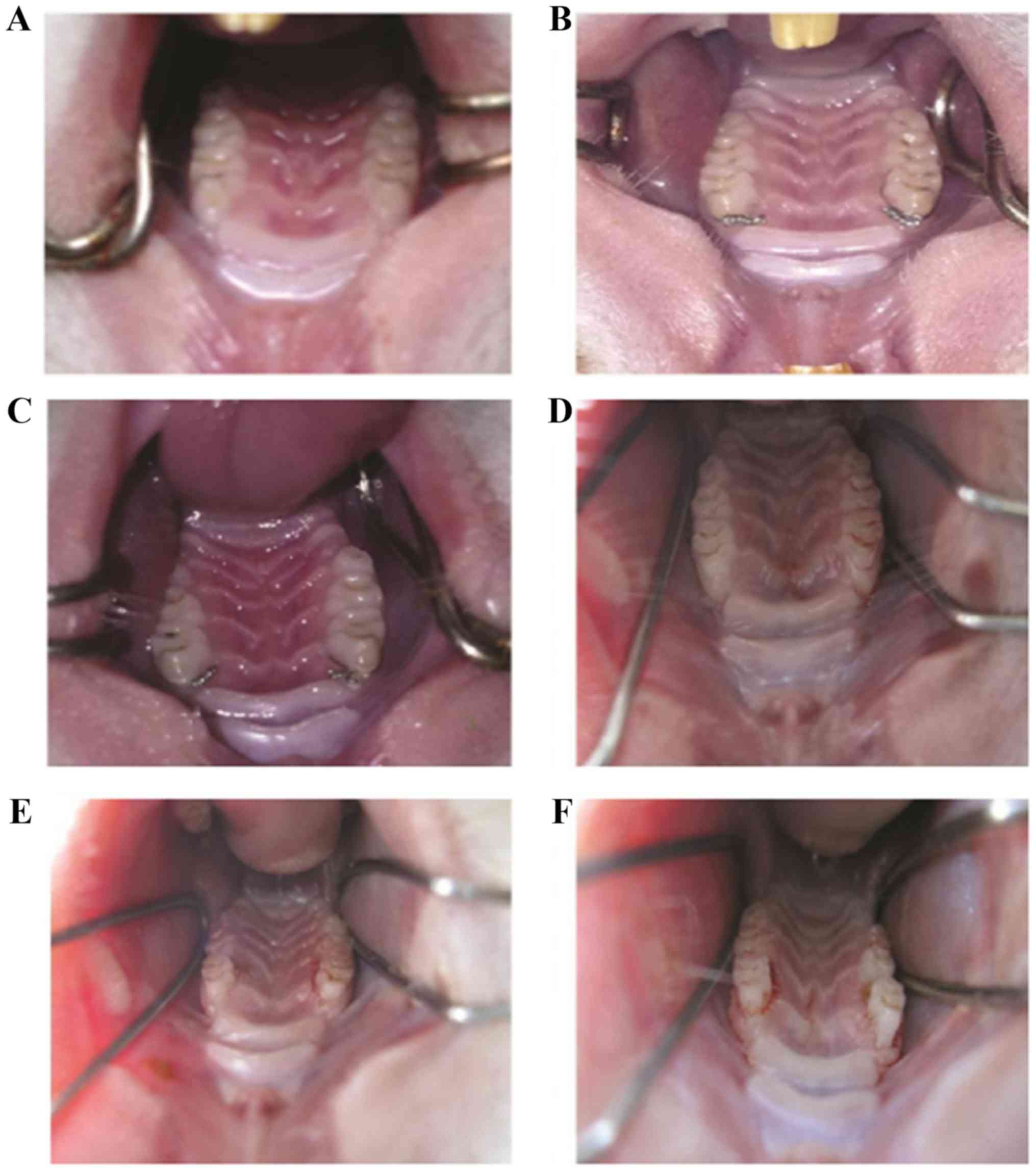
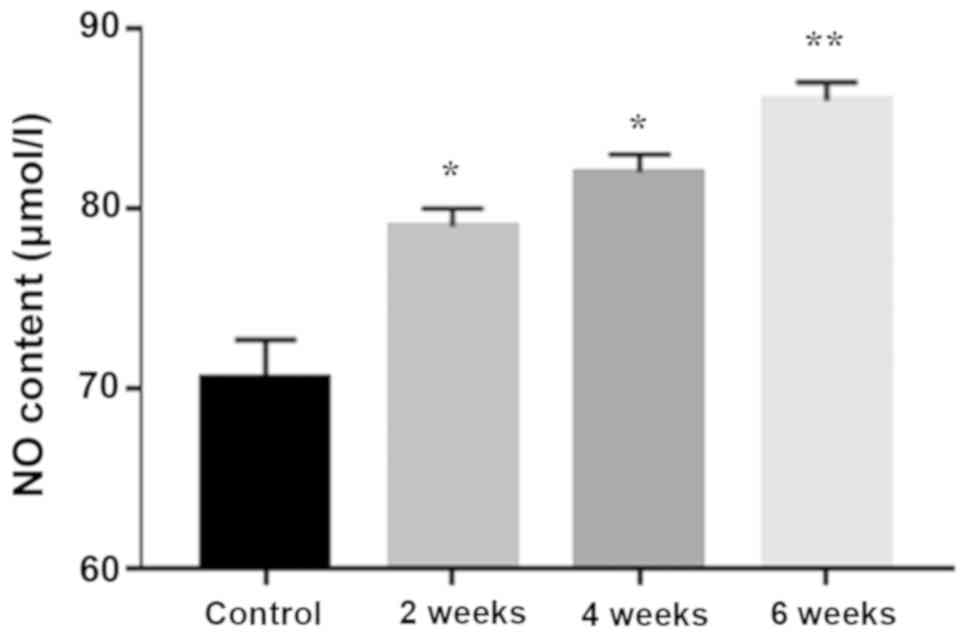
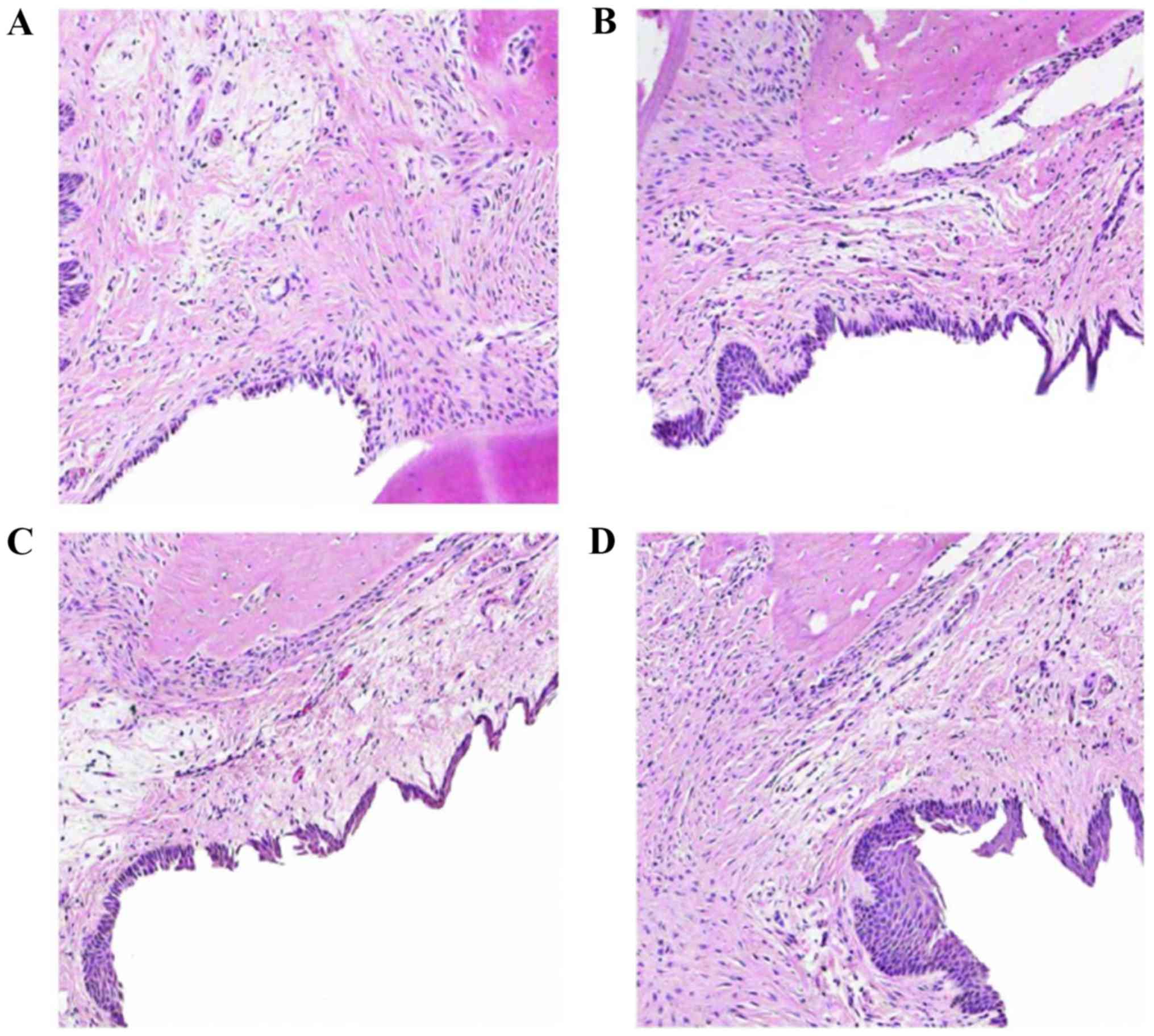
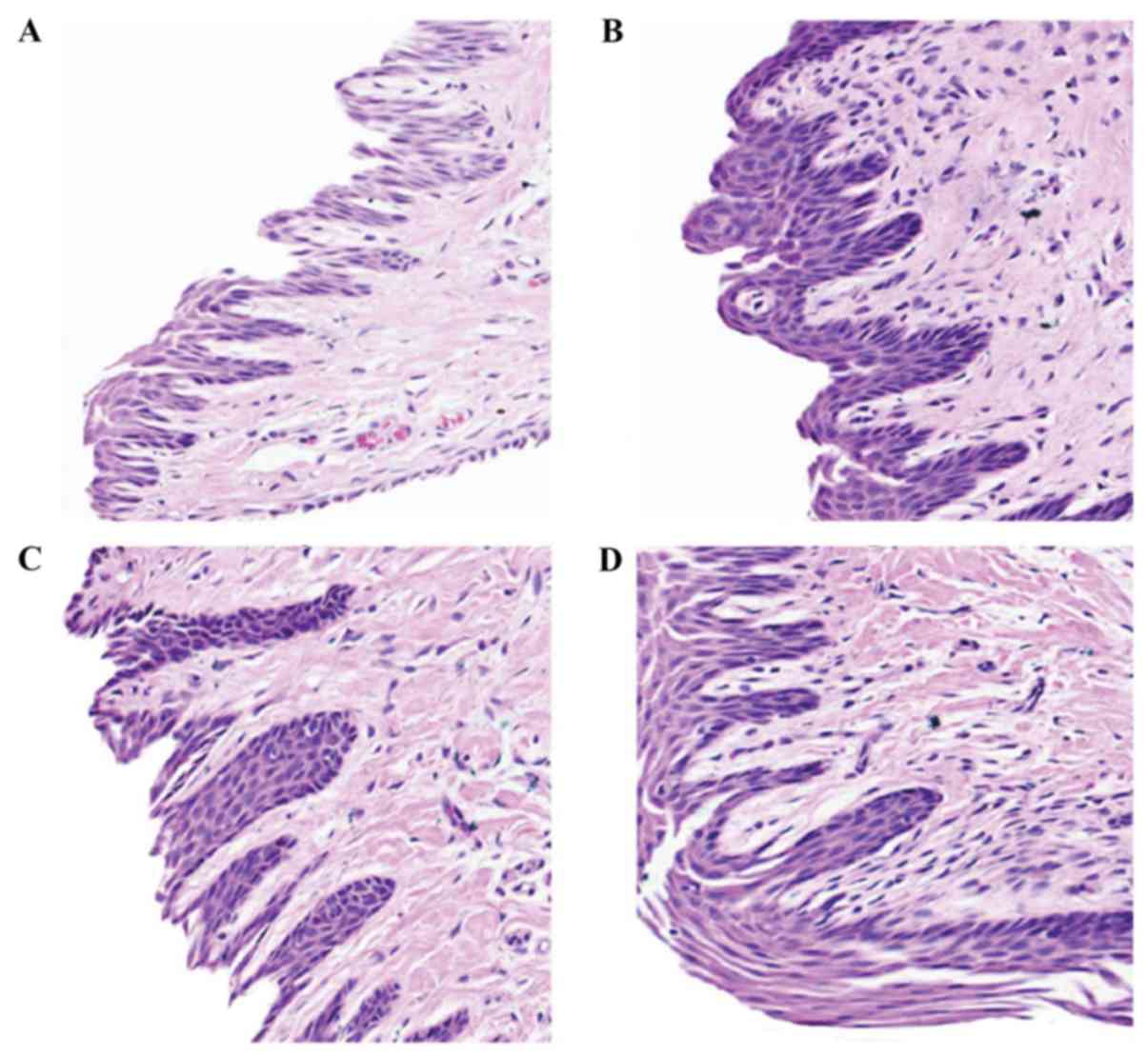
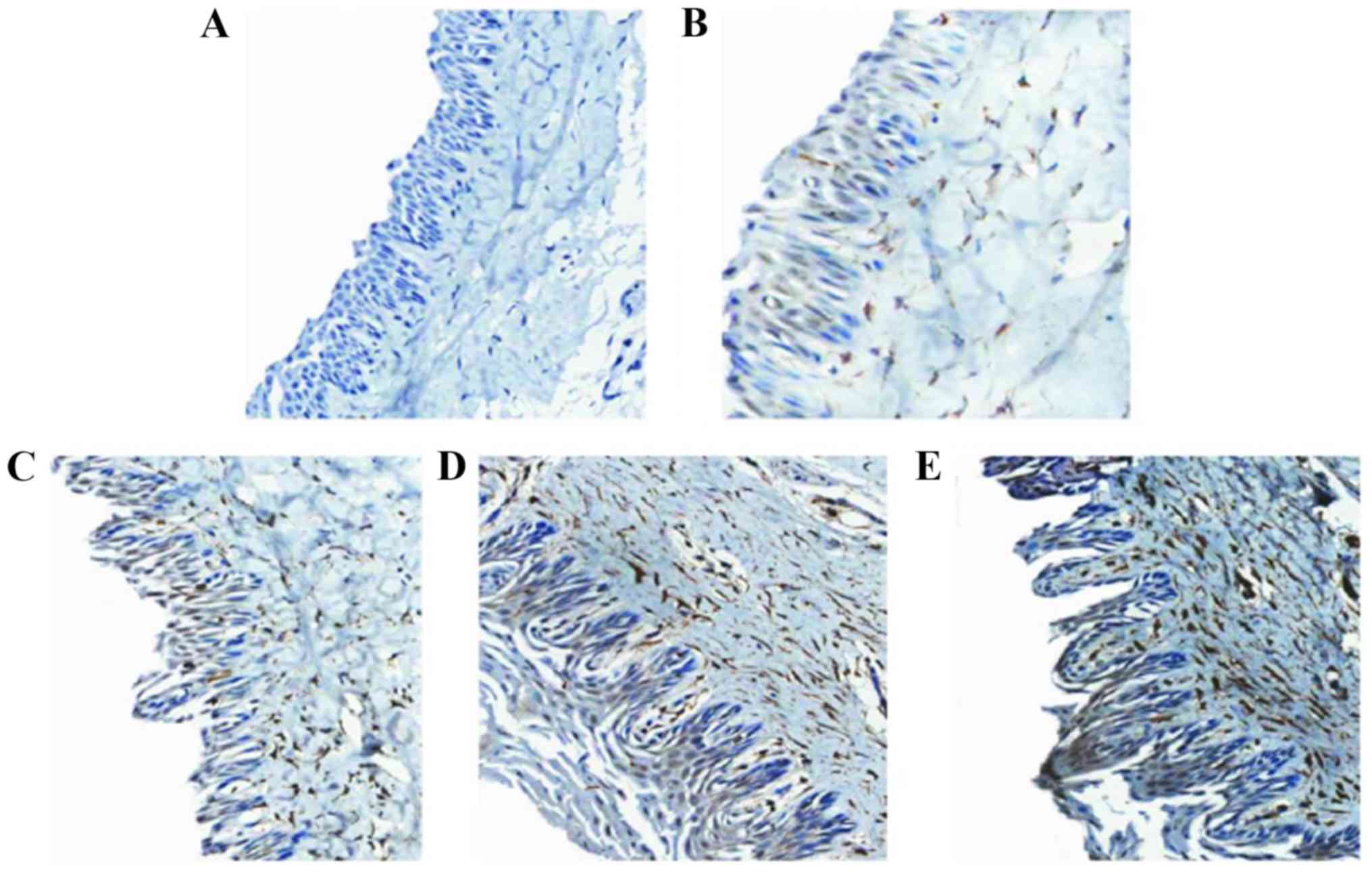
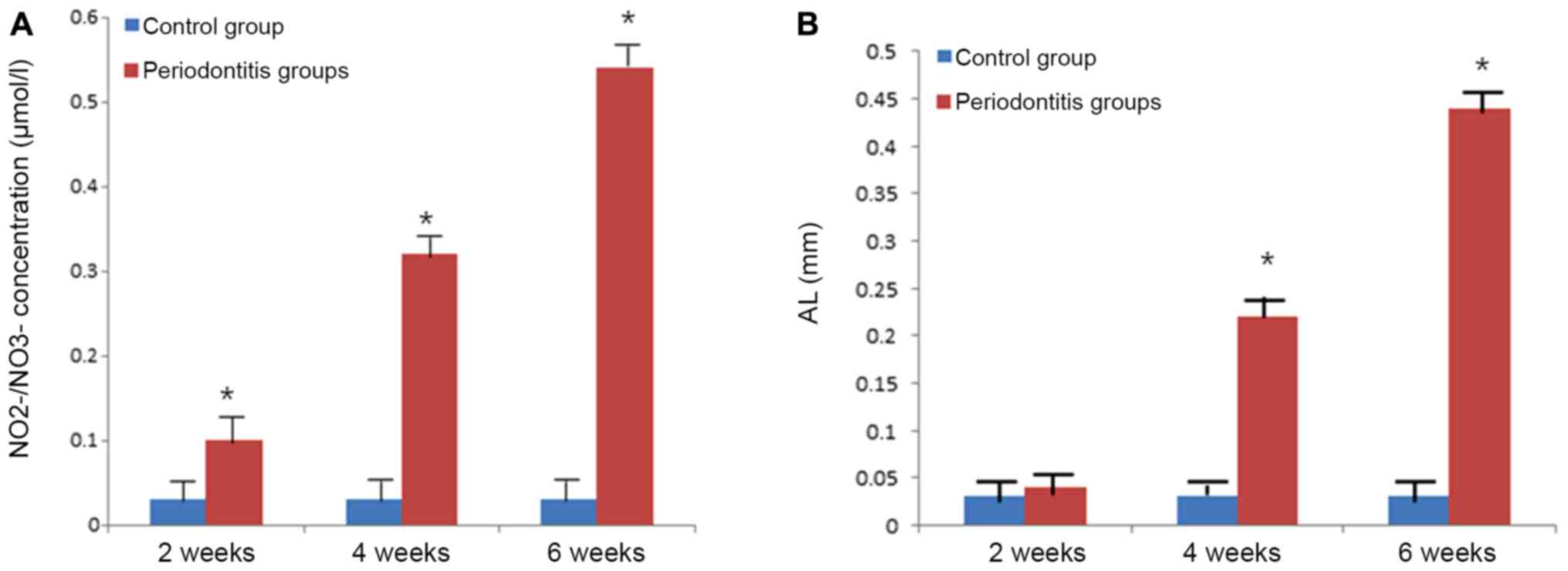
|
1
|
Vonholdt J, Gonzáles JR, Michel J,
Herrmann JM and Meyle J: Interleukin-1 polymorphism in patients
with early onset-and adult periodontitis. Int Poster J Dent Oral
Med. 3:722001.
|
|
2
|
Pacher P, Beckman JS and Liaudet L: Nitric
oxide and peroxynitrite in health and disease. Physiol Rev.
87:315–424. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Reeves SR, Simakajornboon N and Gozal D:
The role of nitric oxide in the neural control of breathing. Respir
Physiol Neurobiol. 164:143–150. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Schmidt HH, Nau H, Wittfoht W, Gerlach J,
Prescher KE, Klein MM, Niroomand F and Böhme E: Arginine is a
physiological precursor of endothelium-derived nitric oxide. Eur J
Pharmacol. 154:213–216. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bodis S and Haregewoin A: Evidence for the
release and possible neural regulation of nitric oxide in human
saliva. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 194:347–350. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Do MJ, Kim K, Lee H, Cha S, Seo T, Park
HJ, Lee JS and Kim TI: Development of animal experimental
periodontitis models. J Periodontal Implant Sci. 43:147–152. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lockhart PB, Bolger AF, Papapanou PN,
Osinbowale O, Trevisan M, Levison ME, Taubert KA, Newburger JW,
Gornik HL, Gewitz MH, et al: Periodontal disease and
atherosclerotic vascular disease: Does the evidence support an
independent association? A scientific statement from the American
heart association. circulation. 125:2520–2544. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Achong R, Nishimura I, Ramachandran H,
Howell TH, Fiorellini JP and Karimbux NY: Membrane type (MT)
1-matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) and MMP-2 expression in
ligature-induced periodontitis in the rat. J Periodontol.
74:494–500. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Albandar JM and Rams TE: Global
epidemiology of periodontal diseases: An overview. Periodontol
2000. 29:7–10. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lappin DF, Kjeldsen M, Sander L and Kinane
DF: Inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in periodontitis. J
Periodontal Res. 35:369–373. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Poorsattar Bejeh Mir A: Focusing on
periodontitis as a vasculupathy: The therapeutic possibilities from
the perspective of a dentistry student. J Pharm Biomed Sci.
13:2011.
|
|
12
|
López NJ, Smith PC and Gutierrez J: Higher
risk of preterm birth and low birth weight in women with
periodontal disease. J Dent Res. 81:58–63. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Teng YT: Protective and destructive
immunity in the periodontium: Part 1-innate and humoral immunity
and the periodontium. J Dent Res. 85:198–208. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Förstermann U, Schmidt HH, Pollock JS,
Sheng H, Mitchell JA, Warner TD, Nakane M and Murad F: Isoforms of
nitric oxide synthase. Characterization and purification from
different cell types. Biochem Pharmacol. 42:1849–1857. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Menaka K, Ramesh A, Thomas B and Kumari
NS: Estimation of nitric oxide as an inflammatory marker in
periodontitis. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 13:75–78. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Moshage H, Kok B, Huizenga JR and Jansen
P: Nitrite and nitrate determinations in plasma: A critical
evaluation. Clin Chem. 41:892–896. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lamster IB and Novak MJ: Host mediators in
gingival crevicular fluid: Implications for the pathogenesis of
periodontal disease. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 3:31–60. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wadhwa D, Bey A, Hasija M, Moin S, Kumar
A, Aman S and Sharma VK: Determination of levels of nitric oxide in
smoker and nonsmoker patients with chronic periodontitis. J
Periodontal Implant Sci. 43:215–220. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gautam DK, Jindal V, Gupta SC, Tuli A,
Kotwal B and Thakur R: Effect of cigarette smoking on the
periodontal health status: A comparative, cross sectional study. J
Indian Soc Periodontol. 15:383–387. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Reher VG, Zenóbio EG, Costa FO, Reher P
and Soares RV: Nitric oxide levels in saliva increase with severity
of chronic periodontitis. J Oral Sci. 49:271–276. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sreedevi M, Ramesh A and Dwarakanath C:
Periodontal status in smokers and nonsmokers: A clinical,
microbiological, and histopathological study. Int J Dent.
2012:5715902012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hussain QA, McKay IJ, Gonzales-Marin C and
Allaker RP: Regulation of adrenomedullin and nitric oxide
production by periodontal bacteria. J Periodontal Res. 50:650–657.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Aurer A, Aleksić J, Ivić-Kardum M, Aurer J
and Culo F: Nitric oxide synthesis is decreased in periodontitis. J
Clin Periodontol. 28:565–568. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Andrukhov O, Haririan H, Bertl K, Rausch
WD, Bantleon HP, Moritz A and Rausch-Fan X: Nitric oxide
production, systemic inflammation and lipid metabolism in
periodontitis patients: Possible gender aspect. J Clin Periodontol.
40:916–923. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Förstermann U and Sessa WC: Nitric oxide
synthases: Regulation and function. Eur Heart J. 33:829–837. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chiossone L, Dumas PY, Vienne M and Vivier
E: Natural killer cells and other innate lymphoid cells in cancer.
Nat Rev Immunol. 18:671–688. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bartold PM and Van Dyke TE: Periodontitis:
A host-mediated disruption of microbial homeostasis. Unlearning
learned concepts. Periodontol 2000. 62:203–217. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|