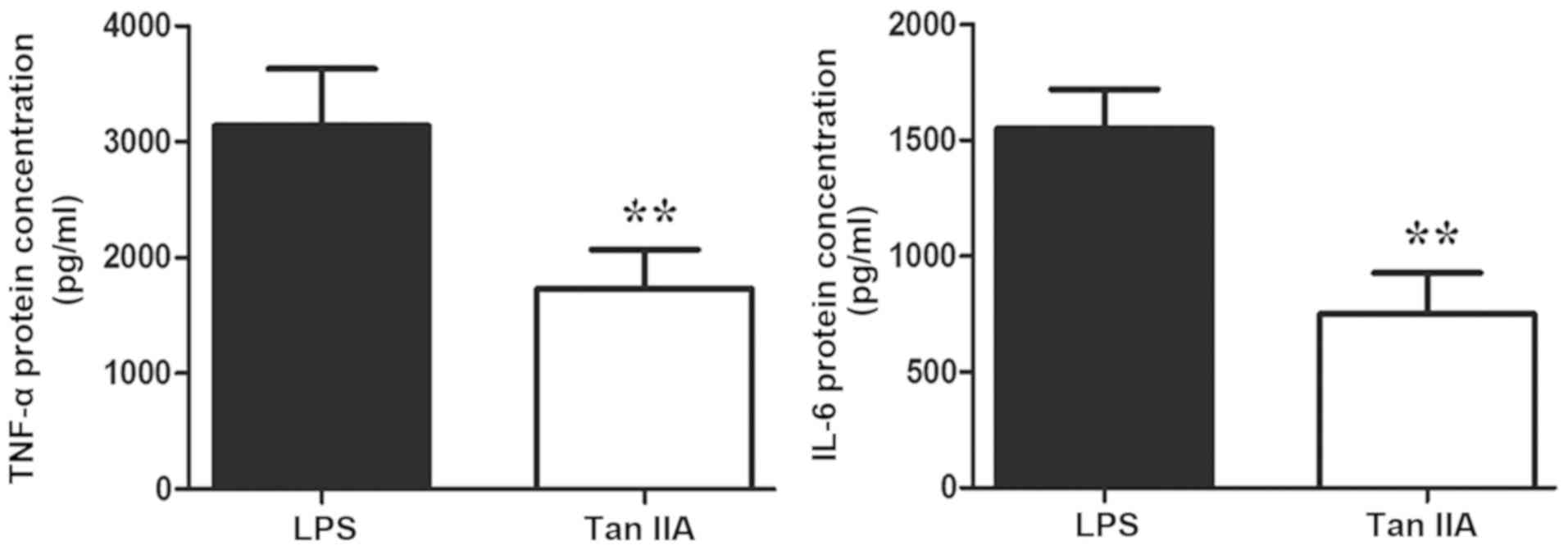
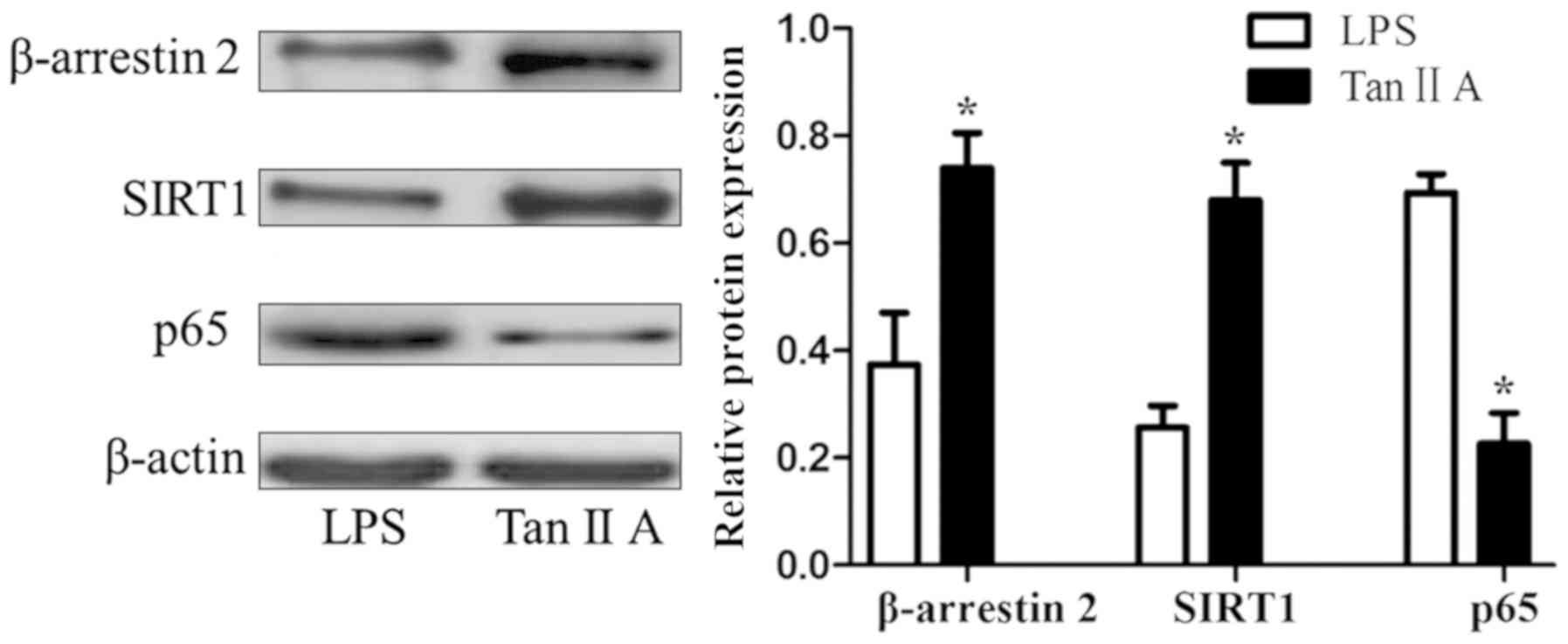
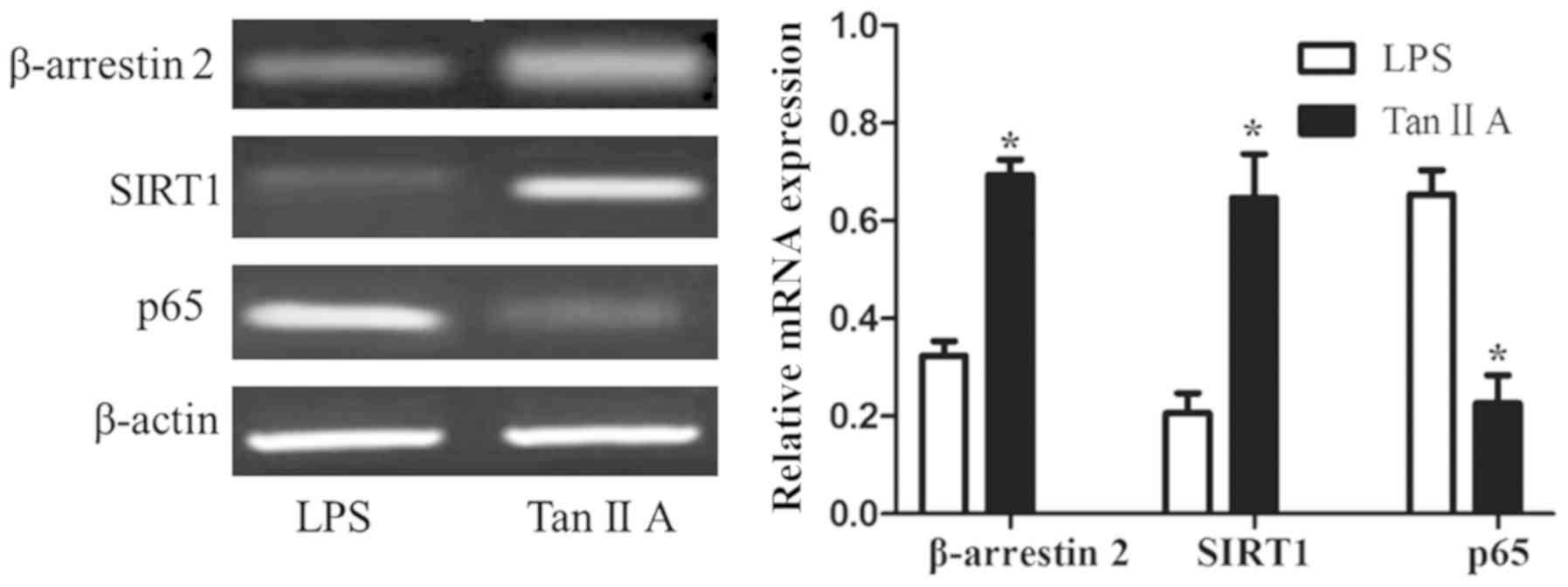
|
1
|
Astry B, Harberts E and Moudgil KD: A
cytokine-centric view of the pathogenesis and treatment of
autoimmune arthritis. J Interferon Cytokine Res Official.
31:927–940. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Mcinnes IB and Schett G: Cytokines in the
pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Immunol. 7:429–442.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kunz M and Ibrahim SM: Cytokines and
cytokine profiles in human autoimmune diseases and animal models of
autoimmunity. Mediators Inflamm. 2009:9792582009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Simsek I: TNF inhibitors for rheumatoid
arthritis-a year in review. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 69:220–224.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Woodrick RS and Ruderman EM: Interleukin 6
inhibition-RA and beyond. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 69:225–229.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kremer JM, Westhovens R, Leon M, Di
Giorgio E, Alten R, Steinfeld S, Russell A, Dougados M, Emery P,
Nuamah IF, et al: Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis by selective
inhibition of T-cell activation with fusion protein CTLA4Ig. N Engl
J Med. 349:1907–1915. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rao DA, Gurish MF, Marshall JL,
Slowikowski K, Fonseka CY, Liu Y, Donlin LT, Henderson LA, Wei K,
Mizoguchi F, et al: Pathologically expanded peripheral T helper
cell subset drives B cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Nature.
542:110–114. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu C, Wang D, Lu S, Xu Q, Zhao L, Zhao J,
Song Y and Wang H: Increased circulating follicular treg cells are
associated with lower levels of autoantibodies in patients with
rheumatoid arthritis in stable remission. Arthritis Rheumatol.
70:711–721. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yu Q, Chen H, Sheng L, Liang Y and Li Q:
Sodium tanshinone IIA sulfonate prolongs the survival of skin
allografts by inhibiting inflammatory cell infiltration and T cell
proliferation. Int immunopharmacol. 22:277–284. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shang Q, Wang H, Li S and Xu H: The effect
of sodium tanshinone IIA sulfate and simvastatin on elevated serum
levels of inflammatory markers in patients with coronary heart
disease: A study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Evid
Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013:7565192013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jie L, Du H, Huang Q, Wei S, Huang R and
Sun W: Tanshinone IIA induces apoptosis in fibroblast-like
synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis via blockade of the cell cycle
in the G2/M phase and a mitochondrial pathway. Biol Pharm Bull.
37:1366–1372. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kay J and Upchurch KS: ACR/EULAR 2010
rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria. Rheumatology
(Oxford):. 51 (Suppl 6):vi5–vi9. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nizamutdinova IT, Kim YM, Jin H, Son KH,
Lee JH, Chang KC and Kim HJ: Tanshinone IIA inhibits TNF-α-mediated
induction of VCAM-1 but not ICAM-1 through the regulation of GATA-6
and IRF-1. Int Immunopharmacol. 14:650–657. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lin C, Wang L, Wang H, Yang L, Guo H and
Wang X: Tanshinone IIA inhibits breast cancer stem cells growth in
vitro and in vivo through attenuation of IL-6/STAT3/NF-κB signaling
pathways. J Cell Biochem. 114:2061–2070. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li P, Cook JA, Gilkeson GS, Luttrell LM,
Wang L, Borg KT, Halushka PV and Fan H: Increased expression of
beta-arrestin 1 and 2 in murine models of rheumatoid arthritis:
Isoform specific regulation of inflammation. Mol Immunol. 49:64–74.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lan W, Petznick A, Heryati S, Rifada M and
Tong L: Nuclear factor-κB: Central regulator in ocular surface
inflammation and diseases. Ocul Surf. 10:137–148. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zheng C, Yin Q and Wu H: Structural
studies of NF-κB signaling. Cell Res. 21:183–195. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Thakur BK, Chandra A, Dittrich T, Welte K
and Chandra P: Inhibition of SIRT1 by HIV-1 viral protein Tat
results in activation of p53 pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
424:245–250. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhao W, Kruse JP, Tang Y, Jung SY, Qin J
and Gu W: Negative regulation of the deacetylase SIRT1 by DBC1.
Nature. 451:587–590. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kuno A, Hori YS, Hosoda R, Tanno M, Miura
T, Shimamoto K and Horio Y: Resveratrol improves cardiomyopathy in
dystrophin-deficient mice through SIRT1 protein-mediated modulation
of p300 protein. J Biol Chem. 288:5963–5972. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zelová H and Hošek J: TNF-α signalling and
inflammation: Interactions between old acquaintances. Inflamm Res.
62:641–651. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Neurath MF and Finotto S: IL-6 signaling
in autoimmunity, chronic inflammation and inflammation-associated
cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 22:83–89. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Seriolo B, Paolino S, Sulli A, Fasciolo D
and Cutolo M: Effects of anti-TNF-alpha treatment on lipid profile
in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis. Ann NY Acad Sci.
1069:414–419. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nishimoto N, Hashimoto J, Miyasaka N,
Yamamoto K, Kawai S, Takeuchi T, Murata N, van der Heijde D and
Kishimoto T: Study of active controlled monotherapy used for
rheumatoid arthritis, an IL-6 inhibitor (SAMURAI): Evidence of
clinical and radiographic benefit from an × ray reader-blinded
randomised controlled trial of tocilizumab. Ann Rheum Dis.
66:1162–1167. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|