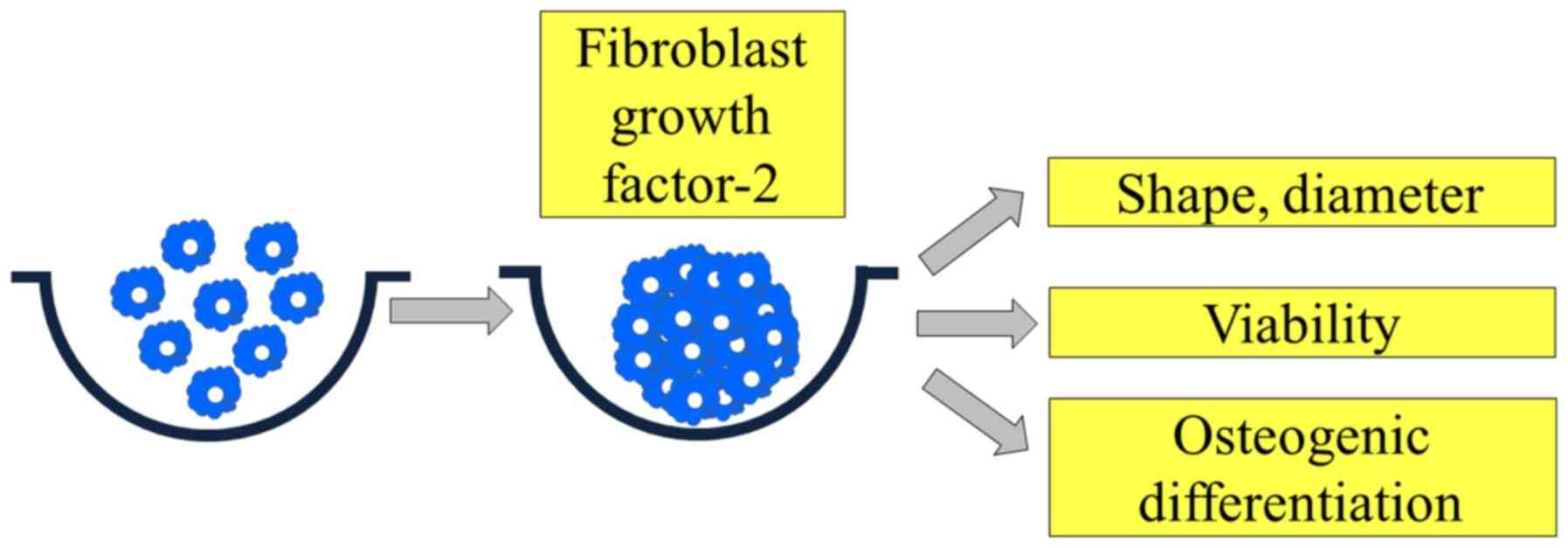
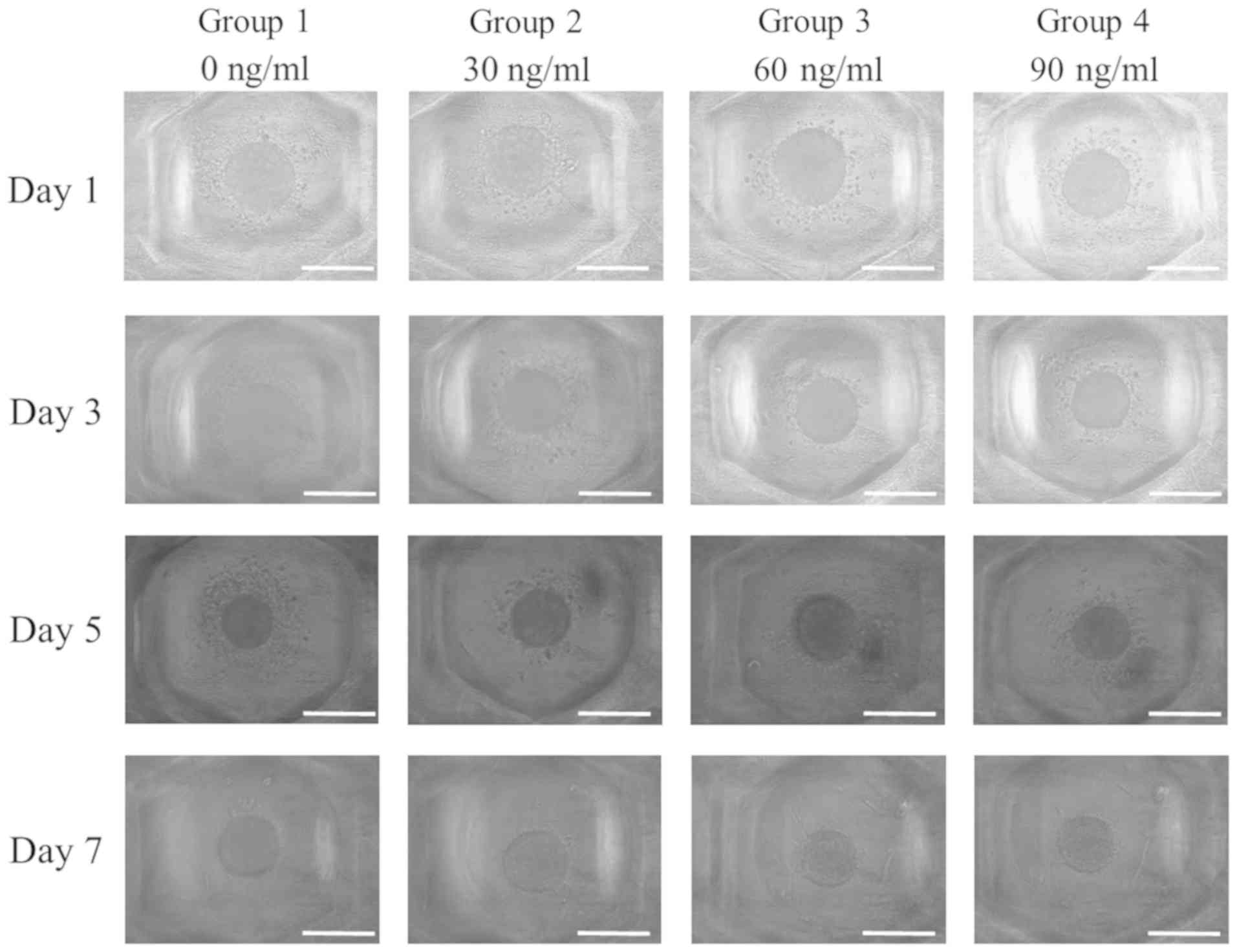
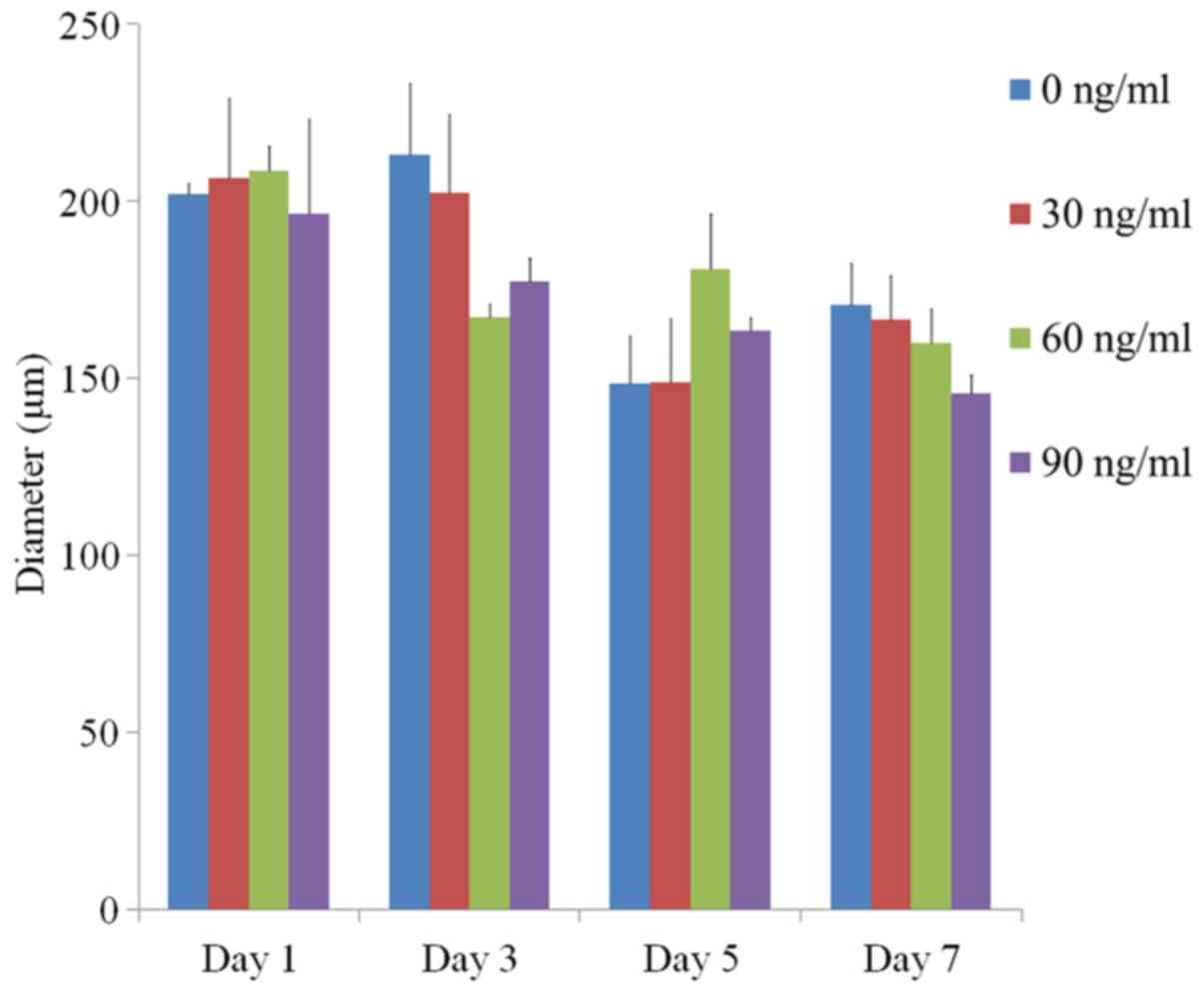
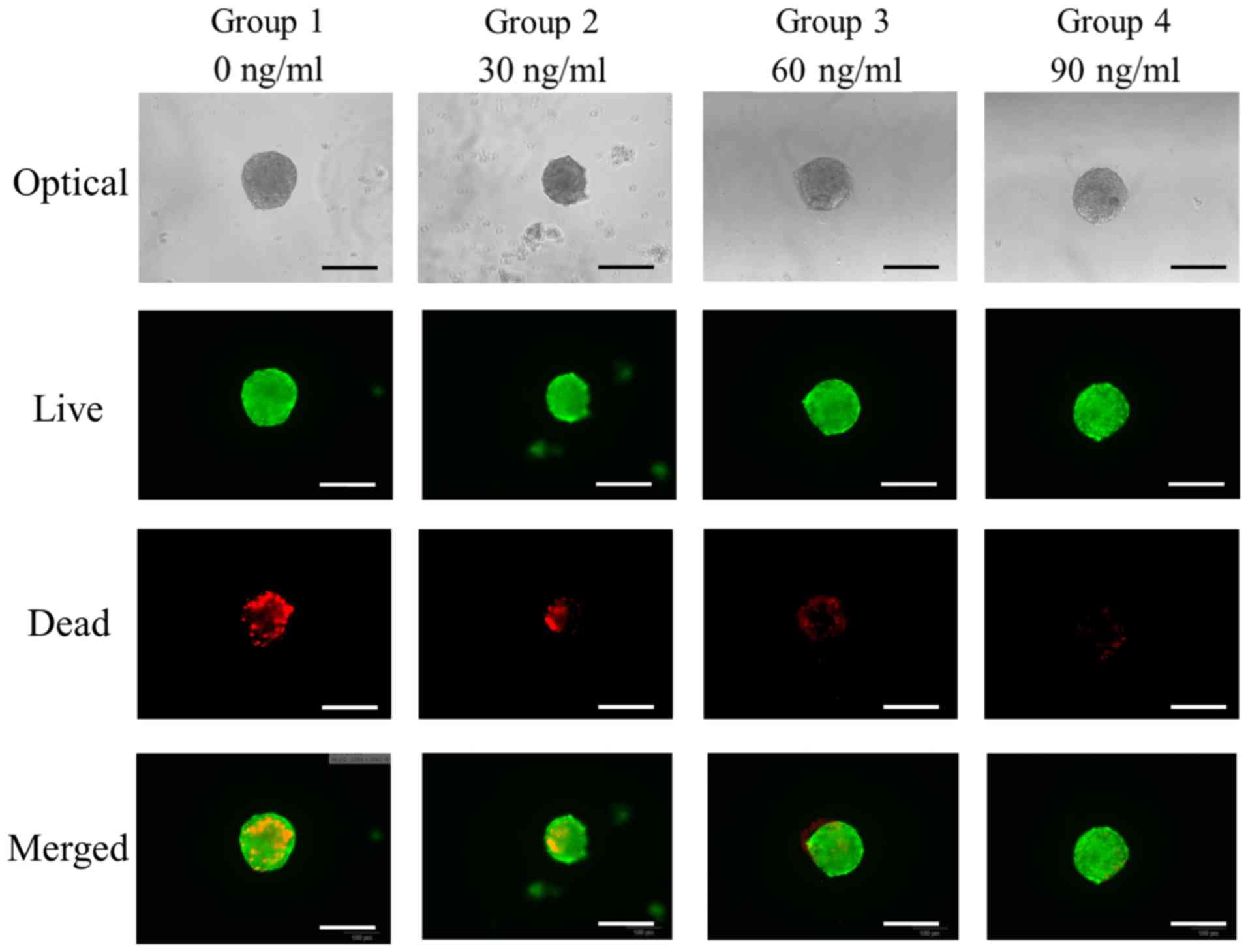
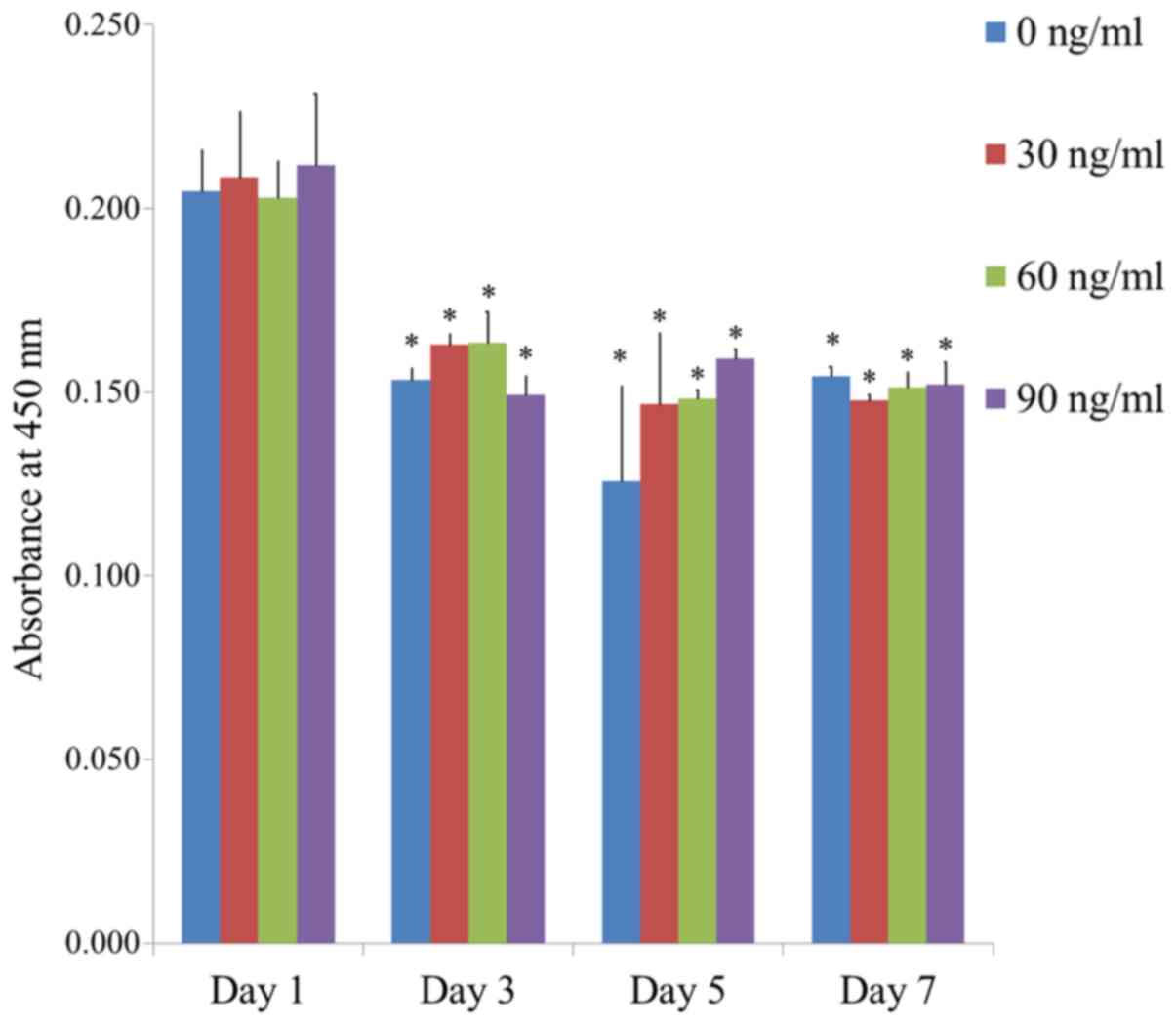
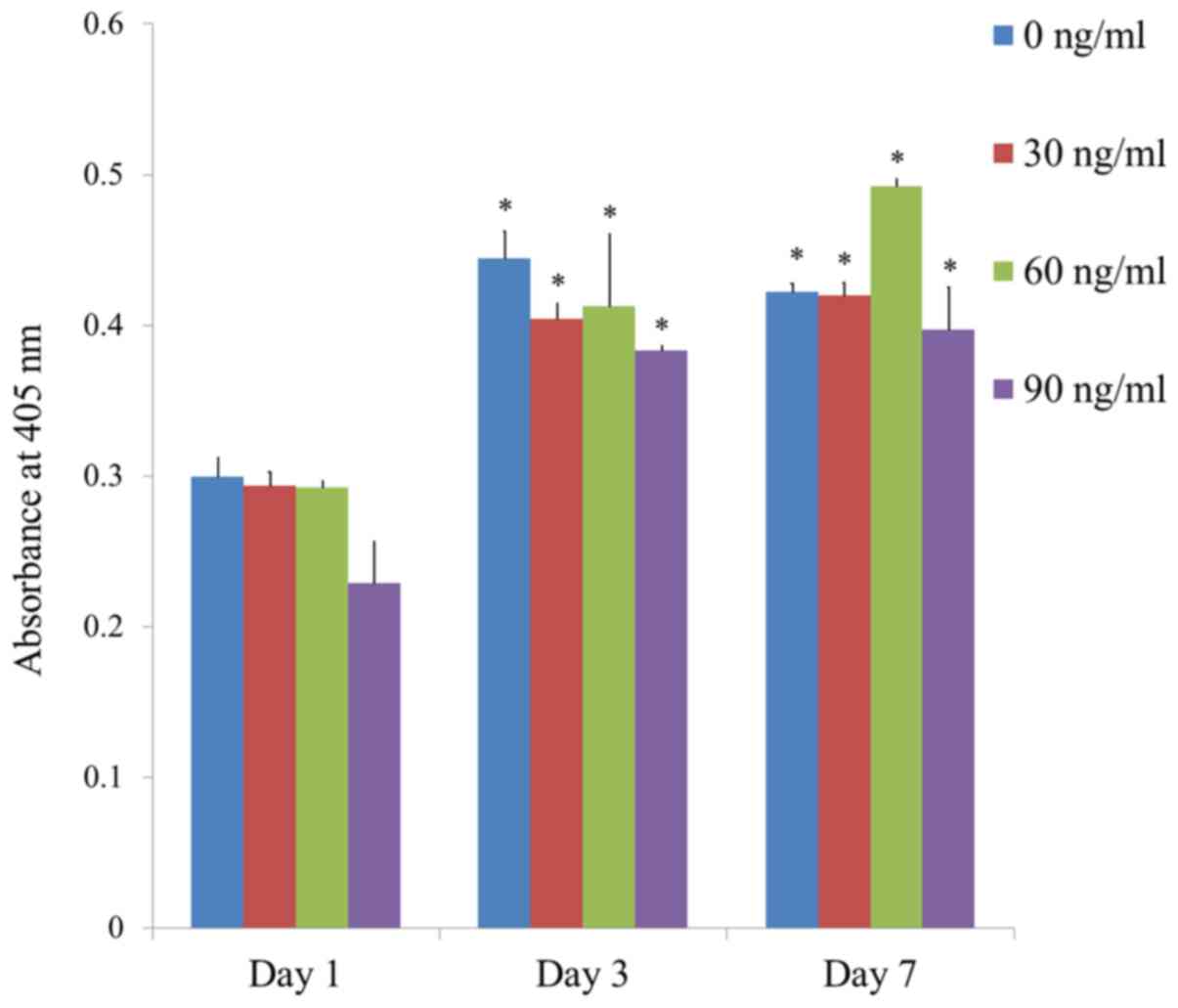
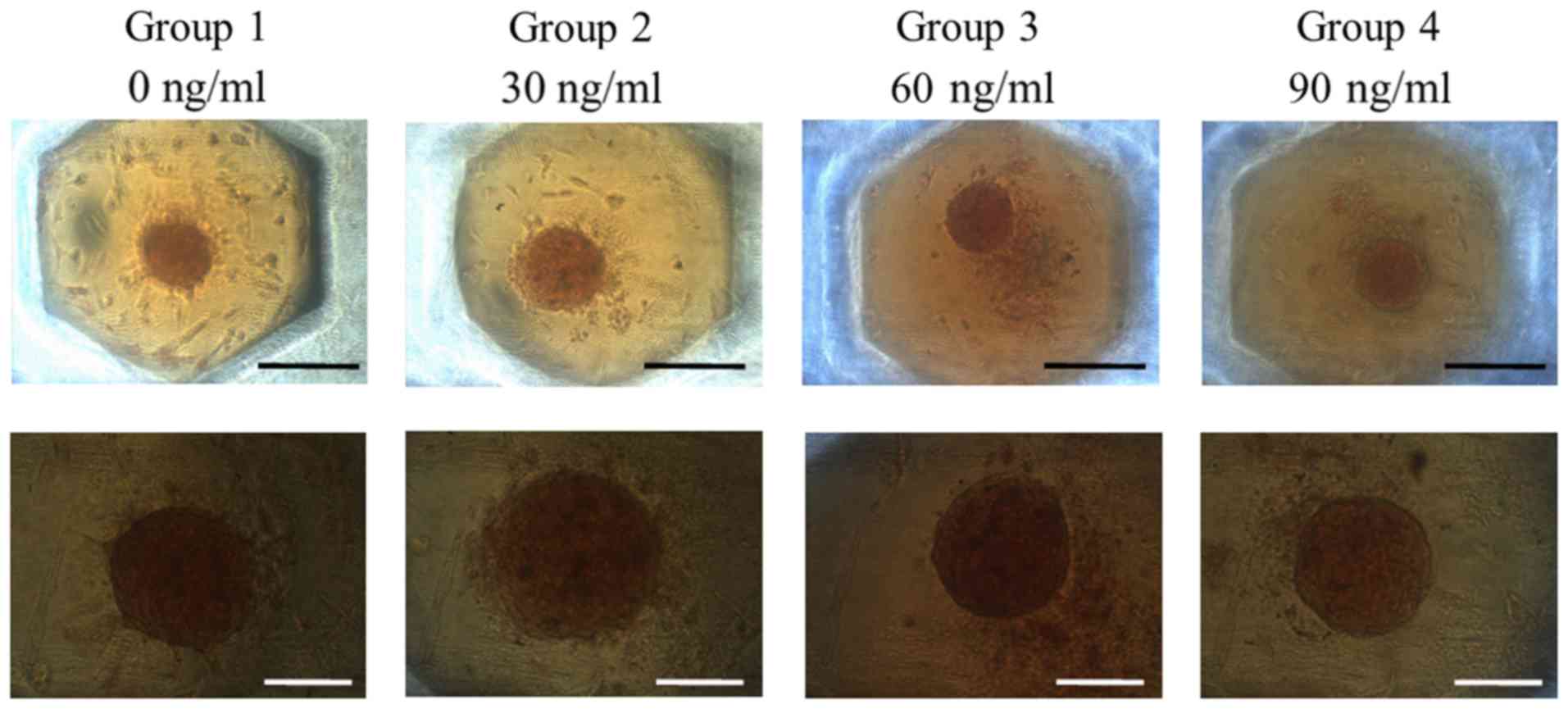
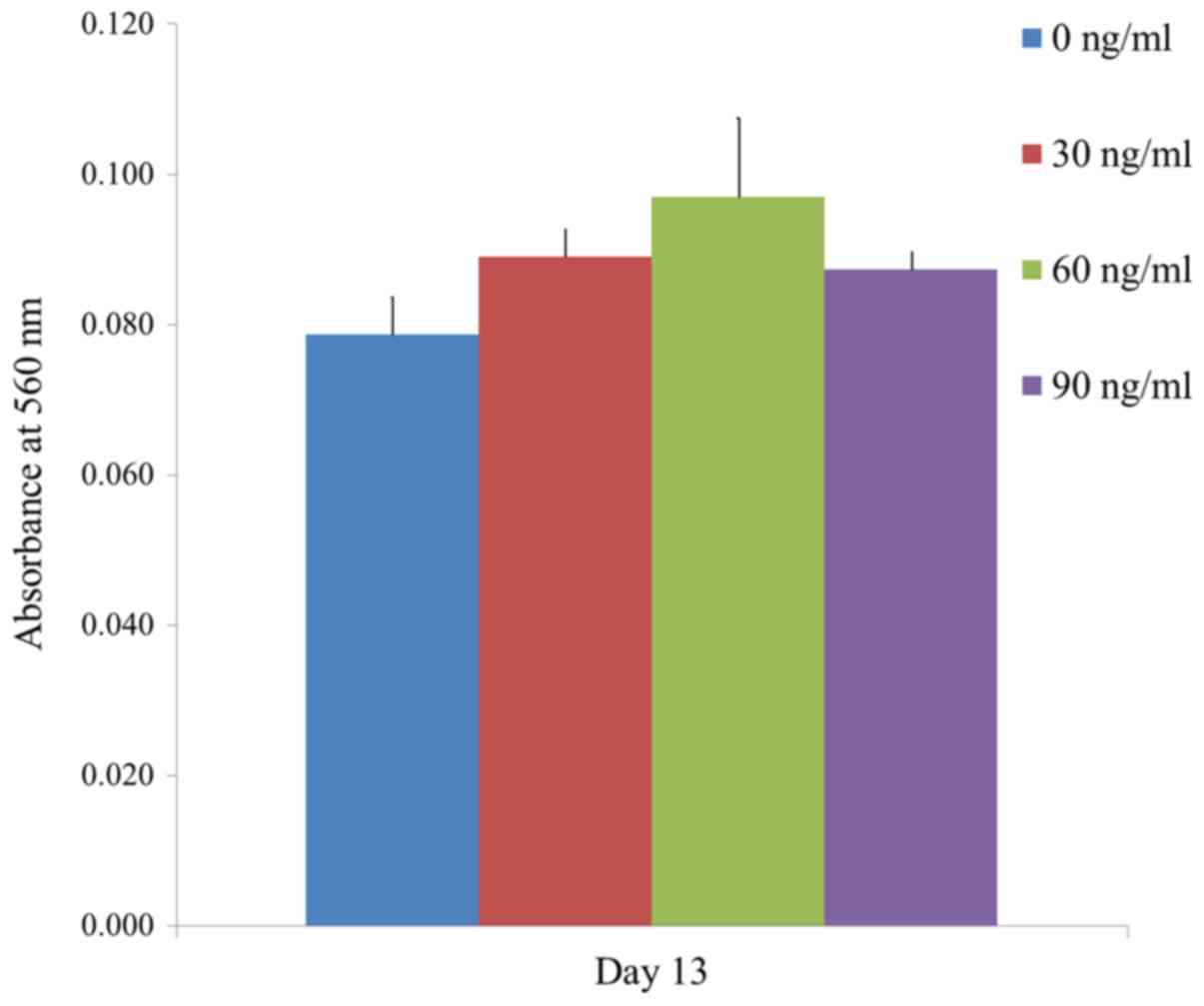
|
1
|
Dvorak P, Bednar D, Vanacek P, Balek L,
Eiselleova L, Stepankova V, Sebestova E, Kunova Bosakova M, Konecna
Z, Mazurenko S, et al: Computer-assisted engineering of hyperstable
fibroblast growth factor 2. Biotechnol Bioeng. 115:850–862. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tang C, Shan Y, Hu Y, Fang Z, Tong Y, Chen
M, Wei X, Fu X and Xu X: FGF2 attenuates neural cell death via
suppressing autophagy after rat mild traumatic brain injury. Stem
Cells Int. 2017:29231822017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhao Y, Cao F, Yu X, Chen C, Meng J, Zhong
R, Zhang Y and Zhu D: Linc-RAM is required for FGF2 function in
regulating myogenic cell differentiation. RNA Biol. 15:404–412.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Titmarsh DM, Tan CL, Glass NR, Nurcombe V,
Cooper-White JJ and Cool SM: Microfluidic screening reveals heparan
sulfate enhances human mesenchymal stem cell growth by modulating
fibroblast growth factor-2 transport. Stem Cells Transl Med.
6:1178–1190. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bruno M, Rizzo IM, Romero-Guevara R,
Bernacchioni C, Cencetti F, Donati C and Bruni P: Sphingosine
1-phosphate signaling axis mediates fibroblast growth factor
2-induced proliferation and survival of murine auditory
neuroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1864:814–824. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Li C, Che LH, Shi L and Yu JL: Suppression
of basic fibroblast growth factor expression by antisense
oligonucleotides inhibits neural stem cell proliferation and
differentiation in rat models with focal cerebral infarction. J
Cell Biochem. 118:3875–3882. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ratajczak J, Hilkens P, Gervois P, Wolfs
E, Jacobs R, Lambrichts I and Bronckaers A: Angiogenic capacity of
periodontal ligament stem cells pretreated with deferoxamine and/or
fibroblast growth factor-2. PLoS One. 11:e01678072016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee J, Lee JY, Chae BC, Jang J, Lee E and
Son Y: Fully dedifferentiated chondrocytes expanded in specific
mesenchymal stem cell growth medium with FGF2 obtains mesenchymal
stem cell phenotype in vitro but retains chondrocyte
phenotype in vivo. Cell Transplant. 26:1673–1687. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee SI, Yeo SI, Kim BB, Ko Y and Park JB:
Formation of size-controllable spheroids using gingiva-derived stem
cells and concave microwells: Morphology and viability tests.
Biomed Rep. 4:97–101. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lee SI, Ko Y and Park JB: Evaluation of
the maintenance of stemness, viability, and differentiation
potential of gingiva-derived stem-cell spheroids. Exp Ther Med.
13:1757–1764. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jeong CH, Kim SM, Lim JY, Ryu CH, Jun JA
and Jeun SS: Mesenchymal stem cells expressing brain-derived
neurotrophic factor enhance endogenous neurogenesis in an ischemic
stroke model. Biomed Res Int. 2014:1291452014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee JH, Lee JE, Kang KJ and Jang YJ:
Functional efficacy of human recombinant FGF-2s tagged with
(His)6 and (His-Asn)6 at the N- and C-termini
in human gingival fibroblast and periodontal ligament-derived
cells. Protein Expr Purif. 135:37–44. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang P, Shu B, Xu Y, Zhu J, Liu J, Zhou Z,
Chen L, Zhao J, Liu X, Qi S, et al: Basic fibroblast growth factor
reduces scar by inhibiting the differentiation of epidermal stem
cells to myofibroblasts via the Notch1/Jagged1 pathway. Stem Cell
Res Ther. 8:1142017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nawrocka D, Kornicka K, Szydlarska J and
Marycz K: Basic fibroblast growth factor inhibits apoptosis and
promotes proliferation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells
isolated from patients with type 2 diabetes by reducing cellular
oxidative stress. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017:30271092017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kim BH, Jung HW, Seo SH, Shin H, Kwon J
and Suh JM: Synergistic actions of FGF2 and bone marrow
transplantation mitigate radiation-induced intestinal injury. Cell
Death Dis. 9:3832018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hyun SY, Lee JH, Kang KJ and Jang YJ:
Effect of FGF-2, TGF-β-1, and BMPs on teno/ligamentogenesis and
osteo/cementogenesis of human periodontal ligament stem cells. Mol
Cells. 40:550–557. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yoon KA, Son Y, Choi YJ, Kim JH and Cho
JY: Fibroblast growth factor 2 supports osteoblastic niche cells
during hematopoietic homeostasis recovery after bone marrow
suppression. Cell Commun Signal. 15:252017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Vidovic-Zdrilic I, Vining KH, Vijaykumar
A, Kalajzic I, Mooney DJ and Mina M: FGF2 enhances odontoblast
differentiation by αSMA(+) progenitors in vivo. J Dent Res.
97:1170–1177. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Singh M, Kakkar A, Sharma R, Kharbanda OP,
Monga N, Kumar M, Chowdhary S, Airan B and Mohanty S: Synergistic
effect of BDNF and FGF2 in efficient generation of functional
dopaminergic neurons from human mesenchymal stem cells. Sci Rep.
7:103782017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li R, Ma J, Wu Y, Nangle M, Zou S, Li Y,
Yin J, Zhao Y, Xu H, Zhang H, et al: Dual delivery of NGF and bFGF
coacervater ameliorates diabetic peripheral neuropathy via
inhibiting schwann cells apoptosis. Int J Biol Sci. 13:640–651.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xu R, Zhao H, Muhammad H, Dong M,
Besenbacher F and Chen M: Dual-delivery of FGF-2/CTGF from silk
fibroin/PLCL-PEO coaxial fibers enhances MSC proliferation and
fibrogenesis. Sci Rep. 7:85092017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Peng WX and Wang L: Adenovirus-mediated
expression of BMP-2 and BFGF in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
combined with demineralized bone matrix for repair of femoral head
osteonecrosis in beagle dogs. Cell Physiol Biochem. 43:1648–1662.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Romero R, Travers JK, Asbury E, Pennybaker
A, Chubb L, Rose R, Ehrhart NP and Kipper MJ: Combined delivery of
FGF-2, TGF-β1, and adipose-derived stem cells from an engineered
periosteum to a critical-sized mouse femur defect. J Biomed Mater
Res A. 105:900–911. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lee JS, Kim SK, Jung BJ, Choi SB, Choi EY
and Kim CS: Enhancing proliferation and optimizing the culture
condition for human bone marrow stromal cells using hypoxia and
fibroblast growth factor-2. Stem Cell Res. 28:87–95. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tay LM, Wiraja C, Wu Y, Yang Z, Lee EH and
Xu C: The effect of temporal manipulation of transforming growth
factor beta 3 and fibroblast growth factor 2 on the derivation of
proliferative chondrocytes from mensenchymal stem cells-A study
monitored by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain
reaction and molecular beacon based nanosensors. J Biomed Mater Res
A. 106:895–904. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|