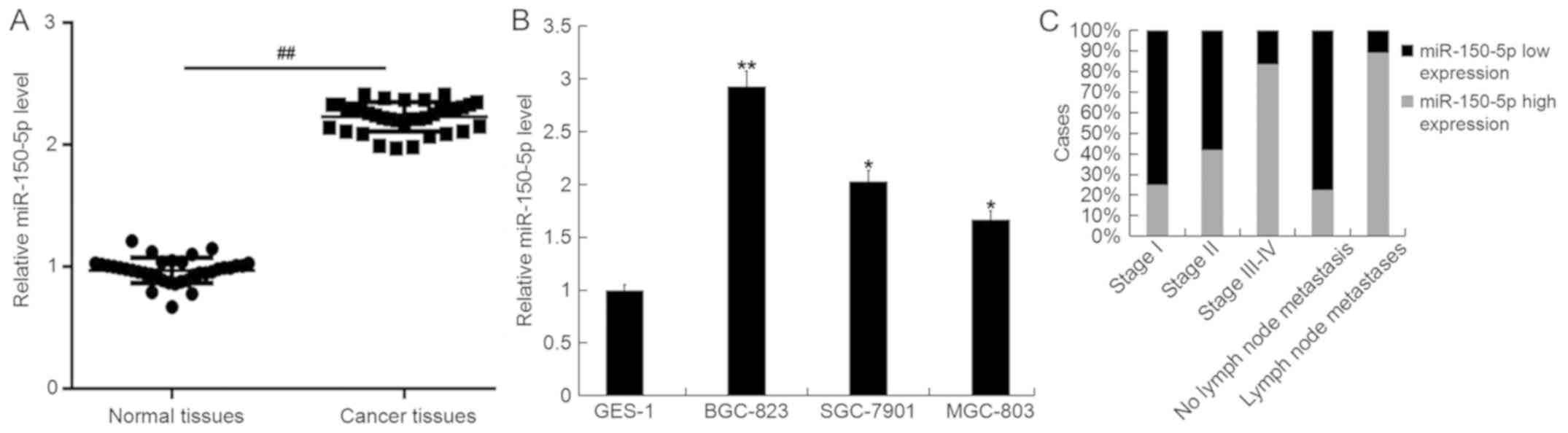
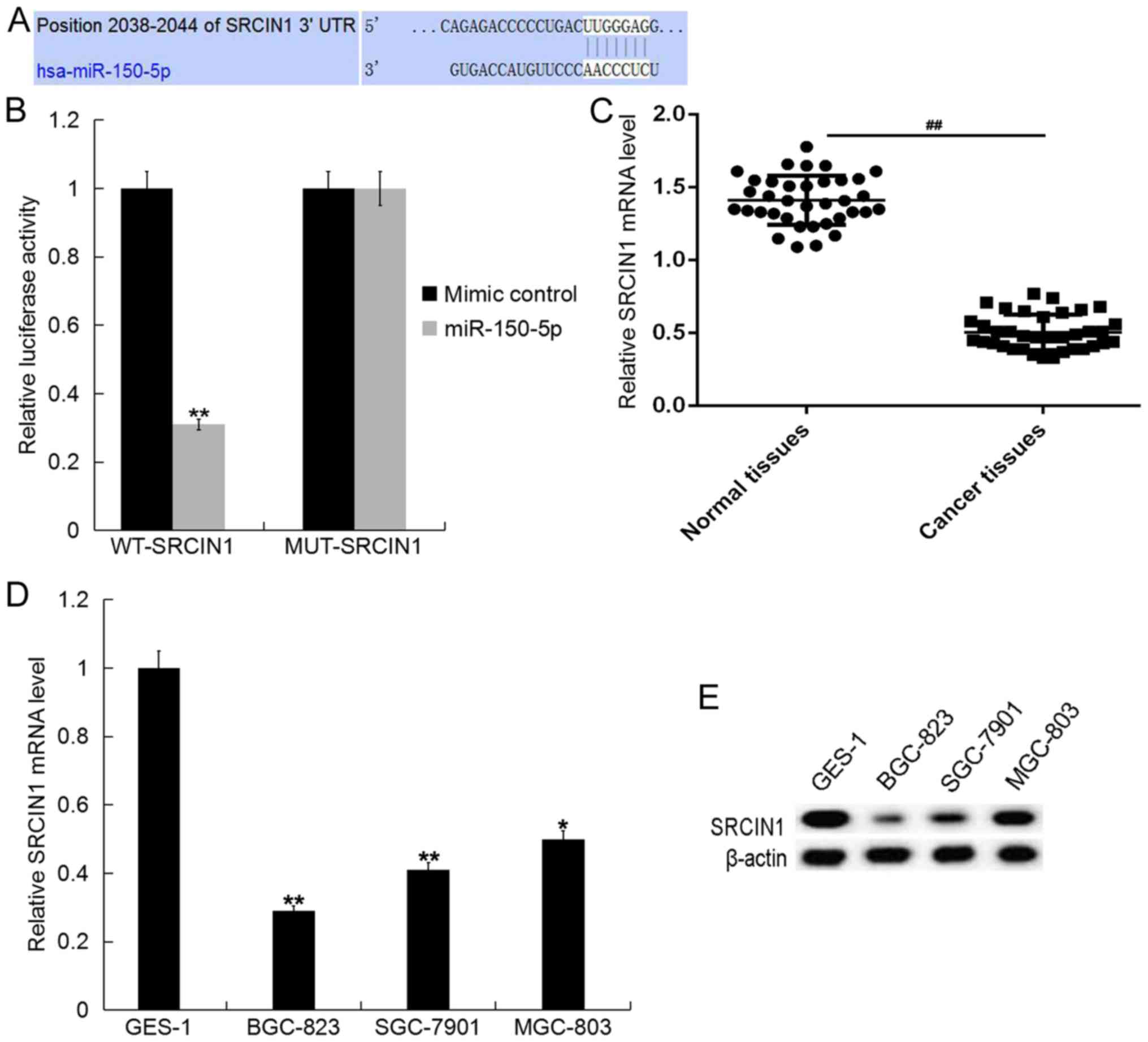
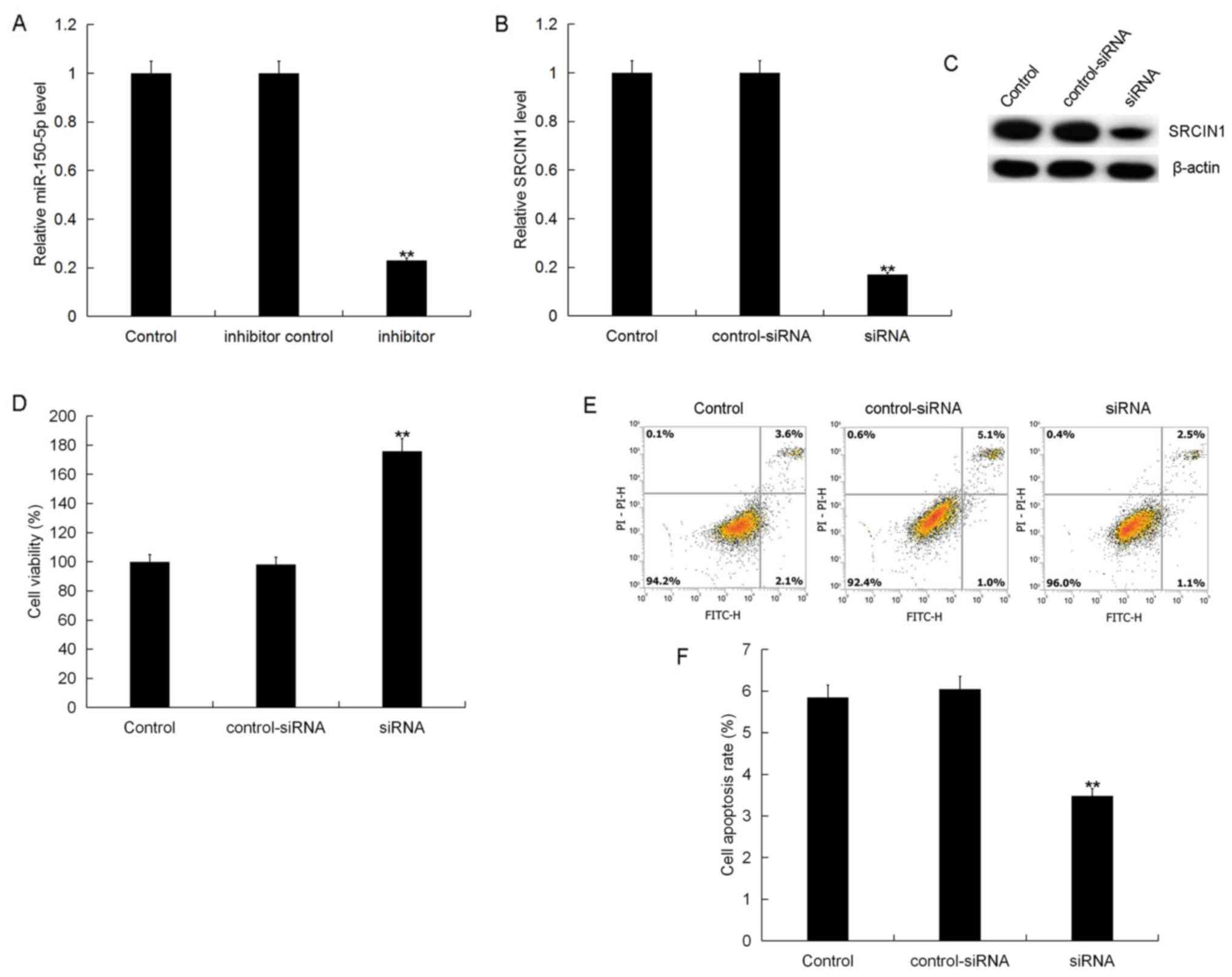
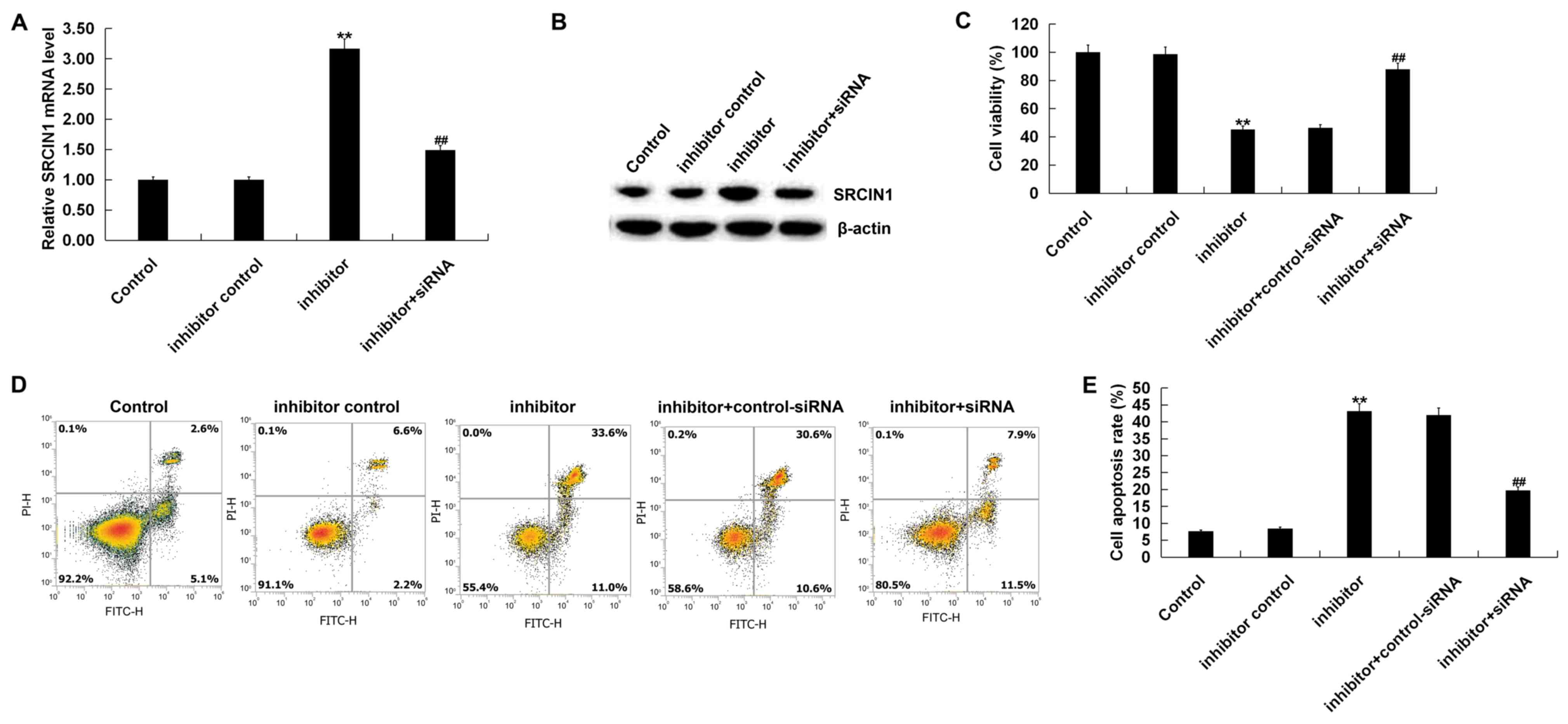
|
1
|
Yu ZY, Wang Z, Lee KY, Yuan P and Ding J:
Effect of silencing colon cancer-associated transcript 2 on the
proliferation, apoptosis and autophagy of gastric cancer BGC-823
cells. Oncol Lett. 15:3127–3132. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Salem M, Xiu J, Eldeiry W, Reddy S, Philip
P, Gatalica Z, Khan S, Denlinger C, Mikhail S, Smaglo B, et al:
Comparative molecular analyses of esophageal adenocarcinoma,
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and gastric adenocarcinoma, and
impact of molecular profile on outcome. Ann Oncol. 27:ii119. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Fu L, Yin F, Li XR, Han BK, Zhang C, Wang
JW, Wang YQ, Bi YF and Liu HM: Generation and characterization of a
paclitaxel-resistant human gastric carcinoma cell line. Anticancer
Drugs. 1:491–502. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Yang BF, Cai W and Chen B: LncRNA SNHG12
regulated the proliferation of gastric carcinoma cell BGC-823 by
targeting microRNA-199a/b-5p. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
22:1297–1306. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu L, Si N, Ma Y, Ge D, Yu X, Fan A, Wang
X, Hu J, Wei P, Ma L, et al: Hydroxysafflor-yellow A induces human
gastric carcinoma BGC-823 cell apoptosis by activating peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ). Med Sci Monit.
24:803–811. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rothmiller S, Wolf M, Worek F, Steinritz
D, Thiermann H and Schmidt A: Alteration of miRNA expression in a
sulfur mustard resistant cell line. Toxicol Lett. 293:38–44. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ultimo S, Martelli AM, Zauli G, Vitale M,
Calin GA and Neri LM: Roles and clinical implications of MicroRNAs
in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Cell Physiol. 233:5642–5654.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sheng N, Zhang L and Yang S: MicroRNA-429
decreases the invasion ability of gastric cancer cell line BGC-823
by downregulating the expression of heparanase. Exp Ther Med.
15:1927–1933. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Meng Y, Tian H, Hu Q, Liang H, Zeng L and
Xiao H: MicroRNA repertoire and comparative analysis of Andrias
davidianus infected with ranavirus using deep sequencing. Dev Comp
Immunol. 85:108–114. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yan J, Li X, Peng L, Shen X, Dang Y and
Zhang G: MicroRNA-150 as a potential biomarker in diagnosis of
cancer: A meta-analysis. Clin Lab. 63:1187–1197. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li C, Du X, Xia S and Chen L: MicroRNA-150
inhibits the proliferation and metastasis potential of colorectal
cancer cells by targeting iASPP. Oncol Rep. 40:252–260.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tang W, Xu P, Wang H, Niu Z, Zhu D, Lin Q,
Tang L and Ren L: MicroRNA-150 suppresses triple-negative breast
cancer metastasis through targeting HMGA2. Onco Targets Ther.
11:2319–2332. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sun X, Zhang C, Cao Y and Liu E: miR-150
suppresses tumor growth in melanoma through downregulation of MYB.
Oncol Res. 27:317–323. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang Z, Wang J, Li J, Wang X and Song W:
MicroRNA-150 promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion of
cervical cancer through targeting PDCD4. Biomed Pharmacother.
97:511–517. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Koshizuka K, Hanazawa T, Kikkawa N, Katada
K, Okato A, Arai T, Idichi T, Osako Y, Okamoto Y and Seki N:
Antitumor miR-150-5p and miR-150-3p, inhibit cancer cell
aggressiveness by targeting SPOCK1, in head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma. Auris Nasus Larynx. 45:854–865. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yan R, Yang T, Zhai H, Zhou Z, Gao L and
Li Y: MicroRNA-150-5p affects cell proliferation, apoptosis and EMT
by regulation of the BRAFV600E mutation in papillary thyroid cancer
cells. J Cell Biochem. 119:8763–8772. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ergun S, Güney S, Temiz E, Petrovic N and
Gunes S: Significance of Mir-15a-5p and Cnksr3 as novel prognostic
biomarkers in non-small cell lung cancer. Anticancer Agents Med
Chem. 18:1695–1701. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yu J, Feng Y, Wang Y and An R: Aryl
hydrocarbon receptor enhances the expression of miR-150-5p to
suppress in prostate cancer progression by regulating MAP3K12. Arch
Biochem Biophys. 654:47–54. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Suetsugu T, Koshizuka K, Seki N, Mizuno K,
Okato A, Arai T, Misono S, Uchida A, Kumamoto T and Inoue H:
Downregulation of matrix metalloproteinase 14 by the antitumor
miRNA, miR-150-5p, inhibits the aggressiveness of lung squamous
cell carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol. 52:913–924. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang S, Yan Y, Cheng Z, Hu Y and Liu T:
Sotetsuflavone suppresses invasion and metastasis in non-small-cell
lung cancer A549 cells by reversing EMT via the TNF-α/NF-κB and
PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Cell Death Discov. 4:262018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zuo L, Zhao H, Yang R, Wang L, Ma H, Xu X,
Zhou P and Kong L: Lamin A/C might be involved in the EMT
signalling pathway. Gene. 663:51–64. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang Y, Gao M, Lin Z, Chen L, Jin Y, Zhu
G, Wang Y and Jin T: DEK promoted EMT and angiogenesis through
regulating PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in triple-negative breast cancer.
Oncotarget. 8:98708–98722. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pal M, Bhattacharya S, Kalyan G and Hazra
S: Cadherin profiling for therapeutic interventions in Epithelial
Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) and tumorigenesis. Exp Cell Res.
368:137–146. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ma Z, Xin Z, Hu W, Jiang S, Yang Z, Yan X,
Li X, Yang Y and Chen F: Forkhead box O proteins: Crucial
regulators of cancer EMT. Semin Cancer Biol. 50:21–31. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu CY, Lin HH, Tang MJ and Wang YK:
Vimentin contributes to epithelial-mesenchymal transition cancer
cell mechanics by mediating cytoskeletal organization and focal
adhesion maturation. Oncotarget. 6:15966–15983. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shang S, Hua F and Hu ZW: The regulation
of β-catenin activity and function in cancer: Therapeutic
opportunities. Oncotarget. 8:33972–33989. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zihni C, Mills C, Matter K and Balda MS:
Tight junctions: From simple barriers to multifunctional molecular
gates. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 17:564–580. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mellis D and Caporali A: MicroRNA-based
therapeutics in cardiovascular disease: Screening and delivery to
the target. Biochem Soc Trans. 46:11–21. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cao DD, Li L and Chan WY: MicroRNAs: Key
regulators in the central nervous system and their implication in
neurological diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 17(pii): E8422016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mannucci C, Casciaro M, Minciullo PL,
Calapai G, Navarra M and Gangemi S: Involvement of microRNAs in
skin disorders: A literature review. Allergy Asthma Proc. 38:9–15.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hu L, Ai J, Long H, Liu W, Wang X, Zuo Y,
Li Y, Wu Q and Deng Y: Intergrative microRNA and gene profiling
data analysis reveals novel biomarkers and mechanisms for lung
cancer. Oncotarget. 7:8441–8454. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tsai MM, Wang CS, Tsai CY, Huang HW, Chi
HC, Lin YH, Lu PH and Lin KH: Potential diagnostic, prognostic and
therapeutic targets of microRNAs in human gastric cancer. Int J Mol
Sci. 17(pii): E9452016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhao H, Li M, Li L, Yang X, Lan G and
Zhang Y: MiR-133b is down-regulated in human osteosarcoma and
inhibits osteosarcoma cells proliferation, migration and invasion
and promotes apoptosis. PLoS One. 8:e835712013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kaukoniemi KM, Rauhala HE, Scaravilli M,
Latonen L, Annala M, Vessella RL, Nykter M, Tammela TL and
Visakorpi T: Epigenetically altered miR-193b targets cyclin D1 in
prostate cancer. Cancer Med. 4:1417–1425. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Schmidt A, Steinritz D, Thiermann H,
Meineke V and Abend M: Alteration of miRNA expression in early
endothelial cells after exposure with sub-lethal sulfur mustard
concentrations. Toxicol Lett. 244:88–94. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gharbi S, Khateri S, Soroush MR, Shamsara
M, Naeli P, Najafi A, Korsching E and Mowla SJ: MicroRNA expression
in serum samples of sulfur mustard veterans as a diagnostic gateway
to improve care. PLoS One. 13:e01945302018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ma M, Zhao J, Wu Q, Xiao K, Li S, Zhu H,
Liu C, Xie H and Zuo C: MiRNA-545 negatively regulates the
oncogenic activity of EMS1 in gastric cancer. Cancer Med.
7:2452–2462. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liao Y, Liao Y, Li J, Xiao K, Li S, Zhu H,
Liu C, Xie H and Zuo C: Genetic variants in miRNA machinery genes
associated with clinicopathological characteristics and outcomes of
gastric cancer patients. Int J Biol Markers. 33:301–307. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|