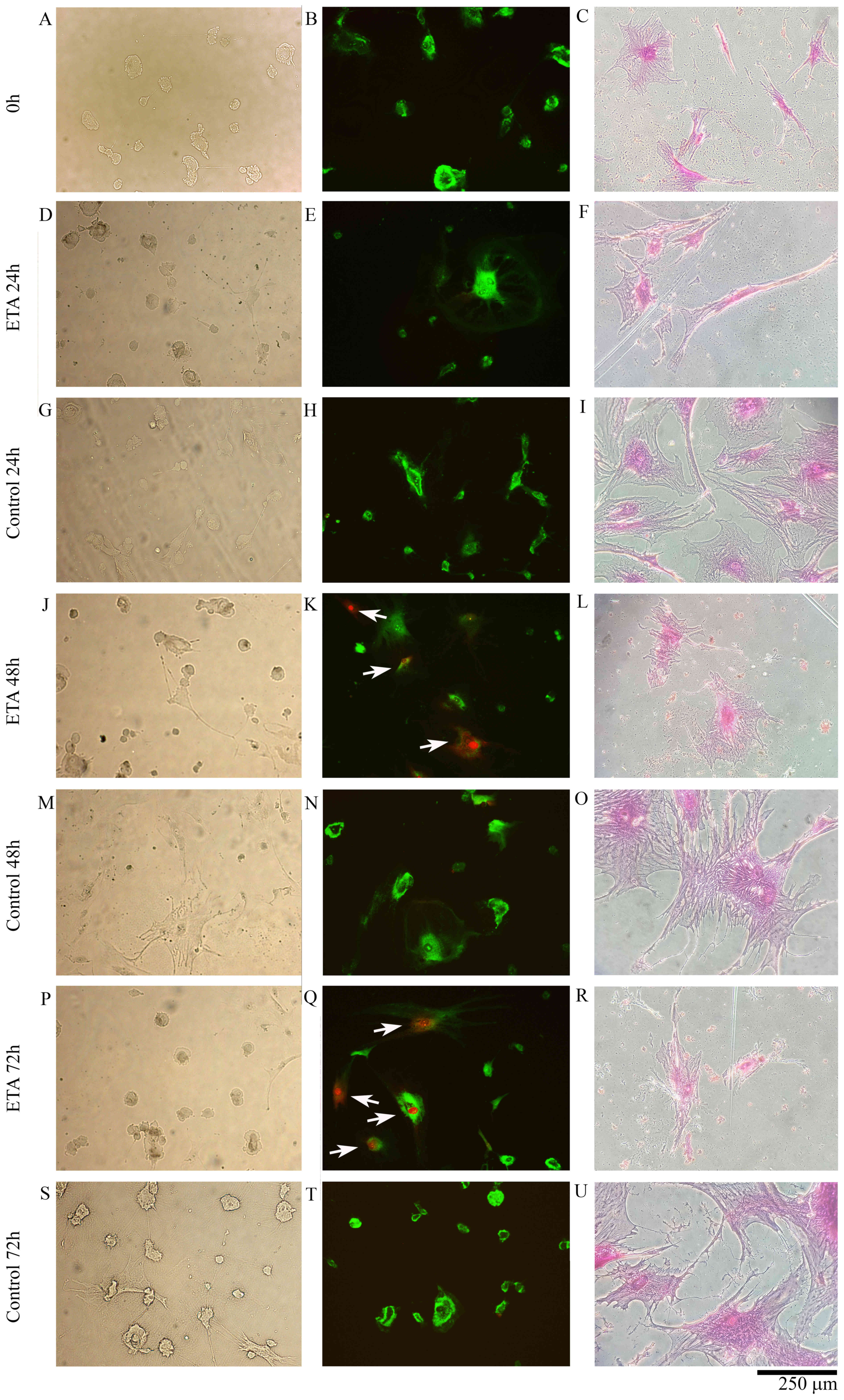
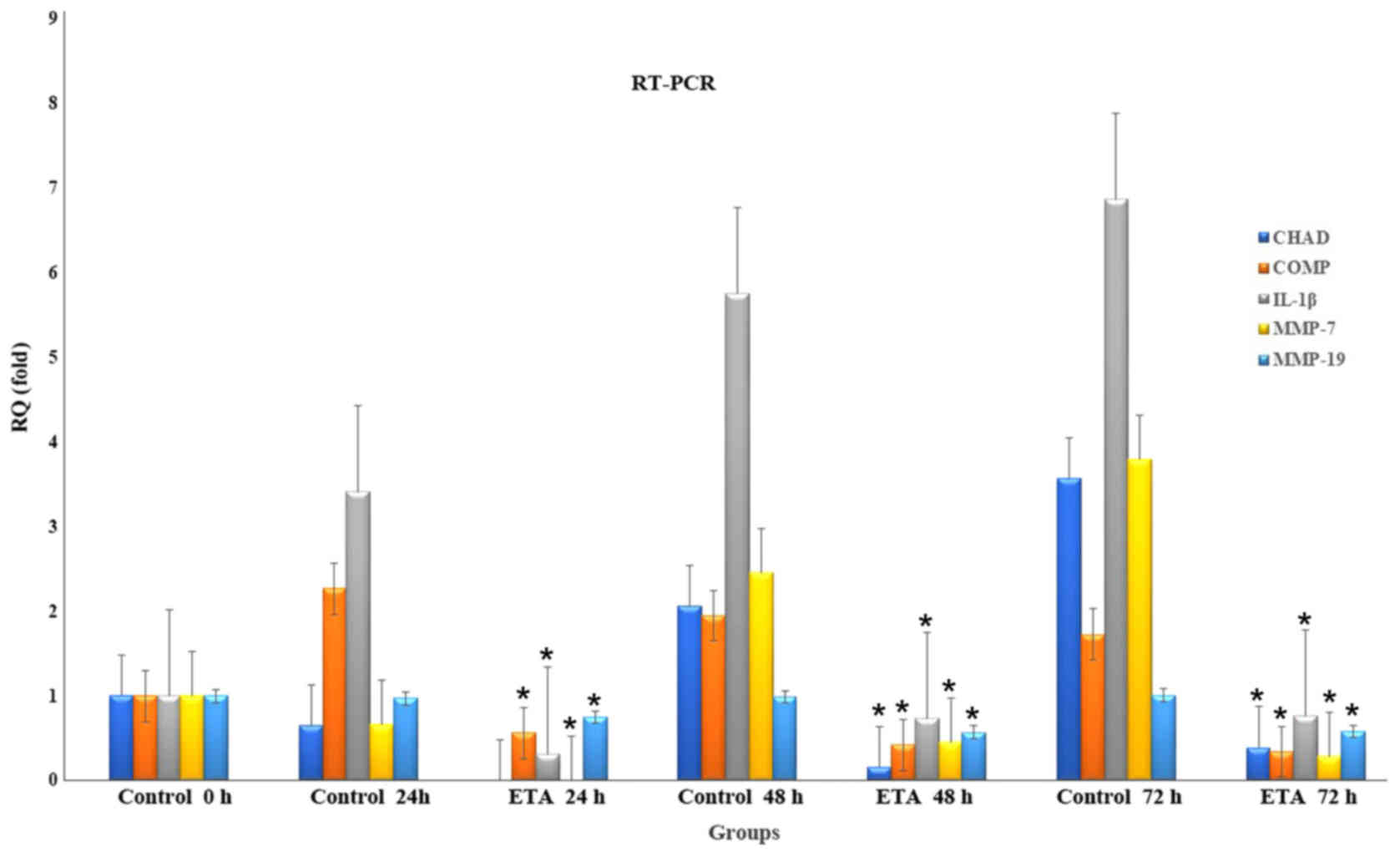
|
1
|
Hasturk AE, Baran C, Yilmaz ER, Arikan M,
Togral G, Hayirli N, Erguder BI and Evirgen O: Etanercept prevents
histopathological damage after spinal cord injury in rats. Asian J
Neurosurg. 13:37–45. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Isyar M, Bilir B, Yilmaz I, Cakmak S,
Sirin DY, Guzelant AY and Mahirogullari M: Are biological agents
toxic to human chondrocytes and osteocytes? J Orthop Surg Res.
10:1182015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Turkoglu E, Tuncer C, Dinc C, Serbes G,
Oktay M and Sekerci Z: Turk Neurosurg. 24:506–511. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhang BF, Song JN, Ma XD, Zhao YL, Liu ZW,
Li Y, Sun P, Li DD, Pang HG and Huang TQ: Etanercept alleviates
early brain injury following experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage
and the possible role of tumor necrosis factor-α and c-Jun
N-terminal kinase pathway. Neurochem Res. 40:591–599. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Roerink ME, Groen RJ, Franssen G,
Lemmers-van de Weem B, Boerman OC and van der Meer JW: Central
delivery of iodine-125-labeled cetuximab, etanercept and anakinra
after perispinal injection in rats: Possible implications for
treating Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Res Ther. 7:702015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bayrakli F, Balaban H, Ozum U, Duger C,
Topaktas S and Kars HZ: Etanercept treatment enhances clinical and
neuroelectrophysiological recovery in partial spinal cord injury.
Eur Spine J. 21:2588–2593. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Guzelant AY, Isyar M, Yilmaz I, Sirin DY,
Cakmak S and Mahirogullari M: Are chondrocytes damaged when
rheumatologic inflammation is suppressed? Drug Chem Toxicol.
40:13–23. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sirin DY and Karaarslan N: Evaluation of
the effects of pregabalin on chondrocyte proliferation and CHAD,
HIF-1α and COL2A1 gene expression. Arch Med Sci. 14:1340–1347.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Karaarslan N, Yilmaz I, Sirin DY, Ozbek H,
Kaplan N, Kaya YE, Akyuva Y, Gurbuz MS, Oznam K and Ates O:
Pregabalin treatment for neuropathic pain may damage intervertebral
disc tissue. Exp Ther Med. 16:1259–1265. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Karaarslan N, Batmaz AG, Yilmaz I, Ozbek
H, Caliskan T, Sirin D, Kaplan N, Oznam K and Ates O: Effect of
naproxen on proliferation and differentiation of primary cell
cultures isolated from human cartilage tissue. Exp Ther Med.
16:1647–1654. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cereda CW, Zecca C, Mazzucchelli L, Valci
L, Staedler C, Bassetti CL and Gobbi C: Tumefactive demyelinating
lesions during etanercept treatment requiring decompressive
hemicraniectomy. Mult Scler. 19:820–823. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bowers CA, Saad D, Clegg DO, Ng P, Clayton
F, Haydoura S and Schmidt RH: Rapidly fatal internal carotid artery
mycotic aneurysm rupture in a rheumatoid patient taking a TNF-α
inhibitor: Case report and literature review. J Neurol Surg A Cent
Eur Neurosurg. 76:249–254. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kasirye Y, Epperla N, Manne JR, Bapani S
and Garcia-Montilla RJ: Brain abscesses complicating acute
pneumococcal meningitis during etanercept therapy. Clin Med Res.
10:230–235. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Karaarslan N, Yilmaz I, Ozbek H, Sirin DY,
Kaplan N, Akyuva Y, Gonultas A and Ates O: Are specific gene
expressions of extracellular matrix and nucleus pulposus affected
by primary cell cultures prepared from intact or degenerative
intervertebral disc tissues? Turk Neurosurg. 29:43–52.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen S, Hu ZJ, Zhou ZJ, Lin XF, Zhao FD,
Ma JJ, Zhang JF, Wang JY, Qin A and Fan SW: Evaluation of 12 novel
molecular markers for degenerated nucleus pulposus in a Chinese
population. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 40:1252–1260. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Goupille P, Jayson MI, Valat JP and
Freemont AJ: Matrix metalloproteinases: The clue to intervertebral
disc degeneration? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 23:1612–1626. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kang JD, Stefanovic-Racic M, McIntyre LA,
Georgescu HI and Evans CH: Toward a biochemical understanding of
human intervertebral disc degeneration and herniation.
Contributions of nitric oxide, interleukins, prostaglandin E2 and
matrix metalloproteinases. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 22:1065–1073.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kang JD, Georgescu HI, McIntyre-Larkin L,
Stefanovic-Racic M, Donaldson WF III and Evans CH: Herniated lumbar
intervertebral discs spontaneously produce matrix
metalloproteinases, nitric oxide, interleukin-6 and prostaglandin
E2. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 21:271–277. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Crean JK, Roberts S, Jaffray DC,
Eisenstein SM and Duance VC: Matrix metalloproteinases in the human
intervertebral disc: Role in disc degeneration and scoliosis. Spine
(Phila Pa 1976). 22:2877–2884. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Doita M, Kanatani T, Ozaki T, Matsui N,
Kurosaka M and Yoshiya S: Influence of macrophage infiltration of
herniated disc tissue on the production of matrix
metalloproteinases leading to disc resorption. Spine (Phila Pa
1976). 26:1522–1527. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Matsui Y, Maeda M, Nakagami W and Iwata H:
The involvement of matrix metalloproteinases and inflammation in
lumbar disc herniation. Spine. 23:863–869. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nishida Y, D'Souza AL, Thonar EJ and
Knudson W: Stimulation of hyaluronan metabolism by
interleukin-1alpha in human articular cartilage. Arthritis Rheum.
43:1315–1326. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
van den Berg WB: The role of cytokines and
growth factors in cartilage destruction in osteoarthritis and
rheumatoid arthritis. Z Rheumatol. 58:136–141. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Takae R, Matsunaga S, Origuchi N, Yamamoto
T, Morimoto N, Suzuki S and Sakou T: Immunolocalization of bone
morphogenetic protein and its receptors in degeneration of
intervertebral disc. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 24:1397–1401. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rannou F, Corvol MT, Hudry C, Anract P,
Dumontier MF, Tsagris L, Revel M and Poiraudeau S: Sensitivity of
anulus fibrosus cells to interleukin 1 beta. Comparison with
articular chondrocytes. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 25:17–23. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shin IS, Baer AN, Kwon HJ, Papadopoulos EJ
and Siegel JN: Guillain-Barré and Miller Fisher syndromes occurring
with tumor necrosis factor alpha antagonist therapy. Arthritis
Rheum. 54:1429–1434. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Highlights of Prescribing Information. In,
. Medication Guide. https://www.pi.amgen.com/~/media/amgen/repositorysites/pi-amgen-com/enbrel/enbrel_pi.pdfMarch
6–2019
|
|
28
|
Akyuva Y, Kaplan N, Yilmaz I, Ozbek H,
Sirin DY, Karaarslan N, Guler O and Ates O: Delivering growth
factors through a polymeric scaffold to cell cultures containing
both nucleus pulposus and annulus fibrosus. Turk Neurosurg.
29:180–193. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Karaarslan N, Yilmaz I, Akgun FS, Caliskan
T, Simsek AT, Kaplan N, Kaya YE, Sirin DY, Ozbek H and Ates O:
Which pharmacological agents may be used to establish healthy,
proliferating human primer nucleus pulposus/annulus fibrosus cell
cultures? Systematic evaluation of our experience in the light of
literature. Merit Res J Med Med Sci. 6:100–110. 2018.
|
|
30
|
Akyuva Y, Karaarslan N, Yilmaz I, Ozbek H,
Sirin DY, Gurbuz MS, Kaya YE, Kaplan N and Ates O: How scaffolds,
which are polymeric drug delivery systems allowing controlled
release, can be tested in human primary nucleus pulposus and
annulus fibrosus cell cultures? Merit Res J Med Med Sci. 5:477–487.
2017.
|
|
31
|
Wadhwa M, Bird C, Dilger P, Rigsby P, Jia
H and Gross MEB; participants of the study, : Establishment of the
first WHO international standard for etanercept, a TNF receptor II
Fc fusion protein: Report of an international collaborative study.
J Immunol Methods. 447:14–22. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jamalzadeh L, Ghafoori H, Sariri R, Rabuti
H, Nasirzade J, Hasani H and Aghamaali MR: Cytotoxic effects of
some common organic solvents on MCF-7, RAW-264.7 and human
umbilical vein endothelial cells. Avicenna J Med Biochem.
4:e334532016.
|
|
33
|
Dolganiuc A and Szabo G: In vitro and in
vivo models of acute alcohol exposure. World J Gastroenterol.
15:1168–1177. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Beyaz SG, İnanmaz ME, Ergönenç T,
Palabiyik O, Tomak Y and Tuna AT: Comparison of the intravenous and
epidural administration of tumor necrosis factor-alpha antagonists
in an experimental rat pain model. Anesth Essays Res. 11:898–901.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Watanabe K, Yabuki S, Sekiguchi M, Kikuchi
S and Konno S: Etanercept attenuates pain-related behavior
following compression of the dorsal root ganglion in the rat. Eur
Spine J. 20:1877–1884. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang SS, Zhang W, Zhang YQ, Zhao Y, Liu Y,
Li JK, Zhang HX, Cheng L and Nie L: IL-17A enhances ADAMTS-7
expression through regulation of TNF-α in human nucleus pulposus
cells. J Mol Histol. 46:475–483. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chen K, Li P, Zhao H, Yan X and Ma Y:
Effects of tumor necrosis factor inhibitor on stress-shielded
tendons. Orthopedics. 40:49–55. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Crnkic M, Månsson B, Larsson L, Geborek P,
Heinegård D and Saxne T: Serum cartilage oligomeric matrix protein
(COMP) decreases in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with
infliximab or Etanercept. Arthritis Res Ther. 5:R181–R185. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Molinos M, Almeiada CR, Calderia J, Cunha
C, Gonçalves RM and Barbosa A: Inflammation in intervertebral disc
degeneration and regeneration. J R Soc Interface. 12:201411912015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Khan AN, Jacobsen HE, Khan J, Filippi CG,
Levine M, Lehman RA Jr, Riew KD, Lenke LG and Chahine NO:
Inflammatory biomarkers of low back pain and disc degeneration: a
review. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1410:68–84. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang S, Liu C, Sun Z, Yan P, Liang H,
Huang K, Li C and Tian J: IL-1β increases asporin expression via
the NF-κB p65 pathway in nucleus pulposus cells during
intervertebral disc degeneration. Sci Rep. 7:41122017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Erwin WM, Islam D, Inman RD, Fehlings MG
and Tsui FW: Notochordal cells protect nucleus pulposus cells from
degradation and apoptosis: Implications for the mechanisms of
intervertebral disc degeneration. Arthritis Res Ther. 13:R2152011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|