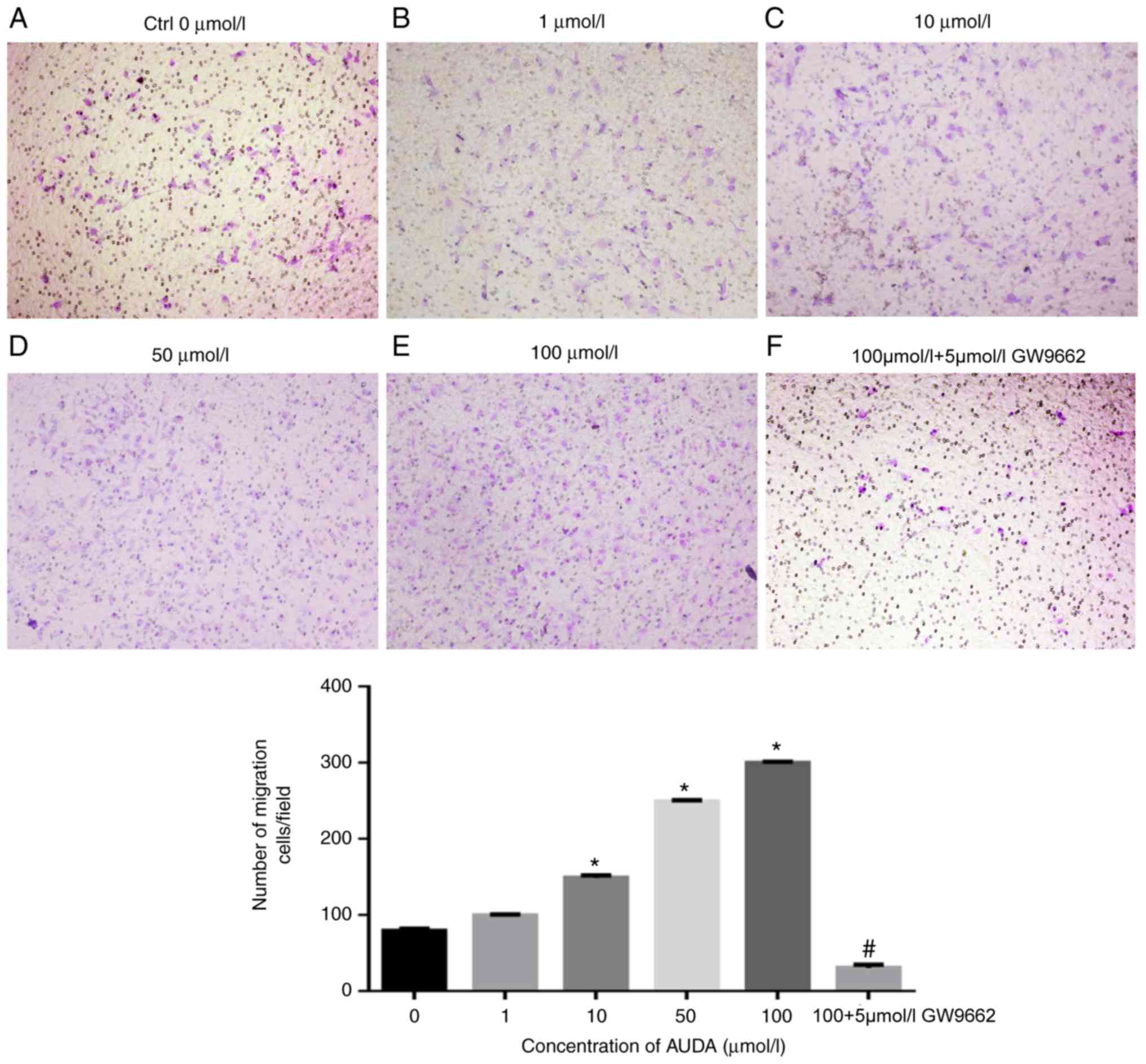
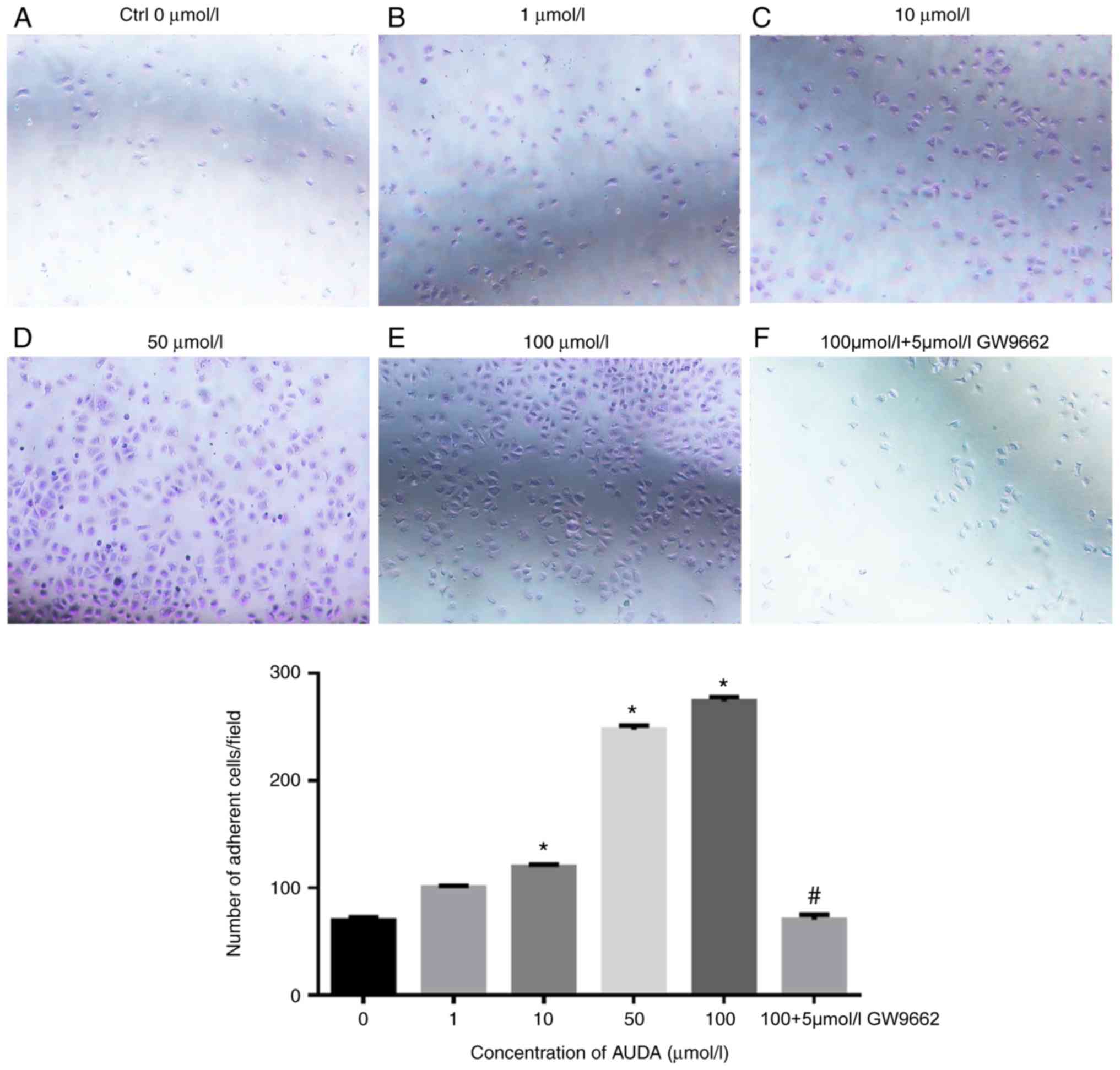
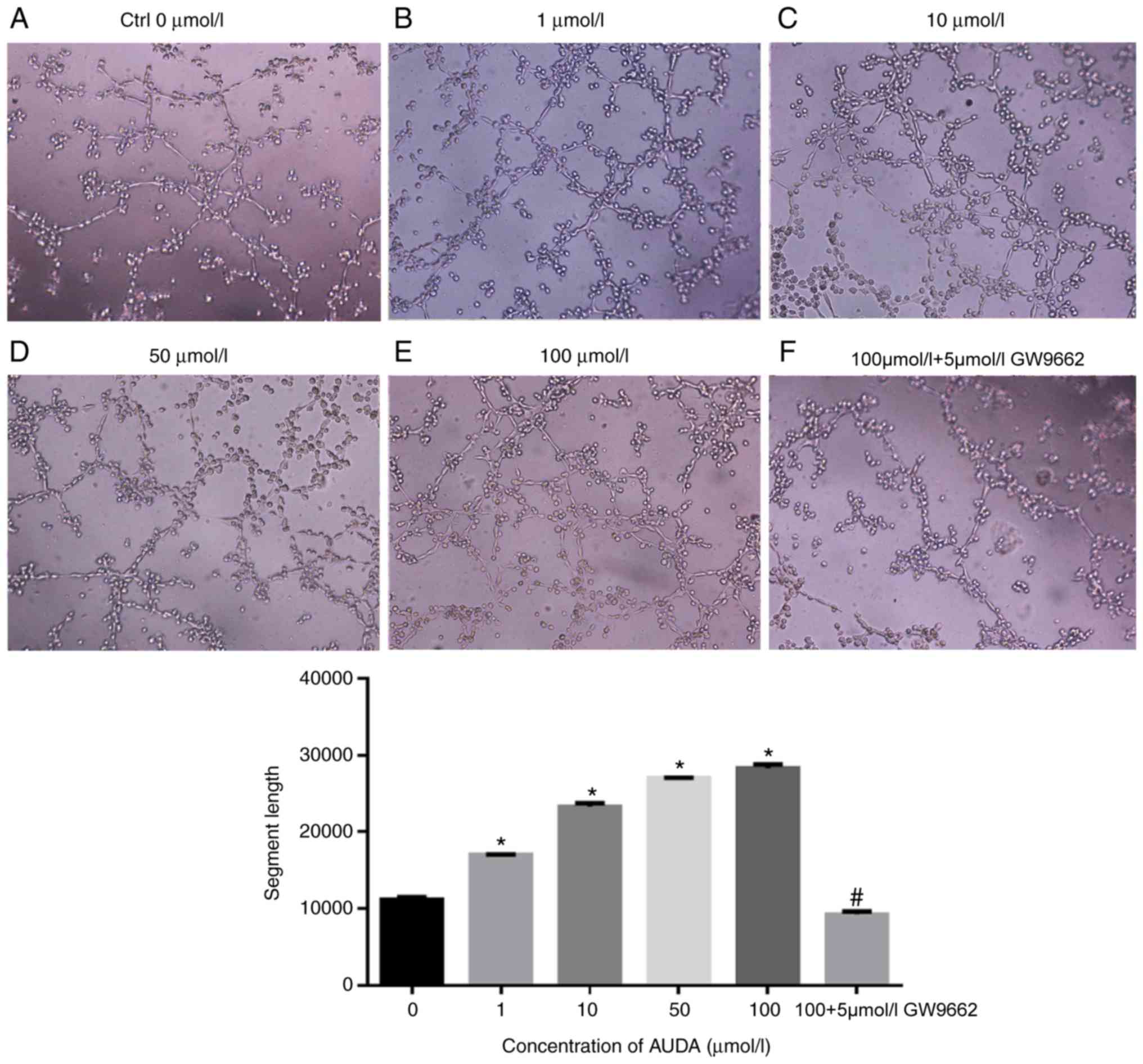
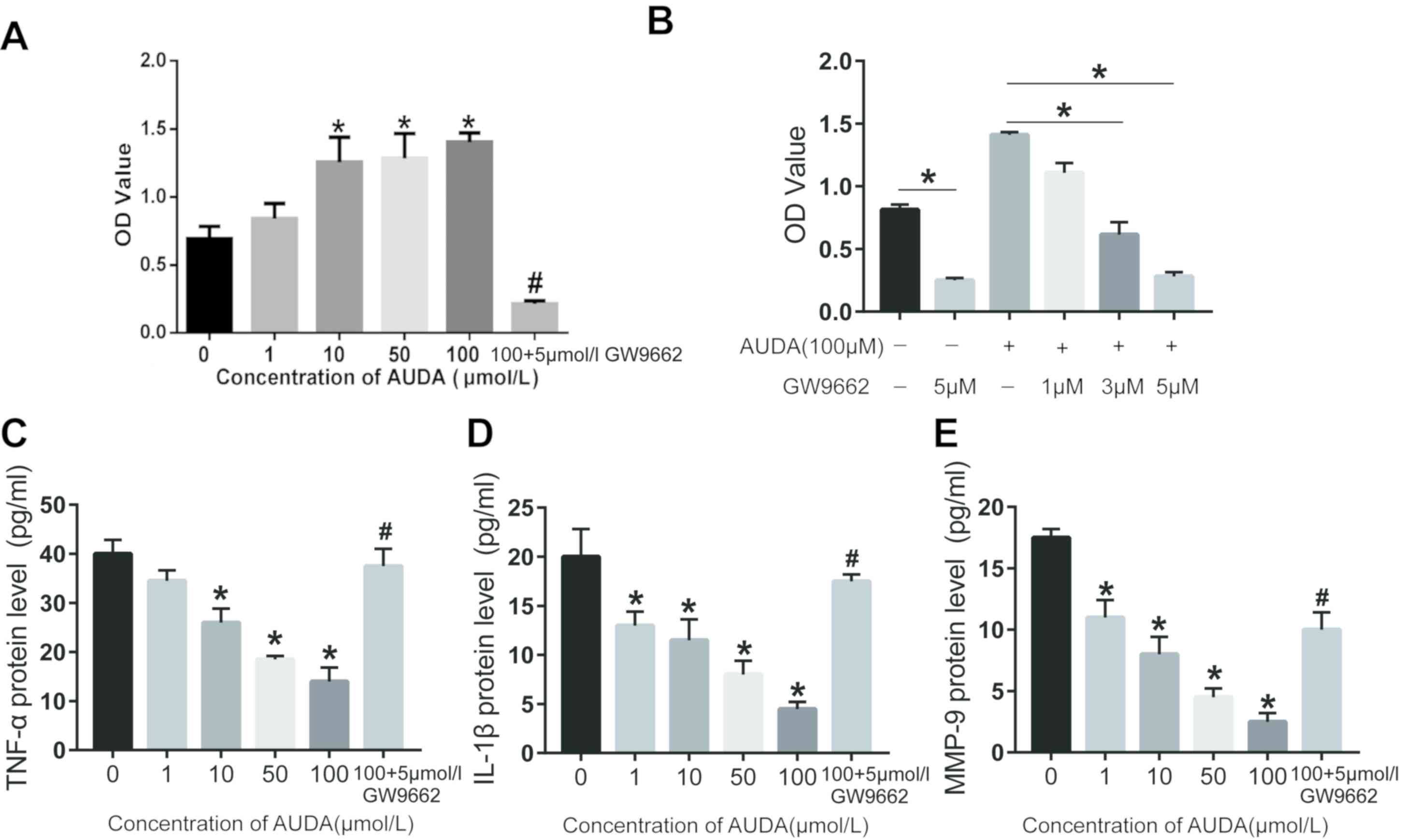
|
1
|
Greco A, De Virgilio A, Rizzo MI,
Tombolini M, Gallo A, Fusconi M, Ruoppolo G, Pagliuca G,
Martellucci S and de Vincentiis M: Kawasaki disease: An evolving
paradigm. Autoimmun Rev. 14:703–709. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fimbres AM and Shulman ST: Kawasaki
disease. Pediatr Rev. 29:308–316. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
McCrindle BW, Rowley AH, Newburger JW,
Burns JC, Bolger AF, Gewitz M, Baker AL, Jackson MA, Takahashi M,
Shah PB, et al: Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of
kawasaki disease: A scientific statement for health professionals
from the american heart association. Circulation. 135:e927–e999.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kato H, Sugimura T, Akagi T, Sato N,
Hashino K, Maeno Y, Kazue T, Eto G and Yamakawa R: Long-term
consequences of Kawasaki disease. A 10-to 21-year follow-up study
of 594 patients. Circulation. 94:1379–1385. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Burns JC, Shike H, Gordon JB, Malhotra A,
Schoenwetter M and Kawasaki T: Sequelae of Kawasaki disease in
adolescents and young adults. J Am Coll Cardiol. 28:253–257. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rowley AH, Baker SC, Orenstein JM and
Shulman ST: Searching for the cause of Kawasaki disease-cytoplasmic
inclusion bodies provide new insight. Nat Rev Microbiol. 6:394–401.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rowley AH, Baker SC, Shulman ST, Garcia
FL, Fox LM, Kos IM, Crawford SE, Russo PA, Hammadeh R, Takahashi K
and Orenstein JM: RNA-containing cytoplasmic inclusion bodies in
ciliated bronchial epithelium months to years after acute Kawasaki
disease. PLoS One. 3:e15822008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rowley AH, Shulman ST, Garcia FL,
Guzman-Cottrill JA, Miura M, Lee HL and Baker SC: Cloning the
arterial IgA antibody response during acute Kawasaki disease. J
Immunol. 175:8386–8391. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Newburger JW, Takahashi M, Beiser AS,
Burns JC, Bastian J, Chung KJ, Colan SD, Duffy CE, Fulton DR, Glode
MP, et al: A single intravenous infusion of gamma globulin as
compared with four infusions in the treatment of acute Kawasaki
syndrome. N Engl J Med. 324:1633–1639. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ingraham RH, Gless RD and Lo HY: Soluble
epoxide hydrolase inhibitors and their potential for treatment of
multiple pathologic conditions. Curr Med Chem. 18:587–603. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Simpkins AN, Rudic RD, Roy S, Tsai HJ,
Hammock BD and Imig JD: Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibition
modulates vascular remodeling. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
298:H795–H806. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang LN, Vincelette J, Cheng Y, Mehra U,
Chen D, Anandan SK, Gless R, Webb HK and Wang YX: Inhibition of
soluble epoxide hydrolase attenuated atherosclerosis, abdominal
aortic aneurysm formation, and dyslipidemia. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 29:1265–1270. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Spector AA, Fang X, Snyder GD and
Weintraub NL: Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs): Metabolism and
biochemical function. Prog Lipid Res. 43:55–90. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zeldin DC, Kobayashi J, Falck JR, Winder
BS, Hammock BD, Snapper JR and Capdevila JH: Regio- and
enantiofacial selectivity of epoxyeicosatrienoic acid hydration by
cytosolic epoxide hydrolase. J Biol Chem. 268:6402–6407.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Spector AA and Norris AW: Action of
epoxyeicosatrienoic acids on cellular function. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 292:C996–C1012. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Newman JW, Morisseau C and Hammock BD:
Epoxide hydrolases: Their roles and interactions with lipid
metabolism. Prog Lipid Res. 44:1–51. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Miller AW, Dimitropoulou C, Han G, White
RE, Busija DW and Carrier GO: Epoxyeicosatrienoic acid-induced
relaxation is impaired in insulin resistance. Am J Physiol Heart
Circ Physiol. 281:H1524–H1531. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bellien J, Joannides R, Richard V and
Thuillez C: Modulation of cytochrome-derived epoxyeicosatrienoic
acids pathway: A promising pharmacological approach to prevent
endothelial dysfunction in cardiovascular diseases? Pharmacol Ther.
131:1–17. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chiamvimonvat N, Ho CM, Tsai HJ and
Hammock BD: The soluble epoxide hydrolase as a pharmaceutical
target for hypertension. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 50:225–237. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Oguro A, Fujita N and Imaoka S: Regulation
of soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) in mice with diabetes: High
glucose suppresses sEH expression. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet.
24:438–445. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chaudhary KR, Abukhashim M, Hwang SH,
Hammock BD and Seubert JM: Inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase
by trans-4-[4-(3-adamantan-1-yl-ureido)-cyclohexyloxy]-benzoic acid
is protective against ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Cardiovasc
Pharmacol. 55:67–73. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Qiu H, Li N, Liu JY, Harris TR, Hammock BD
and Chiamvimonvat N: Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitors and heart
failure. Cardiovasc Ther. 29:99–111. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xu D, Li N, He Y, Timofeyev V, Lu L, Tsai
HJ, Kim IH, Tuteja D, Mateo RK, Singapuri A, et al: Prevention and
reversal of cardiac hypertrophy by soluble epoxide hydrolase
inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:18733–18738. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Imig JD and Hammock BD: Soluble epoxide
hydrolase as a therapeutic target for cardiovascular diseases. Nat
Rev Drug Discov. 8:794–805. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lehman TJ, Walker SM, Mahnovski V and
McCurdy D: Coronary arteritis in mice following the systemic
injection of group B Lactobacillus casei cell walls in
aqueous suspension. Arthritis Rheum. 28:652–659. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Noguchi S, Saito J, Kudo T, Hashiba E and
Hirota K: Safety and efficacy of plasma exchange therapy for
Kawasaki disease in children in intensive care unit: Case series.
JA Clin Rep. 4:252018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lee Y, Schulte DJ, Shimada K, Chen S,
Crother TR, Chiba N, Fishbein MC, Lehman TJ and Arditi M:
Interleukin-1β is crucial for the induction of coronary artery
inflammation in a mouse model of Kawasaki disease. Circulation.
125:1542–1550. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Node K, Huo Y, Ruan X, Yang B, Spiecker M,
Ley K, Zeldin DC and Liao JK: Anti-inflammatory properties of
cytochrome P450 epoxygenase-derived eicosanoids. Science.
285:1276–1279. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cai Z, Zhao G, Yan J, Liu W, Feng W, Ma B,
Yang L, Wang JA, Tu L and Wang DW: CYP2J2 overexpression increases
EETs and protects against angiotensin II-induced abdominal aortic
aneurysm in mice. J Lipid Res. 54:1448–1456. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhao G, Tu L, Li X, Yang S, Chen C, Xu X,
Wang P and Wang DW: Delivery of AAV2-CYP2J2 protects remnant kidney
in the 5/6-nephrectomized rat via inhibition of apoptosis and
fibrosis. Hum Gene Ther. 23:688–699. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhao G, Wang J, Xu X, Jing Y, Tu L, Li X,
Chen C, Cianflone K, Wang P, Dackor RT, et al: Epoxyeicosatrienoic
acids protect rat hearts against tumor necrosis factor-α-induced
injury. J Lipid Res. 53:456–466. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen W, Yang S, Ping W, Fu X, Xu Q and
Wang J: CYP2J2 and EETs protect against lung ischemia/reperfusion
injury via anti-inflammatory effects in vivo and in vitro. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 35:2043–2054. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Spector AA: Arachidonic acid cytochrome
P450 epoxygenase pathway. J Lipid Res. 50 (Suppl):S52–S56. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Larsen BT, Gutterman DD and Hatoum OA:
Emerging role of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids in coronary vascular
function. Eur J Clin Invest. 36:293–300. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Gao F, Si F, Feng S, Yi Q and Liu R:
Resistin enhances inflammatory cytokine production in coronary
artery tissues by activating the NF-κB signaling. Biomed Res Int.
2016:32964372016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hui-Yuen JS, Duong TT and Yeung RS:
TNF-alpha is necessary for induction of coronary artery
inflammation and aneurysm formation in an animal model of Kawasaki
disease. J Immunol. 176:6294–6301. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lau AC, Duong TT, Ito S and Yeung RS:
Matrix metalloproteinase 9 activity leads to elastin breakdown in
an animal model of Kawasaki disease. Arthritis Rheum. 58:854–863.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lau AC, Duong TT, Ito S, Wilson GJ and
Yeung RS: Inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-9 activity
improves coronary outcome in an animal model of Kawasaki disease.
Clin Exp Immunol. 157:300–309. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Maury CP, Salo E and Pelkonen P:
Circulating interleukin-1 beta in patients with Kawasaki disease. N
Engl J Med. 319:1670–1671. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Michaelis UR, Fisslthaler B,
Barbosa-Sicard E, Falck JR, Fleming I and Busse R: Cytochrome P450
epoxygenases 2C8 and 2C9 are implicated in hypoxia-induced
endothelial cell migration and angiogenesis. J Cell Sci.
118:5489–5498. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Cheranov SY, Karpurapu M, Wang D, Zhang B,
Venema RC and Rao GN: An essential role for SRC-activated STAT-3 in
14,15-EET-induced VEGF expression and angiogenesis. Blood.
111:5581–5591. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Potente M, Michaelis UR, Fisslthaler B,
Busse R and Fleming I: Cytochrome P450 2C9-induced endothelial cell
proliferation involves induction of mitogen-activated protein (MAP)
kinase phosphatase-1, inhibition of the c-Jun N-terminal kinase,
and up-regulation of cyclin D1. J Biol Chem. 277:15671–15676. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kireeva ML, Mo FE, Yang GP and Lau LF:
Cyr61, a product of a growth factor-inducible immediate-early gene,
promotes cell proliferation, migration, and adhesion. Mol Cell
Biol. 16:1326–1334. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Deng Y, Theken KN and Lee CR: Cytochrome
P450 epoxygenases, soluble epoxide hydrolase, and the regulation of
cardiovascular inflammation. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 48:331–341. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Delerive P, Fruchart JC and Staels B:
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors in inflammation
control. J Endocrinol. 169:453–459. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Liu Y, Zhang Y, Schmelzer K, Lee TS, Fang
X, Zhu Y, Spector AA, Gill S, Morisseau C, Hammock BD and Shyy JY:
The antiinflammatory effect of laminar flow: The role of PPARgamma,
epoxyeicosatrienoic acids, and soluble epoxide hydrolase. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 102:16747–16752. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|