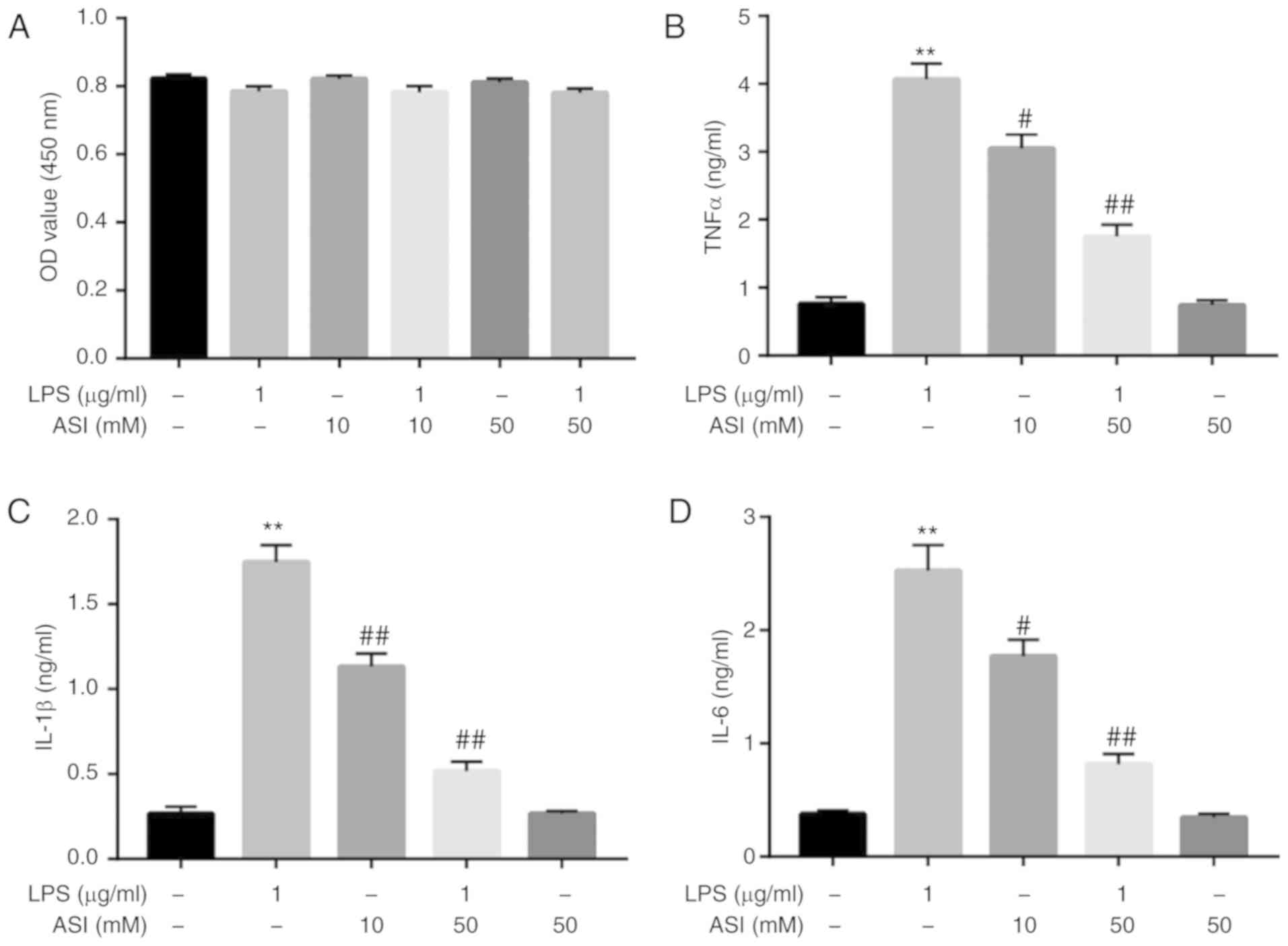
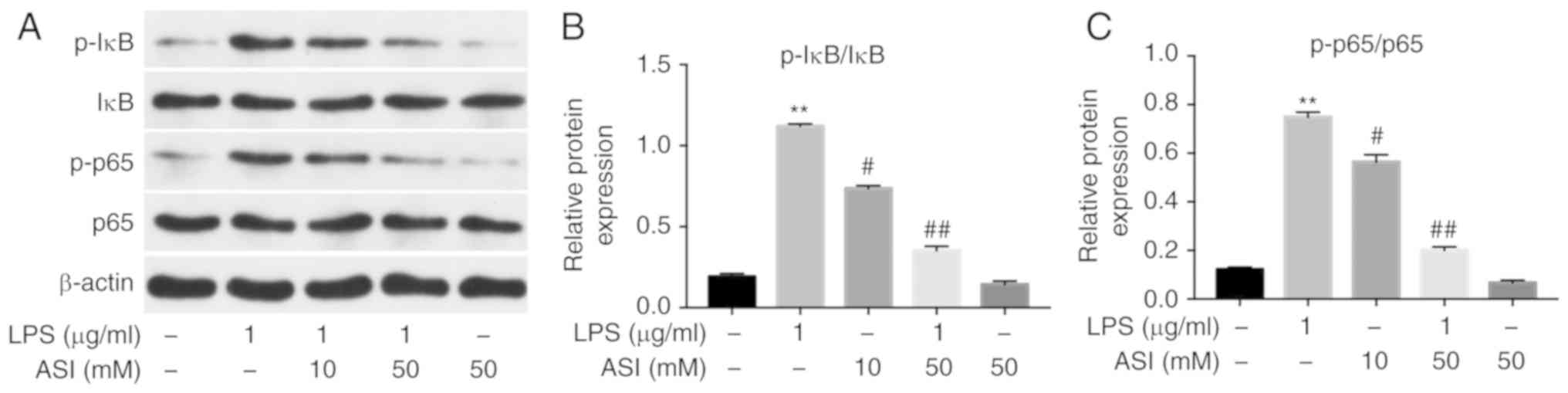
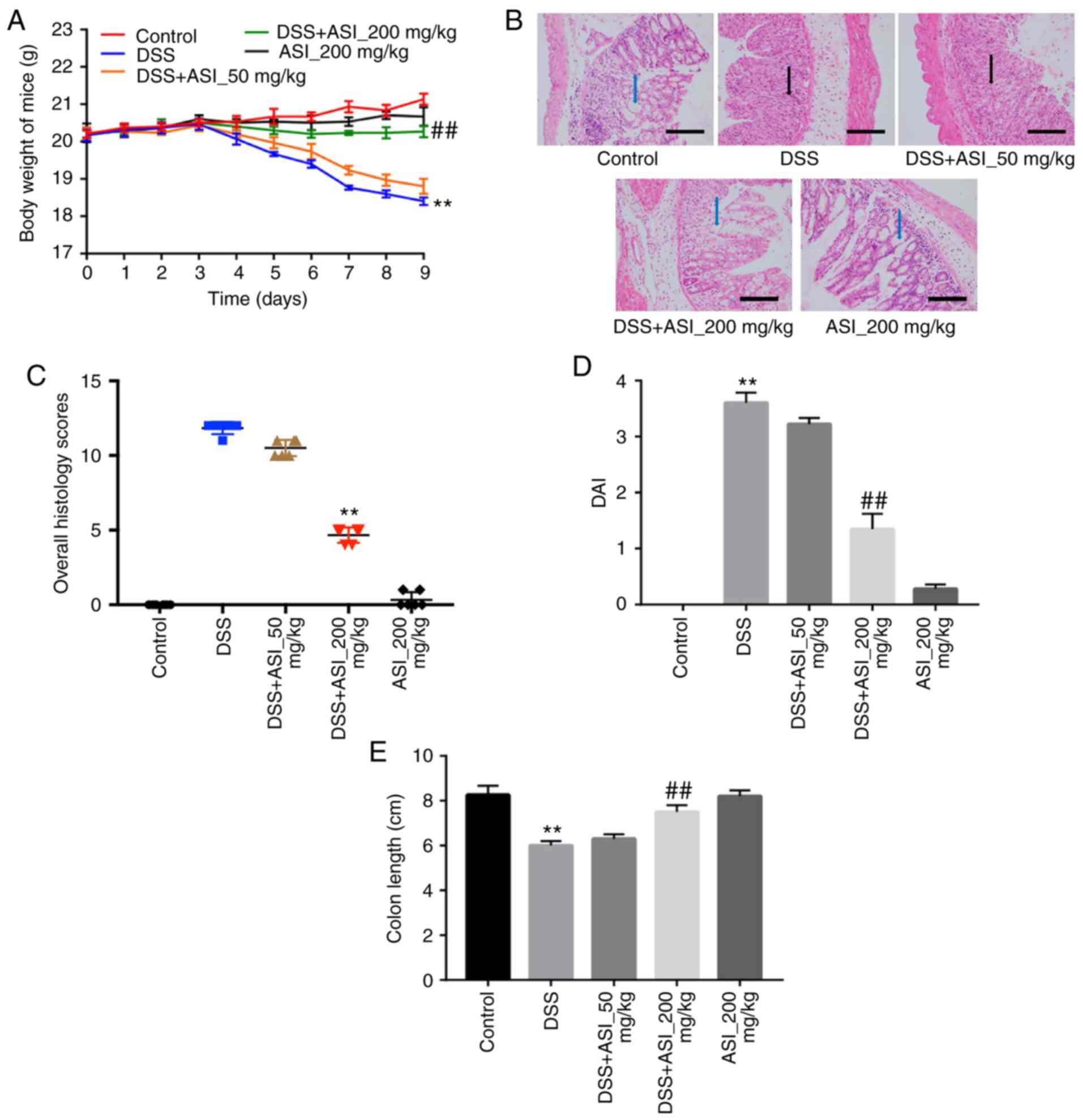
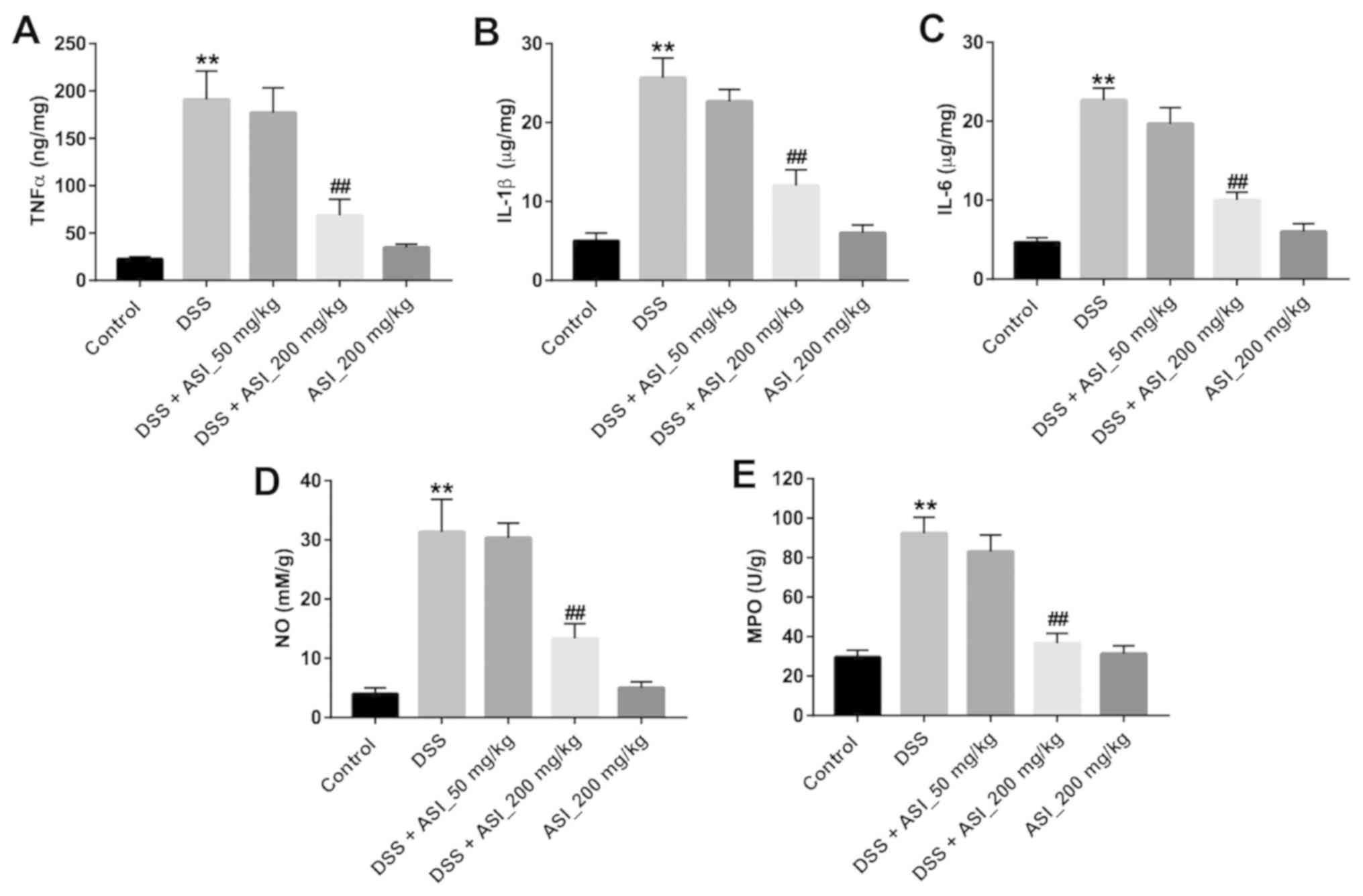
|
1
|
Zhang Z, Liu J, Shen P, Cao Y, Lu X, Gao
X, Fu Y, Liu B and Zhang N: Zanthoxylum bungeanum pericarp
extract prevents dextran sulfate sodium-induced experimental
colitis in mice via the regulation of TLR4 and TLR4-related
signaling pathways. Int Immunopharmacol. 41:127–135. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang H, Deng A, Zhang Z, Yu Z, Liu Y,
Peng S, Wu L, Qin H and Wang W: The protective effect of
epicatechin on experimental ulcerative colitis in mice is mediated
by increasing antioxidation and by the inhibition of NF-κB pathway.
Pharmacol Rep. 68:514–520. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Harris KG and Chang EB: The intestinal
microbiota in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel diseases: New
insights into complex disease. Clin Sci (Lond). 132:2013–2028.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yadav V, Varum F, Bravo R, Furrer E, Bojic
D and Basit AW: Inflammatory bowel disease: Exploring gut
pathophysiology for novel therapeutic targets. Transl Res.
176:38–68. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ordás I, Eckmann L, Talamini M, Baumgart
DC and Sandborn WJ: Ulcerative colitis. Lancet. 380:1606–1619.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Thia KT, Loftus EV Jr, Sandborn WJ and
Yang SK: An update on the epidemiology of inflammatory bowel
disease in Asia. Am J Gastroenterol. 103:3167–3182. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Peyrin-Biroulet L, Deltenre P, Ardizzone
S, D'Haens G, Hanauer SB, Herfarth H, Lémann M and Colombel JF:
Azathioprine and 6-mercaptopurine for the prevention of
postoperative recurrence in Crohn's disease: A meta-analysis. Am J
Gastroenterol. 104:2089–2096. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kemp R, Dunn E and Schultz M:
Immunomodulators in inflammatory bowel disease: An emerging role
for biologic agents. BioDrugs. 27:585–590. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Atanasov AG, Waltenberger B,
Pferschy-Wenzig EM, Linder T, Wawrosch C, Uhrin P, Temml V, Wang L,
Schwaiger S, Heiss EH, et al: Discovery and resupply of
pharmacologically active plant-derived natural products: A review.
Biotechnol Adv. 33:1582–1614. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Maria-Ferreira D, Nascimento AM, Cipriani
TR, Santana-Filho AP, Watanabe PDS, Sant Ana DMG, Luciano FB,
Bocate KCP, van den Wijngaard RM, Werner MFP and Baggio CH:
Rhamnogalacturonan, a chemically-defined polysaccharide, improves
intestinal barrier function in DSS-induced colitis in mice and
human Caco-2 cells. Sci Rep. 8:122612018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sun Y, Zhao Y, Yao J, Zhao L, Wu Z, Wang
Y, Pan D, Miao H, Guo Q and Lu N: Wogonoside protects against
dextran sulfate sodium-induced experimental colitis in mice by
inhibiting NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Biochem
Pharmacol. 94:142–154. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang L, Xing F, Han X, Li Q, Wu H, Shi H,
Wang Z, Huang F and Wu X: Astragaloside IV regulates
differentiation and induces apoptosis of activated CD4+ T cells in
the pathogenesis of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 362:105–115. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xu N, Kan P, Yao X, Yang P, Wang J, Xiang
L and Zhu Y: Astragaloside IV reversed the autophagy and oxidative
stress induced by the intestinal microbiota of AIS in mice. J
Microbiol. 56:838–846. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dai PC, Liu DL, Zhang L, Ye J, Wang Q,
Zhang HW, Lin XH and Lai GX: Astragaloside IV sensitizes non-small
cell lung cancer cells to gefitinib potentially via regulation of
SIRT6. Tumour Biol. 39:10104283176975552017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dong Z, Zhou J, Zhang Y, Chen Y, Yang Z,
Huang G, Chen Y, Yuan Z, Peng Y and Cao T: Astragaloside-IV
alleviates heat-induced inflammation by inhibiting endoplasmic
reticulum stress and autophagy. Cell Physiol Biochem. 42:824–837.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhou X, Sun X, Gong X, Yang Y, Chen C,
Shan G and Yao Q: Astragaloside IV from Astragalus
membranaceus ameliorates renal interstitial fibrosis by
inhibiting inflammation via TLR4/NF-кB in vivo and in vitro. Int
Immunopharmacol. 42:18–24. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kang JH, Choi S, Jang JE, Ramalingam P, Ko
YT, Kim SY and Oh SH: Wasabia japonica is a potential
functional food to prevent colitis via inhibiting the NF-κB
signaling pathway. Food Funct. 8:2865–2874. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhao P, Wang Y, Zeng S, Lu J, Jiang TM and
Li YM: Protective effect of astragaloside IV on
lipopolysaccharide-induced cardiac dysfunction via downregulation
of inflammatory signaling in mice. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol.
37:428–433. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jiang XG, Sun K, Liu YY, Yan L, Wang MX,
Fan JY, Mu HN, Li C, Chen YY, Wang CS and Han JY: Astragaloside IV
ameliorates 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS)-induced
colitis implicating regulation of energy metabolism. Sci Rep.
7:418322017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
He X, Zheng Z, Yang X, Lu Y, Chen N and
Chen W: Tetramethylpyrazine attenuates PPAR-γ
antagonist-deteriorated oxazolone-induced colitis in mice. Mol Med
Rep. 5:645–650. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
National Research Council (US) Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals, . Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 8th.
National Academies Press (US); Washington, DC: 2011
|
|
22
|
Zhou Q, Gong X, Kuang G, Jiang R, Xie T,
Tie H, Chen X, Li K, Wan J and Wang B: Ferulic acid protected from
kidney ischemia reperfusion injury in mice: Possible mechanism
through increasing adenosine generation via HIF-1a. Inflammation.
41:2068–2078. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zheng B, van Bergenhenegouwen J, Overbeek
S, van de Kant HJ, Garssen J, Folkerts G, Vos P, Morgan ME and
Kraneveld AD: Bifidobacterium breve attenuates murine dextran
sodium sulfate-induced colitis and increases regulatory T cell
responses. PLoS One. 9:e954412014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Araki T, Hashimoto K, Okita Y, Fujikawa H,
Kondo S, Kobayashi M, Ohi M, Toiyama Y, Inoue Y, Uchida K, et al:
Colonic histological criteria predict development of pouchitis
after Ileal Pouch: Anal anastomosis for patients with ulcerative
colitis. Dig Surg. 35:138–143. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mao S, Yang G, Li W, Zhang J, Liang H, Li
J and Zhang M: Gastroprotective effects of Astragaloside IV against
acute gastric lesion in rats. PLoS One. 11:e01481462016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ge H, Tang H, Liang Y, Wu J, Yang Q, Zeng
L and Ma Z: Rhein attenuates inflammation through inhibition of
NF-κB and NALP3 inflammasome in vivo and in vitro. Drug Des Devel
Ther. 11:1663–1671. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kim Y, Wu AG, Jaja-Chimedza A, Graf BL,
Waterman C, Verzi MP and Raskin I: Isothiocyanate-enriched moringa
seed extract alleviates ulcerative colitis symptoms in mice. PLoS
One. 12:e01847092017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Qu C, Yuan ZW, Yu XT, Huang YF, Yang GH,
Chen JN, Lai XP, Su ZR, Zeng HF, Xie Y and Zhang XJ: Patchouli
alcohol ameliorates dextran sodium sulfate-induced experimental
colitis and suppresses tryptophan catabolism. Pharmacol Res.
121:70–82. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Venancio VP, Cipriano PA, Kim H, Antunes
LM, Talcott ST and Mertens-Talcott SU: Cocoplum (Chrysobalanus
icaco L.) anthocyanins exert anti-inflammatory activity in
human colon cancer and non-malignant colon cells. Food Funct.
8:307–314. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Buss H, Handschick K, Jurrmann N, Pekkonen
P, Beuerlein K, Muller H, Wait R, Saklatvala J, Ojala PM, Schmitz
ML, et al: Cyclin-dependent kinase 6 phosphorylates NF-κB P65 at
serine 536 and contributes to the regulation of inflammatory gene
expression. PLoS One. 7:e518472012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Song MT, Ruan J, Zhang RY, Deng J, Ma ZQ
and Ma SP: Astragaloside IV ameliorates neuroinflammation-induced
depressive-like behaviors in mice via the PPARγ/NF-κB/NLRP3
inflammasome axis. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 39:1559–1570. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xu H, Wang CY, Zhang HN, Lv CY and Wang
YZ: Astragaloside IV suppresses inflammatory mediator production in
synoviocytes and collagen-induced arthritic rats. Mol Med Rep.
13:3289–3296. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chiu CT, Kuo SN, Hung SW and Yang CY:
Combined treatment with hyaluronic acid and mesalamine protects
rats from inflammatory bowel disease induced by intracolonic
administration of trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid. Molecules. 22(pii):
E9042017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kannan N and Guruvayoorappan C: Protective
effect of Bauhinia tomentosa on acetic acid induced
ulcerative colitis by regulating antioxidant and inflammatory
mediators. Int Immunopharmacol. 16:57–66. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Han XH, Zhong J, Guo JY, Shi R, Wang XH,
Wang CH, Wang K, Du GL, Shen YH and Ma YM: Relationships between
pharmacokinetics and efficacy of Xie-xin decoction in rats with
experimental ulcerative colitis. J Ethnopharmacol. 148:182–189.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Neurath MF: Cytokines in inflammatory
bowel disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 14:329–342. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li Q, Zhang Q, Zhang M, Wang C, Zhu Z, Li
N and Li J: Effect of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on membrane
microdomain localization of tight junction proteins in experimental
colitis. FEBS J. 275:411–420. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|