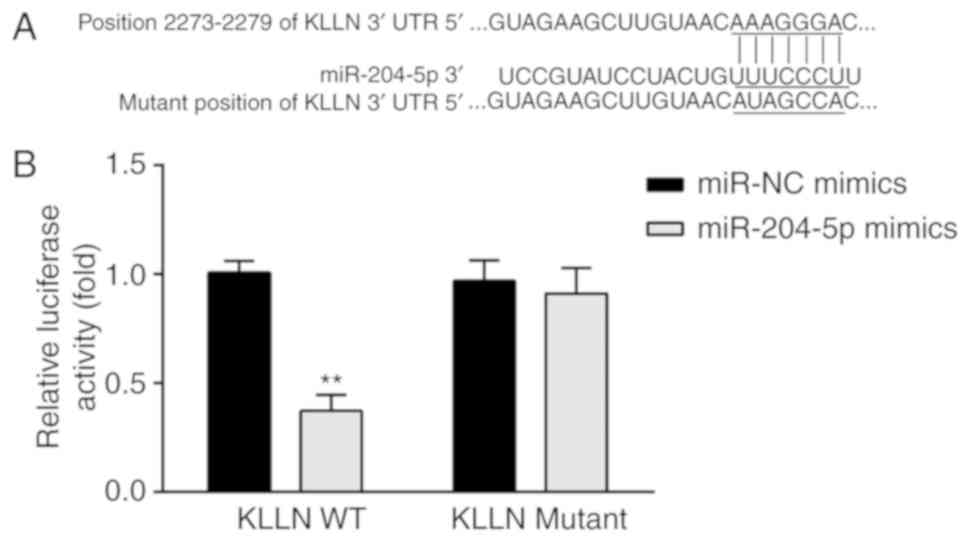
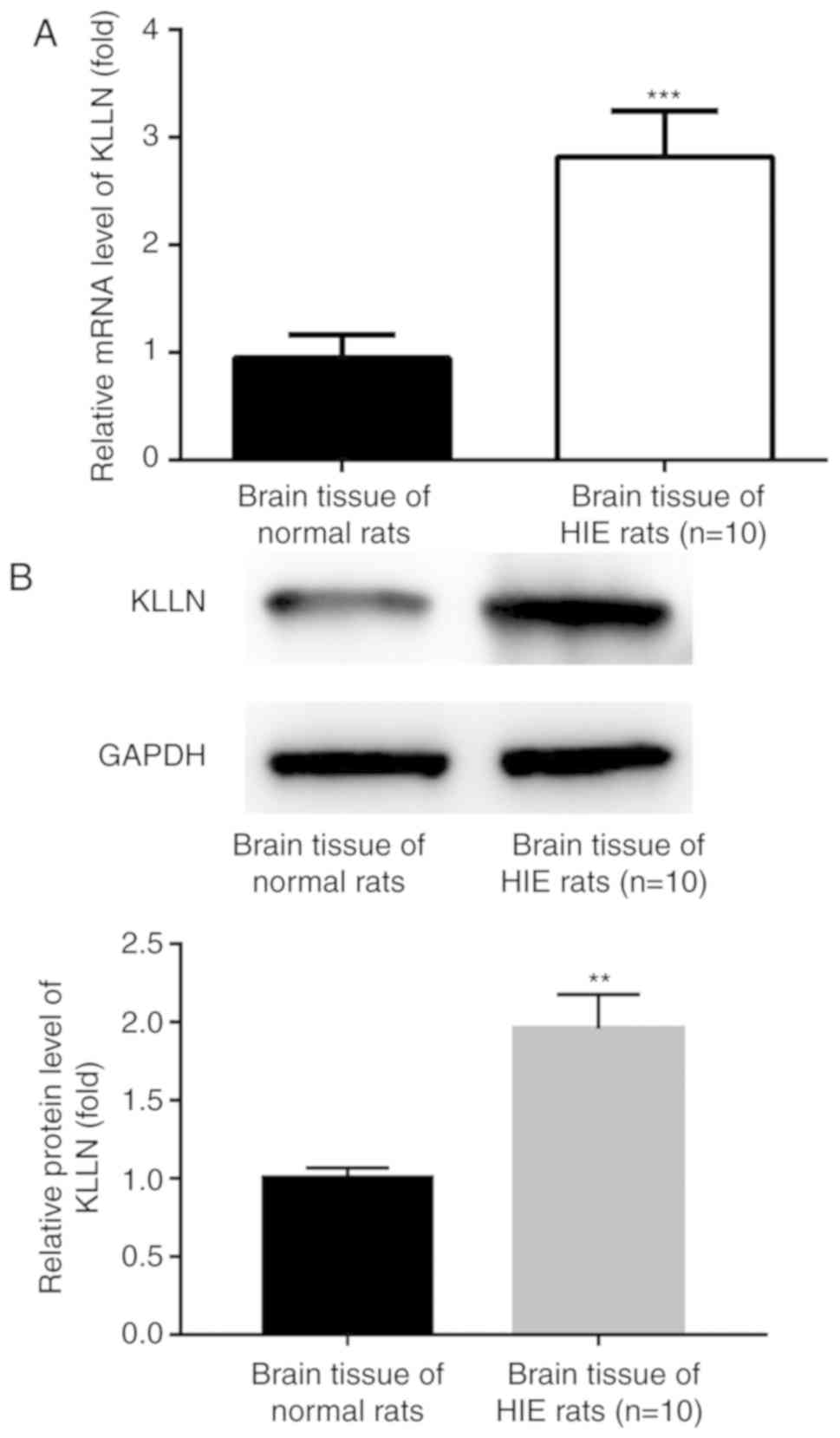
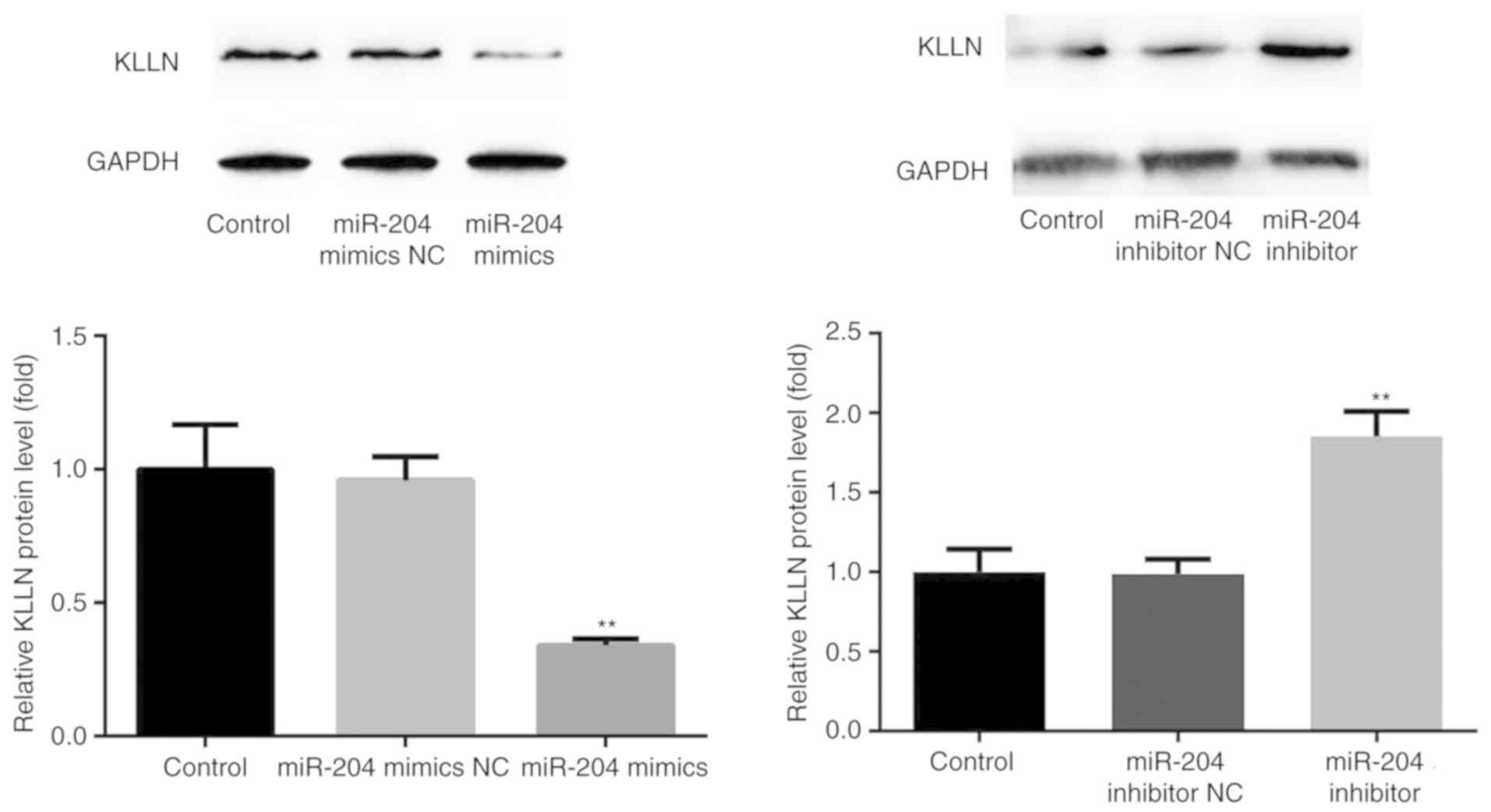
|
1
|
Leroy-Terquem E, Vermersch AI, Dean P,
Assaf Z, Boddaert N, Lapillonne A and Magny JF: Abnormal
interhemispheric synchrony in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic
encephalopathy: A retrospective pilot study. Neonatology.
112:359–364. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yum SK, Seo YM, Kwun Y, Moon CJ, Youn YA
and Sung IK: Therapeutic hypothermia in infants with
hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy and reversible persistent pulmonary
hypertension: Short-term hospital outcomes. J Matern Fetal Neonatal
Med. 31:3108–3114. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jain SV, Pagano L, Gillam-Krakauer M,
Slaughter JC, Pruthi S and Engelhardt B: Cerebral regional oxygen
saturation trends in infants with hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy.
Early Human Dev. 113:55–61. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Ma Q and Zhang L: MiR210 in neonatal
hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Oncotarget. 8:38078–38079.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen J, Cui C, Yang X, Xu J, Venkat P,
Zacharek A, Yu P and Chopp M: MiR-126 affects brain-heart
interaction after cerebral ischemic stroke. Transl Stroke Res.
8:374–385. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang J, Chen T and Shan G: miR-148b
regulates proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells
via Wnt/β-catenin signaling in rat ischemic stroke model. Front
Cell Neurosci. 11:3292017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wei H, Zhang JJ and Tang QL: MiR-638
inhibits cervical cancer metastasis through Wnt/beta-catenin
signaling pathway and correlates with prognosis of cervical cancer
patients. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 21:5587–5593. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wu H, Liu HY, Liu WJ, Shi YL and Bao D:
miR-377-5p inhibits lung cancer cell proliferation, invasion, and
cell cycle progression by targeting AKT1 signaling. J Cell Biochem.
Nov 28–2018.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
9
|
Pan L, Tang Z, Pan L and Tang R: miR-3666
inhibits lung cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion by
targeting BPTF. Biochem Cell Biol. 97:415–422. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mansoori B, Mohammadi A, Ghasabi M,
Shirjang S, Dehghan R, Montazeri V, Holmskov U, Kazemi T, Duijf P,
Gjerstorff M and Baradaran B: miR-142-3p as tumor suppressor miRNA
in the regulation of tumorigenicity, invasion and migration of
human breast cancer by targeting Bach-1 expression. J Cell Physiol.
234:9816–9825. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang L, Hou J, Cui XH, Suo LN and Lv YW:
MiR-133b regulates the expression of CTGF in epithelial-mesenchymal
transition of ovarian cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
21:5602–5609. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Qiao Y, Peng C, Li J, Wu D and Wang X:
Spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion causes damage of neurocyte by
inhibiting RAP2C. Neurol Res. 39:877–884. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Peng T, Jia YJ, Wen QQ, Guan WJ, Zhao EY
and Zhang BA: Expression of microRNA in neonatal rats with
hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi.
12:373–376. 2010.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Edwards AB, Feindel KW, Cross JL, Anderton
RS, Clark VW, Knuckey NW and Meloni BP: Modification to the
Rice-Vannucci perinatal hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy model in
the P7 rat improves the reliability of cerebral infarct development
after 48 hours. J Neurosci Methods. 288:62–71. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gonzalez-Rodriguez PJ, Li Y, Martinez F
and Zhang L: Dexamethasone protects neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain
injury via L-PGDS-dependent PGD2-DP1-pERK signaling pathway. PLoS
One. 9:e1144702014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jin Q, He W, Chen L, Yang Y, Shi K and You
Z: MicroRNA-101-3p inhibits proliferation in retinoblastoma cells
by targeting EZH2 and HDAC9. Exp Ther Med. 16:1663–1670.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ma Q, Dasgupta C, Li Y, Huang L and Zhang
L: MicroRNA-210 suppresses junction proteins and disrupts
blood-brain barrier integrity in neonatal rat hypoxic-ischemic
brain injury. Int J Mol Sci. 18:E13562017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang L, Ke J, Li Y, Ma Q, Dasgupta C,
Huang X, Zhang L and Xiao D: Inhibition of miRNA-210 reverses
nicotine-induced brain hypoxic-ischemic injury in neonatal rats.
Int J Biol Sci. 13:76–84. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Looney AM, Walsh BH, Moloney G, Grenham S,
Fagan A, O'Keeffe GW, Clarke G, Cryan JF, Dinan TG, Boylan GB and
Murray DM: Downregulation of umbilical cord blood levels of
miR-374a in neonatal hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. J Pediatr.
167:269–273.e2. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ding X, Sun B, Huang J, Xu L, Pan J, Fang
C, Tao Y, Hu S, Li R, Han X, et al: The role of miR-182 in
regulating pineal CLOCK expression after hypoxia-ischemia brain
injury in neonatal rats. Neurosci Lett. 591:75–80. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fang C, Xie L, Liu C, Fu C, Ye W, Liu H
and Zhang B: Tanshinone IIA improves hypoxic ischemic
encephalopathy through TLR-4-mediated NF-κB signal pathway. Mol Med
Rep. 18:1899–1908. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang B, Armstrong JS, Lee JH, Bhalala U,
Kulikowicz E, Zhang H, Reyes M, Moy N, Spicer D, Zhu J, et al:
Rewarming from therapeutic hypothermia induces cortical neuron
apoptosis in a swine model of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic
encephalopathy. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 35:781–793. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang CM, Cheng BH, Xue QJ, Chen J and Bai
B: MiR-1298 affects cell proliferation and apoptosis in C6 cells by
targeting SET domain containing 7. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol.
30:264–271. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Huang Q, Zheng Y, Ou Y, Xiong H, Yang H,
Zhang Z, Chen S and Ye Y: miR-34a/Bcl-2 signaling pathway
contributes to age-related hearing loss by modulating hair cell
apoptosis. Neurosci Lett. 661:51–56. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shu Y, Ren L, Xie B, Liang Z and Chen J:
MiR-204 enhances mitochondrial apoptosis in doxorubicin-treated
prostate cancer cells by targeting SIRT1/p53 pathway. Oncotarget.
8:97313–97322. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhao R, He H, Zhu Y, Wan J, Li Y, Gao S
and Zhang C: MiR-204/14-3-3ζ axis regulates osteosarcoma cell
proliferation through SATA3 pathway. Pharmazie. 72:593–598.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lin YC, Lin JF, Tsai TF, Chou KY, Chen HE
and Hwang TI: Tumor suppressor miRNA-204-5p promotes apoptosis by
targeting BCL2 in prostate cancer cells. Asian J Surg. 40:396–406.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sankunny M and Eng C: KLLN-mediated DNA
damage-induced apoptosis is associated with regulation of p53
phosphorylation and acetylation in breast cancer cells. Cell Death
Dis. 4:312018.
|
|
30
|
Cho YJ and Liang P: Killin is a
p53-regulated nuclear inhibitor of DNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 105:5396–5401. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang Y, He X, Yu Q and Eng C: Androgen
receptor-induced tumor suppressor, KLLN, inhibits breast cancer
growth and transcriptionally activates p53/p73-mediated apoptosis
in breast carcinomas. Hum Mol Genet. 22:2263–2272. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang Y, Radhakrishnan D, He X, Peehl DM
and Eng C: Transcription factor KLLN inhibits tumor growth by AR
suppression, induces apoptosis by TP53/TP73 stimulation in prostate
carcinomas, and correlates with cellular differentiation. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 98:E586–E594. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nizialek EA, Mester JL, Dhiman VK,
Smiraglia DJ and Eng C: KLLN epigenotype-phenotype associations in
Cowden syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet. 23:1538–1543. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang Y, Yu Q, He X, Romigh T, Altemus J
and Eng C: Activation of AR sensitizes breast carcinomas to
NVP-BEZ235's therapeutic effect mediated by PTEN and KLLN
upregulation. Mol Cancer Ther. 13:517–527. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hu K and Liang M: Upregulated microRNA-224
promotes ovarian cancer cell proliferation by targeting KLLN. In
Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 53:149–156. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Qiu R, Li W and Liu Y: MicroRNA-204
protects H9C2 cells against hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced injury
through regulating SIRT1-mediated autophagy. Biomed Pharmacother.
100:15–19. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|