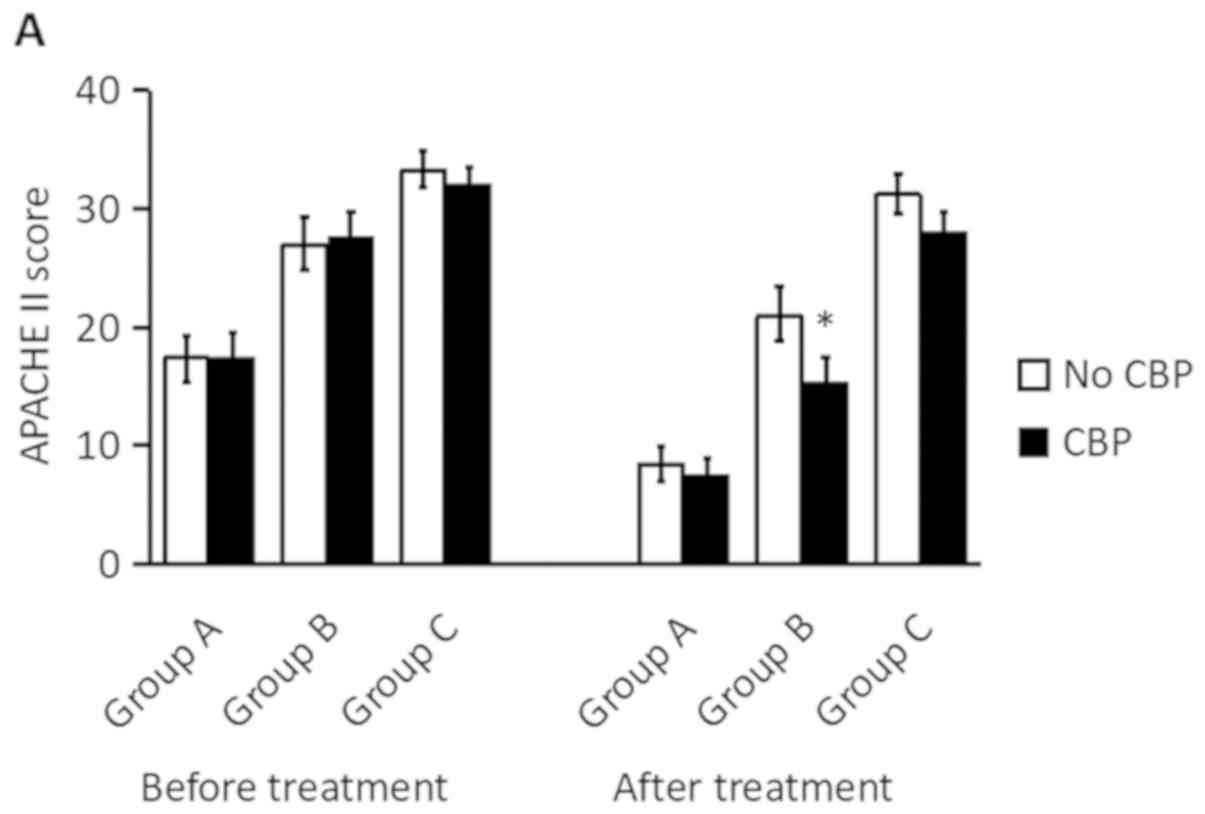
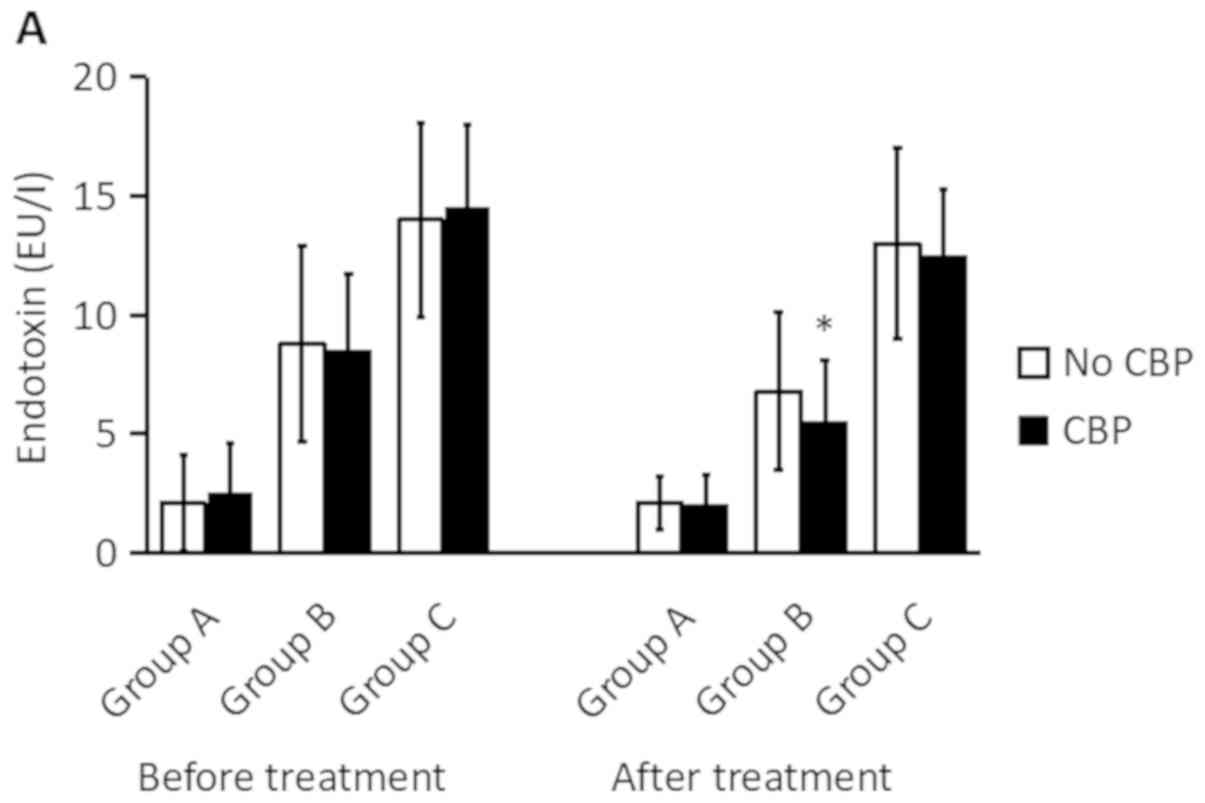
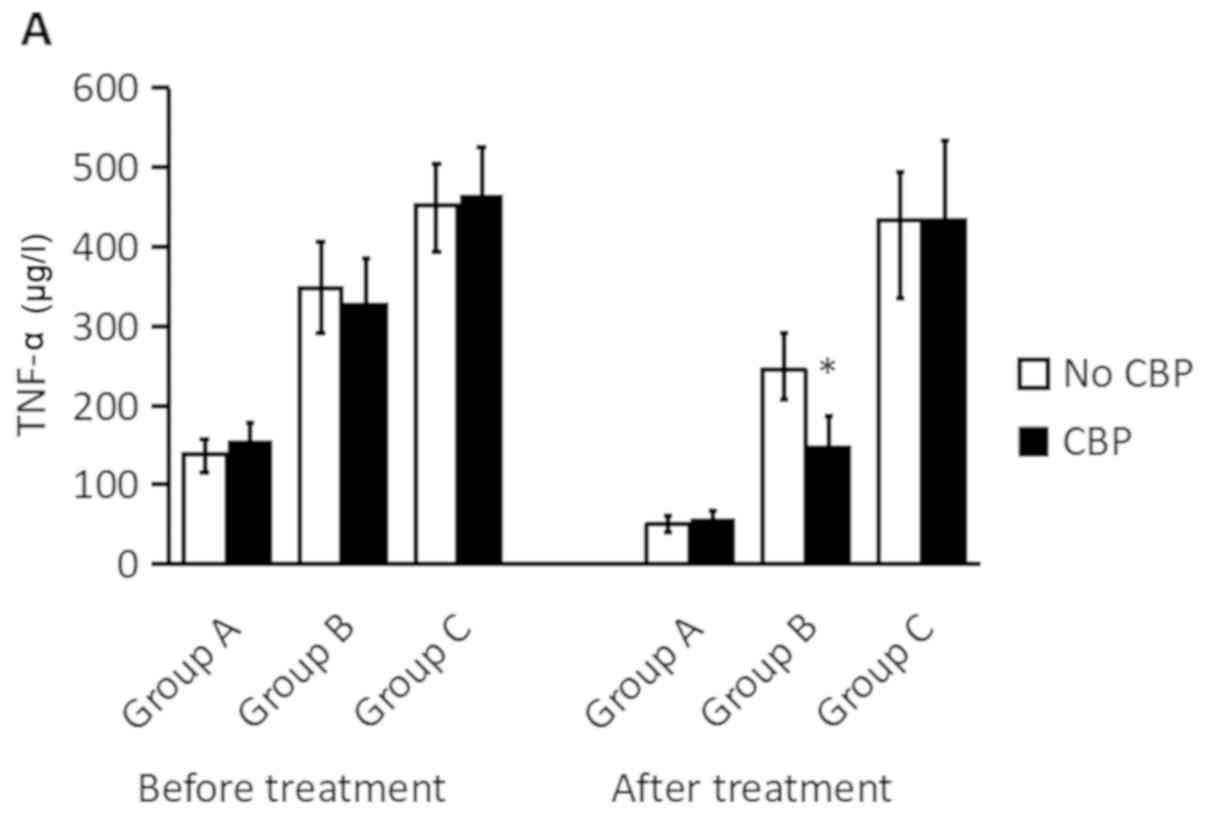
|
1
|
Gong H, Sheng X, Xue J and Zhu D:
Expression and role of TNIP2 in multiple organ dysfunction syndrome
following severe trauma. Mol Med Rep. 19:2906–2912. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jastrow KM III, Gonzalez EA, McGuire MF,
Suliburk JW, Kozar RA, Iyengar S, Motschall DA, McKinley BA, Moore
FA and Mercer DW: Early cytokine production risk stratifies trauma
patients for multiple organ failure. J Am Coll Surg. 209:320–331.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Saadia R and Schein M: Multiple organ
failure. How valid is the ‘two hit’ model? J Accid Emerg Med.
16:163–167. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Yao YM, Redl H, Bahrami S and Schlag G:
The inflammatory basis of trauma/shock-associated multiple organ
failure. Inflamm Res. 47:201–210. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
St John RC and Dorinsky PM: Immunologic
therapy for ARDS, septic shock, and multiple-organ failure. Chest.
103:932–943. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hanafusa N: Application of continuous
replacement therapy: What should we consider based on existing
evidence? Blood Purif. 40:312–319. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Intensive Care Society: Standards and
recommendations for the provision of renal replacement therapy on
intensive care units in the United Kingdom. Intensive Care Society.
2009.
|
|
8
|
Lee S, Hwang H, Yamal JM, Goodman JC,
Aisiku IP, Gopinath S and Robertson CS: IMPACT probability of poor
outcome and plasma cytokine concentrations are associated with
multiple organ dysfunction syndrome following traumatic brain
injury. J Neurosurg. Jan 11–2019.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Finkel KW and Podoll AS: Complications of
continuous renal replacement therapy. Semin Dial. 22:155–159. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cheng J, Hu S, Lu H, Lei Q, Liu J, Yuan F
and Chen R: Comparison of the therapeutic effectiveness of
sustained low-efficiency dialysis (SLED) with continuous blood
purification (CBP) in critically ill patients. Cell Biochem
Biophys. 67:923–927. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dehghani A, Abdeyazdan G and
Davaridolatabadi E: An overview of the predictor standard tools for
patient weaning from mechanical ventilation. Electron Physician.
8:1955–1963. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sadaka F, EthmaneAbouElMaali C, Cytron MA,
Fowler K, Javaux VM and O'Brien J: Predicting mortality of patients
with sepsis: A comparison of APACHE II and APACHE III scoring
systems. J Clin Med Res. 9:907–910. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Baue E: MOF, MODS, and SIRS: What is in a
name or an acronym? Shock. 26:438–449. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Marshall JC, Cook DJ, Christou NV, Bernard
GR, Sprung CL and Sibbald WJ: Multiple organ dysfunction score: A
reliable descriptor of a complex clinical outcome. Crit Care Med.
23:1638–1652. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Baek JH, Kim MS, Lee JC and Lee JH:
Systemic inflammation response syndrome score predicts the
mortality in multiple trauma patients. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc
Surg. 47:523–528. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
NeSmith EG, Weinrich SP, Andrews JO,
Medeiros RS, Hawkins ML and Weinrich M: Systemic inflammatory
response syndrome score and race as predictors of length of stay in
the intensive care unit. Am J Crit Care. 18:339–346. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Knaus WA, Draper EA, Wagner DP and
Zimmerman JE: APACHE II: A severity of disease classification
system. Crit Care Med. 13:818–829. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jacobs S, Zuleika M and Mphansa T: The
multiple organ dysfunction score as a descriptor of patient outcome
in septic shock compared with two other scoring systems. Crit Care
Med. 27:741–744. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhou Z, Guo F and Huan J: Fournier's
gangrene with septic shock and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome.
Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 18:94–96. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zeng J: Values of detection of NF-κB
activation level combined with IL-6 and TNF-α levels in peripheral
neutrophils in the prediction of multiple organ dysfunction
syndrome in patients with severe multiple trauma. Exp Ther Med.
16:2478–2482. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang F, Guan X, Yang J, He W, Wei Y, Chen
H and Li Y: Differential expression and significance of endoplasmic
reticulum golgi intermediate compartment 1 in precancerous gastric
lesions and gastric cancer. Am J Med Sci. 355:228–234. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li A, Xiong J and Chen Z: IL-6, TNF-α, and
iNOS is associated with decreased colonic contraction in rats with
multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. J Surg Res. 178:e51–e57. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee JH, Kim HY, Bae EH, Kim SW and Ma SK:
Biomarkers predicting survival of sepsis patients treated with
continuous renal replacement therapy. Chonnam Med J. 53:64–68.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shimazui T, Matsumura Y, Nakada TA and Oda
S: Serum levels of interleukin-6 may predict organ dysfunction
earlier than SOFA score. Acute Med Surg. 4:255–261. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Seymour CW, Liu VX, Iwashyna TJ,
Brunkhorst FM, Rea TD, Scherag A, Rubenfeld G, Kahn JM,
Shankar-Hari M, Singer M, et al: Assessment of clinical criteria
for sepsis: For the third international consensus definitions for
sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA. 315:762–774. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lee YJ, Park CH, Yun JW and Lee YS:
Predictive comparisons of procalcitonin (PCT) level, arterial
ketone body ratio (AKBR), APACHE III score and multiple organ
dysfunction score (MODS) in systemic inflammatory response syndrome
(SIRS). Yonsei Med J. 45:29–37. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ávalos-López M, Pérez-López MJ,
Aguilar-Martínez C, Díaz-Franco AMC, Esquivel-Chávez A and
Baltazar-Torres JA: Prediction of acute kidney injury in critically
ill patients treated with intermittent hemodialysis versus CRRT.
Rev Med Inst Mex Seguro Soc. 55:696–703. 2017.(In Spanish).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yoon J, Kim Y, Kym D, Hur J, Yim H, Cho YS
and Chun W: Subgroup analysis of continuous renal replacement
therapy in severely burned patients. PLoS One. 12:e01890572017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li YN, Zhou LX, Qiang XH, Yu TO, Mao KJ,
Feng B, Wen WB, Zou YC, Li WY and Li C: Effect of continuous blood
purification and thymosin alpha1 on the cellular immunity in
patients with severe sepsis: A prospective, randomized, controlled
clinical trial. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 21:139–142.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhou R, Weng F, Dai W and Yan J: The organ
protective effects and timing of continuous blood purification in
the treatment of severe sepsis: A double-blind randomized
controlled trial. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue.
28:241–245. 2006.(In Chinese).
|
|
31
|
Sabatino A, Theilla M, Hellerman M, Singer
P, Maggiore U, Barbagallo M, Regolisti G and Fiaccadori E: Energy
and protein in critically ill patients with AKI: A prospective,
multicenter observational study using indirect calorimetry and
protein catabolic rate. Nutrients. 9(pii): E8022017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Allegretti AS, Steele DJ, David-Kasdan JA,
Bajwa E, Niles JL and Bhan I: Continuous renal replacement therapy
outcomes in acute kidney injury and end-stage renal disease: A
cohort study. Crit Care. 17:R1092013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Quinto BM, Iizuka IJ, Monte JC, Santos BF,
Pereira V, Durão MS, Dalboni MA, Cendoroglo M, Santos OF and
Batista MC: TNF-α depuration is a predictor of mortality in
critically ill patients under continuous veno-venous
hemodiafiltration treatment. Cytokine. 71:255–260. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|