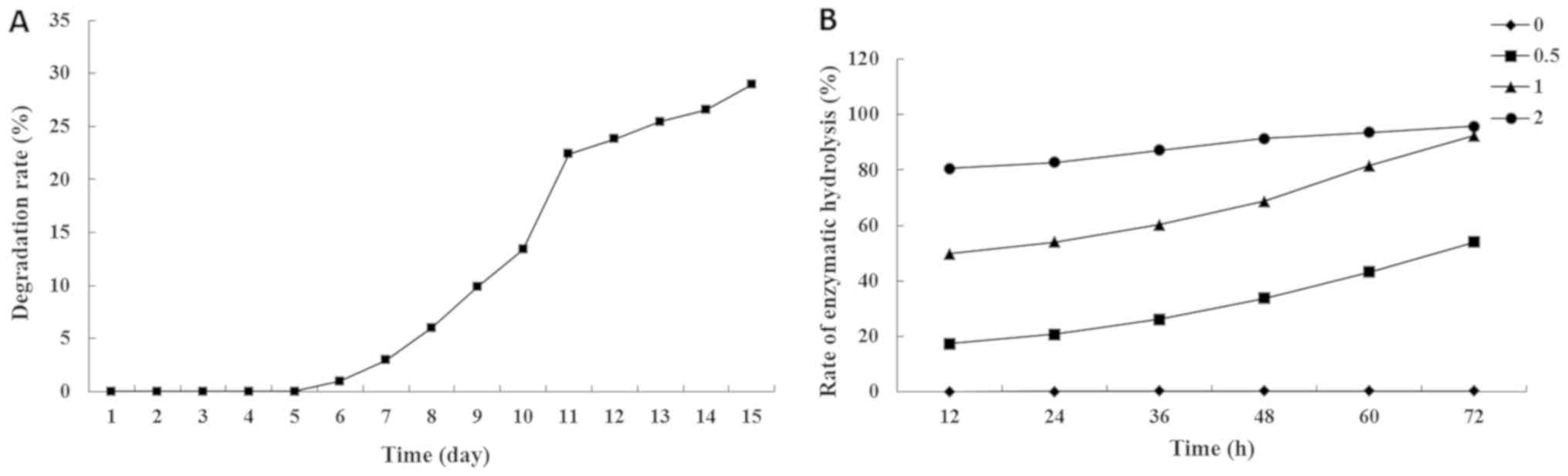
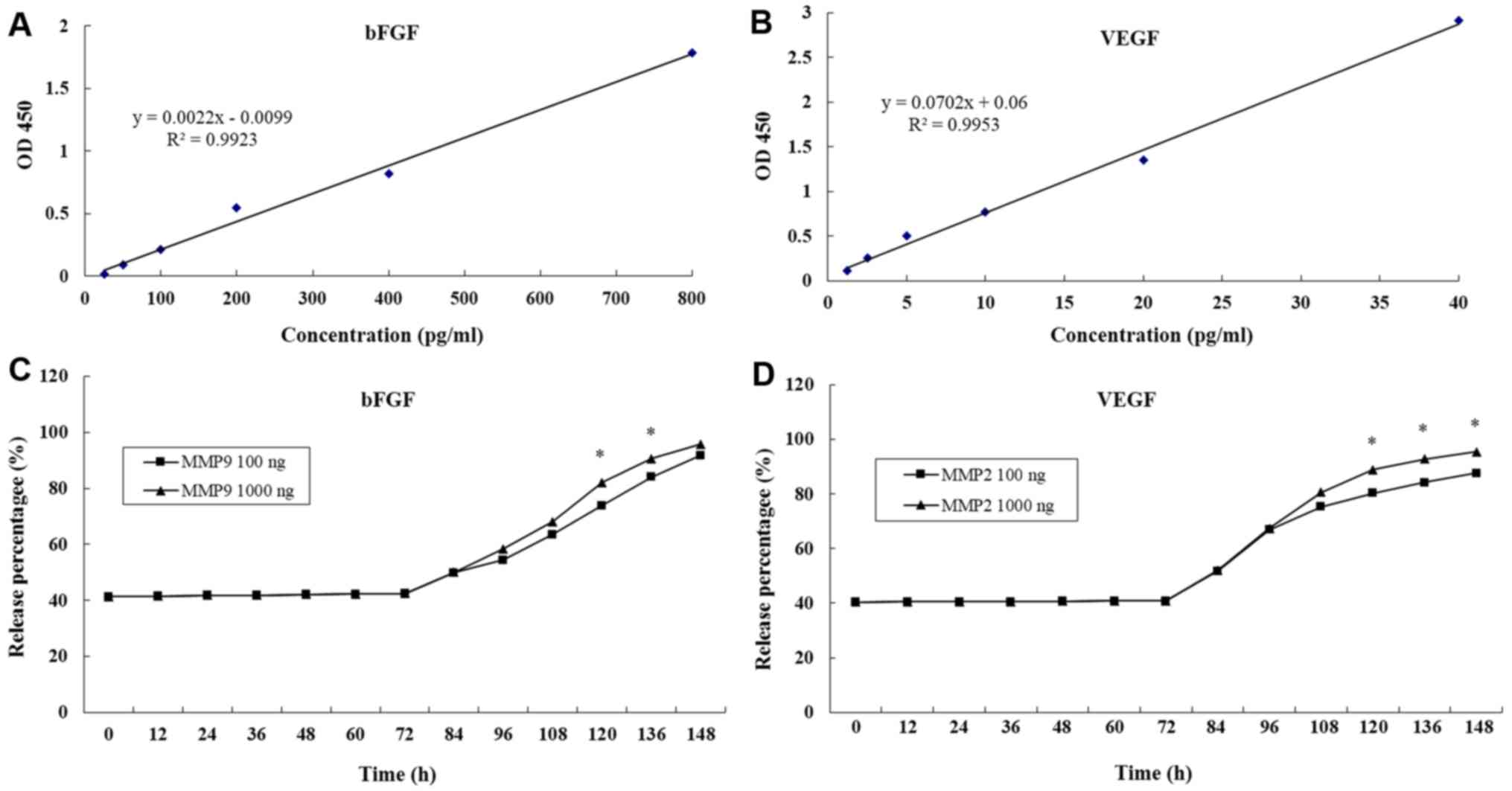
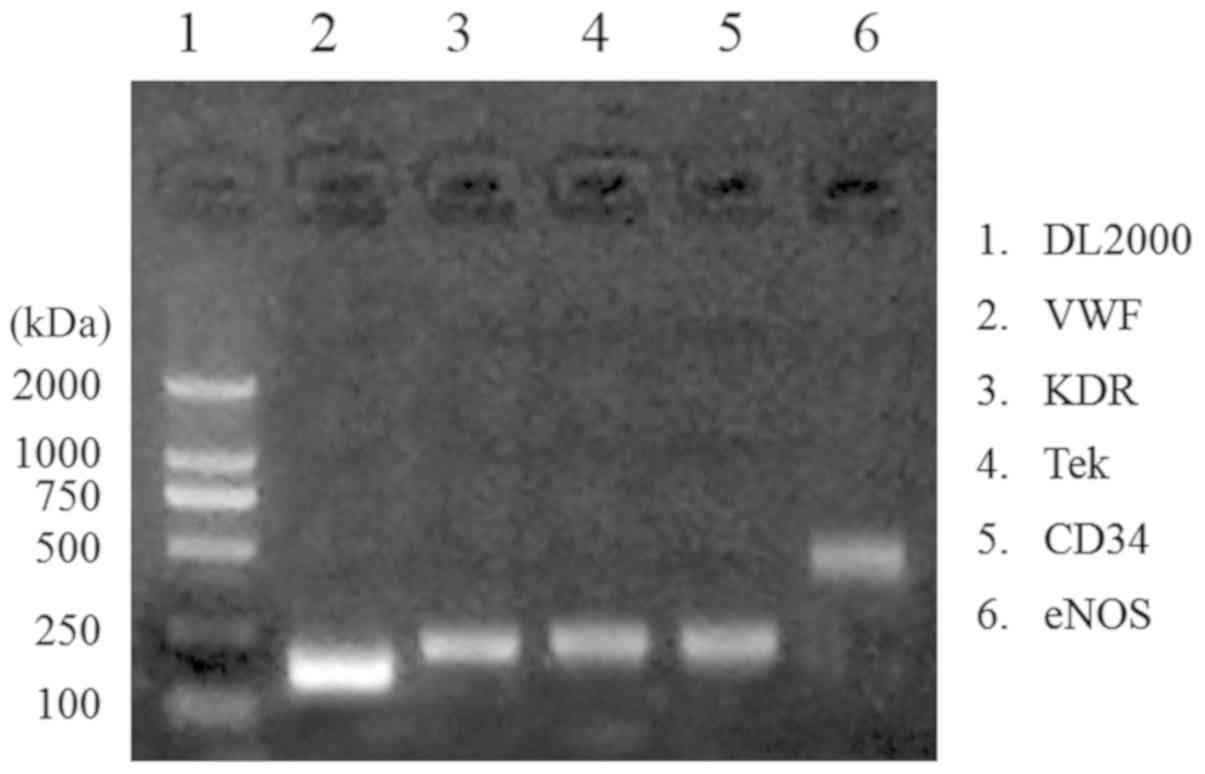
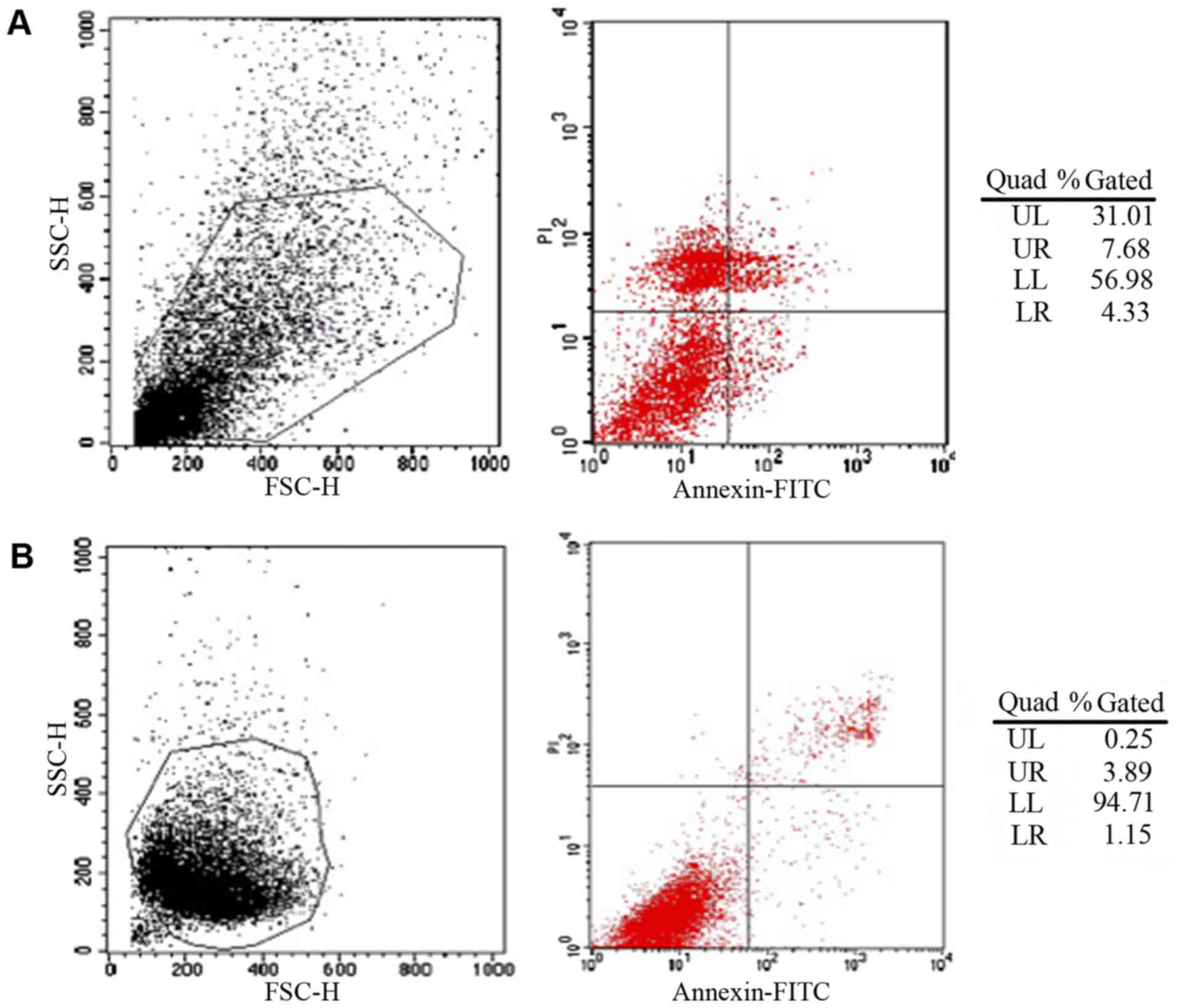
|
1
|
Winkler H: Treatment of chronic
orthopaedic infection. EFORT Open Rev. 2:110–116. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fadini GP, Losordo D and Dimmeler S:
Critical reevaluation of endothelial progenitor cell phenotypes for
therapeutic and diagnostic use. Circ Res. 110:624–637. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Asahara T, Murohara T, Sullivan A, Silver
M, van der Zee R, Li T, Witzenbichler B, Schatteman G and Isner JM:
Isolation of putative progenitor endothelial cells for
angiogenesis. Science. 275:964–967. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Janic B and Arbab AS: The role and
therapeutic potential of endothelial progenitor cells in tumor
neovascularization. ScientificWorldJouralo. 10:1088–1099. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Khoo CP, Pozzilli P and Alison MR:
Endothelial progenitor cells and their potential therapeutic
applications. Regen Med. 3:863–876. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sun Q, Silva EA, Wang A, Fritton JC,
Mooney DJ, Schaffler MB, Grossman PM and Rajagopalan S: Sustained
release of multiple growth factors from injectable polymeric system
as a novel therapeutic approach towards angiogenesis. Pharm Res.
27:264–271. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Marfella R, Luongo C, Coppola A, Luongo M,
Capodanno P, Ruggiero R, Mascolo L, Ambrosino I, Sardu C, Boccardi
V, et al: Use of a non-specific immunomodulation therapy as a
therapeutic vasculogenesis strategy in no-option critical limb
ischemia patients. Atherosclerosis. 208:473–479. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Benton JA, Fairbanks BD and Anseth KS:
Characterization of valvular interstitial cell function in three
dimensional matrix metalloproteinase degradable PEG hydrogels.
Biomaterials. 30:6593–6603. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Brandl F, Kastner F, Gschwind RM, Blunk T,
Tessmar J and Gopferich A: Hydrogel-based drug delivery systems:
Comparison of drug diffusivity and release kinetics. J Control
Release. 142:221–228. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hanjaya-Putra D, Yee J, Ceci D, Truitt R,
Yee D and Gerecht S: Vascular endothelial growth factor and
substrate mechanics regulate in vitro tubulogenesis of endothelial
progenitor cells. J Cell Mol Med. 14:2436–2447. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang QR, Wang BH, Huang YH, Dai G, Li WM
and Yan Q: Purification and growth of endothelial progenitor cells
from murine bone marrow mononuclear cells. J Cell Biochem.
103:21–29. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kraehenbuehl TP, Ferreira LS, Zammaretti
P, Hubbell JA and Langer R: Cell-responsive hydrogel for
encapsulation of vascular cells. Biomaterials. 30:4318–4324. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mieno S, Boodhwani M, Robich MP, Clements
RT, Sodha NR and Sellke FW: Effects of diabetes mellitus on
VEGF-induced proliferation response in bone marrow derived
endothelial progenitor cells. J Card Surg. 25:618–625. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sufen G, Xianghong Y, Yongxia C and Qian
P: bFGF and PDGF-BB have a synergistic effect on the proliferation,
migration and VEGF release of endothelial progenitor cells. Cell
Biol Int. 35:545–551. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Seliktar D, Zisch AH, Lutolf MP, Wrana JL
and Hubbell JA: MMP-2 sensitive, VEGF-bearing bioactive hydrogels
for promotion of vascular healing. J Biomed Mater Res A 68A.
704–716. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Yeo Y, Geng W, Ito T, Kohane DS, Burdick
JA and Radisic M: Photocrosslinkable hydrogel for myocyte cell
culture and injection. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.
81:312–322. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kraehenbuehl TP, Zammaretti P, Van der
Vlies AJ, Schoenmakers RG, Lutolf MP, Jaconi ME and Hubbell JA:
Three-dimensional extracellular matrix-directed cardioprogenitor
differentiation: Systematic modulation of a synthetic
cell-responsive PEG-hydrogel. Biomaterials. 29:2757–2766. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang X, Zhao Z, Zhang H, Hou J, Feng W,
Zhang M, Guo J, Xia J, Ge Q, Chen X and Wu X: Simultaneous
isolation of mesenchymal stem cells and endothelial progenitor
cells derived from murine bone marrow. Exp Ther Med. 16:5171–5177.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Huizer K, Mustafa DAM, Spelt JC, Kros JM
and Sacchetti A: Improving the characterization of endothelial
progenitor cell subsets by an optimized FACS protocol. PLos One.
12:e01848952017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Camci-Unal G, Nichol JW, Bae H, Tekin H,
Bischoff J and Khademhosseini A: Hydrogel surfaces to promote
attachment and spreading of endothelial progenitor cells. J Tissue
Eng Regen Med. 7:337–347. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Valdes TI, Kreutzer D and Moussy F: The
chick chorioallantoic membrane as a novel in vivo model for the
testing of biomaterials. J Biomed Mater Res. 62:273–282. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Deryugina EI and Quigley JP: Chapter 2:
Chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane models to quantify
angiogenesis induced by inflammatory and tumor cells or purified
effector molecules. Methods Enzymol. 444:21–41. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hill-West JL, Chowdhury SM, Slepian MJ and
Hubbell JA: Inhibition of thrombosis and intimal thickening by in
situ photopolymerization of thin hydrogel barriers. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 91:5967–5971. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
West JL and Hubbell JA: Separation of the
arterial wall from blood contact using hydrogel barriers reduces
intimal thickening after balloon injury in the rat: The roles of
medial and luminal factors in arterial healing. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 93:13188–13193. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Reinlib L and Field L: Cell
transplantation as future therapy for cardiovascular disease?: A
workshop of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
Circulation. 101:E182–E187. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kawamoto A and Losordo DW: Endothelial
progenitor cells for cardiovascular regeneration. Trends Cardiovasc
Med. 18:33–37. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shintani S, Murohara T, Ikeda H, Ueno T,
Honma T, Katoh A, Sasaki K, Shimada T, Oike Y and Imaizumi T:
Mobilization of endothelial progenitor cells in patients with acute
myocardial infarction. Circulation. 103:2776–2779. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Richardson TP, Peters MC, Ennett AB and
Mooney DJ: Polymeric system for dual growth factor delivery. Nat
Biotechnol. 19:1029–1034. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Arras M, Mollnau H, Strasser R, Wenz R,
Ito WD, Schaper J and Schaper W: The delivery of angiogenic factors
to the heart by microsphere therapy. Nat Biotechnol. 16:159–162.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Heldman AW, Cheng L, Jenkins GM, Heller
PF, Kim DW, Ware M Jr, Nater C, Hruban RH, Rezai B, Abella BS, et
al: Paclitaxel stent coating inhibits neointimal hyperplasia at 4
weeks in a porcine model of coronary restenosis. Circulation.
103:2289–2295. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Slepian MJ: Polymeric endoluminal paving:
A family of evolving methods for extending endoluminal therapeutics
beyond stenting. Cardiol Clin. 12:715–737. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang X, Xu B, Puperi DS, Wu Y, West JL
and Grande-Allen KJ: Application of hydrogels in heart valve tissue
engineering. J Long Term Eff Med Implants. 25:105–134. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Eichler W, Friedrichs U, Thies A, Tratz C
and Wiedemann P: Modulation of matrix metalloproteinase and TIMP-1
expression by cytokines in human RPE cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis
Sci. 43:2767–2773. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ma C and Chegini N: Regulation of matrix
metalloproteinases (MMPs) and their tissue inhibitors in human
myometrial smooth muscle cells by TGF-beta1. Mol Hum Reprod.
5:950–954. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Overall CM, Wrana JL and Sodek J:
Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of 72-kDa
gelatinase/type IV collagenase by transforming growth factor-beta 1
in human fibroblasts. Comparisons with collagenase and tissue
inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase gene expression. J Biol Chem.
266:14064–14071. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wick W, Platten M and Weller M: Glioma
cell invasion: Regulation of metalloproteinase activity by
TGF-beta. J Neurooncol. 53:177–185. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Guan J, Sacks MS, Beckman EJ and Wagner
WR: Synthesis, characterization, and cytocompatibility of
elastomeric, biodegradable poly(ester-urethane)ureas based on
poly(caprolactone) and putrescine. J Biomed Mater Res. 61:493–503.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ferrara N and Alitalo K: Clinical
applications of angiogenic growth factors and their inhibitors. Nat
Med. 5:1359–1364. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Elbert DL and Hubbell JA: Conjugate
addition reactions combined with free-radical cross-linking for the
design of materials for tissue engineering. Biomacromolecules.
2:430–441. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Henry TD, Rocha-Singh K, Isner JM,
Kereiakes DJ, Giordano FJ, Simons M, Losordo DW, Hendel RC, Bonow
RO, Eppler SM, et al: Intracoronary administration of recombinant
human vascular endothelial growth factor to patients with coronary
artery disease. Am Heart J. 142:872–880. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lee KY, Peters MC, Anderson KW and Mooney
DJ: Controlled growth factor release from synthetic extracellular
matrices. Nature. 408:998–1000. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Mann BK, Gobin AS, Tsai AT, Schmedlen RH
and West JL: Smooth muscle cell growth in photopolymerized
hydrogels with cell adhesive and proteolytically degradable
domains: Synthetic ECM analogs for tissue engineering.
Biomaterials. 22:3045–3051. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lutolf MP and Hubbell JA: Synthesis and
physicochemical characterization of end-linked poly(ethylene
glycol)-co-peptide hydrogels formed by michael-type addition.
Biomacromolecules. 4:713–722. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
West JL and Hubbell JA: Polymeric
biomaterials with degradation sites for proteases involved in cell
migration. Macromolecules. 32:241–244. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|