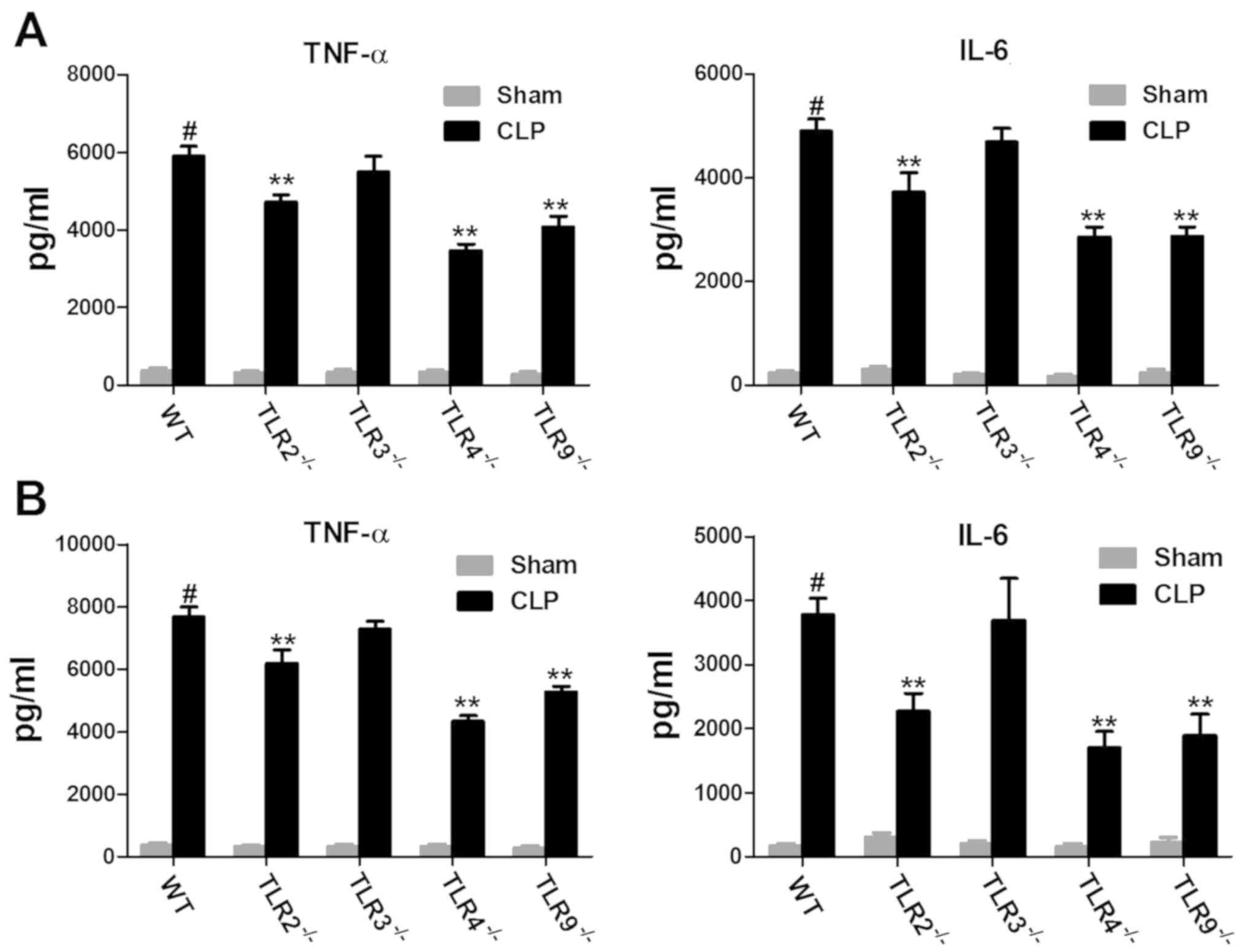
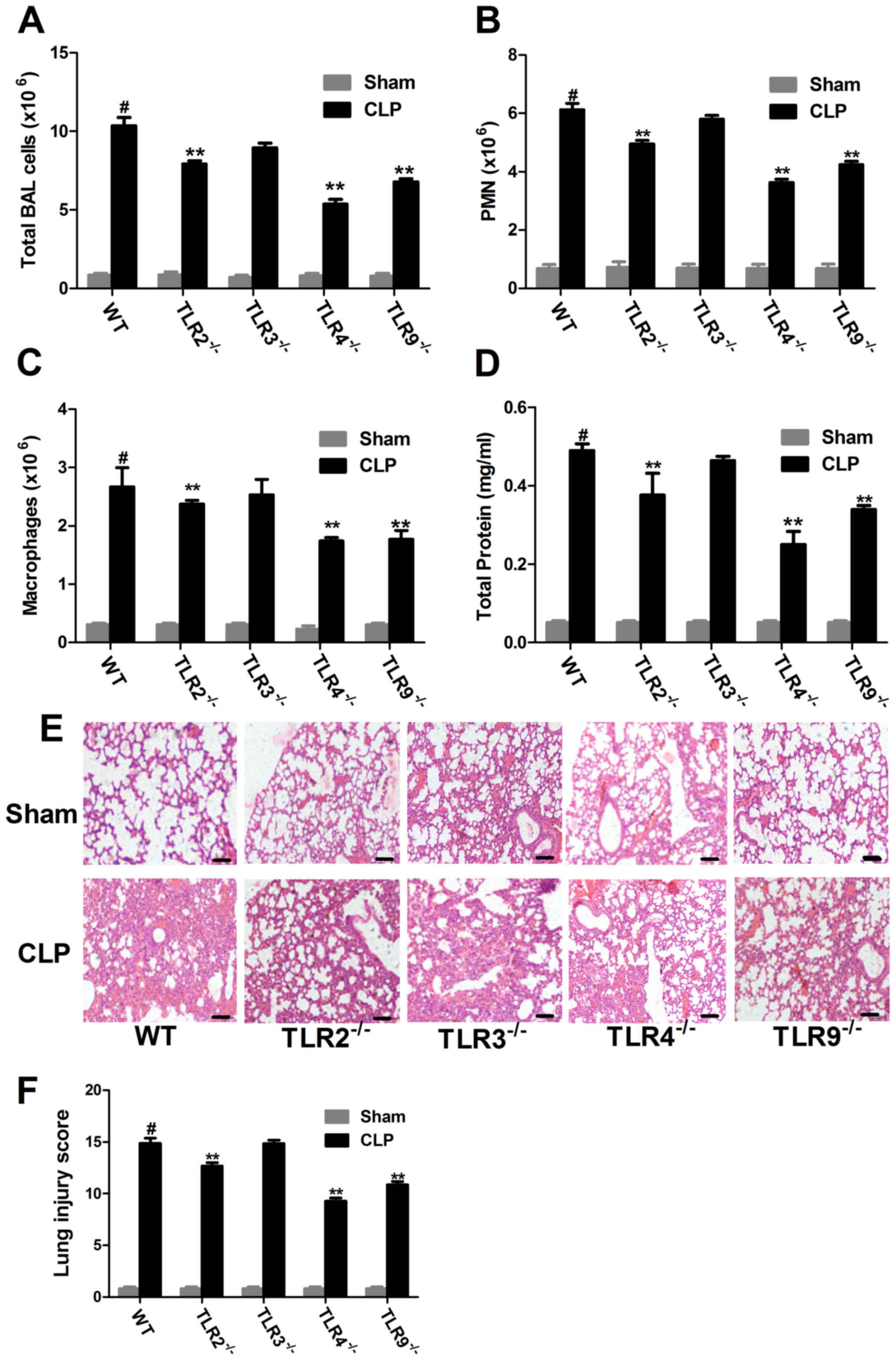
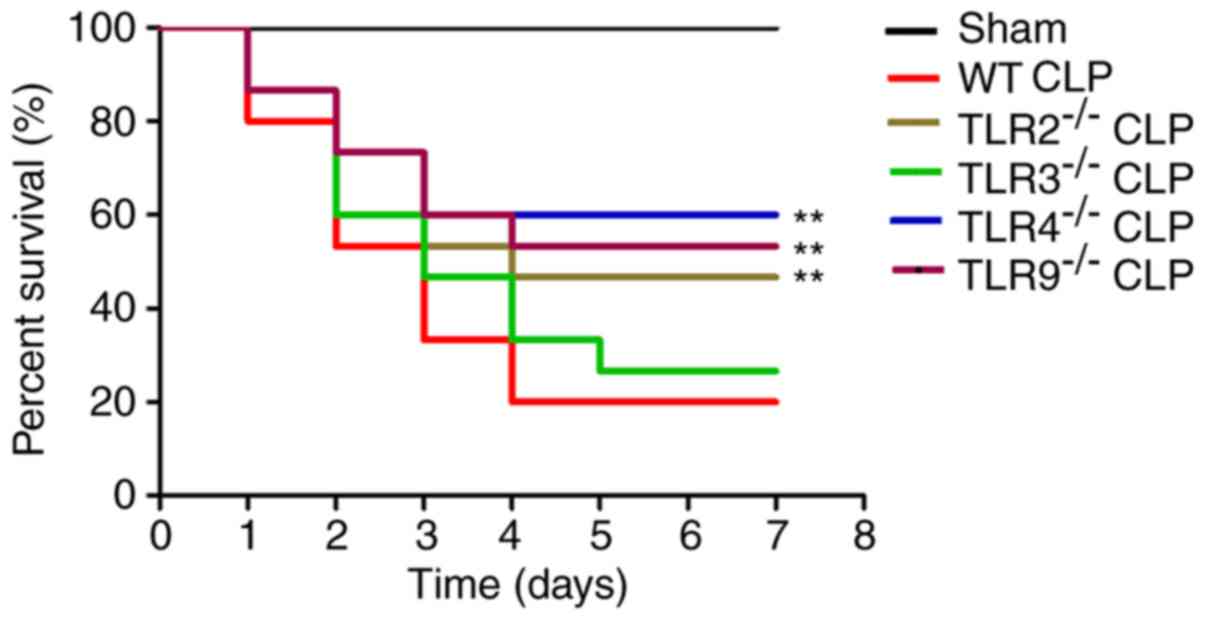
|
1
|
Seeley EJ, Matthay MA and Wolters PJ:
Inflection points in sepsis biology: From local defense to systemic
organ injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 303:L355–L363.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Villar J, Sulemanji D and Kacmarek RM: The
acute respiratory distress syndrome: Incidence and mortality, has
it changed? Curr Opin Crit Care. 20:3–9. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Matthay MA and Zemans RL: The acute
respiratory distress syndrome: Pathogenesis and treatment. Annu Rev
Pathol. 6:147–163. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yuk HJ, Lee JW, Park HA, Kwon OK, Seo KH,
Ahn KS, Oh SR and Ryu HW: Protective effects of coumestrol on
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via the inhibition of
proinflammatory mediators and NF-κB activation. J Funct Foods.
34:181–188. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Miyashita T, Ahmed AK, Nakanuma S, Okamoto
K, Sakai S, Kinoshita J, Makino I, Nakamura K, Hayashi H, Oyama K,
et al: A Three-phase Approach for the Early Identification of Acute
Lung Injury Induced by Severe Sepsis. In Vivo. 30:341–349.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Butt Y, Kurdowska A and Allen TC: Acute
Lung Injury: A Clinical and Molecular Review. Arch Pathol Lab Med.
140:345–350. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Beutler BA: TLRs and innate immunity.
Blood. 113:1399–1407. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cognasse F, Nguyen KA, Damien P, McNicol
A, Pozzetto B, Hamzeh-Cognasse H and Garraud O: The Inflammatory
Role of Platelets via Their TLRs and Siglec Receptors. Front
Immunol. 6:832015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Takeda K and Akira S: TLR signaling
pathways. Semin Immunol. 16:3–9. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Akira S and Hemmi H: Recognition of
pathogen-associated molecular patterns by TLR family. Immunol Lett.
85:85–95. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mukherjee S, Karmakar S and Babu SP: TLR2
and TLR4 mediated host immune responses in major infectious
diseases: A review. Braz J Infect Dis. 20:193–204. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chattopadhyay S and Sen GC:
dsRNA-activation of TLR3 and RLR signaling: Gene
induction-dependent and independent effects. J Interferon Cytokine
Res. 34:427–436. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jelinek I, Leonard JN, Price GE, Brown KN,
Meyer-Manlapat A, Goldsmith PK, Wang Y, Venzon D, Epstein SL and
Segal DM: TLR3-specific double-stranded RNA oligonucleotide
adjuvants induce dendritic cell cross-presentation, CTL responses,
and antiviral protection. J Immunol. 186:2422–2429. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Vollmer J and Krieg AM: Immunotherapeutic
applications of CpG oligodeoxynucleotide TLR9 agonists. Adv Drug
Deliv Rev. 61:195–204. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Blasius AL and Beutler B: Intracellular
toll-like receptors. Immunity. 32:305–315. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
O'Shea JJ and Murray PJ: Cytokine
signaling modules in inflammatory responses. Immunity. 28:477–487.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tan RST, Ho B, Leung BP and Ding JL: TLR
cross-talk confers specificity to innate immunity. Int Rev Immunol.
33:443–453. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Rai V and Agrawal DK: The role of damage-
and pathogen-associated molecular patterns in inflammation-mediated
vulnerability of atherosclerotic plaques. Can J Physiol Pharmacol.
95:1245–1253. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Matute-Bello G, Frevert CW and Martin TR:
Animal models of acute lung injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 295:L379–L399. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Walley KR, Lukacs NW, Standiford TJ,
Strieter RM and Kunkel SL: Balance of inflammatory cytokines
related to severity and mortality of murine sepsis. Infect Immun.
64:4733–4738. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Altemeier WA, Hung CF and Matute-Bello G:
Mouse Models of Acute Lung Injury. In: Acute Lung Injury and
Repair. Respiratory Medicine. Schnapp L and Feghali-Bostwick C
(eds). Humana Press; Cham: pp. 5–23. 2017
|
|
22
|
Dejager L, Pinheiro I, Dejonckheere E and
Libert C: Cecal ligation and puncture: The gold standard model for
polymicrobial sepsis? Trends Microbiol. 19:198–208. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhan J, Liu Y, Zhang Z, Chen C, Chen K and
Wang Y: Effect of penehyclidine hydrochloride on expressions of
MAPK in mice with CLP-induced acute lung injury. Mol Biol Rep.
38:1909–1914. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xiang M and Fan J: Pattern recognition
receptor-dependent mechanisms of acute lung injury. Mol Med.
16:69–82. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bhandari V, Choo-Wing R, Lee CG, Zhu Z,
Nedrelow JH, Chupp GL, Zhang X, Matthay MA, Ware LB, Homer RJ, et
al: Hyperoxia causes angiopoietin 2-mediated acute lung injury and
necrotic cell death. Nat Med. 12:1286–1293. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cartwright M, Rottman M, Shapiro NI,
Seiler B, Lombardo P, Gamini N, Tomolonis J, Watters AL, Waterhouse
A, Leslie D, et al: A Broad-Spectrum Infection Diagnostic that
Detects Pathogen-Associated Molecular Patterns (PAMPs) in Whole
Blood. EBioMedicine. 9:217–227. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Achek A, Yesudhas D and Choi S: Toll-like
receptors: Promising therapeutic targets for inflammatory diseases.
Arch Pharm Res. 39:1032–1049. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kim WY and Hong SB: Sepsis and Acute
Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Recent Update. Tuberc Respir Dis
(Seoul). 79:53–57. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Torun AC, Tutuncu S, Ustun B and Akdemir
HU: A Study of the Therapeutic Effects of Resveratrol on Blunt
Chest Trauma-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Rats and the Potential
Role of Endocan as a Biomarker of Inflammation. Inflammation.
40:1803–1810. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhu Q, He G, Wang J, Wang Y, Chen W and
Guo T: Down-regulation of toll-like receptor 4 alleviates
intestinal ischemia reperfusion injury and acute lung injury in
mice. Oncotarget. 8:13678–13689. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Medvedev AE, Sabroe I, Hasday JD and Vogel
SN: Tolerance to microbial TLR ligands: Molecular mechanisms and
relevance to disease. J Endotoxin Res. 12:133–150. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zarember KA and Godowski PJ: Tissue
expression of human Toll-like receptors and differential regulation
of Toll-like receptor mRNAs in leukocytes in response to microbes,
their products, and cytokines. J Immunol. 168:554–561. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yang CS, Lee JS, Rodgers M, Min CK, Lee
JY, Kim HJ, Lee KH, Kim CJ, Oh B, Zandi E, et al: Autophagy protein
Rubicon mediates phagocytic NADPH oxidase activation in response to
microbial infection or TLR stimulation. Cell Host Microbe.
11:264–276. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chalifour A, Jeannin P, Gauchat JF,
Blaecke A, Malissard M, N'Guyen T, Thieblemont N and Delneste Y:
Direct bacterial protein PAMP recognition by human NK cells
involves TLRs and triggers alpha-defensin production. Blood.
104:1778–1783. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yu M, Shao D, Liu J, Zhu J, Zhang Z and Xu
J: Effects of ketamine on levels of cytokines, NF-kappaB and TLRs
in rat intestine during CLP-induced sepsis. Int Immunopharmacol.
7:1076–1082. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Deng D, Li X, Liu C, Zhai Z, Li B, Kuang
M, Li P, Shang S, Song Y, Cen Y, et al: Systematic investigation on
the turning point of over-inflammation to immunosuppression in CLP
mice model and their characteristics. Int Immunopharmacol.
42:49–58. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhou D, Qiu J, Liang Y, Dai W, Yuan D and
Zhou J: Epidemiological analysis of 9,596 patients with acute lung
injury at Chinese Military Hospitals. Exp Ther Med. 13:983–988.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Creagh-Brown BC, Quinlan GJ, Evans TW and
Burke-Gaffney A: The RAGE axis in systemic inflammation, acute lung
injury and myocardial dysfunction: An important therapeutic target?
Intensive Care Med. 36:1644–1656. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Devaney J, Contreras M and Laffey JG:
Clinical review: gene-based therapies for ALI/ARDS: where are we
now? Crit Care. 15:224–236. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Staples KJ: Editorial: Therapeutics for
acute lung injury: time to call in the DRs? J Leukoc Biol.
101:351–353. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|