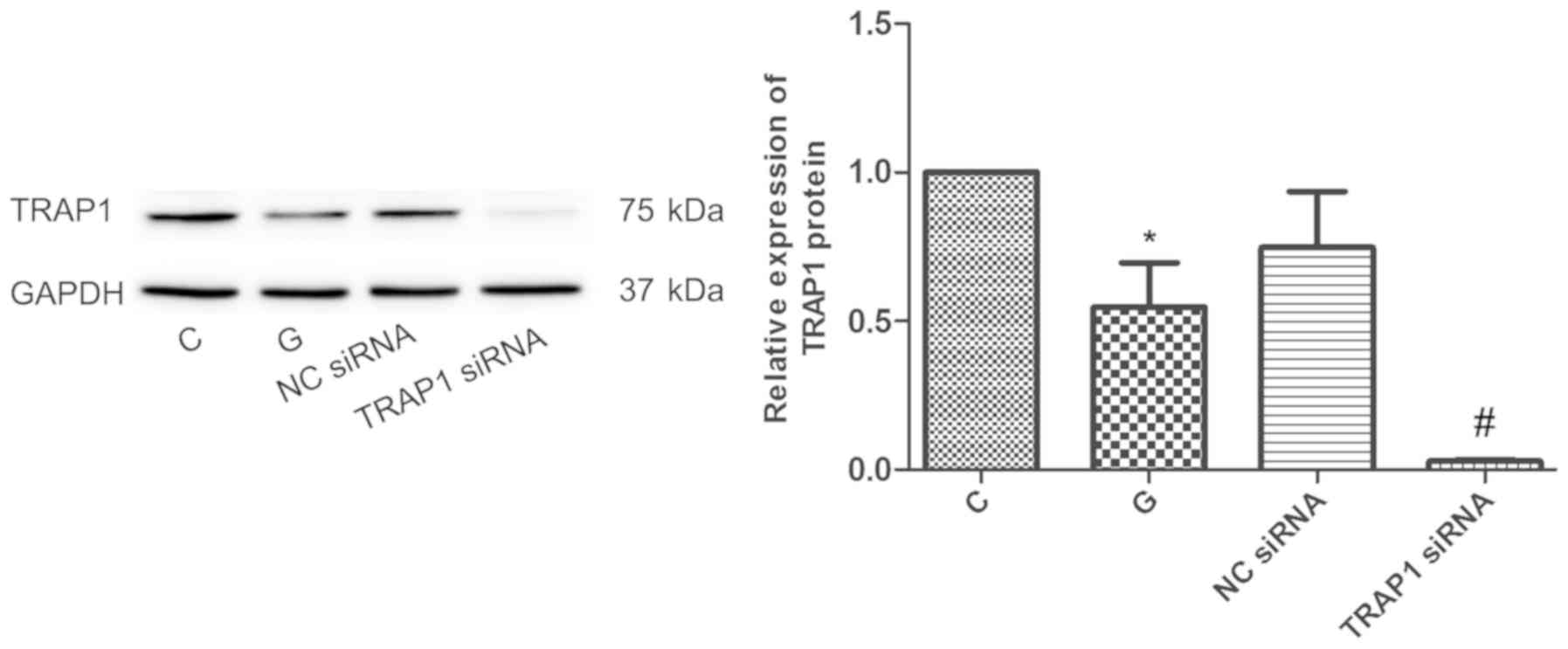
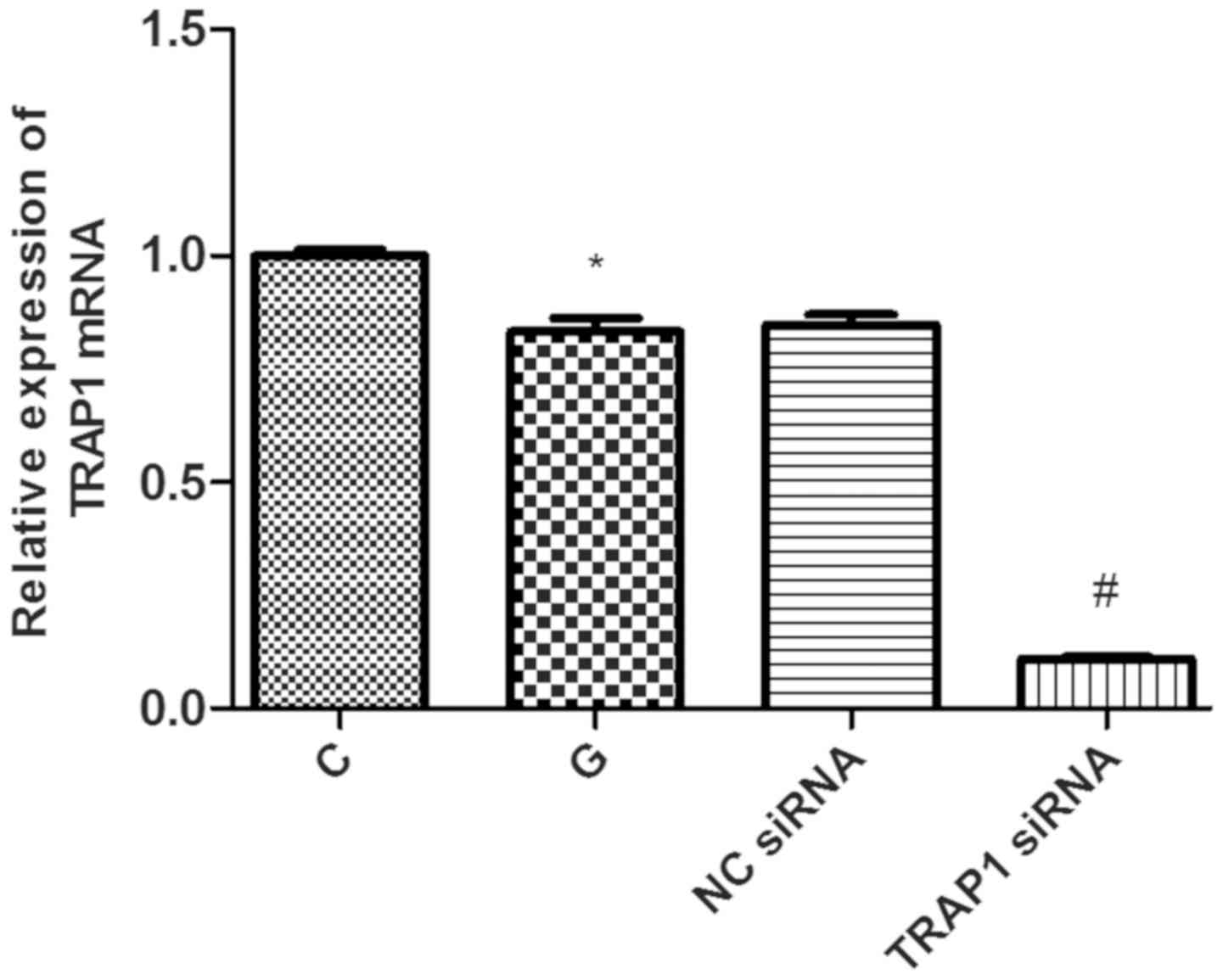
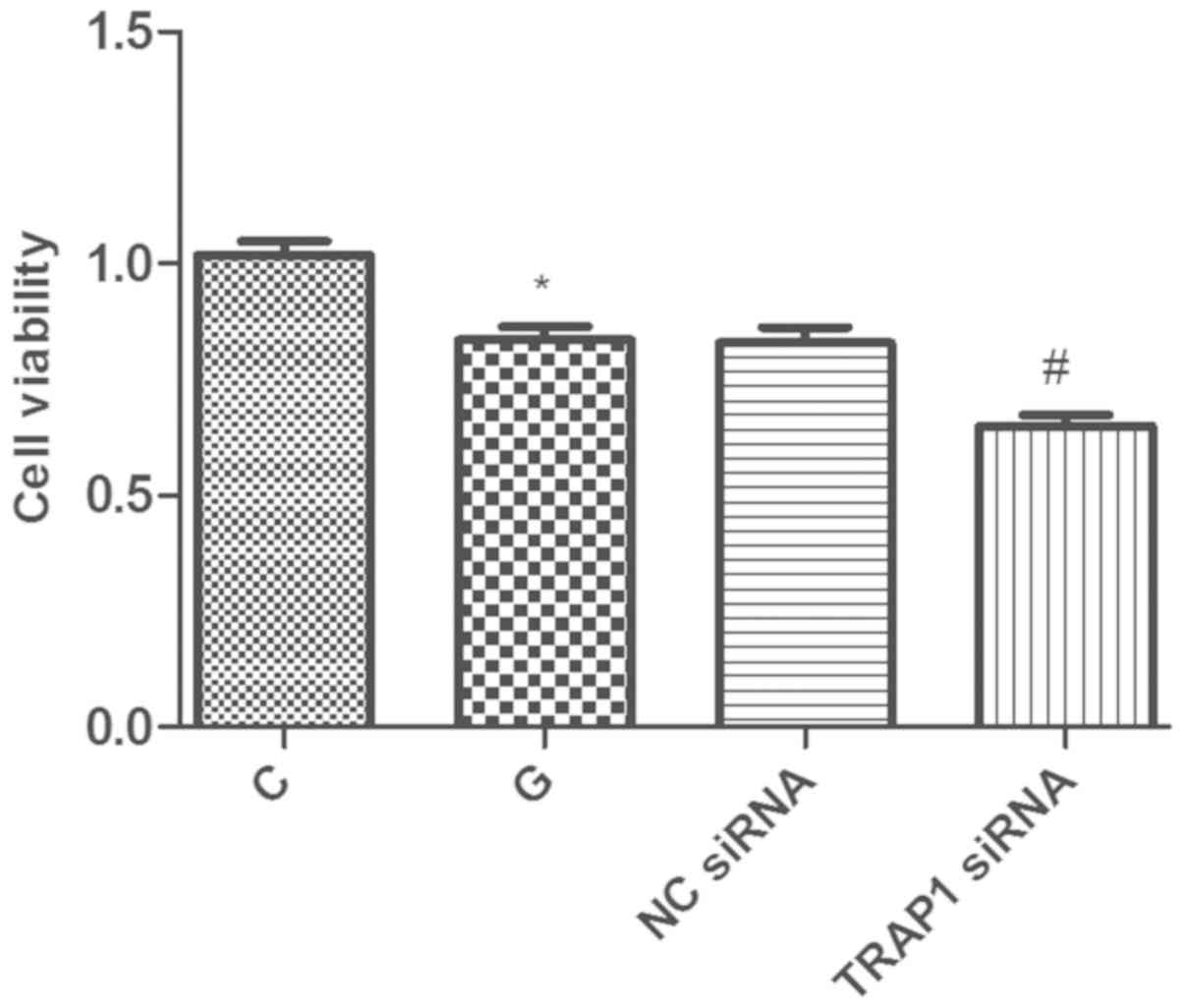
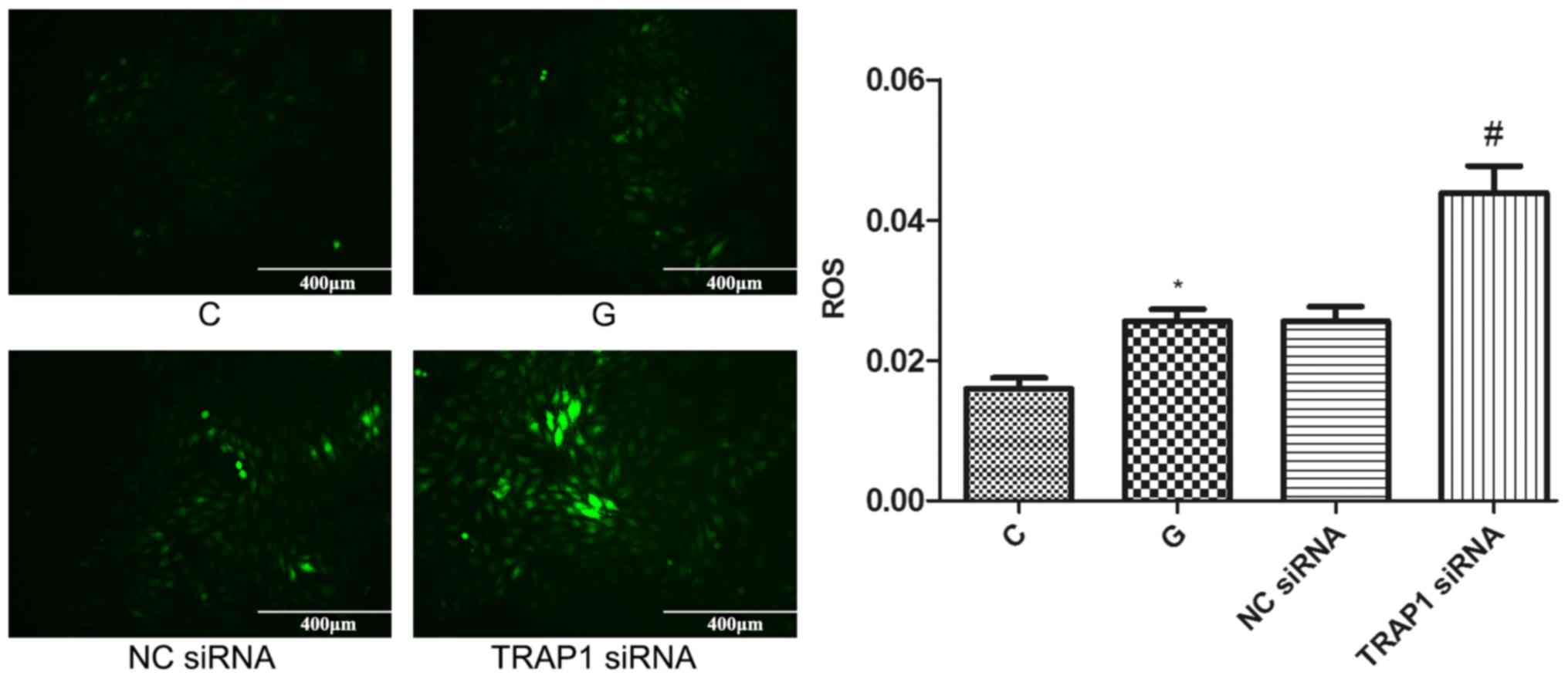
|
1
|
Dei Cas A, Fonarow GC, Gheorghiade M and
Butler J: Concomitant diabetes mellitus and heart failure. Curr
Probl Cardiol. 40:7–43. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Brownlee M: Biochemistry and molecular
cell biology of diabetic complications. Nature. 414:813–820. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Granville DJ and Gottlieb RA:
Mitochondria: Regulators of cell death and survival.
ScientificWorldJournal. 2:1569–1578. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pham T, Loiselle D, Power A and Hickey AJ:
Mitochondrial inefficiencies and anoxic ATP hydrolysis capacities
in diabetic rat heart. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 307:C499–C507.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Anderson EJ, Kypson AP, Rodriguez E,
Anderson CA, Lehr EJ and Neufer PD: Substrate-specific derangements
in mitochondrial metabolism and redox balance in the atrium of the
type 2 diabetic human heart. J Am Coll Cardiol. 54:1891–1898. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Matassa DS, Amoroso MR, Maddalena F,
Landriscina M and Esposito F: New insights into TRAP1 pathway. Am J
Cancer Res. 2:235–248. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Masgras I, Sanchez-Martin C, Colombo G and
Rasola A: The chaperone TRAP1 as a modulator of the mitochondrial
adaptations in cancer cells. Front Oncol. 7:582017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lettini G, Maddalena F, Sisinni L,
Condelli V, Matassa DS, Costi MP, Simoni D, Esposito F and
Landriscina M: TRAP1: A viable therapeutic target for future cancer
treatments? Expert Opin Ther Targets. 21:805–815. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Im CN, Lee JS, Zheng Y and Seo JS: Iron
chelation study in a normal human hepatocyte cell line suggests
that tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated protein 1 (TRAP1)
regulates production of reactive oxygen species. J Cell Biochem.
100:474–486. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang Y, Jiang DS, Yan L, Cheng KJ, Bian
ZY and Lin GS: HSP75 protects against cardiac hypertrophy and
fibrosis. J Cell Biochem. 112:1787–1794. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Voloboueva LA, Duan M, Ouyang Y, Emery JF,
Stoy C and Giffard RG: Overexpression of mitochondrial Hsp70/Hsp75
protects astrocytes against ischemic injury in vitro. J Cereb Blood
Flow Metab. 28:1009–1016. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Roul D and Recchia FA: Metabolic
alterations induce oxidative stress in diabetic and failing hearts:
Different pathways, same outcome. Antioxid Redox Signal.
22:1502–1514. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bragg F, Holmes MV, Iona A, Guo Y, Du H,
Chen Y, Bian Z, Yang L, Herrington W, Bennett D, et al: Association
between diabetes and cause-specific mortality in rural and urban
areas of China. JAMA. 317:280–289. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lee WS and Kim J: Diabetic cardiomyopathy:
Where we are and where we are going. Korean J Intern Med.
32:404–421. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jia G, Whaley-Connell A and Sowers JR:
Diabetic cardiomyopathy: A hyperglycaemia- and
insulin-resistance-induced heart disease. Diabetologia. 61:21–28.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu ZW, Zhu HT, Chen KL, Dong X, Wei J,
Qiu C and Xue JH: Protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum
kinase (PERK) signaling pathway plays a major role in reactive
oxygen species (ROS)-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced
apoptosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc Diabetol.
12:1582013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huynh K, Bernardo BC, Mcmullen JR and
Ritchie RH: Diabetic cardiomyopathy: Mechanisms and new treatment
strategies targeting antioxidant signaling pathways. Pharmacol
Ther. 142:375–415. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu Q, Wang S and Cai L: Diabetic
cardiomyopathy and its mechanisms: Role of oxidative stress and
damage. J Diabetes Investig. 5:623–634. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Song HY, Dunbar JD, Zhang YX, Guo D and
Donner DB: Identification of a protein with homology to hsp90 that
binds the type 1 tumor necrosis factor receptor. J Biol Chem.
270:3574–3581. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang B, Wang J, Huang Z, Wei P, Liu Y,
Hao J, Zhao L, Zhang F, Tu Y and Wei T: Aberrantly upregulated
TRAP1 is required for tumorigenesis of breast cancer. Oncotarget.
6:44495–44508. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gao JY, Song BR, Peng JJ and Lu YM:
Correlation between mitochondrial TRAP-1 expression and lymph node
metastasis in colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol.
18:5965–5971. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee JH, Kang KW, Kim JE, Hwang SW, Park
JH, Kim SH, Ji JH, Kim TG, Nam HY, Roh MS, et al: Differential
expression of heat shock protein 90 isoforms in small cell lung
cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:9487–9493. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yuan M and Li X: Research progress of the
relationship between TRAP1 and malignant tumor. Shi Yong Zhong Liu
Xue Za Zhi. 31:371–375. 2017.(In Chinese).
|
|
25
|
Montesano Gesualdi N, Chirico G, Pirozzi
G, Costantino E, Landriscina M and Esposito F: Tumor necrosis
factor-associated protein 1 (TRAP-1) protects cells from oxidative
stress and apoptosis. Stress. 10:342–350. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kang BH, Plescia J, Dohi T, Rosa J, Doxsey
SJ and Altieri DC: Regulation of tumor cell mitochondrial
homeostasis by an organelle-specific Hsp90 chaperone network. Cell.
131:257–270. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Altieri DC, Stein GS, Lian JB and Languino
LR: TRAP-1, the mitochondrial Hsp90. Biochim Biophys Acta 1823.
767–773. 2012.
|
|
28
|
Landriscina M, Laudiero G, Maddalena F,
Amoroso MR, Piscazzi A, Cozzolino F, Monti M, Garbi C, Fersini A,
Pucci P and Esposito F: Mitochondrial chaperone Trap1 and the
calcium binding protein Sorcin interact and protect cells against
apoptosis induced by antiblastic agents. Cancer Res. 70:6577–6586.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hua G, Zhang Q and Fan Z: Heat shock
protein 75 (TRAP1) antagonizes reactive oxygen species generation
and protects cells from granzyme M-mediated apoptosis. J Biol Chem.
282:20553–20560. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Amoroso MR, Matassa DS, Laudiero G,
Egorova AV, Polishchuk RS, Maddalena F, Piscazzi A, Paladino S,
Sarnataro D, Garbi C, et al: TRAP1 and the proteasome regulatory
particle TBP7/Rpt3 interact in the endoplasmic reticulum and
control cellular ubiquitination of specific mitochondrial proteins.
Cell Death Differ. 19:592–604. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Amoroso MR, Matassa DS, Sisinni L, Lettini
G, Landriscina M and Esposito F: TRAP1 revisited: Novel
localizations and functions of a ‘next-generation’ biomarker
(review). Int J Oncol. 45:969–977. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xiang F, Huang YS, Shi XH and Zhang Q:
Mitochondrial chaperone tumour necrosis factor receptor-associated
protein 1 protects cardiomyocytes from hypoxic injury by regulating
mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening. FEBS J.
277:1929–1938. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Xiang F, Ma SY, Lv YL, Zhang DX, Song HP
and Huang YS: Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated protein 1
regulates hypoxia-induced apoptosis through a
mitochondria-dependent pathway mediated by cytochrome c oxidase
subunit II. Burns Trauma. 7:162019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Xiang F, Zhang DX, Ma SY and Huang YS:
Mechanism of protective effects of tumor necrosis factor receptor
associated protein 1 on hypoxic cardiomyocytes of rats. Zhonghua
Shao Shang Za Zhi. 32:744–751. 2016.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang P, Lu Y, Yu D, Zhang D and Hu W:
TRAP1 provides protection against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion
injury by ameliorating mitochondrial dysfunction. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 36:2072–2082. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|