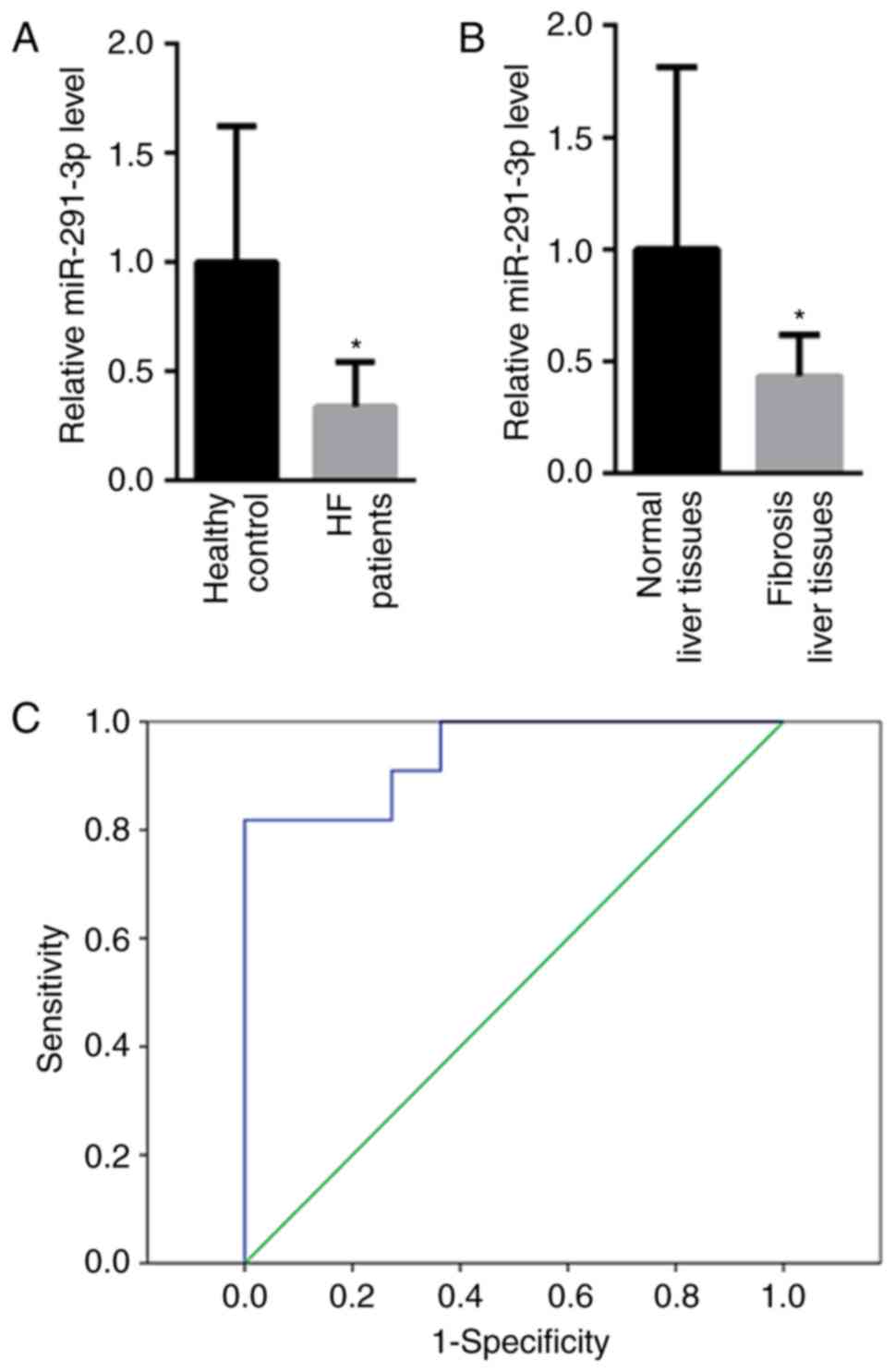
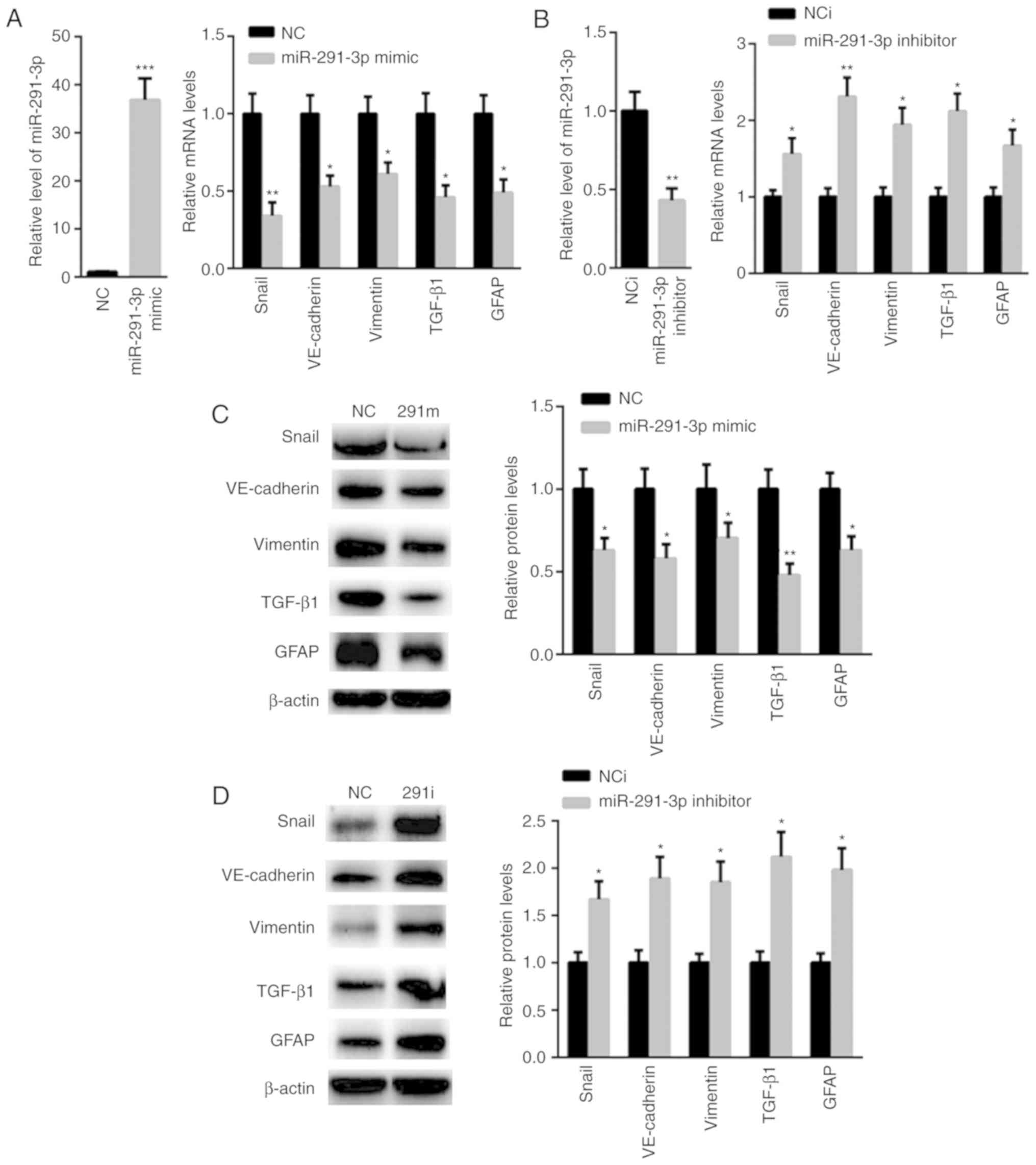
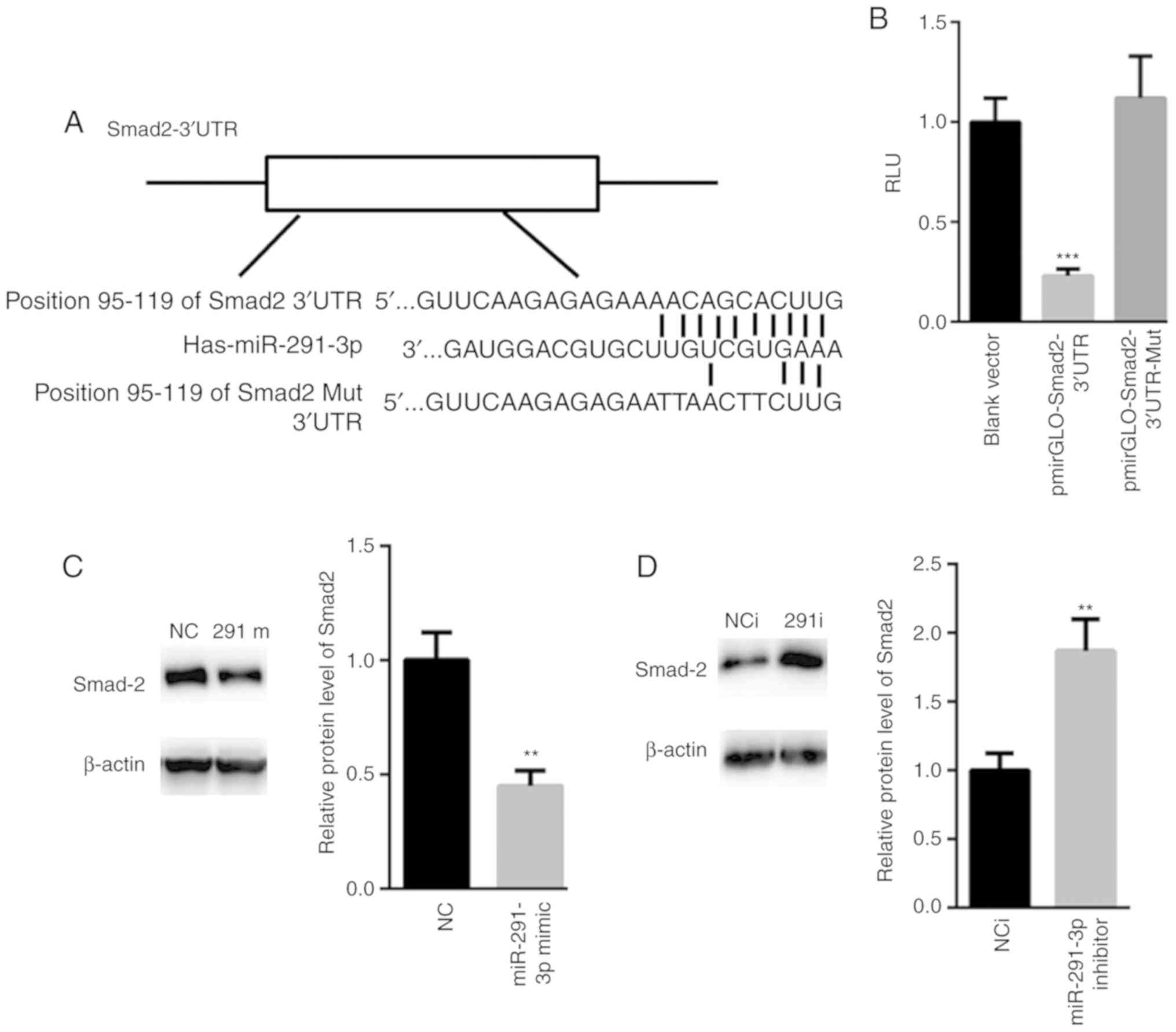
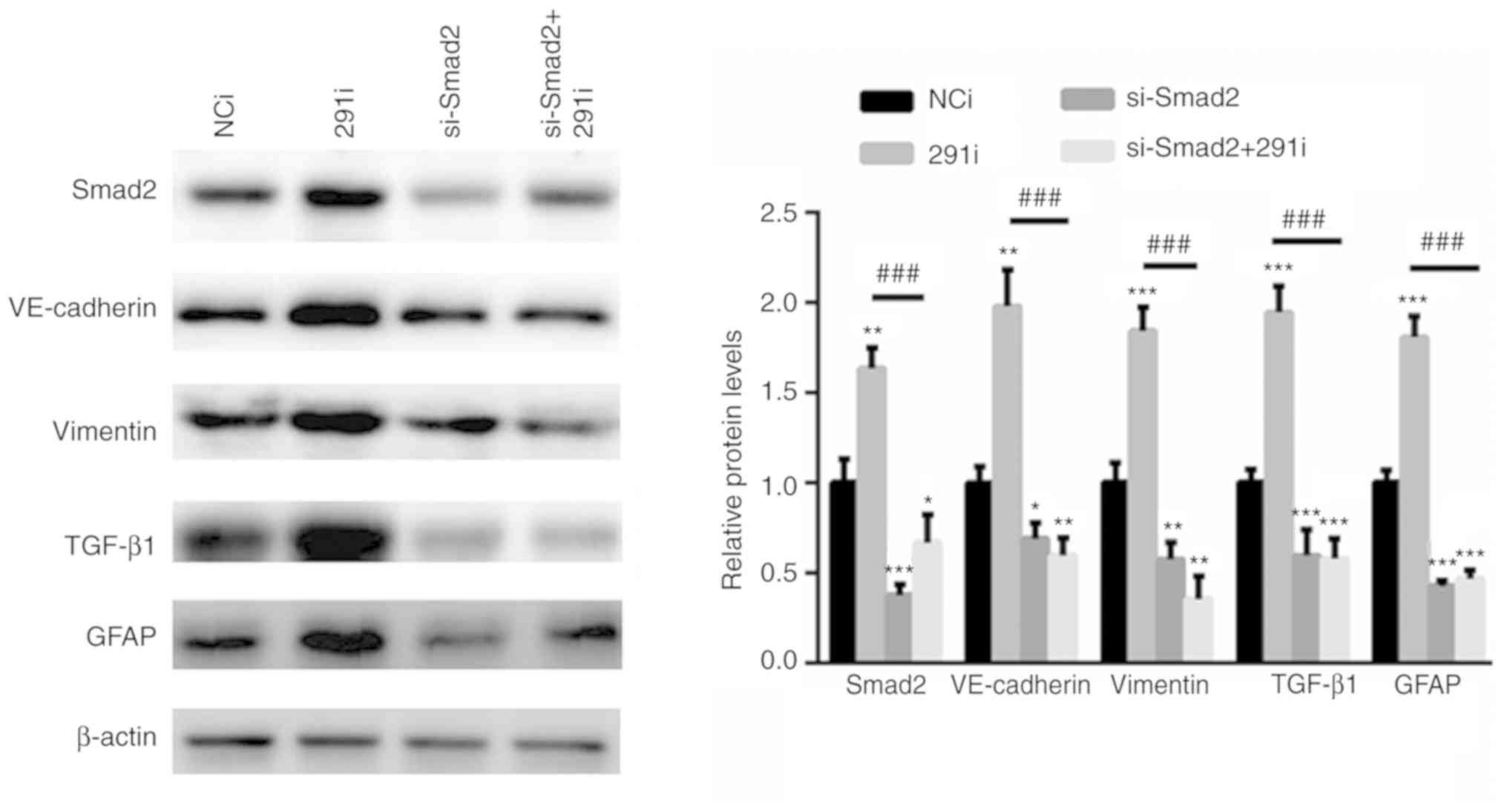
|
1
|
Xu B, Zhou NM, Cao WT and Li XJ:
Evaluation of elastography combined with serological indexes for
hepatic fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B. World J
Gastroenterol. 24:4272–4280. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cargnoni A, Farigu S, Cotti Piccinelli E,
Bonassi Signoroni P, Romele P, Vanosi G, Toschi I, Cesari V, Barros
Sant'Anna L, Magatti M, et al: Effect of human amniotic epithelial
cells on pro-fibrogenic resident hepatic cells in a rat model of
liver fibrosis. J Cell Mol Med. 22:1202–1213. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen J, Li X, Hu Y, Liu W, Zhou Q, Zhang
H, Mu Y and Liu P: Gypenosides ameliorate carbon
tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis by inhibiting the
differentiation of hepatic progenitor cells into myofibroblasts. Am
J Chin Med. 45:1061–1074. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen J, Yu Y, Li S, Liu Y, Zhou S, Cao S,
Yin J and Li G: MicroRNA-30a ameliorates hepatic fibrosis by
inhibiting Beclin1-mediated autophagy. J Cell Mol Med.
21:3679–3692. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wells RG: The epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition in liver fibrosis: Here today, gone tomorrow?
Hepatology. 51:737–740. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fabris L, Brivio S, Cadamuro M and
Strazzabosco M: Revisiting epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in
liver fibrosis: Clues for a better understanding of the ‘reactive’
biliary epithelial phenotype. Stem Cells Int. 2016:29537272016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lim YS, Kim KA, Jung JO, Yoon JH, Suh KS,
Kim CY and Lee HS: Modulation of cytokeratin expression during in
vitro cultivation of human hepatic stellate cells: Evidence of
transdifferentiation from epithelial to mesenchymal phenotype.
Histochem Cell Biol. 118:127–136. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lim YS, Lee HC and Lee HS: Switch of
cadherin expression from E- to N-type during the activation of rat
hepatic stellate cells. Histochem Cell Biol. 127:149–160. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ding YF, Wu ZH, Wei YJ, Shu L and Peng YR:
Hepatic inflammation-fibrosis-cancer axis in the rat hepatocellular
carcinoma induced by diethylnitrosamine. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
143:821–834. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
El-Mezayen NS, El-Hadidy WF, El-Refaie WM,
Shalaby TI, Khattab MM and El-Khatib AS: Hepatic stellate
cell-targeted imatinib nanomedicine versus conventional imatinib: A
novel strategy with potent efficacy in experimental liver fibrosis.
J Control Release. 266:226–237. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shi J, Zhao J, Zhang X, Cheng Y, Hu J, Li
Y, Zhao X, Shang Q, Sun Y, Tu B, et al: Activated hepatic stellate
cells impair NK cell anti-fibrosis capacity through a
TGF-β-dependent emperipolesis in HBV cirrhotic patients. Sci Rep.
7:445442017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tang LY, Heller M, Meng Z, Yu LR, Tang Y,
Zhou M and Zhang YE: Transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) directly
activates the JAK1-STAT3 axis to induce hepatic fibrosis in
coordination with the SMAD pathway. J Biol Chem. 292:4302–4312.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang JJ, Tao H, Liu LP, Hu W, Deng ZY and
Li J: miR-200a controls hepatic stellate cell activation and
fibrosis via SIRT1/Notch1 signal pathway. Inflamm Res. 66:341–352.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhou G, Lin W, Fang P, Lin X, Zhuge L, Hu
Z and Jin L: MiR-10a improves hepatic fibrosis by regulating the
TGFβl/Smads signal transduction pathway. Exp Ther Med.
12:1719–1722. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang Y, Du J, Niu X, Fu N, Wang R, Zhang
Y, Zhao S, Sun D and Nan Y: MiR-130a-3p attenuates activation and
induces apoptosis of hepatic stellate cells in nonalcoholic
fibrosing steatohepatitis by directly targeting TGFBR1 and TGFBR2.
Cell Death Dis. 8:e27922017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yu F, Chen B, Fan X, Li G, Dong P and
Zheng J: Epigenetically-regulated microRNA-9-5p suppresses the
activation of hepatic stellate cells via TGFBR1 and TGFBR2. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 43:2242–2252. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Long J, Menggen Q, Wuren Q, Shi Q and Pi
X: MiR-219-5p inhibits the growth and metastasis of malignant
melanoma by targeting BCL-2. Biomed Res Int. 2017:90325022017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang Q, Zhu L, Jiang Y, Xu J, Wang F and
He Z: miR-219-5p suppresses the proliferation and invasion of
colorectal cancer cells by targeting calcyphosin. Oncol Lett.
13:1319–1324. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Guo J, Li M, Meng X, Sui J, Dou L, Tang W,
Huang X, Man Y, Wang S and Li J: MiR-291b-3p induces apoptosis in
liver cell line NCTC1469 by reducing the level of RNA-binding
protein HuR. Cell Physiol Biochem. 33:810–822. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Meng X, Guo J, Fang W, Dou L, Li M, Huang
X, Zhou S, Man Y, Tang W, Yu L and Li J: Liver microRNA-291b-3p
promotes hepatic lipogenesis through negative regulation of
adenosine 5′-monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase α1. J
Biol Chem. 291:10625–10634. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Guo J, Dou L, Meng X, Chen Z, Yang W, Fang
W, Yang C, Huang X, Tang W, Yang J and Li J: Hepatic MiR-291b-3p
mediated glucose metabolism by directly targeting p65 to upregulate
PTEN expression. Sci Rep. 7:398992017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Weiskirchen R and Gressner AM: Isolation
and culture of hepatic stellate cells. Methods Mol Med. 117:99–113.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Carotti S, Morini S, Corradini SG, Burza
MA, Molinaro A, Carpino G, Merli M, De Santis A, Muda AO, Rossi M,
et al: Glial fibrillary acidic protein as an early marker of
hepatic stellate cell activation in chronic and posttransplant
recurrent hepatitis C. Liver Transpl. 14:806–814. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bai X, Saab AS, Huang W, Hoberg IK,
Kirchhoff F and Scheller A: Genetic background affects human glial
fibrillary acidic protein promoter activity. PLoS One.
8:e668732013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Romão LF, Sousa Vde O, Neto VM and Gomes
FC: Glutamate activates GFAP gene promoter from cultured astrocytes
through TGF-beta1 pathways. J Neurochem. 106:746–756. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zheng JY, Sun J, Ji CM, Shen L, Chen ZJ,
Xie P, Sun YZ and Yu RT: Selective deletion of apolipoprotein E in
astrocytes ameliorates the spatial learning and memory deficits in
Alzheimer's disease (APP/PS1) mice by inhibiting TGF-β/Smad2/STAT3
signaling. Neurobiol Aging. 54:112–132. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hassan S, Syed S and Kehar SI: Glial
fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) as a mesenchymal marker of early
hepatic stellate cells activation in liver fibrosis in chronic
hepatitis C infection. Pak J Med Sci. 30:1027–1032. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hu Z, Qin F, Gao S, Zhen Y, Huang D and
Dong L: Paeoniflorin exerts protective effect on radiation-induced
hepatic fibrosis in rats via TGF-β1/Smads signaling pathway. Am J
Transl Res. 10:1012–1021. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jiang Y, Wang C, Li YY, Wang XC, An JD,
Wang YJ and Wang XJ: Mistletoe alkaloid fractions alleviates carbon
tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis through inhibition of hepatic
stellate cell activation via TGF-β/Smad interference. J
Ethnopharmacol 158 Pt A. 230–238. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Wang J, Chu ES, Chen HY, Man K, Go MY,
Huang XR, Lan HY, Sung JJ and Yu J: microRNA-29b prevents liver
fibrosis by attenuating hepatic stellate cell activation and
inducing apoptosis through targeting PI3K/AKT pathway. Oncotarget.
6:7325–7338. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lamb CL, Cholico GN, Pu X, Hagler GD,
Cornell KA and Mitchell KA: 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin
(TCDD) increases necroinflammation and hepatic stellate cell
activation but does not exacerbate experimental liver fibrosis in
mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 311:42–51. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu YW, Chiu YT, Fu SL and Huang YT:
Osthole ameliorates hepatic fibrosis and inhibits hepatic stellate
cell activation. J Biomed Sci. 22:632015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nunez Lopez O, Bohanon FJ, Wang X, Ye N,
Corsello T, Rojas-Khalil Y, Chen H, Chen H, Zhou J and
Radhakrishnan RS: STAT3 inhibition suppresses hepatic stellate cell
fibrogenesis: HJC0123, a potential therapeutic agent for liver
fibrosis. RSC Adv. 6:100652–100663. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Perumal N, Perumal M, Halagowder D and
Sivasithamparam N: Morin attenuates diethylnitrosamine-induced rat
liver fibrosis and hepatic stellate cell activation by co-ordinated
regulation of Hippo/Yap and TGF-β1/Smad signaling. Biochimie.
140:10–19. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang Z, Zha Y, Hu W, Huang Z, Gao Z, Zang
Y, Chen J, Dong L and Zhang J: The autoregulatory feedback loop of
microRNA-21/programmed cell death protein 4/activation protein-1
(MiR-21/PDCD4/AP-1) as a driving force for hepatic fibrosis
development. J Biol Chem. 288:37082–37093. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhou L, Liu S, Han M, Ma Y, Feng S, Zhao
J, Lu H, Yuan X and Cheng J: miR-185 inhibits fibrogenic activation
of hepatic stellate cells and prevents liver fibrosis. Mol Ther
Nucleic Acids. 10:91–102. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Roderburg C, Luedde M, Vargas Cardenas D,
Vucur M, Mollnow T, Zimmermann HW, Koch A, Hellerbrand C,
Weiskirchen R, Frey N, et al: miR-133a mediates TGF-β-dependent
derepression of collagen synthesis in hepatic stellate cells during
liver fibrosis. J Hepatol. 58:736–742. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Xiao YH, Liu DW and Li Q: Effects of drug
serum of anti-fibrosis I herbal compound on calcium in hepatic
stellate cell and its molecular mechanism. World J Gastroenterol.
11:1515–1520. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liu LX, Zhang HY, Zhang QQ and Guo XH:
Effects of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-related
protein 1 in mice with hepatic fibrosis induced by thioacetamide.
Chin Med J (Engl). 123:2521–2526. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zakaria S, Youssef M, Moussa M, Akl M,
El-Ahwany E, El-Raziky M, Mostafa O, Helmy AH and El-Hindawi A:
Value of α-smooth muscle actin and glial fibrillary acidic protein
in predicting early hepatic fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C virus
infection. Arch Med Sci. 6:356–365. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Castera L: Invasive and non-invasive
methods for the assessment of fibrosis and disease progression in
chronic liver disease. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol.
25:291–303. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Crisan D, Radu C, Lupsor M, Sparchez Z,
Grigorescu MD and Grigorescu M: Two or more synchronous combination
of noninvasive tests to increase accuracy of liver fibrosis
assessement in chronic hepatitis C; results from a cohort of 446
patients. Hepat Mon. 12:177–184. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|