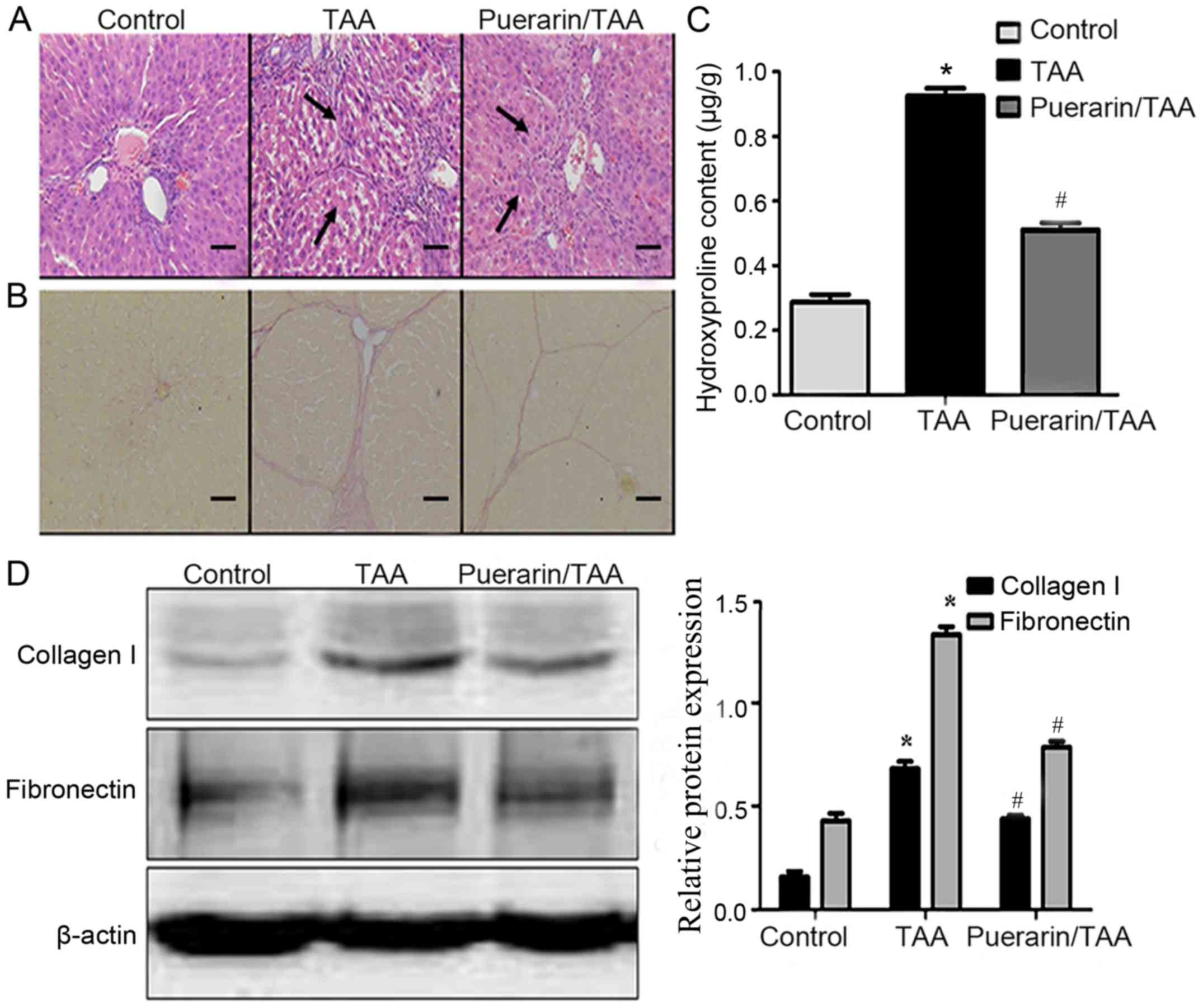
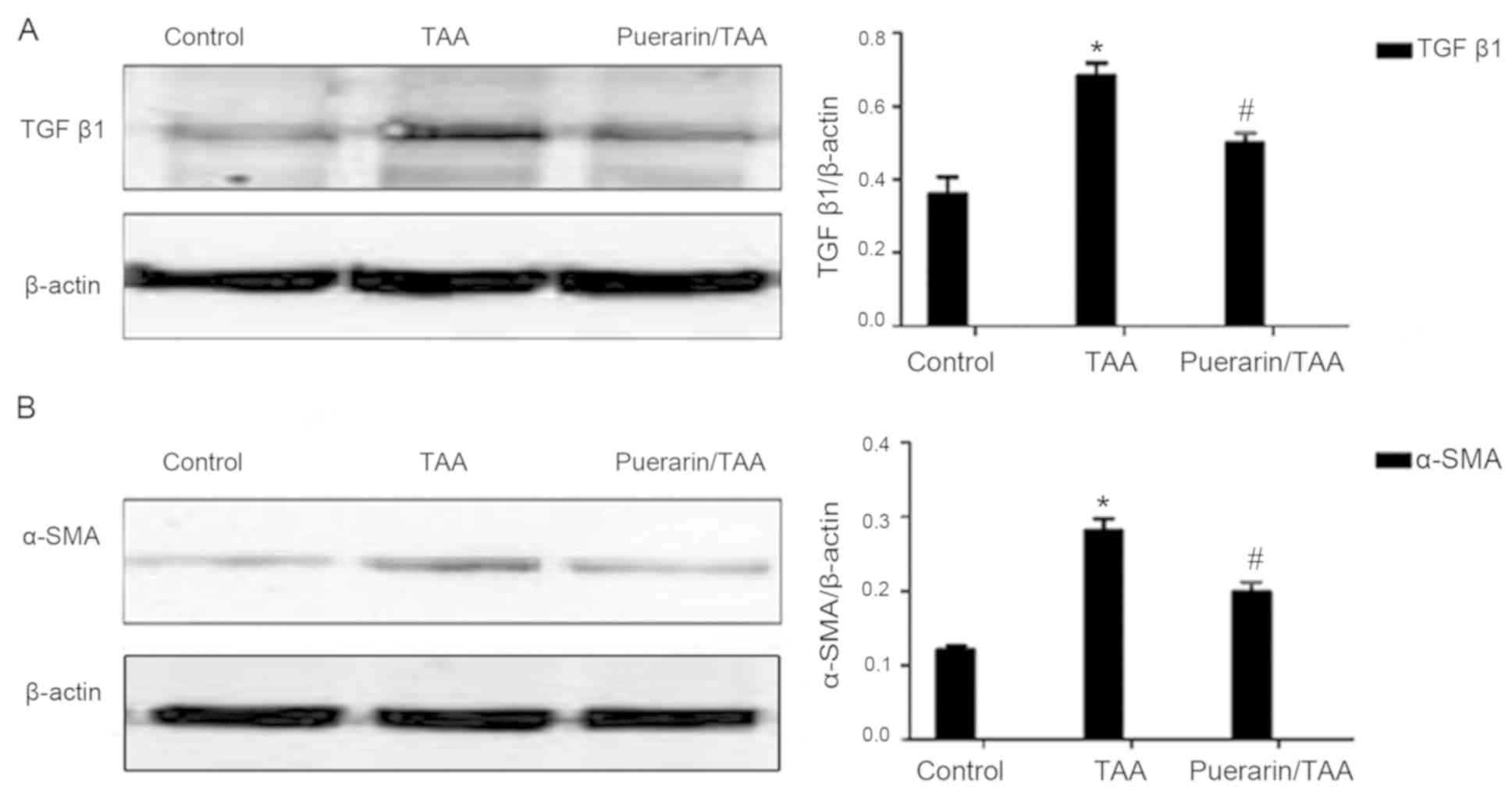
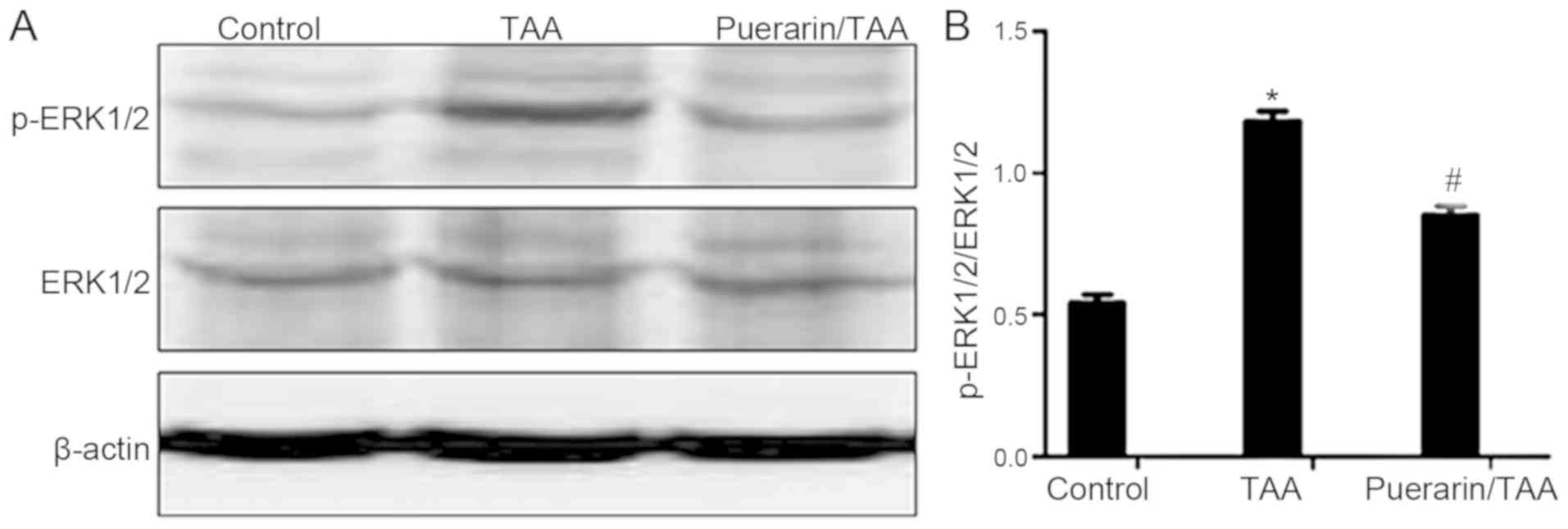
|
1
|
Higashi T, Friedman SL and Hoshida Y:
Hepatic stellate cells as key target in liver fibrosis. Adv Drug
Deliv Rev. 121:27–42. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Qian H, Deng X, Huang ZW, Wei J, Ding CH,
Feng RX, Zeng X, Chen YX, Ding J, Qiu L, et al: An HNF1α-regulated
feedback circuit modulates hepatic fibrogenesis via the crosstalk
between hepatocytes and hepatic stellate cells. Cell Res.
25:930–945. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Palmer DH, Hussain SA and Johnson PJ:
Gene- and immunotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Expert Opin
Biol Ther. 5:507–523. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tao LL, Zhai YZ, Ding D, Yin WH, Liu XP
and Yu GY: The role of C/EBP-α expression in human liver and liver
fibrosis and its relationship with autophagy. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 8:13102–13107. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lewindon PJ, Pereira TN, Hoskins AC,
Bridle KR, Williamson RM, Shepherd RW and Ramm GA: The role of
hepatic stellate cells and transforming growth factor-beta(1) in
cystic fibrosis liver disease. Am J Pathol. 160:1705–1715. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sheppard D: Transforming growth factor
beta: A central modulator of pulmonary and airway inflammation and
fibrosis. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 3:413–417. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fabregat I, Moreno-Càceres J, Sánchez A,
Dooley S, Dewidar B, Giannelli G and Ten Dijke P; IT-LIVER
Consortium, : TGF-β signalling and liver disease. FEBS J.
283:2219–2232. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cai FF, Wu R, Song YN, Xiong AZ, Chen XL,
Yang MD, Yang L, Hu Y, Sun MY and Su SB: Yinchenhao decoction
alleviates liver fibrosis by regulating bile acid metabolism and
TGF-β/Smad/ERK signalling pathway. Sci Rep. 8:153672018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lestari N, Louisa M, Soetikno V, Suwana
AG, Ramadhan PA, Akmal T and Arozal W: Alpha mangostin inhibits the
proliferation and activation of acetaldehyde induced hepatic
stellate cells through TGF-β and ERK 1/2 pathways. J Toxicol.
2018:53604962018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Guo Y, Zhang Y, Zhang Q, Guo X, Zhang H,
Zheng G and Liu L: Insulin-like growth factor binding
protein-related protein 1 (IGFBPrP1) contributes to liver
inflammation and fibrosis via activation of the ERK1/2 pathway.
Hepatol Int. 9:130–141. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Benyon RC and Iredale JP: Is liver
fibrosis reversible? Gut. 46:443–446. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Issa R, Zhou X, Constandinou CM,
Fallowfield J, Millward-Sadler H, Gaca MD, Sands E, Suliman I, Trim
N, Knorr A, et al: Spontaneous recovery from micronodular
cirrhosis: Evidence for incomplete resolution associated with
matrix cross-linking. Gastroenterology. 126:1795–1808. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dienstag JL, Goldin RD, Heathcote EJ, Hann
HW, Woessner M, Stephenson SL, Gardner S, Gray DF and Schiff ER:
Histological outcome during long-term lamivudine therapy.
Gastroenterology. 124:105–117. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bataller R and Brenner DA: Hepatic
stellate cells as a target for the treatment of liver fibrosis.
Semin Liver Dis. 21:437–451. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Iredale JP, Pellicoro A and Fallowfield
JA: Liver fibrosis: Understanding the dynamics of bidirectional
wound repair to inform the design of markers and therapies. Dig
Dis. 35:310–313. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Schuppan D: Liver fibrosis: Common
mechanisms and antifibrotic therapies. Clin Res Hepatol
Gastroenterol. 39 (Suppl 1):S51–S59. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Friedman SL: Mechanisms of hepatic
fibrogenesis. Gastroenterology. 134:1655–1669. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hernandez-Gea V and Friedman SL:
Pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. Annu Rev Pathol. 6:425–456. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lee JH, Jeon YD, Lee YM and Kim DK: The
suppressive effect of puerarin on atopic dermatitis-like skin
lesions through regulation of inflammatory mediators in vitro and
in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 498:707–714. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen X, Yu J and Shi J: Management of
diabetes mellitus with puerarin, a natural isoflavone from pueraria
lobata. Am J Chin Med. 46:1771–1789. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yuan M, Liu G, Zheng X, Li P, Liu J, Wang
S and Cao Y: Effects of puerarin combined with conventional therapy
on ischemic stroke. Exp Ther Med. 14:2943–2946. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhou X, Bai C, Sun X, Gong X, Yang Y, Chen
C, Shan G and Yao Q: Puerarin attenuates renal fibrosis by reducing
oxidative stress induced-epithelial cell apoptosis via MAPK signal
pathways in vivo and in vitro. Ren Fail. 39:423–431. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Guo BQ, Xu JB, Xiao M, Ding M and Duan LJ:
Puerarin reduces ischemia/reperfusion-induced myocardial injury in
diabetic rats via upregulation of vascular endothelial growth
factor A/angiotensin-1 and suppression of apoptosis. Mol Med Rep.
17:7421–7427. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li R, Xu L, Liang T, Li Y, Zhang S and
Duan X: Puerarin mediates hepatoprotection against CCl4-induced
hepatic fibrosis rats through attenuation of inflammation response
and amelioration of metabolic function. Food Chem Toxicol.
52:69–75. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Guo C, Xu L, He Q, Liang T, Duan X and Li
R: Anti-fibrotic effects of puerarin on CCl4-induced hepatic
fibrosis in rats possibly through the regulation of PPAR-γ
expression and inhibition of PI3K/Akt pathway. Food Chem Toxicol.
56:436–442. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xu L, Zheng N, He Q, Li R, Zhang K and
Liang T: Puerarin, isolated from Pueraria lobata (Willd.), protects
against hepatotoxicity via specific inhibition of the TGF-β1/Smad
signaling pathway, thereby leading to anti-fibrotic effect.
Phytomedicine. 20:1172–1179. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Al-Attar AM, Alrobai AA and Almalki DA:
Effect of Olea oleaster and Juniperus procera leaves extracts on
thioacetamide induced hepatic cirrhosis in male albino mice. Saudi
J Biol Sci. 23:363–371. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wickert L, Steinkrüger S, Abiaka M,
Bolkenius U, Purps O, Schnabel C and Gressner AM: Quantitative
monitoring of the mRNA expression pattern of the TGF-beta-isoforms
(beta 1, beta 2, beta 3) during transdifferentiation of hepatic
stellate cells using a newly developed real-time SYBR Green PCR.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 295:330–335. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Carpino G, Morini S, Ginanni Corradini S,
Franchitto A, Merli M, Siciliano M, Gentili F, Onetti Muda A,
Berloco P, Rossi M, et al: Alpha-SMA expression in hepatic stellate
cells and quantitative analysis of hepatic fibrosis in cirrhosis
and in recurrent chronic hepatitis after liver transplantation. Dig
Liver Dis. 37:349–356. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
El-Tanbouly DM, Wadie W and Sayed RH:
Modulation of TGF-β/Smad and ERK signaling pathways mediates the
anti-fibrotic effect of mirtazapine in mice. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 329:224–230. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sánchez-Valle V, Chávez-Tapia NC, Uribe M
and Méndez-Sánchez N: Role of oxidative stress and molecular
changes in liver fibrosis: A review. Curr Med Chem. 19:4850–4860.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mormone E, George J and Nieto N: Molecular
pathogenesis of hepatic fibrosis and current therapeutic
approaches. Chem Biol Interact. 193:225–231. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Elpek GÖ: Cellular and molecular
mechanisms in the pathogenesis of liver fibrosis: An update. World
J Gastroenterol. 20:7260–7276. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Toosi AE: Liver fibrosis: Causes and
methods of assessment, a review. Rom J Intern Med. 53:304–314.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sharma L, Gupta D and Abdullah ST:
Thioacetamide potentiates high cholesterol and high fat diet
induced steato-hepatitic changes in livers of C57BL/6J mice: A
novel eight weeks model of fibrosing NASH. Toxicol Lett. 304:21–29.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Schyman P, Printz RL, Estes SK, Boyd KL,
Shiota M and Wallqvist A: Identification of the toxicity pathways
associated with thioacetamide-induced injuries in rat liver and
kidney. Front Pharmacol. 9:12722018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Amirtharaj GJ, Natarajan SK, Pulimood A,
Balasubramanian KA, Venkatraman A and Ramachandran A: Role of
oxygen free radicals, nitric oxide and mitochondria in mediating
cardiac alterations during liver cirrhosis induced by
thioacetamide. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 17:175–184. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Golbar HM, Izawa T, Wijesundera KK, Bondoc
A, Tennakoon AH, Kuwamura M and Yamate J: Depletion of hepatic
macrophages aggravates liver lesions induced in rats by
thioacetamide (TAA). Toxicol Pathol. 44:246–258. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lakner AM, Moore CC, Gulledge AA and
Schrum LW: Daily genetic profiling indicates JAK/STAT signaling
promotes early hepatic stellate cell transdifferentiation. World J
Gastroenterol. 16:5047–5056. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang S, Shi XL, Feng M, Wang X, Zhang ZH,
Zhao X, Han B, Ma HC, Dai B and Ding YT: Puerarin protects against
CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in mice: Possible role of PARP-1
inhibition. Int Immunopharmacol. 38:238–245. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hou B, Zhao Y, Qiang G, Yang X, Xu C, Chen
X, Liu C, Wang X, Zhang L and Du G: Puerarin mitigates diabetic
hepatic steatosis and fibrosis by inhibiting TGF-β signaling
pathway activation in type 2 diabetic rats. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2018:45453212018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bataller R and Brenner DA: Liver fibrosis.
J Clin Invest. 115:209–218. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chen A: Acetaldehyde stimulates the
activation of latent transforming growth factor-beta1 and induces
expression of the type II receptor of the cytokine in rat cultured
hepatic stellate cells. Biochem J. 368:683–693. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Jin L, Gao H, Wang J, Yang S, Wang J, Liu
J, Yang Y, Yan T, Chen T, Zhao Y and He Y: Role and regulation of
autophagy and apoptosis by nitric oxide in hepatic stellate cells
during acute liver failure. Liver Int. 37:1651–1659. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wu GL, Chen J, Yu GY, Li JP and Lu WW:
Effect of puerarin on levels of TGF-beta1 and alpha-SMA in rats
with alcoholic injury liver. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi.
33:2245–2249. 2008.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wu T, Liu T, Xing L and Ji G: Baicalin and
puerarin reverse epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the
TGF-β1/Smad3 pathway in vitro. Exp Ther Med. 16:1968–1974.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Liu X, Zhao W, Wang W, Lin S and Yang L:
Puerarin suppresses LPS-induced breast cancer cell migration,
invasion and adhesion by blockage NF-κB and Erk pathway. Biomed
Pharmacother. 92:429–436. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|