|
1
|
Ji Q, Wang P and He C: Extracorporeal
shockwave therapy as a novel and potential treatment for
degenerative cartilage and bone disease: Osteoarthritis. A
qualitative analysis of the literature. Prog Biophys Mol Biol.
121:255–265. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hsu SL, Cheng JH, Wang CJ, Ko JY and Hsu
CH: Extracorporeal shockwave therapy enhances expression of Pdia-3
which is a key factor of the 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D 3 rapid
membrane signaling pathway in treatment of early osteoarthritis of
the knee. Int J Med Sci. 14:1220–1230. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li JW, Zheng SJ, Zhang JC, Huang JJ and
Liu XG: Effect of acupuncture plus different frequency shock-wave
interventions on pain reactions and motor function in knee
osteoarthritis patients. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 40:300–303. 2015.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pu W, Yujing Z, Xiaofei W, Xiaotian Y,
Chengqi H and Chuan L: Effects of extracorporeal shock wave therapy
on cartilage protection and subchondral bone remodeling in rabbits
osteoarthritis induced by ACLT. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 57:e372014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Maricar N, Callaghan MJ, Parkes MJ, Felson
DT and O'Neill TW: Clinical assessment of effusion in knee
osteoarthritis-A systematic review. Semin Arthritis Rheum.
45:556–563. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim JH, Kim JY, Choi CM, Lee JK, Kee HS,
Jung KI and Yoon SR: The dose-related effects of extracorporeal
shock wave therapy for knee osteoarthritis. Ann Rehabil Med.
39:616–623. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liao CD, Tsauo JY, Liou TH, Chen HC and
Huang SW: Clinical efficacy of extracorporeal shockwave therapy for
knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-regression of
randomized controlled trials. Clin Rehabil.
8:2692155198469422019.
|
|
8
|
Hou X.D..Liu H.B..Liu K.M.: Effects of
extracorporeal shock wave therapy on interleukin-1beta and matrix
metalloproteinase-13 expression in rabbits with knee
osteoarthritis. Zhong Guo Zu Zhi Gong Cheng Yan Jiu Za Zhi.
18:2397–2402. 2014.(In Chinese).
|
|
9
|
Zhao Z, Ji H, Jing R, Liu C, Wang M, Zhai
L, Bai X and Xing G: Extracorporeal shock-wave therapy reduces
progression of knee osteoarthritis in rabbits by reducing nitric
oxide level and chondrocyte apoptosis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.
132:1547–1553. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yoon SR and Kim JH: Effect of
extracorporeal shock wave therapy on knee osteoarthritis. Ann Phys
Rehabil Med. 57:e37–e38. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wang P, Liu C, Yang XT, Wei XF, Zhou YJ,
Yang L and He CQ: Effect of extracorporeal shock wave therapy on
cartilage and subchondral bone remodeling in rabbits with
ACLT-induced osteoarthritis. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban.
45:120–125. 2014.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Frisbie DD, Kawcak CE and McIlwraith CW:
Evaluation of the effect of extracorporeal shock wave treatment on
experimentally induced osteoarthritis in middle carpal joints of
horses. Am J Vet Res. 70:449–454. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ochiai N, Ohtori S, Sasho T, Nakagawa K,
Takahashi K, Takahashi N, Murata R, Takahashi K, Moriya H, Wada Y
and Saisu T: Extracorporeal shock wave therapy improves motor
dysfunction and pain originating from knee osteoarthritis in rats.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 15:1093–1096. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mueller M, Bockstahler B, Skalicky M,
Mlacnik E and Lorinson D: Effects of radial shockwave therapy on
the limb function of dogs with hip osteoarthritis. Vet Rec.
160:762–765. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Imamura M, Alamino S, Hsing WT, Alfieri
FM, Schmitz C and Battistella LR: Radial extracorporeal shock wave
therapy for disabling pain due to severe primary knee
osteoarthritis. J Rehabil Med. 49:54–62. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wright JG, Swiontkowski MF and Tolo VT:
Meta-analyses and systematic reviews: New guidelines for JBJS. J
Bone Joint Surg Am. 94:15372012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jokstad A: Cochrane collaboration
systematic reviews may be based on trials not approved by a
research ethics committee. Clin Exp Dent Res. 3:179–182. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen TW, Lin CW, Lee CL, Chen CH, Chen YJ,
Lin TY and Huang MH: The efficacy of shock wave therapy in patients
with knee osteoarthritis and popliteal cyamella. Kaohsiung J Med
Sci. 30:362–370. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cho SJ, Yang JR, Yang HS and Yang HE:
Effects of extracorporeal shockwave therapy in chronic stroke
patients with knee osteoarthritis: A pilot study. Ann Rehabil Med.
40:862–870. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
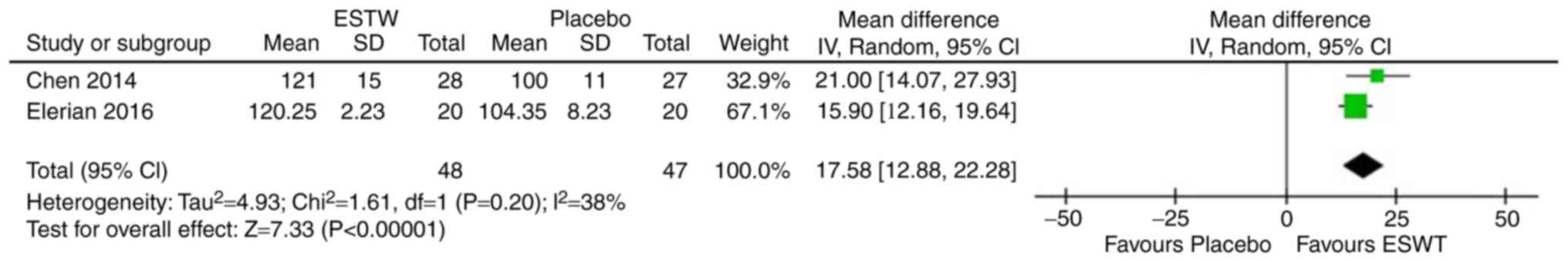
Elerian AE, Ewidea TMA and Ali N: Effect
of shock wave therapy versus corticosteroid injection in management
of knee osteoarthritis. Int J Physiother. 3:246–251. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
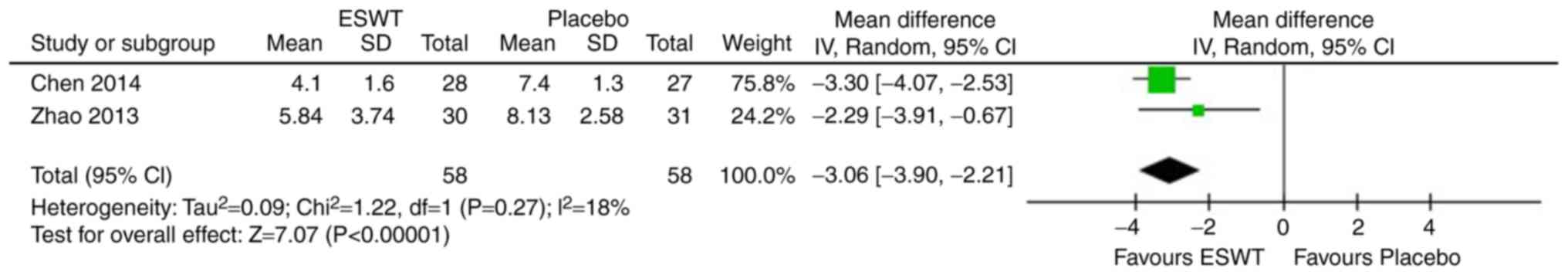
Zhao Z, Jing R, Shi Z, Zhao B, Ai Q and
Xing G: Efficacy of extracorporeal shockwave therapy for knee
osteoarthritis: A randomized controlled trial. J Surg Res.
185:661–666. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
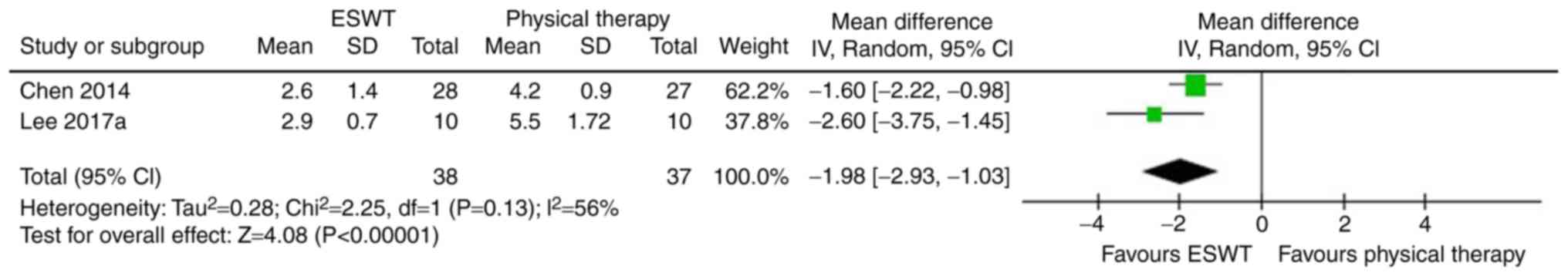
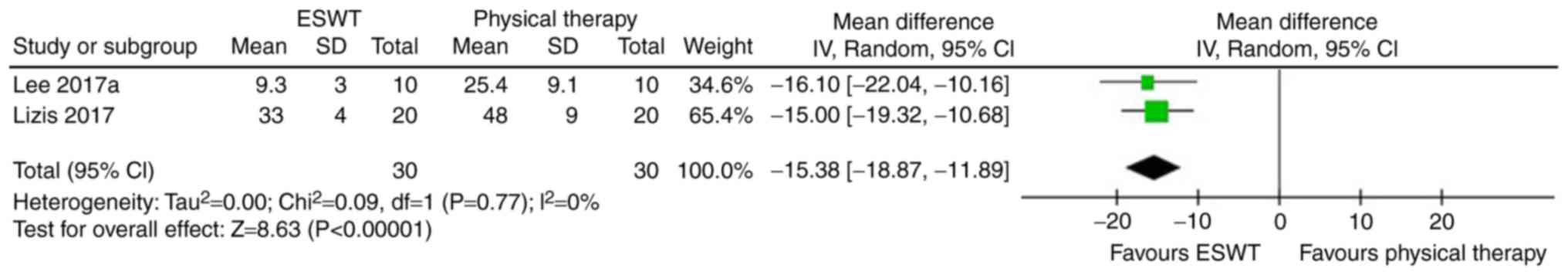
Lee JH, Lee S, Choi S, Choi YH and Lee K:
The effects of extracorporeal shock wave therapy on the pain and
function of patients with degenerative knee arthritis. J Phys Ther
Sci. 29:536–538. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
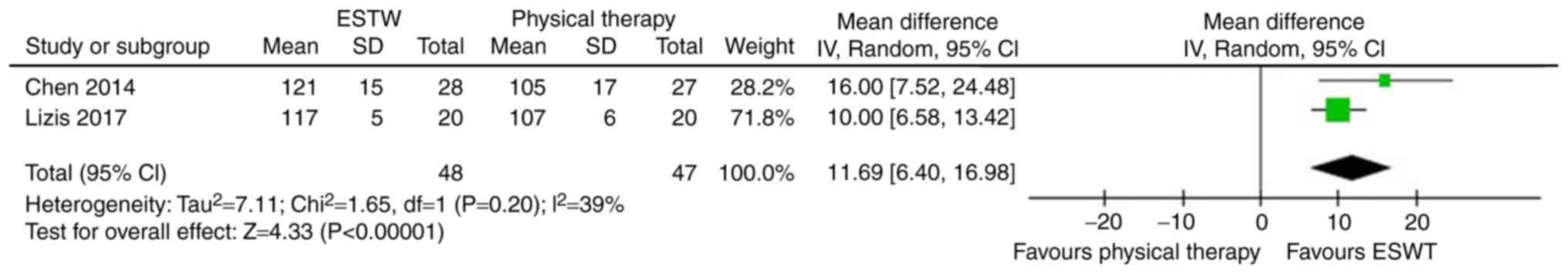
Lizis P, Kobza W and Manko G:
Extracorporeal shockwave therapy vs. kinesiotherapy for
osteoarthritis of the knee: A pilot randomized controlled trial. J
Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 30:1121–1128. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|