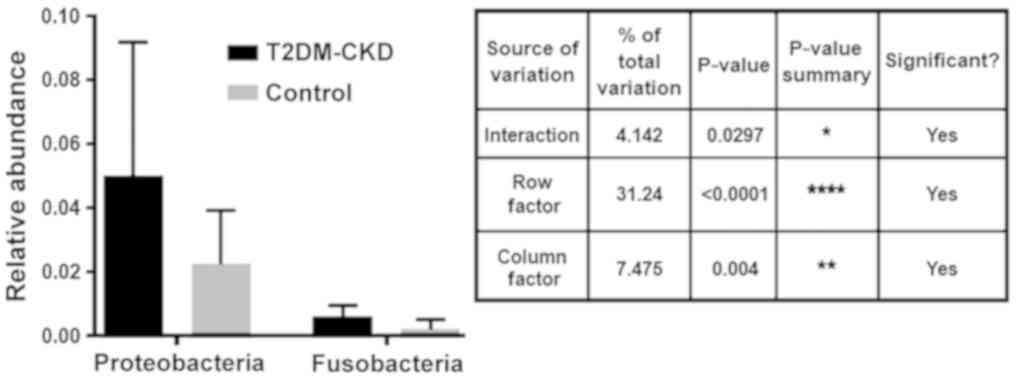
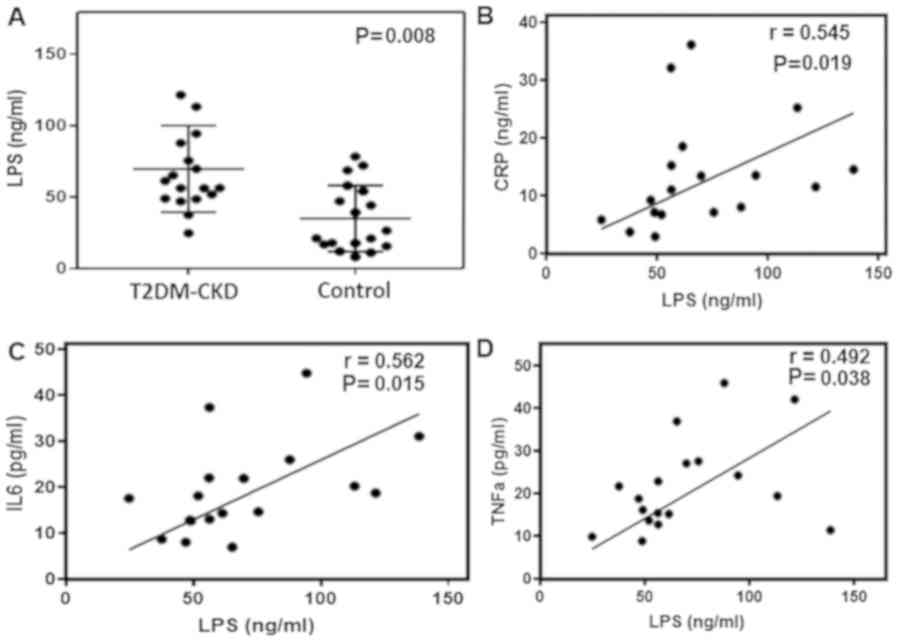
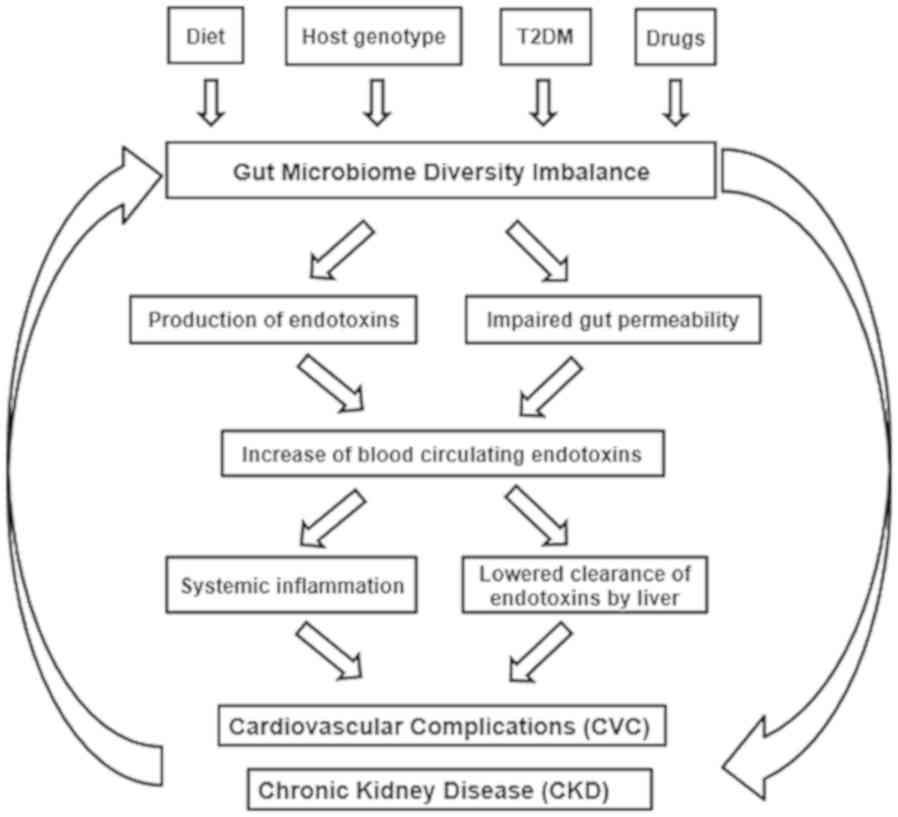
|
1
|
Chaves LD, McSkimming DI, Bryniarski MA,
Honan AM, Abyad S, Thomas SA, Wells S, Buck M, Sun Y, Genco RJ, et
al: Chronic kidney disease, uremic milieu, and its effects on gut
bacterial microbiota dysbiosis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
315:F487–F502. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mafra D, Lobo JC, Barros AF, Koppe L,
Vaziri ND and Fouque D: Role of altered intestinal microbiota in
systemic inflammation and cardiovascular disease in chronic kidney
disease. Future Microbiol. 9:399–410. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bu J and Wang Z: Cross-Talk between gut
microbiota and heart via the routes of metabolite and immunity.
Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2018:64580942018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tang WW and Hazen SL: The contributory
role of gut microbiota in cardiovascular disease. J Clin Invest.
124:4204–4211. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Harsch IA and Konturek PC: The role of gut
microbiota in obesity and type 2 and type 1 diabetes mellitus: New
insights into ‘old’ diseases. Med Sci (Basel). 6(pii):
E322018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gomes JMG, Costa JA and Alfenas RCG:
Metabolic endotoxemia and diabetes mellitus: A systematic review.
Metabolism. 68:133–144. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sabatino A, Regolisti G, Cosola C,
Gesualdo L and Fiaccadori E: Intestinal microbiota in type 2
diabetes and chronic kidney disease. Curr Diab Rep. 17:162017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fallucca F, Porrata C, Fallucca S and
Pianesi M: Influence of diet on gut microbiota, inflammation and
type 2 diabetes mellitus. First experience with macrobiotic Ma-Pi 2
diet. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 30 (Suppl 1):S48–S54. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Harley IT and Karp CL: Obesity and the gut
microbiome: Striving for causality. Mol Metab. 1:21–31. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Raetz CR and Whitfield C:
Lipopolysaccharide endotoxins. Annu Rev Biochem. 71:635–700. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Guo S, Al-Sadi R, Said HM and Ma TY:
Lipopolysaccharide causes an increase in intestinal tight junction
permeability in vitro and in vitro and in vivo by inducing
enterocyte membrane expression and localization of TLR-4 and CD14.
Am J Pathol. 182:375–387. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tidswell M, Tillis W, Larosa SP, Lynn M,
Wittek AE, Kao R, Wheeler J, Gogate J and Opal SM; Eritoran Sepsis
Study Group, : Phase 2 trial of eritoran tetrasodium (E5564), a
toll-like receptor 4 antagonist, in patients with severe sepsis.
Crit Care Med. 38:72–83. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bohannon JK, Hernandez A, Enkhbaatar P,
Adams WL and Sherwood ER: The immunobiology of toll-like receptor 4
agonists: From endotoxin tolerance to immunoadjuvants. Shock.
40:451–462. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dauphinee SM and Karsan A:
Lipopolysaccharide signaling in endothelial cells. Lab Invest.
86:9–22. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Carpenter S and O'Neill LA: Recent
insights into the structure of Toll-like receptors and
post-translational modifications of their associated signalling.
Biochem J. 422:1–10. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kuzmich NN, Sivak KV, Chubarev VN, Porozov
YB, Savateeva-Lyubimova TN and Peri F: TLR4 signaling pathway
modulators as potential therapeutics in inflammation and sepsis.
Vaccines (Basel). 5(pii): E342017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang F, Liu J, Weng T, Shen K, Chen Z, Yu
Y, Huang Q, Wang G, Liu Z and Jin S: The inflammation induced by
lipopolysaccharide can be mitigated by short-chain fatty acid,
butyrate, through upregulation of IL-10 in septic shock. Scand J
Immunol. 85:258–263. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nicholson JK, Holmes E, Kinross J,
Burcelin R, Gibson G, Jia W and Pettersson S: Host-gut microbiota
metabolic interactions. Science. 336:1262–1267. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wu H, Esteve E, Tremaroli V, Khan MT,
Caesar R, Mannerås-Holm L, Ståhlman M, Olsson LM, Serino M,
Planas-Fèlix M, et al: Metformin alters the gut microbiome of
individuals with treatment-naive type 2 diabetes, contributing to
the therapeutic effects of the drug. Nat Med. 23:850–858. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ahola AJ, Lassenius MI, Forsblom C,
Harjutsalo V, Lehto M and Groop PH: Dietary patterns reflecting
healthy food choices are associated with lower serum LPS activity.
Sci Rep. 7:65112017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cani PD, Neyrinck AM, Fava F, Knauf C,
Burcelin RG Tuohy KM, Gibson GR and Delzenne NM: Selective
increases of bifidobacteria in gut microflora improve
high-fat-diet-induced diabetes in mice through a mechanism
associated with endotoxaemia. Diabetologia. 50:2374–2383. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Montandon SA and Jornayvaz FR: Effects of
antidiabetic drugs on gut microbiota composition. Genes (Basel).
8(pii): E2502017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Al Khodor S and Shatat IF: Gut microbiome
and kidney disease: A bidirectional relationship. Pediatr Nephrol.
32:921–931. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Vaziri ND, Wong J, Pahl M, Piceno YM, Yuan
J, DeSantis TZ, Ni Z, Nguyen TH and Andersen GL: Chronic kidney
disease alters intestinal microbial flora. Kidney Int. 83:308–315.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Forsyth CB, Shannon KM, Kordower JH, Voigt
RM, Shaikh M, Jaglin JA, Estes JD, Dodiya HB and Keshavarzian A:
Increased intestinal permeability correlates with sigmoid mucosa
alpha-synuclein staining and endotoxin exposure markers in early
Parkinson's disease. PLoS One. 6:e280322011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Terawaki H, Yokoyama K, Yamada Y, Maruyama
Y, Iida R, Hanaoka K, Yamamoto H, Obata T and Hosoya T: Low-grade
endotoxemia contributes to chronic inflammation in hemodialysis
patients: Examination with a novel lipopolysaccharide detection
method. Ther Apher Dial. 14:477–482. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ussar S, Griffin NW, Bezy O, Fujisaka S,
Vienberg S, Softic S, Deng L, Bry L, Gordon JI and Kahn CR:
Interactions between gut microbiota, host genetics and diet
modulate the predisposition to obesity and metabolic syndrome. Cell
Metab. 22:516–530. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Richesson RL, Rusincovitch SA, Wixted D,
Batch BC, Feinglos MN, MirandaM L, Hammond WE, Califf RM and Spratt
SE: A comparison of phenotype definitions for diabetes mellitus. J
Am Med Inform Assoc. 20:e319–e326. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
National Kidney Foundation: GFR
calculator. https://www.kidney.org/professionals/kdoqi/gfr_calculatorAugust
9–2017PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
National Kidney Foundation: K/DOQI
clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease:
Evaluation, classification, and stratification. Am J Kidney Dis. 39
(Suppl 1):S1–S266. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Al-Obaide MAI, Singh R, Datta P,
Rewers-Felkins KA, Salguero MV, Al-Obaidi I, Kottapalli KR and
Vasylyeva TL: Gut microbiota-dependent trimethylamine-N-oxide and
serum biomarkers in patients with T2DM and advanced CKD. J Clin
Med. 6(pii): E862017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hiergeist A, Reischl U; Priority Program
1656 Intestinal Microbiota Consortium/quality assessment
participants, ; Gessner A: Multicenter quality assessment of 16S
ribosomal DNA-sequencing for microbiome analyses reveals high
inter-center variability. Int J Med Microbiol. 306:334–342. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Balvočiūtė M and Huson DH: SILVA, RDP,
greengenes, NCBI and OTT-how do these taxonomies compare? BMC
Genomics. 18 (Suppl 2):S1142017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Raetz CR, Ulevitch RJ, Wright SD, Sibley
CH, Ding A and Nathan CF: Gram-negative endotoxin: An extraordinary
lipid with profound effects on eukaryotic signal transduction.
FASEB J. 5:2652–2660. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Raetz CR, Guan Z, Ingram BO, Six DA, Song
F, Wang X and Zhao J: Discovery of new biosynthetic pathways: The
lipid a story. J Lipid Res. 50 (Suppl):S103–S108. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Thomas F, Hehemann JH, Rebuffet E, Czjzek
M and Michel G: Environmental and gut bacteroidetes: The food
connection. Front Microbiol. 2:932011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
d'Hennezel E, Abubucker S, Murphy LO and
Cullen TW: Total lipopolysaccharide from the human gut microbiome
silences Toll-like receptor signaling. mSystems. 2(pii): e00046–17.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Santoru ML, Piras C, Murgia A, Palmas V,
Camboni T, Liggi S, Ibba I, Lai MA, Orrù S, Blois S, et al: Cross
sectional evaluation of the gut-microbiome metabolome axis in an
Italian cohort of IBD patients. Sci Rep. 7:95232017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sun J and Kato I: Gut microbiota,
inflammation and colorectal cancer. Genes Dis. 3:130–143. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Guerrero-Preston R, Godoy-Vitorino F,
Jedlicka A, Rodríguez-Hilario A, González H, Bondy J, Lawson F,
Folawiyo O, Michailidi C, Dziedzic A, et al: 16S rRNA amplicon
sequencing identifies microbiota associated with oral cancer, human
papilloma virus infection and surgical treatment. Oncotarget.
7:51320–51334. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Jiang S, Xie S, Lv D, Wang P, He H, Zhang
T, Zhou Y, Lin Q, Zhou H, Jiang J, et al: Alteration of the gut
microbiota in Chinese population with chronic kidney disease. Sci
Rep. 7:28702017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lindberg AA, Weintraub A, Zähringer U and
Rietschel ET: Structure-activity relationships in
lipopolysaccharides of Bacteroides fragilis. Rev Infect Dis.
12 (Suppl 2):S133–S241. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ramachandran G: Gram-positive and
gram-negative bacterial toxins in sepsis: A brief review.
Virulence. 5:213–218. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lukiw WJ: Bacteroides fragilis
lipopolysaccharide and inflammatory signaling in alzheimer's
disease. Front Microbiol. 7:15442016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Couturier MR, Slechta ES, Goulston C,
Fisher MA and Hanson KE: Leptotrichia bacteremia in patients
receiving high-dose chemotherapy. J Clin Microbiol. 50:1228–1232.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Cekanaviciute E, Yoo BB, Runia TF,
Debelius JW, Singh S, Nelson CA, Kanner R, Bencosme Y, Lee YK,
Hauser SL, et al: Gut bacteria from multiple sclerosis patients
modulate human T cells and exacerbate symptoms in mouse models.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 114:10713–10718. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Hsieh YY, Tung SY, Pan HY, Yen CW, Xu HW,
Lin YJ, Deng YF, Hsu WT, Wu CS and Li C: Increased abundance of
Clostridium and Fusobacterium in gastric microbiota
of patients with gastric cancer in Taiwan. Sci Rep. 8:1582018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Apte RN, Pluznik DH and Galanos C: Lipid
A, the active part of bacterial endotoxins in inducing serum colony
stimulating activity and proliferation of splenic
granulocyte/macrophage progenitor cells. J Cell Physiol. 87:71–78.
1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lu YC, Yeh WC and Ohashi PS: LPS/TLR4
signal transduction pathway. Cytokine. 42:145–151. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Park BS, Song DH, Kim HM, Choi BS, Lee H
and Lee JO: The structural basis of lipopolysaccharide recognition
by the TLR4-MD-2 complex. Nature. 458:1191–1195. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
McGettrick AF and O'Neill LA: Regulators
of TLR4 signaling by endotoxins. Subcell Biochem. 53:153–171. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Oberholzer A, Oberholzer C and Moldawer
LL: Sepsis syndromes: Understanding the role of innate and acquired
immunity. Shock. 16:83–96. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Grasset E, Puel A, Charpentier J, Collet
X, Christensen JE, Tercé F and Burcelin R: A specific gut
microbiota dysbiosis of type 2 diabetic mice induces GLP-1
resistance through an enteric NO-dependent and gut-brain axis
mechanism. Cell Metab. 25:1075–1090.e5. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Farhadi A, Banan A, Fields J and
Keshavarzian A: Intestinal barrier: An interface between health and
disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 18:479–497. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Camilleri M, Madsen K, Spiller R,
Greenwood-Van Meerveld B and Verne GN: Intestinal barrier function
in health and gastrointestinal disease. Neurogastroenterol Motil.
24:503–512. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Tripathi A, Lammers KM, Goldblum S,
Shea-Donohue T, Netzel-Arnett S, Buzza MS, Antalis TM, Vogel SN,
Zhao A, Yang S, et al: Identification of human zonulin, a
physiological modulator of tight junctions, as prehaptoglobin-2.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:16799–16804. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Li C, Gao M, Zhang W, Chen C, Zhou F, Hu Z
and Zeng C: Zonulin regulates intestinal permeability and
facilitates enteric bacteria permeation in coronary artery disease.
Sci Rep. 6:291422016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Kelly JR, Kennedy PJ, Cryan JF, Dinan TG,
Clarke G and Hyland NP: Breaking down the barriers: The gut
microbiome, intestinal permeability and stress-related psychiatric
disorders. Front Cell Neurosci. 9:3922015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Bischoff SC, Barbara G, Buurman W,
Ockhuizen T, Schulzke JD, Serino M, Tilg H, Watson A and Wells JM:
Intestinal permeability-a new target for disease prevention and
therapy. BMC Gastroenterol. 14:1892014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Wang L, Llorente C, Hartmann P, Yang AM,
Chen P and Schnabl B: Methods to determine intestinal permeability
and bacterial translocation during liver disease. J Immunol
Methods. 421:44–53. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Fukui H, Brauner B, Bode JC and Bode C:
Plasma endotoxin concentrations in patients with alcoholic and
non-alcoholic liver disease: Reevaluation with an improved
chromogenic assay. J Hepatol. 12:162–169. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
de Rekeneire N, Peila R, Ding J, Colbert
LH, Visser M, Shorr RI, Kritchevsky SB, Kuller LH, Strotmeyer ES,
Schwartz AV, et al: Diabetes, hyperglycemia, and inflammation in
older individuals: The health, aging and body composition study.
Diabetes Care. 29:1902–1908. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Anderson AJ and Vingrys AJ: Small samples:
Does size matter? Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 42:1411–1413.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|