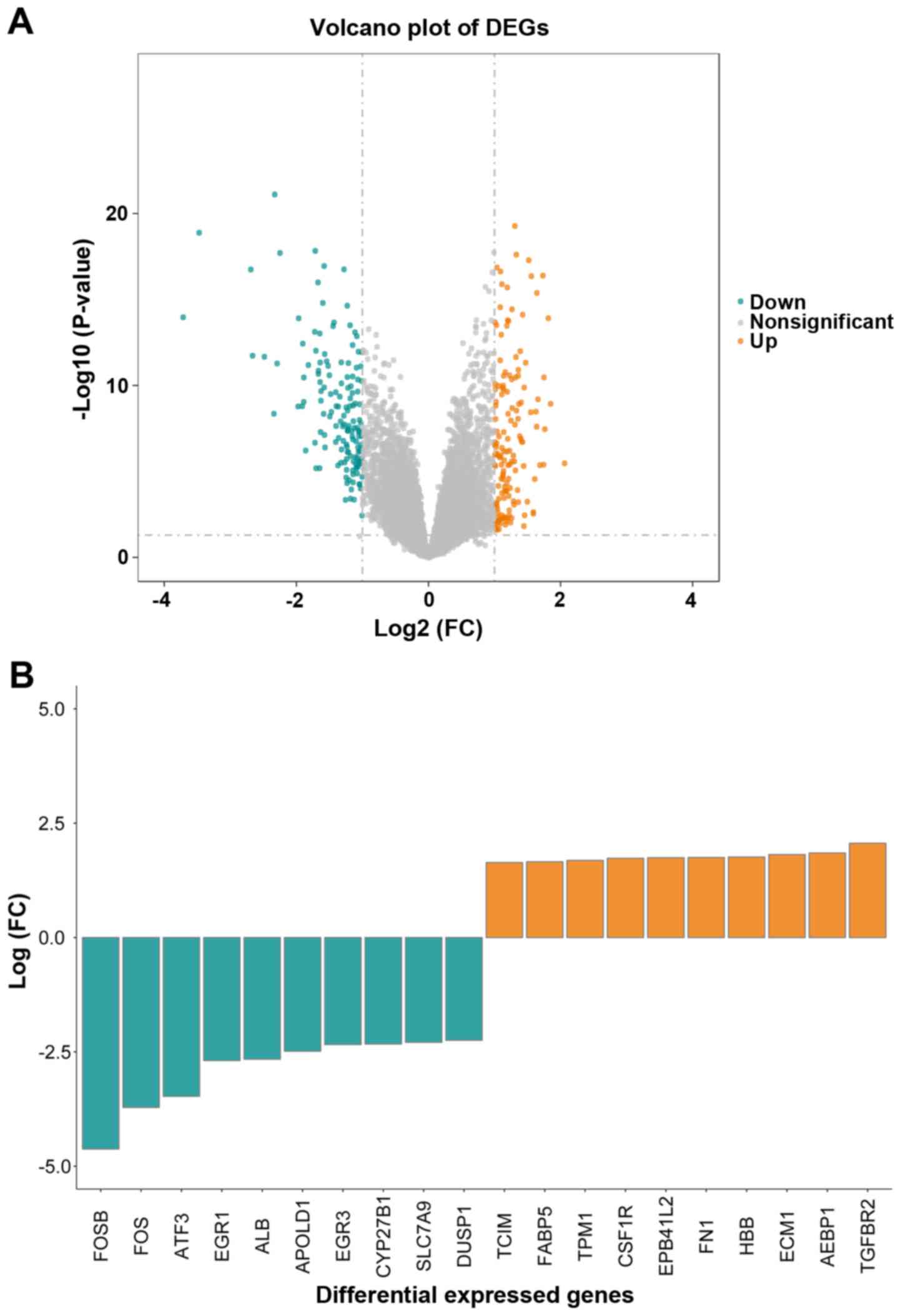
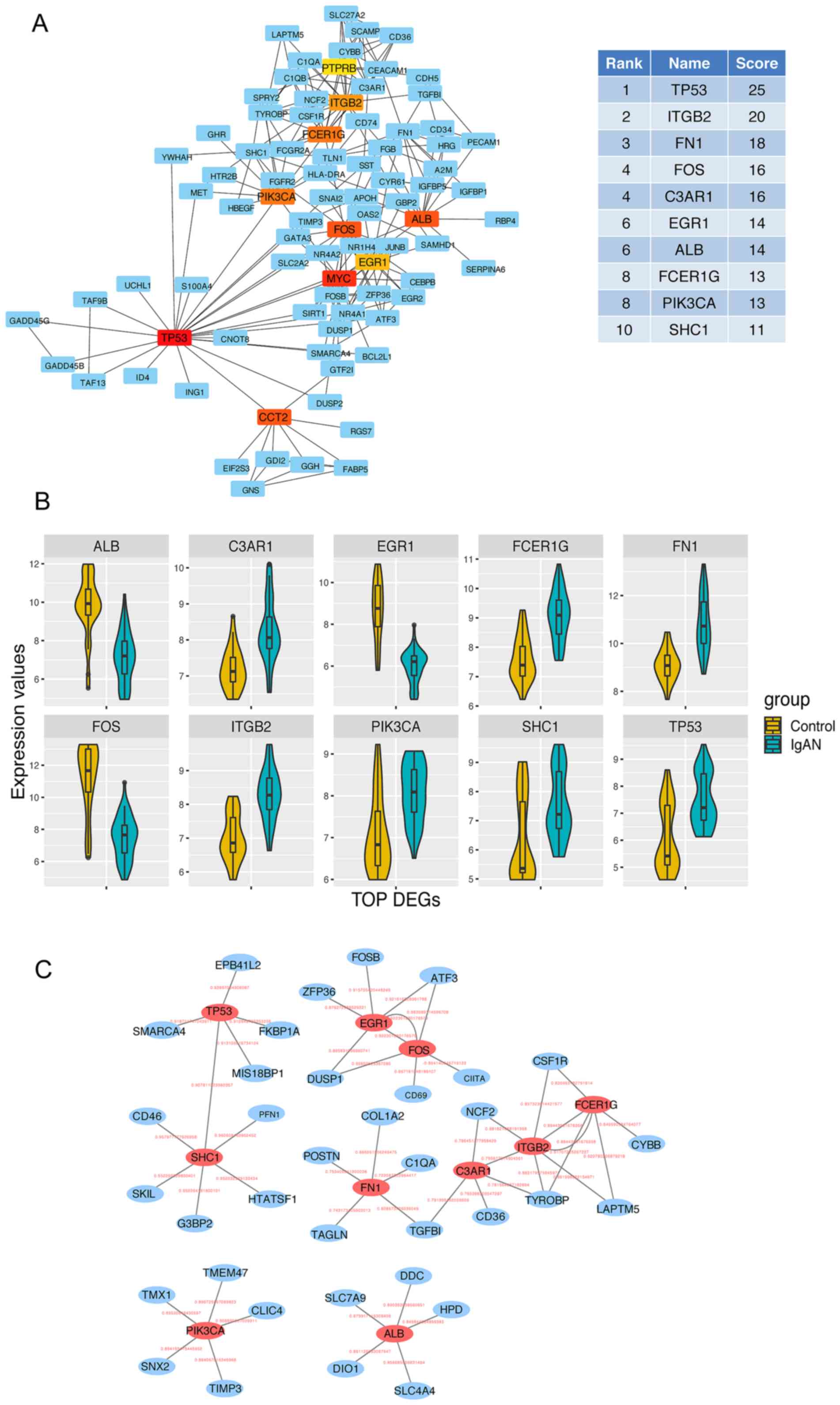
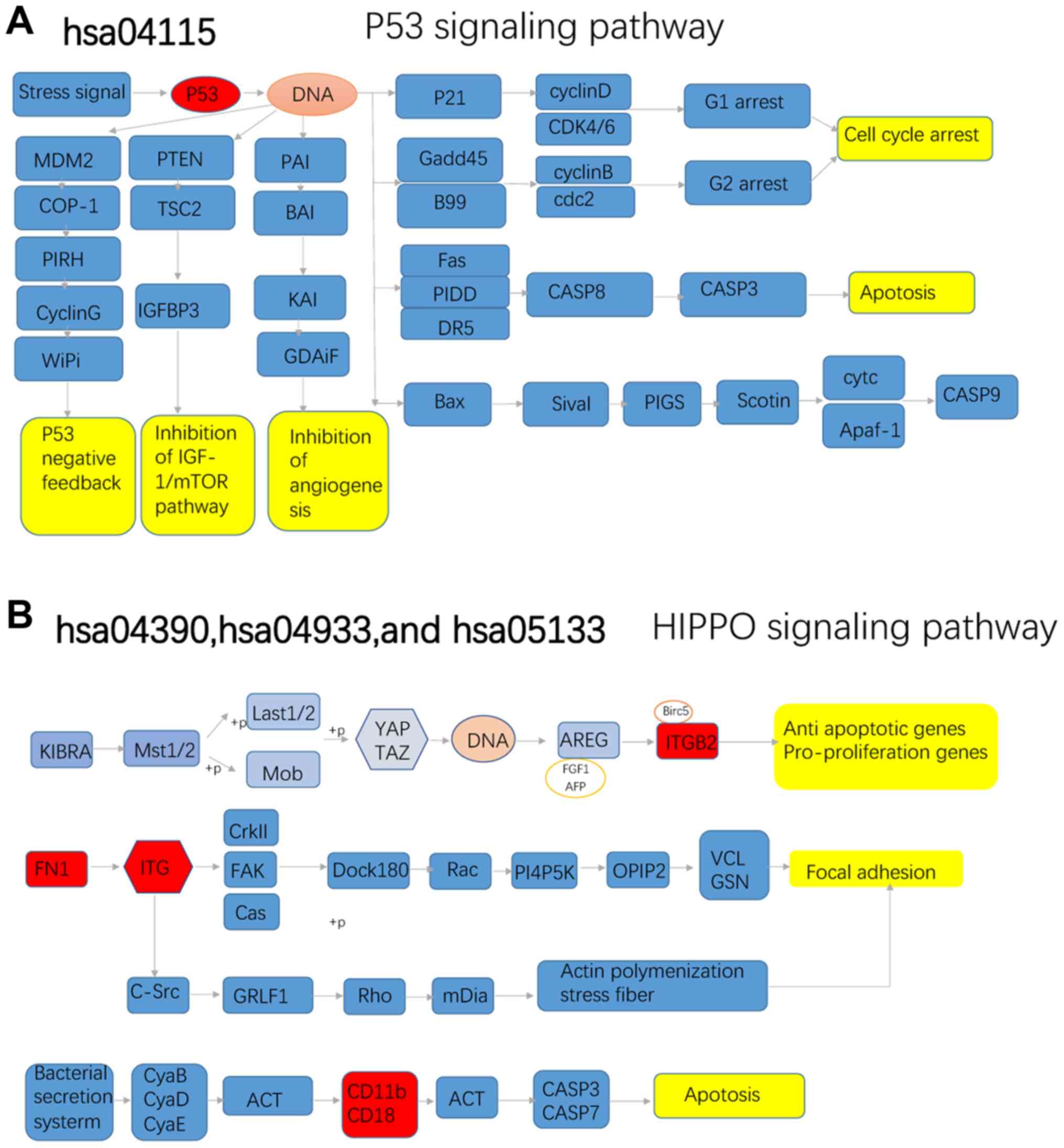
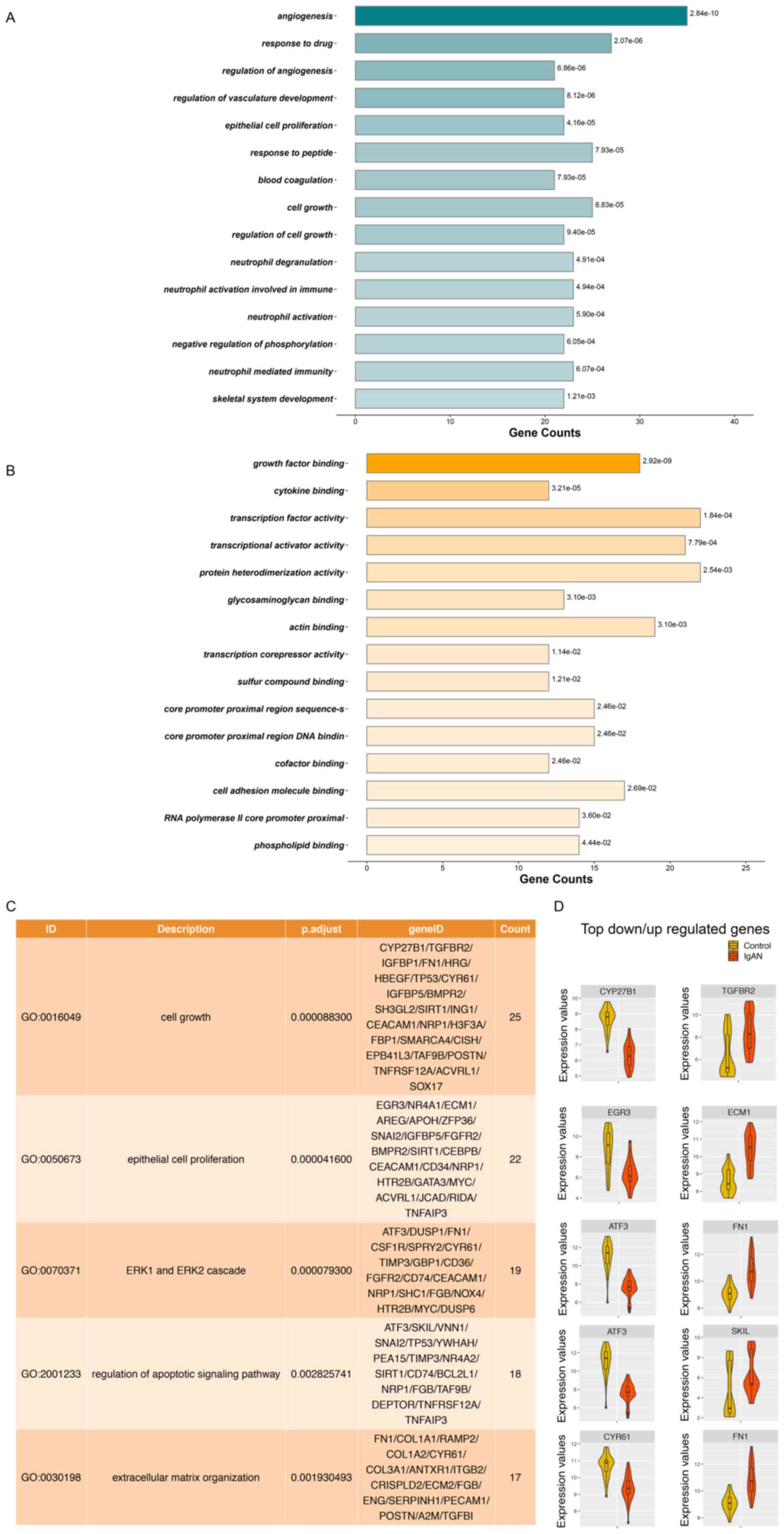
|
1
|
Wyatt RJ and Julian BA: IgA nephropathy. N
Engl J Med. 368:2402–2414. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rodrigues JC, Haas M and Reich HN: IgA
nephropathy. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 12:677–686. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Schena FP: A retrospective analysis of the
natural history of primary IgA nephropathy worldwide. Am J Med.
89:209–215. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhang Y, Yan X, Zhao T, Xu Q, Peng Q, Hu
R, Quan S, Zhou Y and Xing G: Targeting C3a/C5a receptors inhibits
human mesangial cell proliferation and alleviates immunoglobulin A
nephropathy in mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 189:60–70. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rops A, Jansen E, van der Schaaf A,
Pieterse E, Rother N, Hofstra J, Dijkman HBPM, van de Logt AE,
Wetzels J, van der Vlag J and van Spriel AB: Interleukin-6 is
essential for glomerular immunoglobulin A deposition and the
development of renal pathology in Cd37-deficient mice. Kidney Int.
93:1356–1366. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hennino MF, Buob D, Van der Hauwaert C,
Gnemmi V, Jomaa Z, Pottier N, Savary G, Drumez E, Noël C, Cauffiez
C and Glowacki F: miR-21-5p renal expression is associated with
fibrosis and renal survival in patients with IgA nephropathy. Sci
Rep. 6:272092016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tanaka K, Sugiyama H, Yamanari T, Mise K,
Morinaga H, Kitagawa M, Onishi A, Ogawa-Akiyama A, Tanabe K, Eguchi
J, et al: Renal expression of trefoil factor 3 mRNA in association
with tubulointerstitial fibrosis in IgA nephropathy. Nephrology
(Carlton). 23:855–862. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liang S, Jin J, Lin B, Gong J, Li Y and He
Q: Rapamycin induces autophagy and reduces the apoptosis of
podocytes under a stimulated condition of immunoglobulin a
nephropathy. Kidney Blood Press Res. 42:177–187. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Leung JC, Chan LY, Saleem MA, Mathieson
PW, Tang SC and Lai KN: Combined blockade of angiotensin II and
prorenin receptors ameliorates podocytic apoptosis induced by
IgA-activated mesangial cells. Apoptosis. 20:907–920. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rauen T and Floege J: Inflammation in IgA
nephropathy. Pediatr Nephrol. 32:2215–2224. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bao H, Chen H, Zhu X, Zhang M, Yao G, Yu
Y, Qin W, Zeng C, Zen K and Liu Z: MiR-223 downregulation promotes
glomerular endothelial cell activation by upregulating importin α4
and α5 in IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 85:624–635. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hodgin JB, Berthier CC, John R, Grone E,
Porubsky S, Gröne HJ, Herzenberg AM, Scholey JW, Hladunewich M,
Cattran DC, et al: The molecular phenotype of endocapillary
proliferation: Novel therapeutic targets for IgA nephropathy. PLoS
One. 9:e1034132014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang L, Tan RZ, Chen Y, Wang HL, Liu YH,
Wen D and Fan JM: CagA promotes proliferation and secretion of
extracellular matrix by inhibiting signaling pathway of apoptosis
in rat glomerular mesangial cells. Ren Fail. 38:458–464. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cui H, Zhang Y, Zhang Q, Chen W, Zhao H
and Liang J: A comprehensive genome-wide analysis of long noncoding
RNA expression profile in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Med.
6:2932–2941. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tian W, Liu J, Pei B, Wang X, Guo Y and
Yuan L: Identification of miRNAs and differentially expressed genes
in early phase non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Rep. 35:2171–2176.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dong B, Wang G, Yao J, Yuan P, Kang W, Zhi
L and He X: Predicting novel genes and pathways associated with
osteosarcoma by using bioinformatics analysis. Gene. 628:32–37.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu D: LYN, a key gene from bioinformatics
analysis, contributes to development and progression of esophageal
adenocarcinoma. Med Sci Monit Basic Res. 21:253–261. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhou LT, Qiu S, Lv LL, Li ZL, Liu H, Tang
RN, Ma KL and Liu BC: Integrative bioinformatics analysis provides
insight into the molecular mechanisms of chronic kidney disease.
Kidney Blood Press Res. 43:568–581. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shu B, Fang Y, He W, Yang J and Dai C:
Identification of macrophage-related candidate genes in lupus
nephritis using bioinformatics analysis. Cell Signal. 46:43–51.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu P, Lassen E, Nair V, Berthier CC,
Suguro M, Sihlbom C, Kretzler M, Betsholtz C, Haraldsson B, Ju W,
et al: Transcriptomic and proteomic profiling provides insight into
mesangial cell function in IgA nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol.
28:2961–2972. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Berthier CC, Bethunaickan R,
Gonzalez-Rivera T, Nair V, Ramanujam M, Zhang W, Bottinger EP,
Segerer S, Lindenmeyer M, Cohen CD, et al: Cross-species
transcriptional network analysis defines shared inflammatory
responses in murine and human lupus nephritis. J Immunol.
189:988–1001. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shved N, Warsow G, Eichinger F, Hoogewijs
D, Brandt S, Wild P, Kretzler M, Cohen CD and Lindenmeyer MT:
Transcriptome-based network analysis reveals renal cell
type-specific dysregulation of hypoxia-associated transcripts. Sci
Rep. 7:85762017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gautier L, Cope L, Bolstad BM and Irizarry
RA: Affy-analysis of affymetrix GeneChip data at the probe level.
Bioinformatics. 20:307–315. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Forero DA, Guio-Vega GP and
Gonzalez-Giraldo Y: A comprehensive regional analysis of
genome-wide expression profiles for major depressive disorder. J
Affect Disord. 218:86–92. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Leek JT, Johnson WE, Parker HS, Jaffe AE
and Storey JD: The sva package for removing batch effects and other
unwanted variation in high-throughput experiments. Bioinformatics.
28:882–883. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Diboun I, Wernisch L, Orengo CA and
Koltzenburg M: Microarray analysis after RNA amplification can
detect pronounced differences in gene expression using limma. BMC
Genomics. 7:2522006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y and He QY:
ClusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among
gene clusters. OMICS. 16:284–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Szklarczyk D, Morris JH, Cook H, Kuhn M,
Wyder S, Simonovic M, Santos A, Doncheva NT, Roth A, Bork P, et al:
The STRING database in 2017: Quality-controlled protein-protein
association networks, made broadly accessible. Nucleic Acids Res.
45:D362–D368. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kohl M, Wiese S and Warscheid B:
Cytoscape: Software for visualization and analysis of biological
networks. Methods Mol Biol. 696:291–303. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chin CH, Chen SH, Wu HH, Ho CW, Ko MT and
Lin CY: cytoHubba: Identifying hub objects and sub-networks from
complex interactome. BMC Syst Biol. 8 (Suppl 4):S112014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kawai Y, Masutani K, Torisu K, Katafuchi
R, Tanaka S, Tsuchimoto A, Mitsuiki K, Tsuruya K and Kitazono T:
Association between serum albumin level and incidence of end-stage
renal disease in patients with immunoglobulin A nephropathy: A
possible role of albumin as an antioxidant agent. PLoS One.
13:e01966552018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Park HJ, Kim JW, Cho BS and Chung JH:
Association of FOS-like antigen 1 promoter polymorphism with
podocyte foot process effacement in immunoglobulin A nephropathy
patients. J Clin Lab Anal. 28:391–397. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Qiu LQ, Sinniah R and Hsu SI: Coupled
induction of iNOS and p53 upregulation in renal resident cells may
be linked with apoptotic activity in the pathogenesis of
progressive IgA nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 15:2066–2078. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Boguslawska J, Kedzierska H, Poplawski P,
Rybicka B, Tanski Z and Piekielko-Witkowska A: Expression of genes
involved in cellular adhesion and extracellular matrix remodeling
correlates with poor survival of patients with renal cancer. J
Urol. 195:1892–1902. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Livingston MJ, Ding HF, Huang S, Hill JA,
Yin XM and Dong Z: Persistent activation of autophagy in kidney
tubular cells promotes renal interstitial fibrosis during
unilateral ureteral obstruction. Autophagy. 12:976–998. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Glasner A, Levi A, Enk J, Isaacson B,
Viukov S, Orlanski S, Scope A, Neuman T, Enk CD, Hanna JH, et al:
NKp46 receptor-mediated interferon-γ production by natural killer
cells increases fibronectin 1 to alter tumor architecture and
control metastasis. Immunity. 48:107–119.e4. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jovanovic KK, Escure G, Demonchy J,
Willaume A, Van de Wyngaert Z, Farhat M, Chauvet P, Facon T,
Quesnel B and Manier S: Deregulation and targeting of TP53 pathway
in multiple myeloma. Front Oncol. 8:6652019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yogosawa S and Yoshida K: Tumor
suppressive role for kinases phosphorylating p53 in DNA
damage-induced apoptosis. Cancer Sci. 109:3376–3382. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang SZ, Qiu XJ, Dong SS, Zhou LN, Zhu Y,
Wang MD and Jin LW: MicroRNA-770-5p is involved in the development
of diabetic nephropathy through regulating podocyte apoptosis by
targeting TP53 regulated inhibitor of apoptosis 1. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 23:1248–1256. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chen SN, Lombardi R, Karmouch J, Tsai JY,
Czernuszewicz G, Taylor MRG, Mestroni L, Coarfa C, Gurha P and
Marian AJ: DNA damage Response/TP53 pathway is activated and
contributes to the pathogenesis of dilated cardiomyopathy
associated With LMNA (Lamin A/C) mutations. Circ Res. 124:856–873.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu GC, Zhou YF, Su XC and Zhang J:
Interaction between TP53 and XRCC1 increases susceptibility to
cervical cancer development: A case control study. BMC Cancer.
19:242019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Robin M, Issa AR, Santos CC, Napoletano F,
Petitgas C, Chatelain G, Ruby M, Walter L, Birman S, Domingos PM,
et al: Drosophila p53 integrates the antagonism between autophagy
and apoptosis in response to stress. Autophagy. 15:771–784. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Dai J, Xu LJ, Han GD, Jiang HT, Sun HL,
Zhu GT and Tang XM: Down-regulation of long non-coding RNA
ITGB2-AS1 inhibits osteosarcoma proliferation and metastasis by
repressing Wnt/β-catenin signalling and predicts favourable
prognosis. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 46 (Suppl 3):S783–S790.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Liu H, Dai X, Cao X, Yan H, Ji X, Zhang H,
Shen S, Si Y, Zhang H, Chen J, et al: PRDM4 mediates YAP-induced
cell invasion by activating leukocyte-specific integrin β2
expression. EMBO Rep. 19(pii): e451802018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Aziz MH, Cui K, Das M, Brown KE, Ardell
CL, Febbraio M, Pluskota E, Han J, Wu H, Ballantyne CM, et al: The
upregulation of integrin αDβ2 (CD11d/CD18) on inflammatory
macrophages promotes macrophage retention in vascular lesions and
development of atherosclerosis. J Immunol. 198:4855–4867. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kijas JM, Bauer TR Jr, Gafvert S, Marklund
S, Trowald-Wigh G, Johannisson A, Hedhammar A, Binns M, Juneja RK,
Hickstein DD and Andersson L: A missense mutation in the beta-2
integrin gene (ITGB2) causes canine leukocyte adhesion deficiency.
Genomics. 61:101–107. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yee NK and Hamerman JA: β(2) integrins
inhibit TLR responses by regulating NF-κB pathway and p38 MAPK
activation. Eur J Immunol. 43:779–792. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Duan J, Zhang X, Zhang S, Hua S and Feng
Z: miR-206 inhibits FN1 expression and proliferation and promotes
apoptosis of rat type II alveolar epithelial cells. Exp Ther Med.
13:3203–3208. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wang J, Deng L, Huang J, Cai R, Zhu X, Liu
F, Wang Q, Zhang J and Zheng Y: High expression of Fibronectin 1
suppresses apoptosis through the NF-κB pathway and is associated
with migration in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Am J Transl Res.
9:4502–4511. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Liu C, Feng Z, Chen T, Lv J, Liu P, Jia L,
Zhu J, Chen F, Yang C and Deng Z: Downregulation of NEAT1 reverses
the radioactive iodine resistance of papillary thyroid carcinoma
cell via miR-101-3p/FN1/PI3K-AKT signaling pathway. Cell Cycle.
18:167–203. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Liao YX, Zhang ZP, Zhao J and Liu JP:
Effects of Fibronectin 1 on cell proliferation, senescence and
apoptosis of human glioma cells through the PI3K/AKT signaling
pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 48:1382–1396. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Bakiri L, Hamacher R, Grana O,
Guío-Carrión A, Campos-Olivas R, Martinez L, Dienes HP, Thomsen MK,
Hasenfuss SC and Wagner EF: Liver carcinogenesis by FOS-dependent
inflammation and cholesterol dysregulation. J Exp Med.
214:1387–1409. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Xu X, Kwon OK, Shin IS, Mali JR, Harmalkar
DS, Lim Y, Lee G, Lu Q, Oh SR, Ahn KS, et al: Novel benzofuran
derivative DK-1014 attenuates lung inflammation via blocking of
MAPK/AP-1 and AKT/mTOR signaling in vitro and in vivo. Sci Rep.
9:8622019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Chen M, Li X, Shi Q, Zhang Z and Xu S:
Hydrogen sulfide exposure triggers chicken trachea inflammatory
injury through oxidative stress-mediated FOS/IL8 signaling. J
Hazard Mater. 368:243–254. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Nagesh R, Kiran Kumar KM, Naveen Kumar M,
Patil RH and Sharma SC: Stress activated p38 MAPK regulates cell
cycle via AP-1 factors in areca extract exposed human lung
epithelial cells. Cytotechnology. 71:507–520. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Wu DM, Zhang YT, Lu J and Zheng YL:
Effects of microRNA-129 and its target gene c-Fos on proliferation
and apoptosis of hippocampal neurons in rats with epilepsy via the
MAPK signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol. 233:6632–6643. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Liu C, Ding L, Bai L, Chen X, Kang H, Hou
L and Wang J: Folate receptor alpha is associated with cervical
carcinogenesis and regulates cervical cancer cells growth by
activating ERK1/2/c-Fos/c-Jun. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
491:1083–1091. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Hwang MS, Strainic MG, Pohlmann E, Kim H,
Pluskota E, Ramirez-Bergeron DL, Plow EF and Medof ME: VEGFR2
survival and mitotic signaling depends on joint-activation of
associated C3ar1/C5ar1 and IL-6R-gp130. J Cell Sci. 132(pii):
jcs2193522019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Mathern DR, K Horwitz J and Heeger PS:
Absence of recipient C3aR1 signaling limits expansion and
differentiation of alloreactive CD8+ T cell immunity and
prolongs murine cardiac allograft survival. Am J Transplant.
198:1628–1640. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Matsumoto N, Satyam A, Geha M, Lapchak PH,
Dalle Lucca JJ, Tsokos MG and Tsokos GC: C3a enhances the formation
of intestinal organoids through C3aR1. Front Immunol. 8:10462017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Lokman FE, Seman NA, Ismail AA, Yaacob NA,
Mustafa N, Khir AS, Hussein Z and Wan Mohamud WN: Gene expression
profiling in ethnic Malays with type 2 diabetes mellitus, with and
without diabetic nephropathy. J Nephrol. 24:778–789. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Wang D, Guan MP, Zheng ZJ, Li WQ, Lyv FP,
Pang RY and Xue YM: Transcription factor Egr1 is involved in high
glucose-induced proliferation and fibrosis in rat glomerular
mesangial cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 36:2093–2107. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Liu F, Zhang ZP, Xin GD, Guo LH, Jiang Q
and Wang ZX: miR-192 prevents renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis in
diabetic nephropathy by targeting Egr1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
22:4252–4260. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Wu C, Ma X, Zhou Y, Liu Y, Shao Y and Wang
Q: Klotho restraining Egr1/TLR4/mTOR axis to reducing the
expression of fibrosis and inflammatory cytokines in high glucose
cultured rat mesangial cells. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. Jun
11–2018.(Epub ahead of print). doi: 10.1055/s-0044-101601.
|
|
65
|
Hu F, Xue M, Li Y, Jia YJ, Zheng ZJ, Yang
YL, Guan MP, Sun L and Xue YM: Early growth response 1 (Egr1) is a
transcriptional activator of NOX4 in oxidative stress of diabetic
kidney disease. J Diabetes Res. 2018:34056952018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Li Y, Hu F, Xue M, Jia YJ, Zheng ZJ, Wang
L, Guan MP and Xue YM: Klotho down-regulates Egr-1 by inhibiting
TGF-β1/Smad3 signaling in high glucose treated human mesangial
cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 487:216–222. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Wu SY, Rupaimoole R, Shen F, Pradeep S,
Pecot CV, Ivan C, Nagaraja AS, Gharpure KM, Pham E, Hatakeyama H,
et al: A miR-192-EGR1-HOXB9 regulatory network controls the
angiogenic switch in cancer. Nat Commun. 7:111692016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Sun S, Ning X, Zhai Y, Du R, Lu Y, He L,
Li R, Wu W, Sun W and Wang H: Egr-1 mediates chronic
hypoxia-induced renal interstitial fibrosis via the PKC/ERK
pathway. Am J Nephrol. 39:436–448. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Lin CY, Lin TY, Lee MC, Chen SC and Chang
JS: Hyperglycemia: GDNF-EGR1 pathway target renal epithelial cell
migration and apoptosis in diabetic renal embryopathy. PLoS One.
8:e567312013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Singh R, Yadav V, Kumar S and Saini N:
MicroRNA-195 inhibits proliferation, invasion and metastasis in
breast cancer cells by targeting FASN, HMGCR, ACACA and CYP27B1.
Sci Rep. 5:174542015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Banks M and Holick MF: Molecular
mechanism(s) involved in 25-hydroxyvitamin D's antiproliferative
effects in CYP27B1-transfected LNCaP cells. Anticancer Res.
35:3773–3779. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Li G, Wu F, Yang H, Deng X and Yuan Y:
MiR-9-5p promotes cell growth and metastasis in non-small cell lung
cancer through the repression of TGFBR2. Biomed Pharmacother.
96:1170–1178. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Ebefors K, Liu P, Lassén E, Elvin J,
Candemark E, Levan K, Haraldsson B and Nyström J: Mesangial cells
from patients with IgA nephropathy have increased susceptibility to
galactose-deficient IgA1. BMC Nephrol. 17:402016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
You Z, Xu J, Li B, Ye H, Chen L, Liu Y and
Xiong X: The mechanism of ATF3 repression of epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and suppression of cell viability in cholangiocarcinoma
via p53 signal pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 23:2184–2193. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Hsu YJ, Hsu SC, Chang YL, Huang SM, Shih
CC, Tsai CS and Lin CY: Indoxyl sulfate upregulates the cannabinoid
type 1 receptor gene via an ATF3/c-Jun complex-mediated signaling
pathway in the model of uremic cardiomyopathy. Int J Cardiol.
252:128–135. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Armstrong HK, Gillis JL, Johnson IRD,
Nassar ZD, Moldovan M, Levrier C, Sadowski MC, Chin MY, Tomlinson
Guns ES, Tarulli G, et al: Dysregulated fibronectin trafficking by
Hsp90 inhibition restricts prostate cancer cell invasion. Sci Rep.
8:20902018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Wei X, Zhou D, Wang H, Ding N, Cui XX,
Wang H, Verano M, Zhang K, Conney AH, Zheng X and DU ZY: Effects of
pyridine analogs of curcumin on growth, apoptosis and NF-κB
activity in prostate cancer PC-3 cells. Anticancer Res.
33:1343–1350. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Bork P: The modular architecture of a new
family of growth regulators related to connective tissue growth
factor. FEBS Lett. 327:125–130. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Chen CC and Lau LF: Functions and
mechanisms of action of CCN matricellular proteins. Int J Biochem
Cell Biol. 41:771–783. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Quan T, He T, Shao Y, Lin L, Kang S,
Voorhees JJ and Fisher GJ: Elevated cysteine-rich 61 mediates
aberrant collagen homeostasis in chronologically aged and photoaged
human skin. Am J Pathol. 169:482–490. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Mizwicki MT, Liu G, Fiala M, Magpantay L,
Sayre J, Siani A, Mahanian M, Weitzman R, Hayden EY, Rosenthal MJ,
et al: 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and resolvin D1 retune the balance
between amyloid-β phagocytosis and inflammation in Alzheimer's
disease patients. J Alzheimers Dis. 34:155–170. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Carl M, Akagi Y, Weidner S, Isaka Y, Imai
E and Rupprecht HD: Specific inhibition of Egr-1 prevents mesangial
cell hypercellularity in experimental nephritis. Kidney Int.
63:1302–1312. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Mohamad T, Kazim N, Adhikari A and Davie
JK: EGR1 interacts with TBX2 and functions as a tumor suppressor in
rhabdomyosarcoma. Oncotarget. 9:18084–18098. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Carver KA, Smith TL, Gallagher PE and
Tallant EA: Angiotensin-(1–7) prevents angiotensin II-induced
fibrosis in cremaster microvessels. Microcirculation. 22:19–27.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Heider A and Alt R: virtualArray: A
R/bioconductor package to merge raw data from different microarray
platforms. BMC Bioinformatics. 14:752013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Tokunaga K, Uto H, Takami Y, Mera K,
Nishida C, Yoshimine Y, Fukumoto M, Oku M, Sogabe A, Nosaki T, et
al: Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 levels are
increased in patients with IgA nephropathy. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 399:144–149. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|