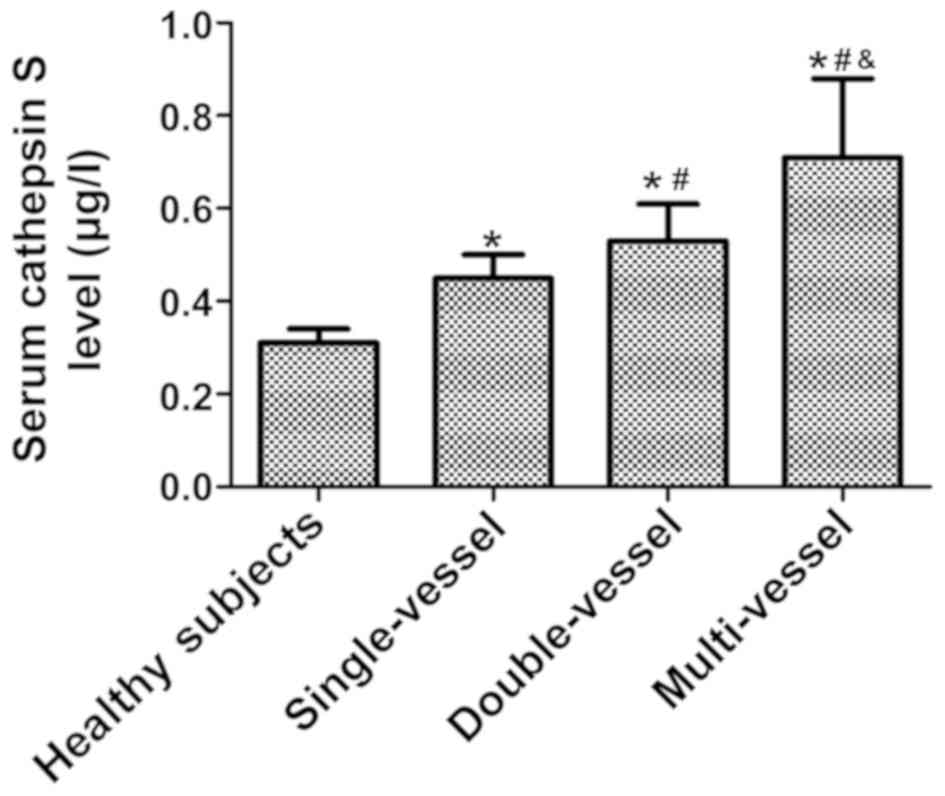
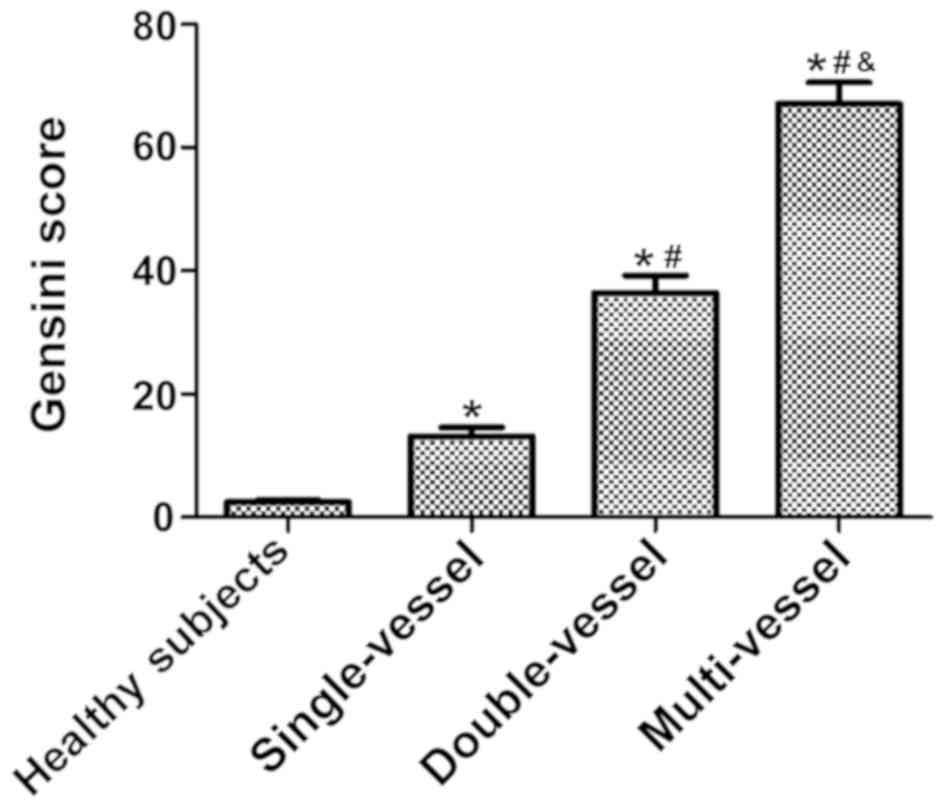
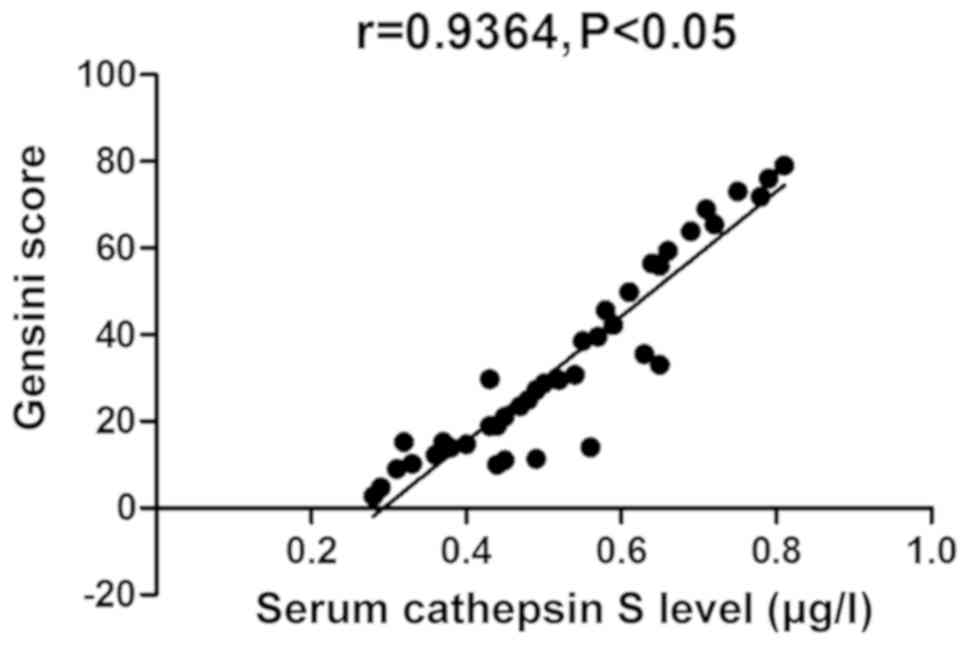
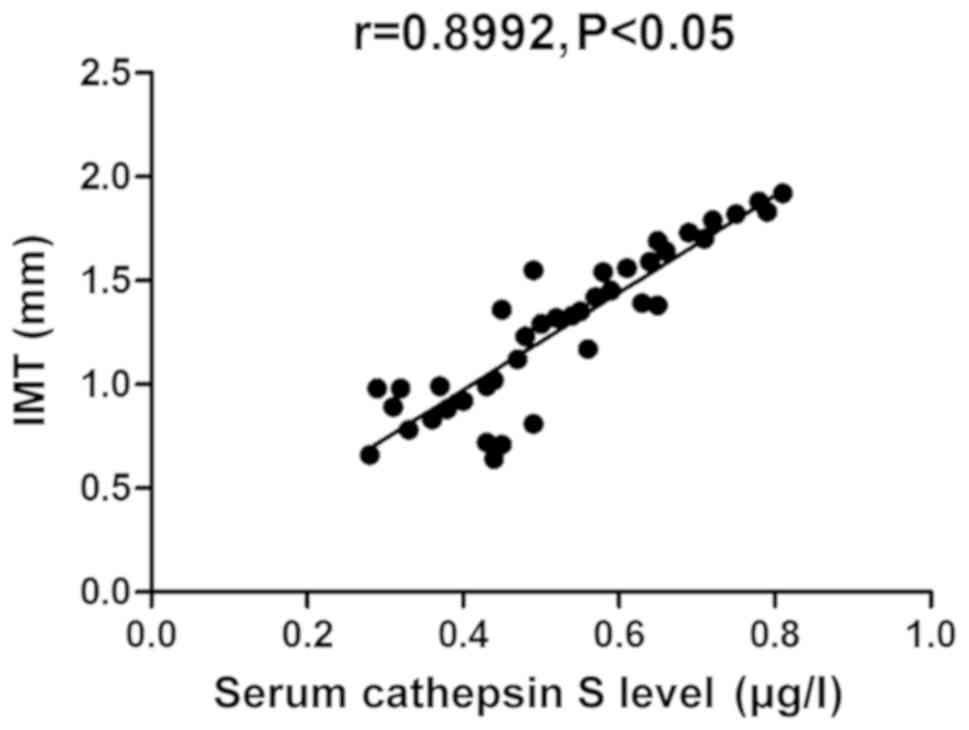
|
1
|
Zhou PP, Zhang WY, Li ZF, Chen YR, Kang XC
and Jiang YX: Association between SNPs in the promoter region in
cathepsin S and risk of asthma in Chinese Han population. Eur Rev
Med Pharmacol Sci. 20:2070–2076. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ignatov M, Liu C, Alekseenko A, Sun Z,
Padhorny D, Kotelnikov S, Kazennov A, Grebenkin I, Kholodov Y,
Kolosvari I, et al: Monte Carlo on the manifold and MD refinement
for binding pose prediction of protein-ligand complexes: 2017 D3R
Grand Challenge. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 33:119–127. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Xiao L, Han X, Wang XE, Li Q and Chen Y,
Cui Y and Chen Y: Cathepsin S in the spinal microglia facilitates
morphine-induced antinociceptive tolerance in rats. Neurosci Lett.
690:225–231. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Luo L, Zhu M and Zhou J: Association
between CTSS gene polymorphism and the risk of acute
atherosclerotic cerebral infarction in Chinese population: A
case-control study. Biosci Rep. 38:BSR201805862018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lee BC, Kang I, Lee SE, Lee JY, Shin N,
Kim JJ, Choi SW and Kang KS: Human umbilical cord blood plasma
alleviates age-related olfactory dysfunction by attenuating
peripheral TNF-α expression. BMB Rep. 52:259–264. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen CY, Chen CY, Liu CC and Chen CP:
Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids reduce preterm labor by
inhibiting trophoblast cathepsin S and inflammasome activation.
Clin Sci (Lond). 132:2221–2239. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wuopio J, Hilden J, Bring C, Kastrup J,
Sajadieh A, Jensen GB, Kjøller E, Kolmos HJ, Larsson A, Jakobsen
JC, et al: Cathepsin B and S as markers for cardiovascular risk and
all-cause mortality in patients with stable coronary heart disease
during 10 years: A CLARICOR trial sub-study. Atherosclerosis.
278:97–102. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Poulsen CB, Al-Mashhadi AL, von
Wachenfeldt K, Bentzon JF, Nielsen LB, Al-Mashhadi RH, Thygesen J,
Tolbod L, Larsen JR, Frøkiær J, et al: Treatment with a human
recombinant monoclonal IgG antibody against oxidized LDL in
atherosclerosis-prone pigs reduces cathepsin S in coronary lesions.
Int J Cardiol. 215:506–515. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bonfante R, Napimoga MH, Macedo CG,
Abdalla HB, Pieroni V and Clemente-Napimoga JT: The P2X7 receptor,
cathepsin S and fractalkine in the trigeminal subnucleus caudalis
signal persistent hypernociception in temporomandibular rat joints.
Neuroscience. 391:120–130. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ji C, Tang M, Harrison J, Paciorkowski A
and Johnson GVW: Nuclear transglutaminase 2 directly regulates
expression of cathepsin S in rat cortical neurons. Eur J Neurosci.
48:3043–3051. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
He X, Man VH, Ji B, Xie XQ and Wang J:
Calculate protein-ligand binding affinities with the extended
linear interaction energy method: Application on the Cathepsin S
set in the D3R Grand Challenge 3. J Comput Aided Mol Des.
33:105–117. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chaput L, Selwa E, Elisée E and Iorga BI:
Blinded evaluation of cathepsin S inhibitors from the D3RGC3
dataset using molecular docking and free energy calculations. J
Comput Aided Mol Des. 33:93–103. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Taleb S, Lacasa D, Bastard JP, Poitou C,
Cancello R, Pelloux V, Viguerie N, Benis A, Zucker JD, Bouillot JL,
et al: Cathepsin S, a novel biomarker of adiposity: Relevance to
atherogenesis. FASEB J. 19:1540–1542. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kubo K, Kawato Y, Nakamura K, Nakajima Y,
Nakagawa TY, Hanaoka K, Oshima S, Fukahori H, Inami M, Morokata T,
et al: Effective suppression of donor specific antibody production
by cathepsin S inhibitors in a mouse transplantation model. Eur J
Pharmacol. 838:145–152. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen RP, Ren A and Ye SD: Correlation
between serum cathepsin S and insulin resistance in type 2
diabetes. Exp Ther Med. 6:1237–1242. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gautam J, Banskota S, Lee H, Lee YJ, Jeon
YH, Kim JA and Jeong BS: Down-regulation of cathepsin S and matrix
metalloproteinase-9 via Src, a non-receptor tyrosine kinase,
suppresses triple-negative breast cancer growth and metastasis. Exp
Mol Med. 50:1182018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Janga SR Sr, Shah M, Ju Y, Meng Z, Edman
MC and Hamm-Alvarez SF: Longitudinal analysis of tear cathepsin S
activity levels in male non-obese diabetic mice suggests its
potential as an early stage biomarker of Sjögren's Syndrome.
Biomarkers. 24:91–102. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Seo SU, Min KJ, Woo SM and Kwon TK:
Z-FL-COCHO, a cathepsin S inhibitor, enhances oxaliplatin-mediated
apoptosis through the induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress.
Exp Mol Med. 50:1072018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nguyen DD, Cang Z, Wu K, Wang M, Cao Y and
Wei GW: Mathematical deep learning for pose and binding affinity
prediction and ranking in D3R Grand Challenges. J Comput Aided Mol
Des. 33:71–82. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Altieri A, Piyadasa H, Recksiedler B,
Spicer V and Mookherjee N: Cytokines IL-17, TNF and IFN-γ alter the
expression of antimicrobial peptides and proteins disparately: A
targeted proteomics analysis using SOMAscan technology. Vaccines
(Basel). 6:512018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Cheng XW, Kikuchi R, Ishii H, Yoshikawa D,
Hu L, Takahashi R, Shibata R, Ikeda N, Kuzuya M, Okumura K, et al:
Circulating cathepsin K as a potential novel biomarker of coronary
artery disease. Atherosclerosis. 228:211–216. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu Y, Li X, Peng D, Tan Z, Liu H, Qing Y,
Xue Y and Shi GP: Usefulness of serum cathepsin L as an independent
biomarker in patients with coronary heart disease. Am J Cardiol.
103:476–481. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|