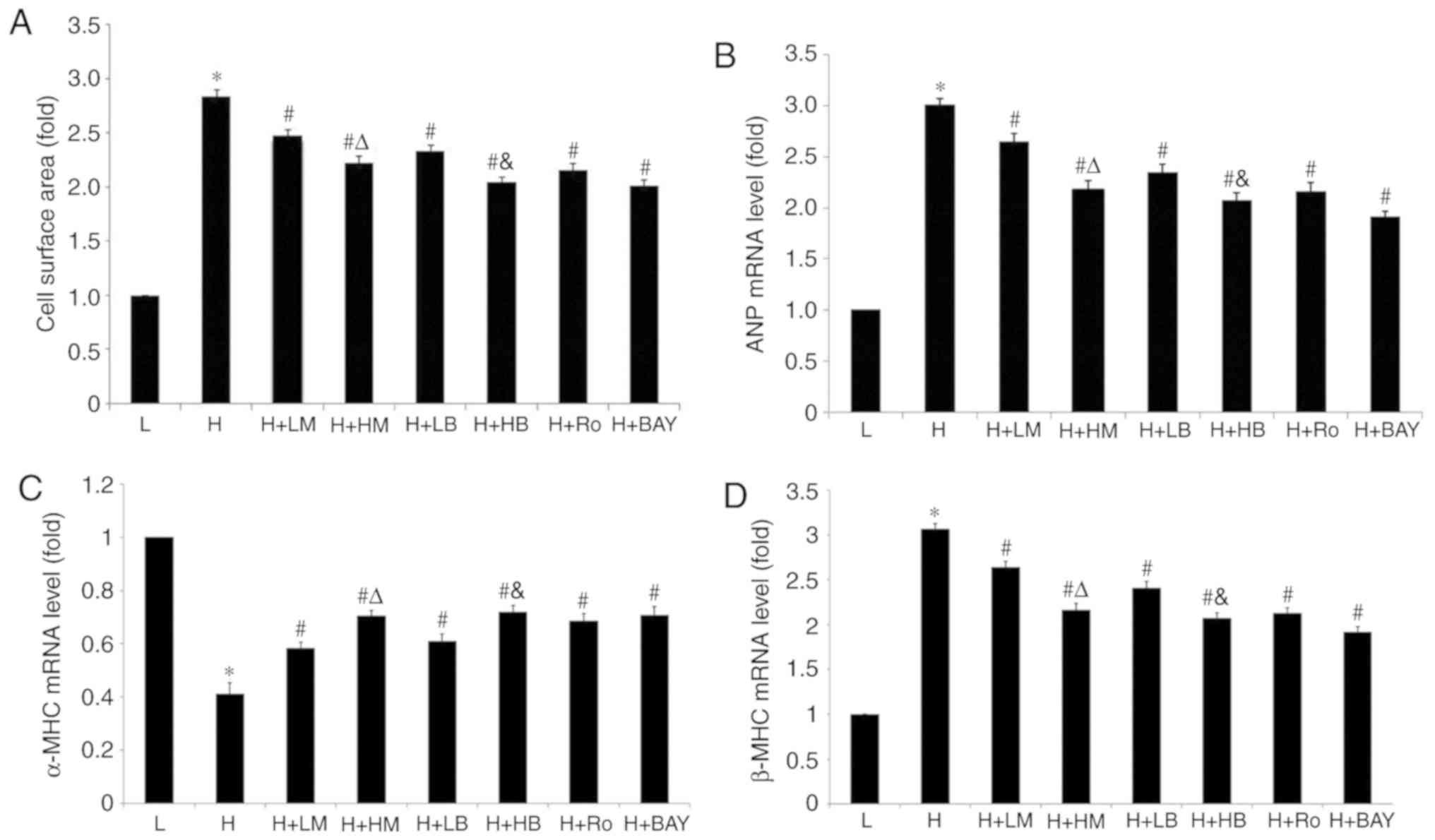
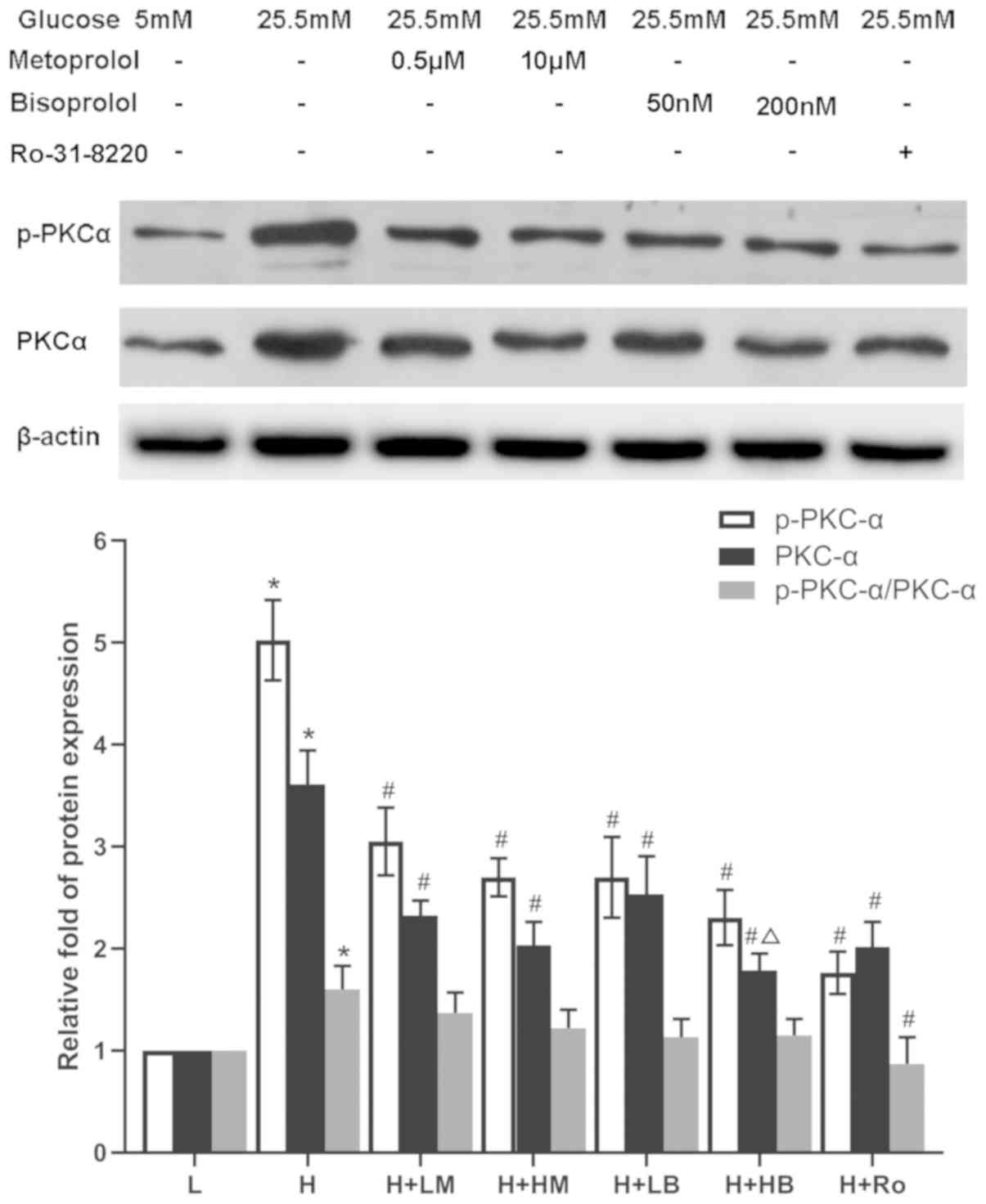
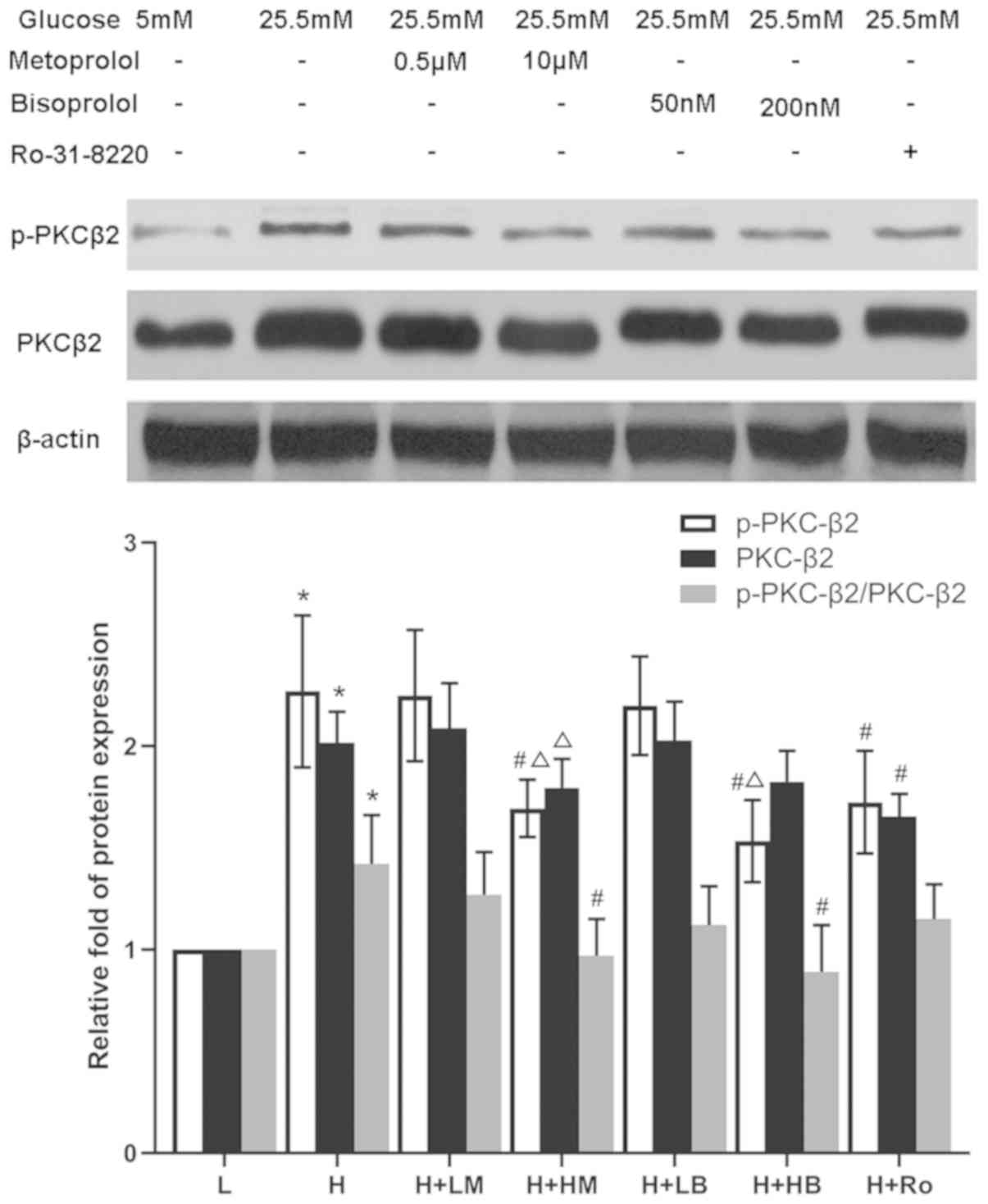
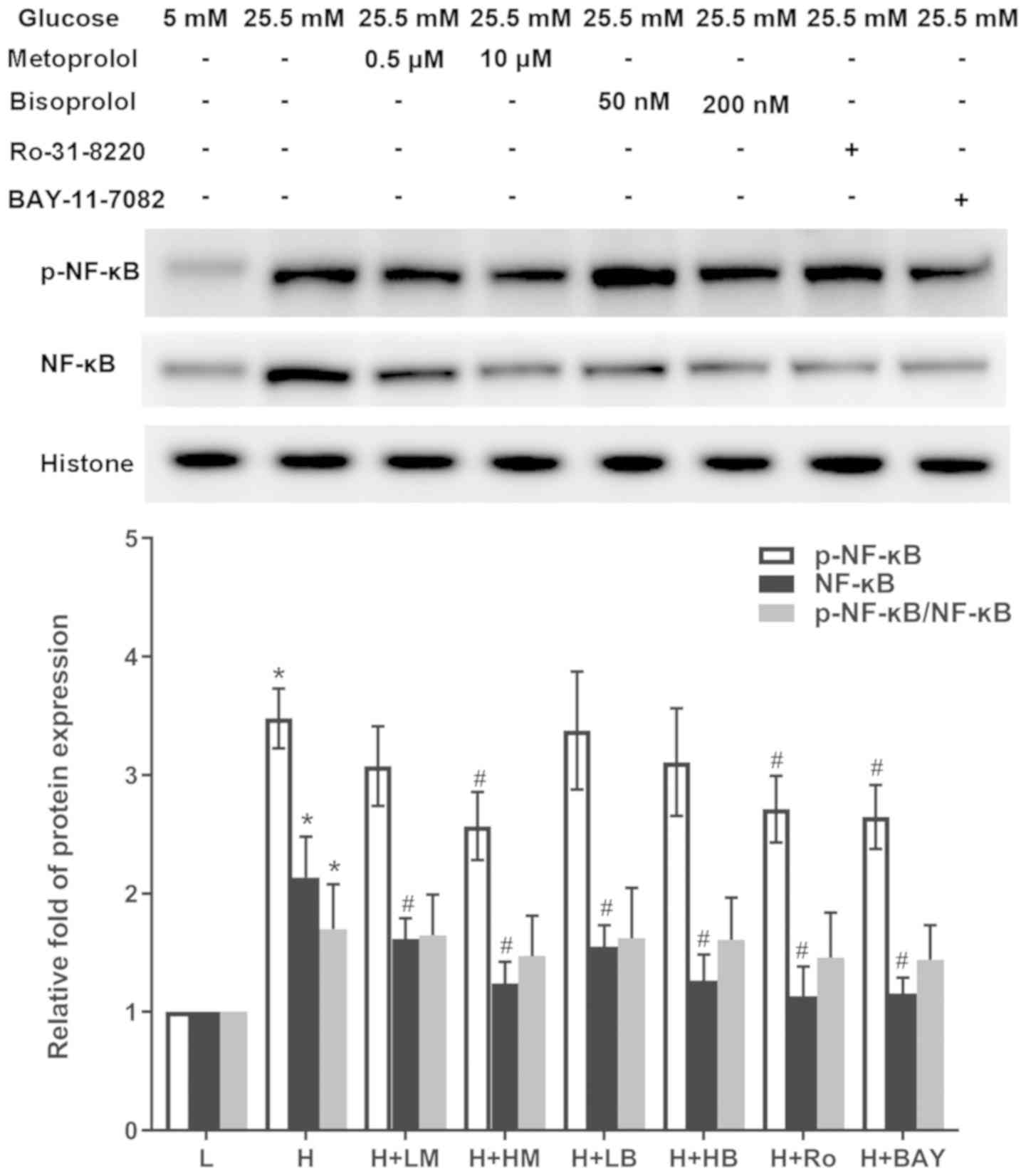
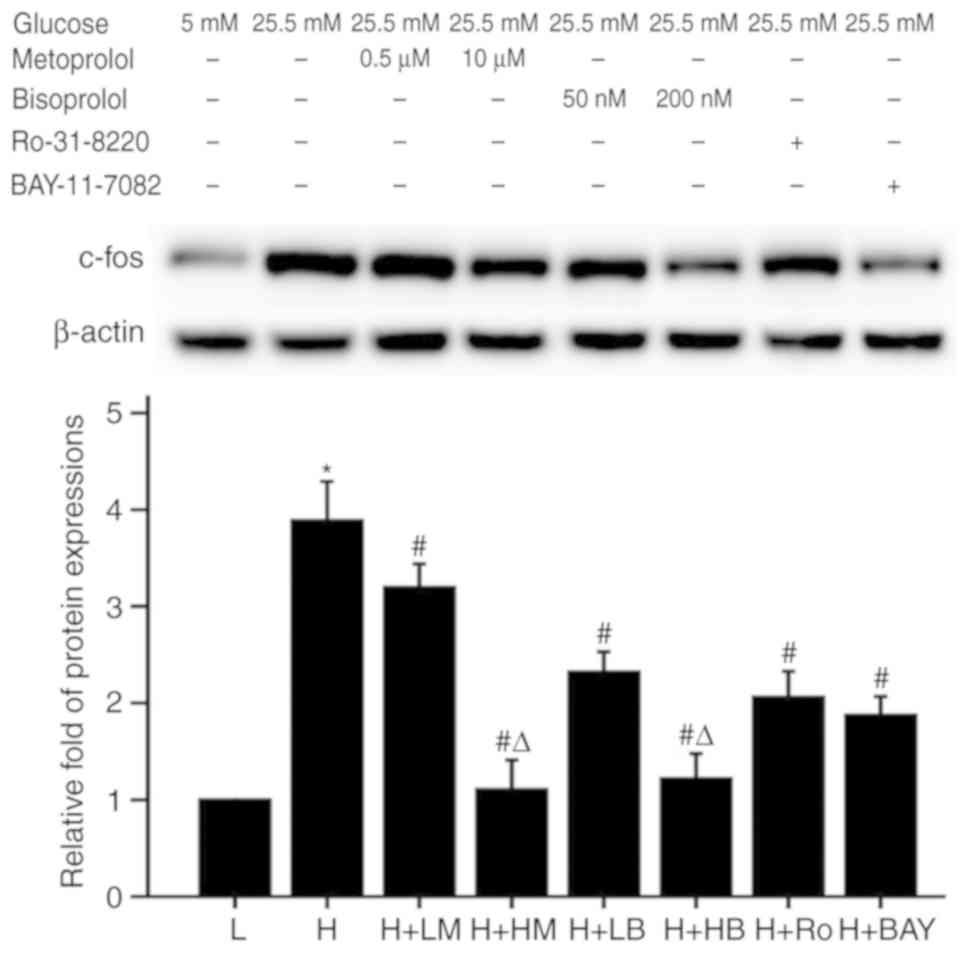
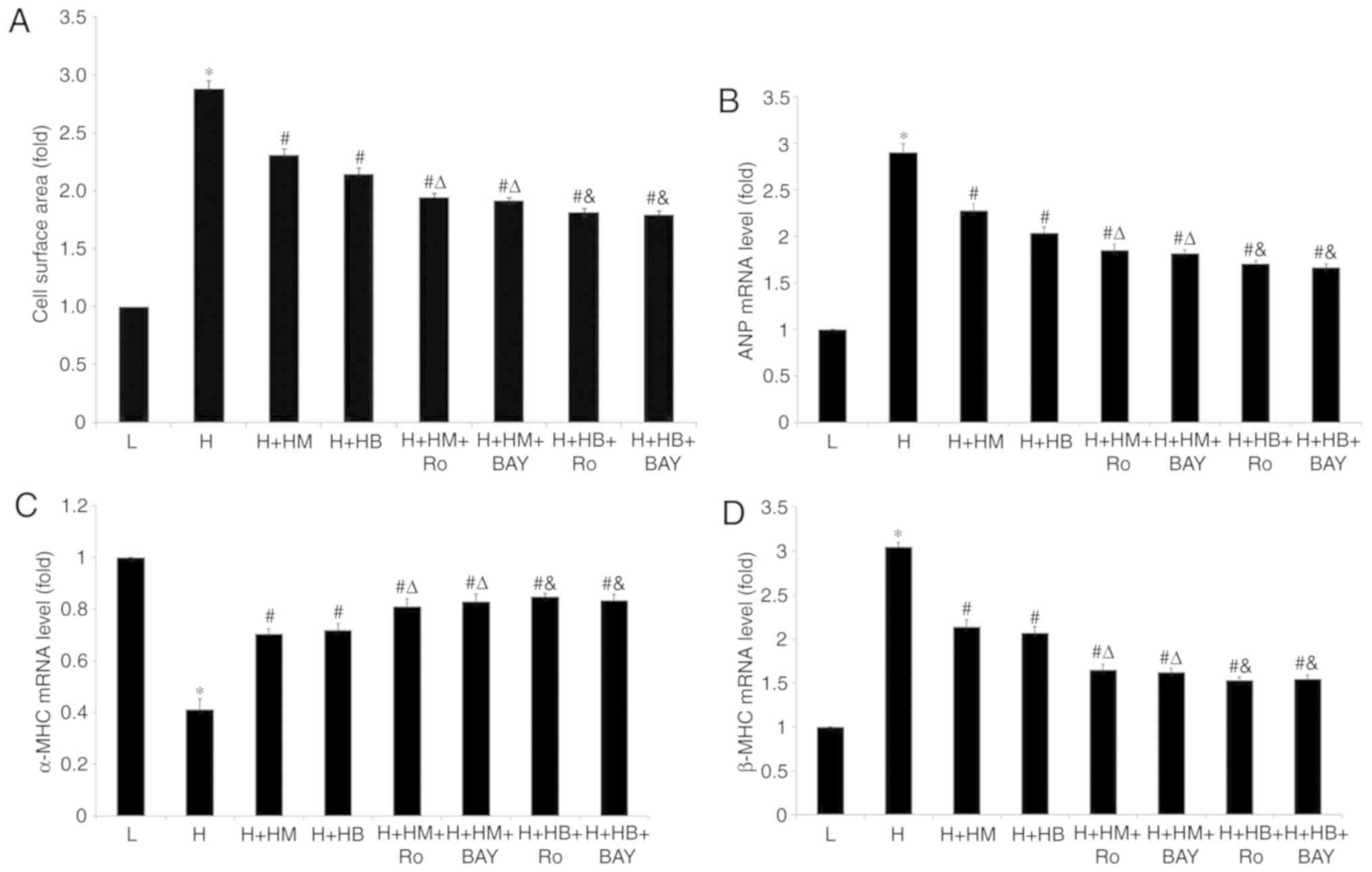
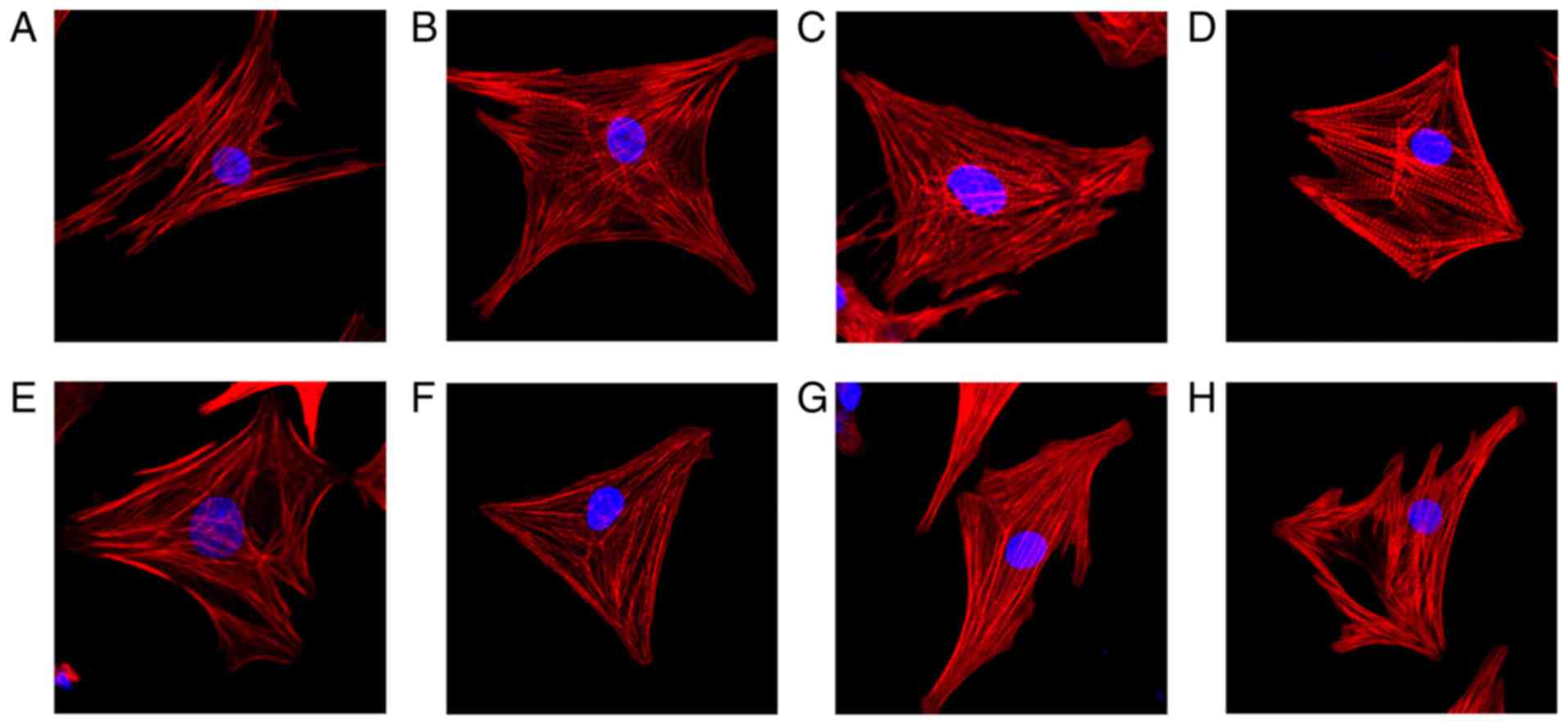
|
1
|
Whiting DR, Guariguata L, Weil C and Shaw
J: IDF diabetes atlas: Global estimates of the prevalence of
diabetes for 2011 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 94:311–321.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jia G, Whaley-Connell A and Sowers JR:
Diabetic cardiomyopathy: A hyperglycaemia- and
insulin-resistance-induced heart disease. Diabetologia. 61:21–28.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Suhara T, Baba Y, Shimada BK, Higa JK and
Matsui T: The mTOR signaling pathway in myocardial dysfunction in
type 2 diabetes mellitus. Curr Diab Rep. 17:382017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gao JR, Qin XJ, Fang ZH, Li-Sha n, Han LP,
Hui-Jian g, Guo MF and Jiang NN: To explore the pathogenesis of
vascular lesion of type 2 diabetes mellitus based on the PI3K/Akt
signaling pathway. J Diabetes Res. 2019:46509062019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang WK, Lu QH, Wang X, Wang B, Wang J,
Gong HP, Wang L, Li H and Du YM: Ulinastatin attenuates
diabetes-induced cardiac dysfunction by the inhibition of
inflammation and apoptosis. Exp Ther Med. 14:2497–2504. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Brownlee M: The pathobiology of diabetic
complications: A unifying mechanism. Diabetes. 54:1615–1625. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ferreira JC, Brum PC and Mochly-Rosen D:
βIIPKC and εPKC isozymes as potential pharmacological targets in
cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
51:479–484. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Churchill EN and Mochly-Rosen D: The roles
of PKCdelta and epsilon isoenzymes in the regulation of myocardial
ischaemia/reperfusion injury. Biochem Soc Trans. 35:1040–1042.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Weng LQ, Zhang WB, Ye Y, Yin PP, Yuan J,
Wang XX, Kang L, Jiang SS, You JY, Wu J, et al: Aliskiren
ameliorates pressure overload-induced heart hypertrophy and
fibrosis in mice. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 35:1005–1014. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Das Evcimen N and King GL: The role of
protein kinase C activation and the vascular complications of
diabetes. Pharmacol Res. 55:498–510. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Min W, Bin ZW, Quan ZB, Hui ZJ and Sheng
FG: The signal transduction pathway of PKC/NF-kappa B/c-fos may be
involved in the influence of high glucose on the cardiomyocytes of
neonatal rats. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 8:82009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Norozi K: The role of beta-blocker in
heart failure in adults with congenital heart disease. Rev Recent
Clin Trials. 9:64–67. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chia N, Fulcher J and Keech A:
Beta-blocker, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor/angiotensin
receptor blocker, nitrate-hydralazine, diuretics, aldosterone
antagonist, ivabradine, devices and digoxin [BANDAID(2)]: An
evidence-based mnemonic for the treatment of systolic heart
failure. Intern Med J. 46:653–662. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Spoladore R, Fragasso G, Perseghin G, De
Cobelli F, Esposito A, Maranta F, Calori G, Locatelli M, Lattuada
G, Scifo P, et al: Beneficial effects of beta-blockers on left
ventricular function and cellular energy reserve in patients with
heart failure. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 27:455–464. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tsujimoto T, Sugiyama T, Shapiro MF, Noda
M and Kajio H: Risk of cardiovascular events in patients with
diabetes mellitus on beta-blockers. Hypertension. 70:103–110. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bakris GL, Fonseca V, Katholi RE, McGill
JB, Messerli FH, Phillips RA, Raskin P, Wright JT Jr, Oakes R,
Lukas MA, et al: Metabolic effects of carvedilol vs. metoprolol in
patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension: A
randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 292:2227–2236. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kveiborg B, Hermann TS, Major-Pedersen A,
Christiansen B, Rask-Madsen C, Raunsø J, Køber L, Torp-Pedersen C
and Dominguez H: Metoprolol compared to carvedilol deteriorates
insulin-stimulated endothelial function in patients with type 2
diabetes-a randomized study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 9:212010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Haas SJ, Vos T, Gilbert RE and Krum H: Are
beta-blockers as efficacious in patients with diabetes mellitus as
in patients without diabetes mellitus who have chronic heart
failure? A meta-analysis of large-scale clinical trials. Am Heart
J. 146:848–853. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rengo G, Cannavo A, Liccardo D, Zincarelli
C, de Lucia C, Pagano G, Komici K, Parisi V, Scala O, Agresta A, et
al: Vascular endothelial growth factor blockade prevents the
beneficial effects of beta-blocker therapy on cardiac function,
angiogenesis, and remodeling in heart failure. Circ Heart Fail.
6:1259–1267. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li X, Zhang X, Wang T, Sun C, Jin T, Yan
H, Zhang J, Li X, Geng T, Chen C, et al: Regulation by bisoprolol
for cardiac microRNA expression in a rat volume-overload heart
failure model. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 13:5267–5275. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cheng K, Wei MQ, Jia GL, Wang HC, Luan RH,
Guo WY, Li WJ, Zong XJ and Zhou X: Effects of metoprolol and small
intestine RNA on marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells
applied for autograft transplantation in heart disease. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 18:1666–1673. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Garcia-Egido A, Andrey JL, Puerto JL,
Aranda RM, Pedrosa MJ, López-Sáez JB, Rosety M and Gomez F:
Beta-blocker therapy and prognosis of heart failure patients with
new-onset diabetes mellitus. Int J Clin Pract. 69:550–559. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Couto M and Cates C: Laboratory guidelines
for animal care. Methods Mol Biol. 1920:407–430. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shen YX, Xiao K, Liang P, Ma YW and Huang
X: Improvement on the modified Lowry method against interference of
divalent cations in soluble protein measurement. Appl Microbiol
Biotechnol. 97:4167–4178. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lekawanvijit S, Adrahtas A, Kelly DJ,
Kompa AR, Wang BH and Krum H: Does indoxyl sulfate, a uraemic
toxin, have direct effects on cardiac fibroblasts and myocytes? Eur
Heart J. 31:1771–1779. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Luo JD, Xie F, Zhang WW, Ma XD, Guan JX
and Chen X: Simvastatin inhibits noradrenaline-induced hypertrophy
of cultured neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. Br J Pharmacol.
132:159–164. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nishiga M, Horie T, Kuwabara Y, Nagao K,
Baba O, Nakao T, Nishino T, Hakuno D, Nakashima Y, Nishi H, et al:
MicroRNA-33 controls adaptive fibrotic response in the remodeling
heart by preserving lipid raft cholesterol. Circ Res. 120:835–847.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang M, Zhang WB, Zhu JH, Fu GS and Zhou
BQ: Breviscapine ameliorates hypertrophy of cardiomyocytes induced
by high glucose in diabetic rats via the PKC signaling pathway.
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 30:1081–1091. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang M, Zhang WB, Zhu JH, Fu GS and Zhou
BQ: Breviscapine ameliorates cardiac dysfunction and regulates the
myocardial Ca(2+)-cycling proteins in streptozotocin-induced
diabetic rats. Acta Diabetol. 47 (Suppl 1):S209–S218. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Song X, Qian X, Shen M, Jiang R, Wagner
MB, Ding G, Chen G and Shen B: Protein kinase C promotes cardiac
fibrosis and heart failure by modulating galectin-3 expression.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1853:513–521. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kawamura N, Kubota T, Kawano S, Monden Y,
Feldman AM, Tsutsui H, Takeshita A and Sunagawa K: Blockade of
NF-kappaB improves cardiac function and survival without affecting
inflammation in TNF-alpha-induced cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc Res.
66:520–529. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lu J, Liu F, Chen F, Jin Y, Chen H, Liu D
and Cui W: Amlodipine and atorvastatin improve ventricular
hypertrophy and diastolic function via inhibiting TNF-α, IL-1β and
NF-κB inflammatory cytokine networks in elderly spontaneously
hypertensive rats. Biomed Pharmacother. 83:330–339. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hers I, Tavaré JM and Denton RM: The
protein kinase C inhibitors bisindolylmaleimide I (GF 109203×) and
IX (Ro 31-8220) are potent inhibitors of glycogen synthase kinase-3
activity. FEBS Lett. 460:433–436. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Catley MC, Cambridge LM, Nasuhara Y, Ito
K, Chivers JE, Beaton A, Holden NS, Bergmann MW, Barnes PJ and
Newton R: Inhibitors of protein kinase C (PKC) prevent activated
transcription: Role of events downstream of NF-kappaB DNA binding.
J Biol Chem. 279:18457–18466. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Abe J: Role of PKCs and NF-kappaB
activation in myocardial inflammation: Enemy or ally? J Mol Cell
Cardiol. 43:404–408. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Guo Y, Zhuang X, Huang Z, Zou J, Yang D,
Hu X, Du Z, Wang L and Liao X: Klotho protects the heart from
hyperglycemia-induced injury by inactivating ROS and NF-κB-mediated
inflammation both in vitro and in vivo. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol
Basis Dis. 1864:238–251. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ren XM, Zuo GF, Wu W, Luo J, Ye P, Chen SL
and Hu ZY: Atorvastatin alleviates experimental diabetic
cardiomyopathy by regulating the GSK-3β-PP2Ac-NF-κB signaling axis.
PLoS One. 11:e01667402016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Freund C, Schmidt-Ullrich R, Baurand A,
Dunger S, Schneider W, Loser P, El-Jamali A, Dietz R, Scheidereit C
and Bergmann MW: Requirement of nuclear factor-kappaB in
angiotensin II- and isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy in
vivo. Circulation. 111:2319–2325. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Higuchi Y, Otsu K, Nishida K, Hirotani S,
Nakayama H, Yamaguchi O, Matsumura Y, Ueno H, Tada M and Hori M:
Involvement of reactive oxygen species-mediated NF-kappa B
activation in TNF-alpha-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. J Mol
Cell Cardiol. 34:233–240. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Higuchi Y, Chan TO, Brown MA, Zhang J,
DeGeorge BR Jr, Funakoshi H, Gibson G, McTiernan CF, Kubota T,
Jones WK and Feldman AM: Cardioprotection afforded by NF-kappaB
ablation is associated with activation of Akt in mice
overexpressing TNF-alpha. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
290:H590–H598. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hattori Y, Hattori S, Akimoto K, Nishikimi
T, Suzuki K, Matsuoka H and Kasai K: Globular adiponectin activates
nuclear factor-kappaB and activating protein-1 and enhances
angiotensin II-induced proliferation in cardiac fibroblasts.
Diabetes. 56:804–808. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Dawn B, Guo Y, Rezazadeh A, Wang OL, Stein
AB, Hunt G, Varma J, Xuan YT, Wu WJ, Tan W, et al: Tumor necrosis
factor-alpha does not modulate ischemia/reperfusion injury in naive
myocardium but is essential for the development of late
preconditioning. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 37:51–61. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhu XX, Niu XL, Chen DZ, Zhou XD, Pei JM,
Zhu MZ, Guo J, Zhu XL and Wang WQ: Inhibitory effects of
rosiglitazone against endothelin-1-induced proliferation of rat
cardiac myocytes: The role of PKC-c-fos pathway. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da
Xue Xue Bao. 28:1056–1060. 2008.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Maniar R, Pecherskaya A, Ila R and Solem
M: PKC alpha-dependent regulation of the IGF1 receptor in adult and
embryonic rat cardiomyocytes. Mol Cell Biochem. 275:15–24. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Rizzi E, Guimaraes DA, Ceron CS, Prado CM,
Pinheiro LC, Martins-Oliveira A, Gerlach RF and Tanus-Santos JE:
β1-Adrenergic blockers exert antioxidant effects, reduce matrix
metalloproteinase activity, and improve renovascular
hypertension-induced cardiac hypertrophy. Free Radic Biol Med.
73:308–317. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Amanfu RK and Saucerman JJ: Modeling the
effects of β1-adrenergic receptor blockers and polymorphisms on
cardiac myocyte Ca2+ handling. Mol Pharmacol. 86:222–230. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Sharma V, Dhillon P, Wambolt R, Parsons H,
Brownsey R, Allard MF and McNeill JH: Metoprolol improves cardiac
function and modulates cardiac metabolism in the
streptozotocin-diabetic rat. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
294:H1609–H1620. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chen RJ, Chu H and Tsai LW: Impact of
beta-blocker initiation timing on mortality risk in patients with
diabetes mellitus undergoing noncardiac surgery: A nationwide
population-based cohort study. J Am Heart Assoc. 6:e0043922017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Fröhlich H, Torres L, Täger T, Schellberg
D, Corletto A, Kazmi S, Goode K, Grundtvig M, Hole T, Katus HA, et
al: Bisoprolol compared with carvedilol and metoprolol succinate in
the treatment of patients with chronic heart failure. Clin Res
Cardiol. 106:711–721. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Arnold SV, Spertus JA, Lipska KJ, Lanfear
DE, Tang F, Grodzinsky A, McGuire DK, Gore MO, Goyal A, Maddox TM
and Kosiborod M: Type of β-blocker use among patients with versus
without diabetes after myocardial infarction. Am Heart J.
168:273–279.e1. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhao L, Xu C and Xu J: Autoantibodies
against β1 receptor and AT1 receptor in type 2 diabetes patients
with left ventricular dilatation. Cardiology. 129:191–196. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Saran V, Sharma V, Wambolt R, Yuen VG,
Allard M and McNeill JH: Combined metoprolol and ascorbic acid
treatment prevents intrinsic damage to the heart during diabetic
cardiomyopathy. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 92:827–837. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wai B, Kearney LG, Hare DL, Ord M, Burrell
LM and Srivastava PM: Beta blocker use in subjects with type 2
diabetes mellitus and systolic heart failure does not worsen
glycaemic control. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 11:142012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Hirst JA, Farmer AJ, Feakins BG, Aronson
JK and Stevens RJ: Quantifying the effects of diuretics and
β-adrenoceptor blockers on glycaemic control in diabetes mellitus-a
systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Clin Pharmacol.
79:733–743. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Phan D, Stratton MS, Huynh QK and McKinsey
TA: A novel protein kinase C target site in protein kinase D is
phosphorylated in response to signals for cardiac hypertrophy.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 411:335–341. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Wang N, Guan P, Zhang JP, Li YQ, Chang YZ,
Shi ZH, Wang FY and Chu L: Fasudil hydrochloride hydrate, a
Rho-kinase inhibitor, suppresses isoproterenol-induced heart
failure in rats via JNK and ERK1/2 pathways. J Cell Biochem.
112:1920–1929. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Kovacs K, Hanto K, Bognar Z, Tapodi A,
Bognar E, Kiss GN, Szabo A, Rappai G, Kiss T, Sumegi B and Gallyas
F Jr: Prevalent role of Akt and ERK activation in cardioprotective
effect of Ca(2+) channel- and beta-adrenergic receptor blockers.
Mol Cell Biochem. 321:155–164. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Fujioka H, Yoshihara S, Tanaka T, Fukumoto
T, Kuroiwa A, Tanonaka K, Hayashi M and Takeo S: Enhancement of
post-hypoxic contractile and metabolic recovery of perfused rat
hearts by dl-propranolol: Possible involvement of non-beta-receptor
mediated activity. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 23:949–962. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|