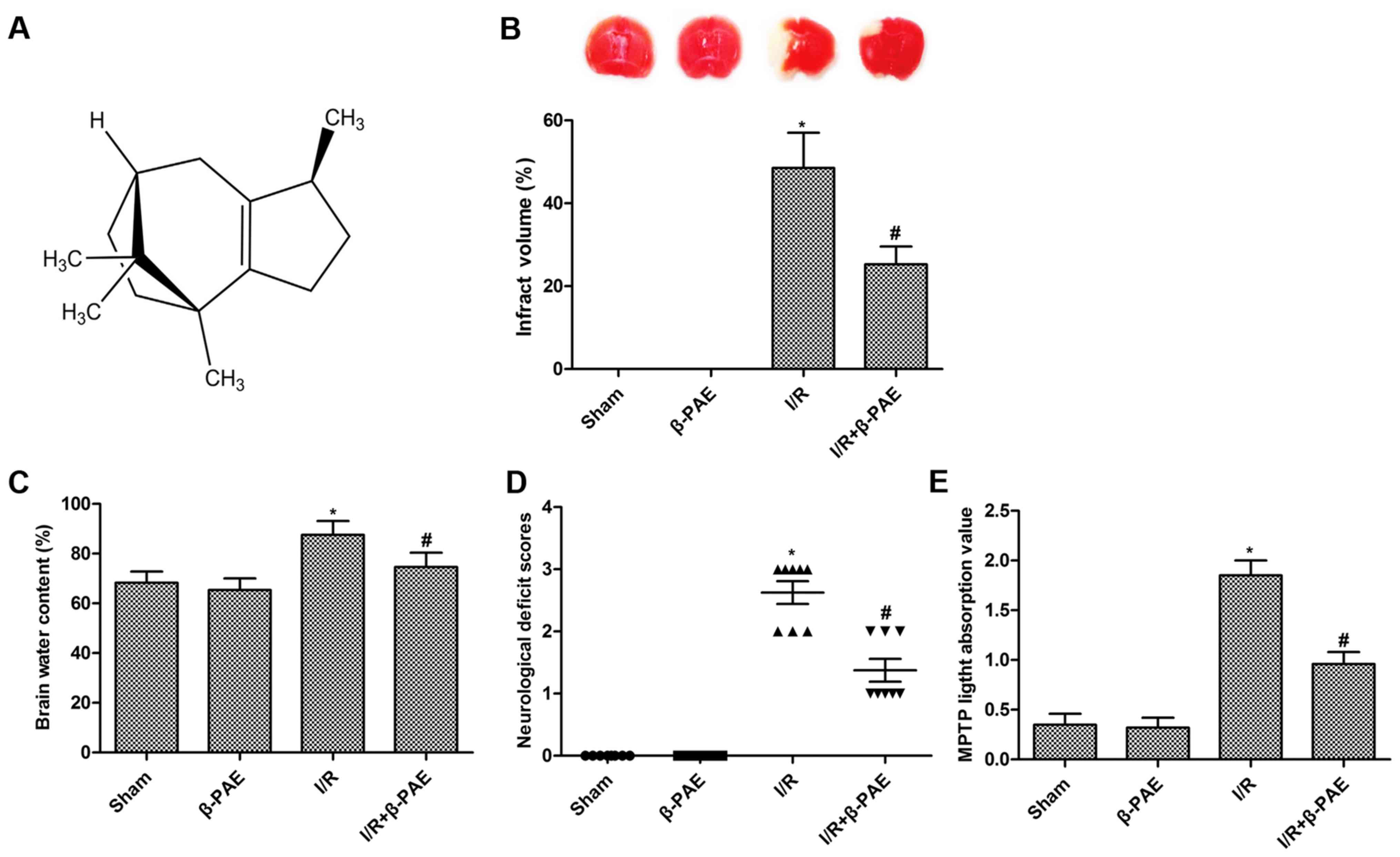
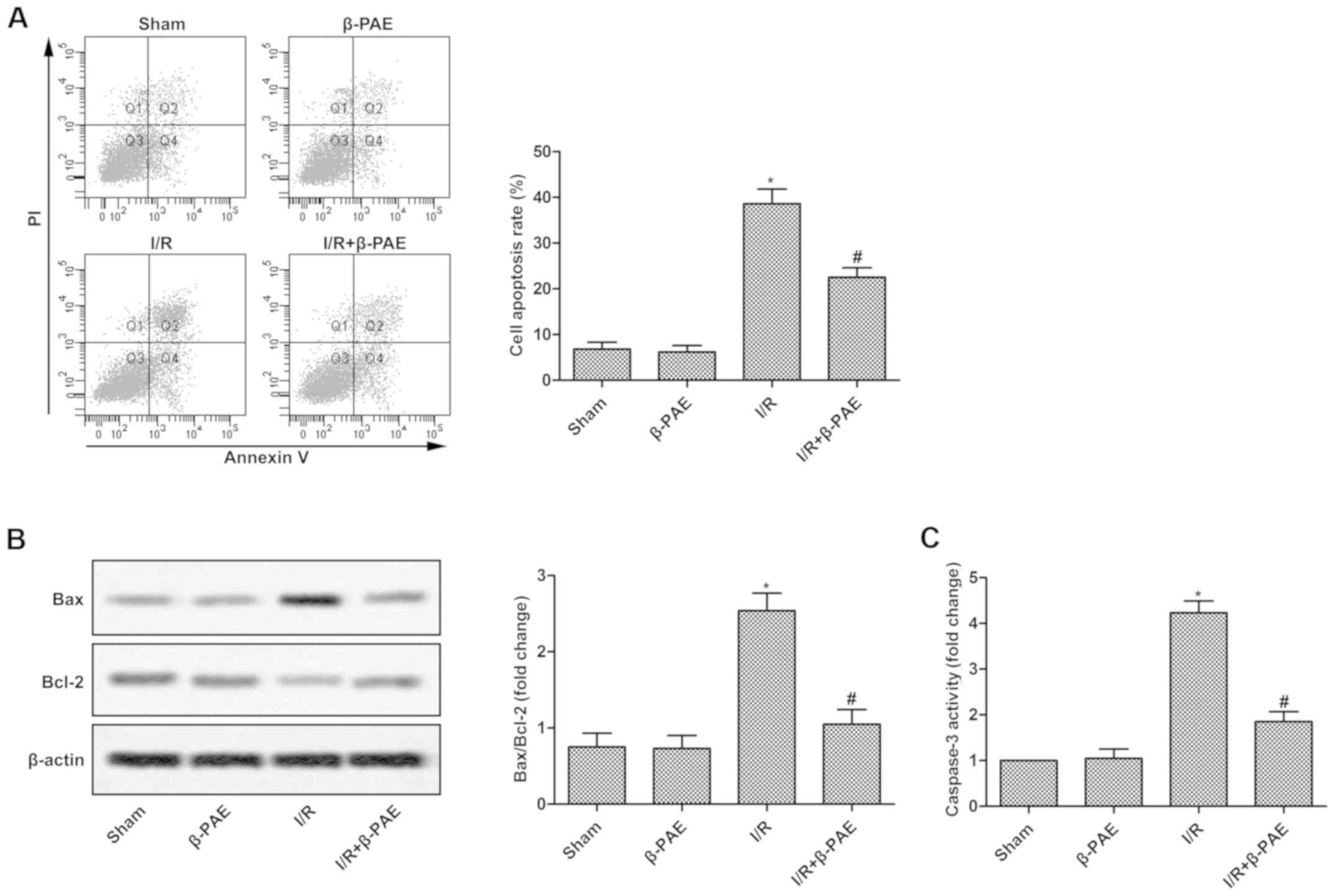
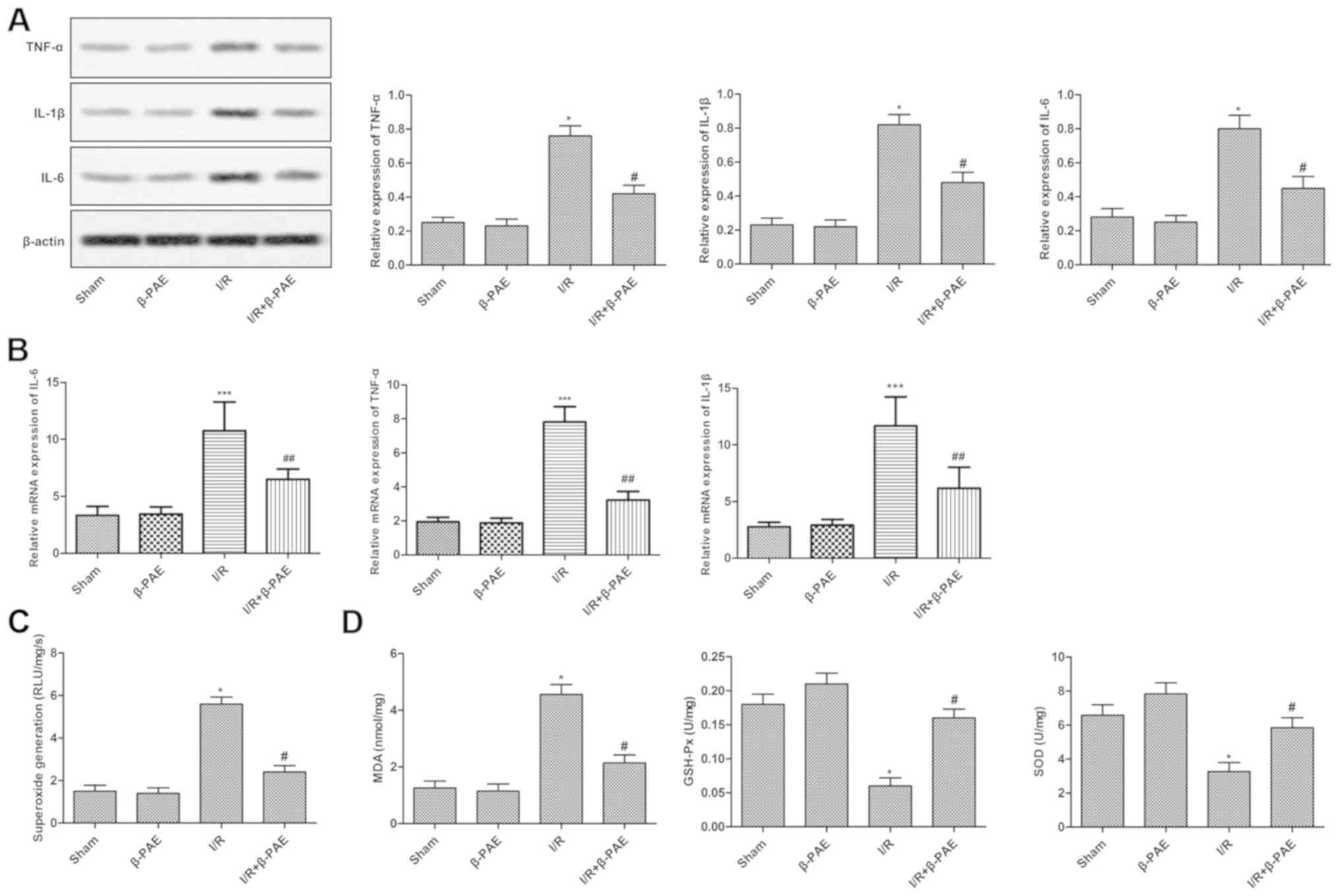
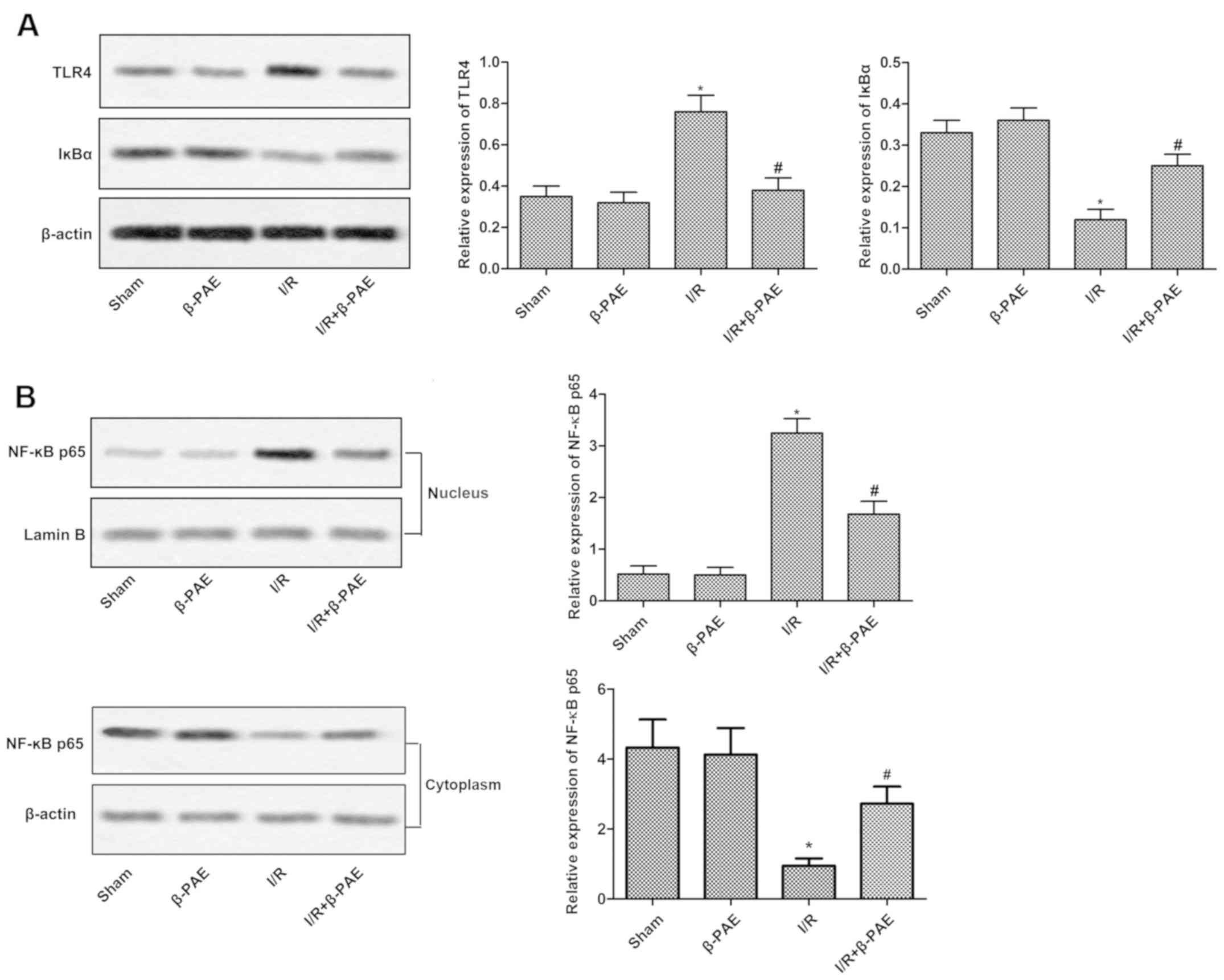
|
1
|
Zhao L, Liu X, Liang J, Han S, Wang Y, Yin
Y, Luo Y and Li J: Phosphorylation of p38 MAPK mediates hypoxic
preconditioning-induced neuroprotection against cerebral ischemic
injury via mitochondria translocation of Bcl-xL in mice. Brain Res.
1503:78–88. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jiang M, Li J, Peng Q, Liu Y, Liu W, Luo
C, Peng J, Li J, Yung KK and Mo Z: Neuroprotective effects of
bilobalide on cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury are
associated with inhibition of pro-inflammatory mediator production
and down-regulation of JNK1/2 and p38 MAPK activation. J
Neuroinflammation. 11:1672014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chien A and Vinuela F: Analyzing Circle of
Willis blood flow in ischemic stroke patients through 3D stroke
arterial flow estimation. Interv Neuroradiol. 23:427–432. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhao P, Zhou R, Zhu XY, Hao YJ, Li N, Wang
J, Niu Y, Sun T, Li YX and Yu JQ: Matrine attenuates focal cerebral
ischemic injury by improving antioxidant activity and inhibiting
apoptosis in mice. Int J Mol Med. 36:633–644. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wu J, Chen Y, Yu S, Li L, Zhao X, Li Q,
Zhao J and Zhao Y: Neuroprotective effects of sulfiredoxin-1 during
cerebral ischemia/reperfusion oxidative stress injury in rats.
Brain Res Bull. 132:99–108. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhou L, Bondy SC, Jian L, Wen P, Yang F,
Luo H, Li W and Zhou J: Tanshinone IIA attenuates the cerebral
ischemic injury-induced increase in levels of GFAP and of
caspases-3 and −8. Neuroscience. 288:105–111. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wu JZ, Liu YH, Liang JL, Huang QH, Dou YX,
Nie J, Zhuo JY, Wu X, Chen JN, Su ZR and Wu QD: Protective role of
β-patchoulene from Pogostemon cablin against indomethacin-induced
gastric ulcer in rats: Involvement of anti-inflammation and
angiogenesis. Phytomedicine. 39:111–118. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen XY, Dou YX, Luo DD, Zhang ZB, Li CL,
Zeng HF, Su ZR, Xie JH, Lai XP and Li YC: β-Patchoulene from
patchouli oil protects against LPS-induced acute lung injury via
suppressing NF-κB and activating Nrf2 pathways. Int
Immunopharmacol. 50:270–278. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang Z, Chen X, Chen H, Wang L, Liang J,
Luo D, Liu Y, Yang H, Li Y, Xie J and Su Z: Anti-inflammatory
activity of β-patchoulene isolated from patchouli oil in mice. Eur
J Pharmacol. 781:229–238. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bi Y, Zhu Y, Zhang M, Zhang K, Hua X, Fang
Z, Zhou J, Dai W, Cui Y, Li J and You T: Effect of shikonin on
spinal cord injury in rats via regulation of HMGB1/TLR4/NF-kB
signaling pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 43:481–491. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ntoufa S, Vilia MG, Stamatopoulos K, Ghia
P and Muzio M: Toll-like receptors signaling: A complex network for
NF-κB activation in B-cell lymphoid malignancies. Semin Cancer
Biol. 39:15–25. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li X, Su L, Zhang X, Zhang C, Wang L, Li
Y, Zhang Y, He T, Zhu X and Cui L: Ulinastatin downregulates TLR4
and NF-kB expression and protects mouse brains against
ischemia/reperfusion injury. Neurol Res. 39:367–373. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu Y, Liang J, Wu J, Chen H, Zhang Z,
Yang H, Chen L, Chen H, Su Z and Li Y: Transformation of patchouli
alcohol to β-patchoulene by gastric juice: β-patchoulene is more
effective in preventing ethanol-induced gastric injury. Sci Rep.
7:55912017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen J, Sanberg PR, Li Y, Wang L, Lu M,
Willing AE, Sanchez-Ramos J and Chopp M: Intravenous administration
of human umbilical cord blood reduces behavioral deficits after
stroke in rats. Stroke. 32:2682–2688. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S and
Cummins R: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xiong D, Deng Y, Huang B, Yin C, Liu B,
Shi J and Gong Q: Icariin attenuates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion
injury through inhibition of inflammatory response mediated by
NF-κB, PPARα and PPARγ in rats. Int Immunopharmacol. 30:157–162.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang L, Wang L, Ning FB, Wang T, Liang YC
and Liu YL: Erythropoietin reduces hippocampus injury in neonatal
rats with hypoxic ischemic brain damage via targeting matrix
metalloprotein-2. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 21:4327–4333.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tao T, Li CL, Yang WC, Zeng XZ, Song CY,
Yue ZY, Dong H and Qian H: Protective effects of propofol against
whole cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats through the
inhibition of the apoptosis-inducing factor pathway. Brain Res.
1644:9–14. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yuan J, Guo X, Liu Z, Zhao X, Feng Y, Song
S, Cui C and Jiang P: Vitamin D receptor activation influences the
ERK pathway and protects against neurological deficits and neuronal
death. Int J Mol Med. 41:364–372. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang W, Fang H, Groom L, Cheng A, Zhang W,
Liu J, Wang X, Li K, Han P, Zheng M, et al: Superoxide flashes in
single mitochondria. Cell. 134:279–290. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lopez AD, Mathers CD, Ezzati M, Jamison DT
and Murray CJ: Global and regional burden of disease and risk
factors, 2001: Systematic analysis of population health data.
Lancet. 367:1747–1757. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gomis M and Dávalos A: Recanalization and
reperfusion therapies of acute ischemic stroke: What have we
learned, what are the major research questions and where are we
headed? Front Neurol. 5:2262014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang M, Wang J, Liu Z, Guo X, Wang N, Jia
N, Zhang Y and Yuan J: Effects of intermedin on autophagy in
cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Neuropeptides. 68:15–21.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Qiao Z and Xu Y: Salvianolic acid B
alleviating myocardium injury in ischemia reperfusion rats. Afr J
Tradit Complement Altern Med. 13:157–161. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ming D, Songyan L, Yawen C, Na Z, Jing M,
Zhaowen X, Ye L, Wa D and Jie L: Trans-Polydatin protects the mouse
heart against ischemia/reperfusion injury via inhibition of the
renin-angiotensin system (RAS) and Rho kinase (ROCK) activity. Food
Funct. 8:2309–2321. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Che X, Wang X, Zhang J, Peng C, Zhen Y,
Shao X, Zhang G and Dong L: Vitexin exerts cardioprotective effect
on chronic myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats via
inhibiting myocardial apoptosis and lipid peroxidation. Am J Transl
Res. 8:3319–3328. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang B, Song C, Feng B and Fan W:
Neuroprotection by triptolide against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion
injury through the inhibition of NF-κB/PUMA signal in rats. Ther
Clin Risk Manag. 12:817–824. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Miao M, Yan X, Guo L and Shao S: Effects
of the Rabdosia rubescens total flavonoids on focal cerebral
ischemia reperfusion model in rats. Saudi Pharm J. 25:607–614.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tan H, Chen L and Ma J: Penehyclidine
hydrochloride post-conditioning reduces
ischemia/reperfusion-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis in rats. Exp
Ther Med. 14:4272–4278. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shabanzadeh AP, D'Onofrio PM, Monnier PP
and Koeberle PD: Targeting caspase-6 and caspase-8 to promote
neuronal survival following ischemic stroke. Cell Death Dis.
6:e19672015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Elmore S: Apoptosis: A review of
programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol. 35:495–516. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Broughton BR, Reutens DC and Sobey CG:
Apoptotic mechanisms after cerebral ischemia. Stroke. 40:e331–339.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ren Z, Zhang R, Li Y, Li Y, Yang Z and
Yang H: Ferulic acid exerts neuroprotective effects against
cerebral ischemia/reperfusion-induced injury via antioxidant and
anti-apoptotic mechanisms in vitro and in vivo. Int J Mol Med.
40:1444–1456. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu Y, Zhang L and Liang J: Activation of
the Nrf2 defense pathway contributes to neuroprotective effects of
phloretin on oxidative stress injury after cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion in rats. J Neurol Sci. 351:88–92. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hoshino K, Takeuchi O, Kawai T, Sanjo H,
Ogawa T, Takeda Y, Takeda K and Akira S: Pillars Article: Cutting
edge: Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-deficient mice are hyporesponsive
to lipopolysaccharide: Evidence for TLR4 as the Lps gene product. J
Immunol. 162:3749–3752. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang D, Wang X, Tong W, Cui Y, Li X and
Sun H: Umbelliferone alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced
inflammatory responses in acute lung injury by down-regulating
TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling. Inflammation. Jan 15–2019.(Epub ahead
of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Wan F and Lenardo MJ: The nuclear
signaling of NF-kappaB: Current knowledge, new insights, and future
perspectives. Cell Res. 20:24–33. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang J, Fu B, Zhang X, Chen L, Zhang L,
Zhao X, Bai X, Zhu C, Cui L and Wang L: Neuroprotective effect of
bicyclol in rat ischemic stroke: Down-regulates TLR4, TLR9, TRAF6,
NF-κB, MMP-9 and up-regulates claudin-5 expression. Brain Res.
1528:80–88. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|