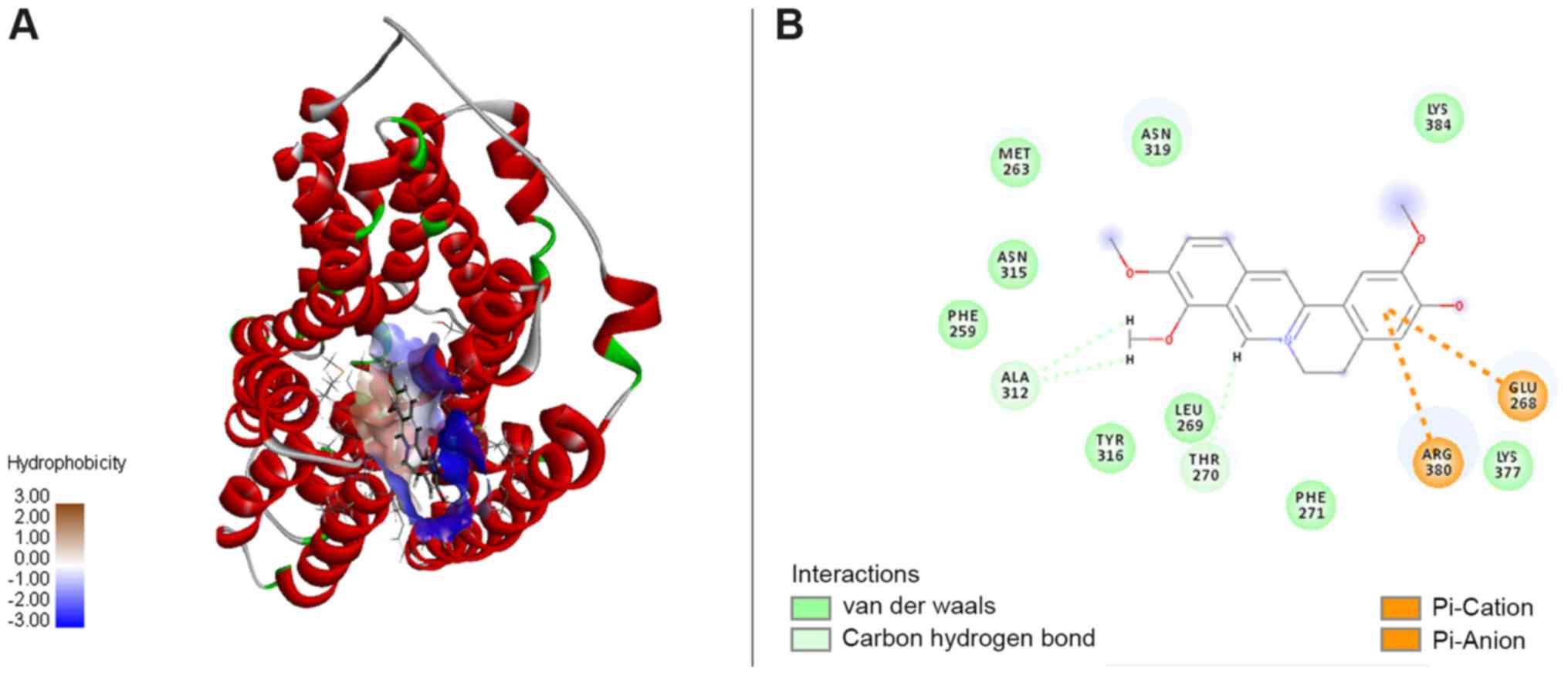
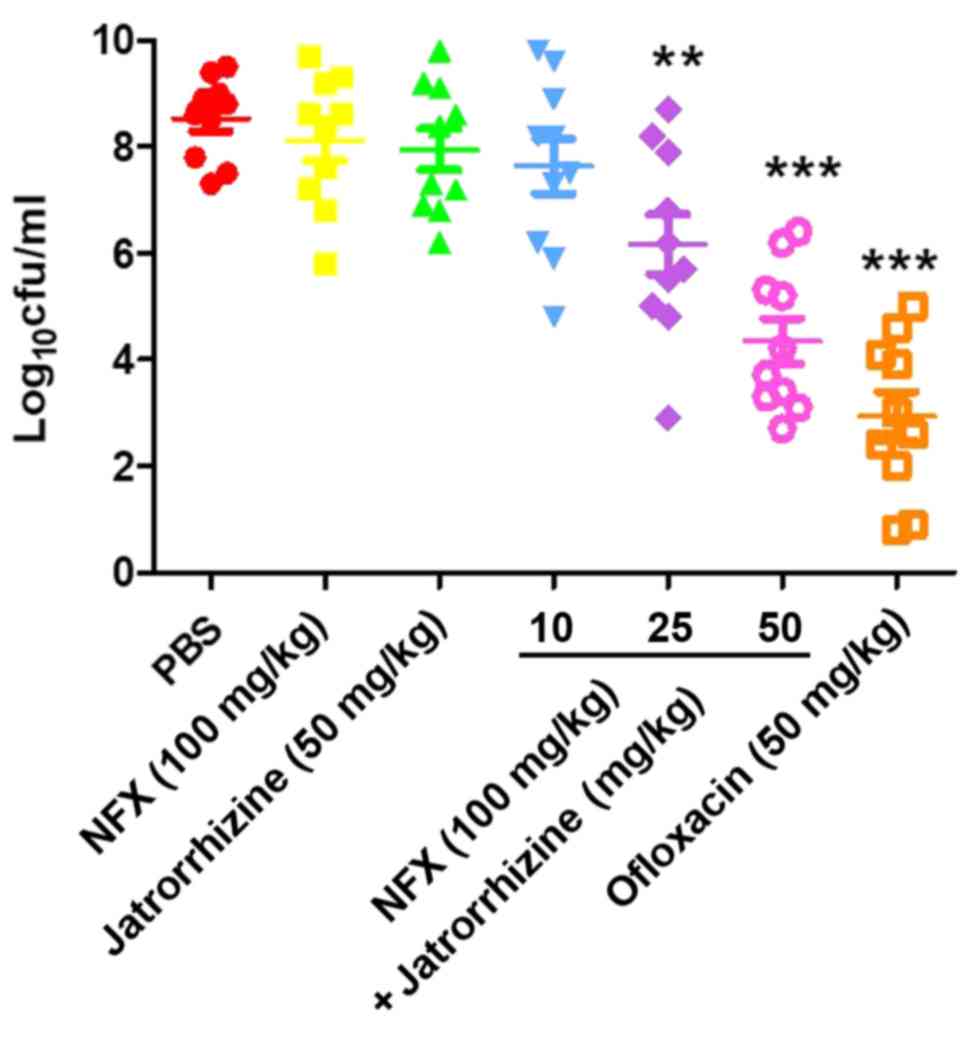
|
1
|
Russell AD: Biocide use and antibiotic
resistance: The relevance of laboratory findings to clinical and
environmental situations. Lancet Infect Dis. 3:794–803. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Abreu AC, McBain AJ and Simoes M: Plants
as sources of new antimicrobials and resistance-modifying agents.
Nat Prod Rep. 29:1007–1021. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hooper DC: Efflux pumps and nosocomial
antibiotic resistance: A primer for hospital epidemiologists. Clin
Infect Dis. 40:1811–1817. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Oluwatuyi M, Kaatz GW and Gibbons S:
Antibacterial and resistance modifying activity of Rosmarinus
officinalis. Phytochemistry. 65:3249–3254. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wright GD: Bacterial resistance to
antibiotics: Enzymatic degradation and modification. Adv Drug Deliv
Rev. 57:1451–1470. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hoffman SB: Mechanisms of antibiotic
resistance. Compendium on Continuing Education for the Practising
Veterinarian-North American Edition. 23:464–472. 2001.
|
|
7
|
Gould IM, Reilly J, Bunyan D and Walker A:
Costs of healthcare-associated methicillin-resistant
Staphylococcus aureus and its control. Clin Microbiol
Infect. 16:1721–1728. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Neyfakh AA, Borsch CM and Kaatz GW:
Fluoroquinolone resistance protein NorA of Staphylococcus
aureus is a multidrug efflux transporter. Antimicrob Agents
Chemother. 37:128–129. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Truong-Bolduc QC, Zhang X and Hooper DC:
Characterization of NorR protein, a multifunctional regulator of
norA expression in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol.
185:3127–3138. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Alekshun MN and Levy SB: Molecular
mechanisms of antibacterial multidrug resistance. Cell.
128:1037–1050. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mallea M, Mahamoud A, Chevalier J,
Alibert-Franco S, Brouant P, Barbe J and Pagès JM:
Alkylaminoquinolines inhibit the bacterial antibiotic efflux pump
in multidrug-resistant clinical isolates. Biochem J. 376:801–805.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Phillipson JD: Phytochemistry and
pharmacognosy. Phytochemistry. 68:2960–2972. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gibbons S: Anti-staphylococcal plant
natural products. Nat Prod Rep. 21:263–277. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kalia NP, Mahajan P, Mehra R, Nargotra A,
Sharma JP, Koul S and Khan IA: Capsaicin, a novel inhibitor of the
NorA efflux pump, reduces the intracellular invasion of
Staphylococcus aureus. J Antimicrob Chemother. 67:2401–2408.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
He JM and Mu Q: The medicinal uses of the
genus Mahonia in traditional Chinese medicine: An
ethnopharmacological, phytochemical and pharmacological review. J
Ethnopharmacol. 175:668–683. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kaatz GW, Seo SM and Ruble CA: Mechanisms
of fluoroquinolone resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. J
Infectious Dis. 163:1080–1086. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ross JI, Farrell AM, Eady EA, Cove JH and
Cunliffe WJ: Characterisation and molecular cloning of the novel
macrolide-streptogramin B resistance determinant from
Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Antimicrob Chemother.
24:851–862. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute
(CLSI), . Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility
Testing; Twentieth Informational Supplement. M100-S2030. CLSI;
Wayne, PA: pp. 54–62. 2010
|
|
19
|
Hemaiswarya S, Kruthiventi AK and Doble M:
Synergism between natural products and antibiotics against
infectious diseases. Phytomedicine. 15:639–652. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Abascal K and Yarnell E: Herbs and drug
resistane: Part 2-Clinical implications of research on microbial
resistance to antibiotics. Complementary Therapies. 8:237–241.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Pearson RD, Steigbigel RT and Davis HT:
Method of reliable determination of minimal lethal antibiotic
concentrations. Antimicrobial Agents Chemotherapy. 18:699–708.
1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lechner D, Gibbons S and Bucar F: Plant
phenolic compounds as ethidium bromide efflux inhibitors in
Mycobacterium smegmatis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 62:345–348.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang Y: I-TASSER server for protein 3D
structure prediction. BMC Bioinformatics. 9:402008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Roy A, Kucukural A and Zhang Y: I-TASSER:
A unified platform for automated protein structure and function
prediction. Nat Protoc. 5:725–738. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yang J, Yan R, Roy A, Dong X, Poisson J
and Yang Z: The I-TASSER Suite: Protein structure and function
prediction. Nat Methods. 12:7–8. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang J, Liang Y and Zhang Y: Atomic-level
protein structure refinement using fragment guided molecular
dynamics conformation sampling. Structure. 19:1784–1795. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Aguinagalde L, Diez-Martinez R, Yuste J,
Royo I, Gil C, Lasa Í, Martín-Fontecha M, Marín-Ramos NI, Ardanuy
C, Liñares J, et al: Auranofin efficacy against MDR Streptococcus
pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus infections. J
Antimicrob Chemother. 70:2608–2617. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Newman DJ and Cragg GM: Natural products
as sources of new drugs from 1981 to 2014. J Nat Prod. 79:629–661.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sibanda T and Okoh AI: The challenges of
overcoming antibiotic resistance: Plant extracts as potential
sources of antimicrobial and resistance modifying agents. African J
Biotechnol. 6:2886–2896. 2007.
|
|
31
|
Sriram D, Bal TR and Yogeeswari P: Design,
synthesis and biological evaluation of novel non-nucleoside HIV-1
reverse transcriptase inhibitors with broad-spectrum
chemotherapeutic properties. Bioorg Med Chem. 12:5865–5873. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zou D, Xie K, Wang H, Chen Y and Xie M:
Inhibitory effects of biochanin A on the efflux pump of
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Wei
Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 54:1204–1211. 2014.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Fu Y, Wu X and Chen Z: A new approach for
flexible molecular docking based on swarm intelligence.
Mathematical Problems Engineering. 2015:1–10. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|