|
1
|
Ohkubo S, Dalla Via L, Grancara S,
Kanamori Y, García-Argáez AN, Canettieri G, Arcari P, Toninello A
and Agostinelli E: The antioxidant, aged garlic extract, exerts
cytotoxic effects on wild-type and multidrug-resistant human cancer
cells by altering mitochondrial permeability. Int J Oncol.
53:1257–1268. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fleischauer AT, Poole C and Arab L: Garlic
consumption and cancer prevention: Meta-analyses of colorectal and
stomach cancers. Am J Clin Nutr. 72:1047–1052. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rahman K and Lowe GM: Garlic and
cardiovascular disease: A critical review. J Nutr. 136 (Suppl
3):736S–740S. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Banerjee SK and Maulik SK: Effect of
garlic on cardiovascular disorders: A review. Nutr J. 1:42002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sundaresan S and Subramanian P: Prevention
of N-nitrosodiethylamine-induced hepatocarcinogenesis by
S-allylcysteine. Mol Cell Biochem. 310:209–214. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Thomson M and Ali M: Garlic [Allium
sativum]: A review of its potential use as an anti-cancer
agent. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 3:67–81. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ray B, Chauhan NB and Lahiri DK: Oxidative
insults to neurons and synapse are prevented by aged garlic extract
and S-allyl-L-cysteine treatment in the neuronal culture and APP-Tg
mouse model. J Neurochem. 117:388–402. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Amagase H, Petesch BL, Matsuura H, Kasuga
S and Itakura Y: Intake of garlic and its bioactive components. J
Nutr. 131:955S–962S. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cemil B, Gokce EC, Kahveci R, Gokce A,
Aksoy N, Sargon MF, Erdogan B and Kosem B: Aged garlic extract
attenuates neuronal injury in a rat model of spinal cord
ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Med Food. 19:601–606. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hu X, Cao BN, Hu G, He J, Yang DQ and Wan
YS: Attenuation of cell migration and induction of cell death by
aged garlic extract in rat sarcoma cells. Int J Mol Med. 9:641–643.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fallah-Rostami F, Tabari MA, Esfandiari B,
Aghajanzadeh H and Behzadi MY: Immunomodulatory activity of aged
garlic extract against implanted fibrosarcoma tumor in mice. N Am J
Med Sci. 5:207–212. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li G, Qiao C, Lin R, Pinto J, Osborne M
and Tiwari R: Antiproliferative effects of garlic constituents in
cultured human breast-cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 2:787–791.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shirin H, Pinto JT, Kawabata Y, Soh JW,
Delohery T, Moss SF, Murty V, Rivlin RS, Holt PR and Weinstein IB:
Antiproliferative effects of S-allylmercaptocysteine on
colon cancer cells when tested alone or in combination with
sulindac sulfide. Cancer Res. 61:725–731. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hosono T, Fukao T, Ogihara J, Ito Y, Shiba
H, Seki T and Ariga T: Diallyl trisulfide suppresses the
proliferation and induces apoptosis of human colon cancer cells
through oxidative modification of beta-tubulin. J Biol Chem.
280:41487–41493. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Howard EW, Ling MT, Chua CW, Cheung HW,
Wang X and Wong YC: Garlic-derived S-allylmercaptocysteine is a
novel in vivo antimetastatic agent for androgen-independent
prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 13:1847–1856. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sriram N, Kalayarasan S, Ashokkumar P,
Sureshkumar A and Sudhandiran G: Diallyl sulfide induces apoptosis
in Colo 320 DM human colon cancer cells: Involvement of caspase-3,
NF-kappaB, and ERK-2. Mol Cell Biochem. 311:157–165. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lai KC, Kuo CL, Ho HC, Yang JS, Ma CY, Lu
HF, Huang HY, Chueh FS, Yu CC and Chung JG: Diallyl sulfide,
diallyl disulfide and diallyl trisulfide affect drug resistant gene
expression in colo 205 human colon cancer cells in vitro and in
vivo. Phytomedicine. 19:625–630. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yan JY, Tian FM, Hu WN, Zhang JH, Cai HF
and Li N: Apoptosis of human gastric cancer cells line SGC 7901
induced by garlicderived compound S-allylmercaptocysteine (SAMC).
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 17:745–751. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang H, Wang K, Lin G and Zhao Z:
Antitumor mechanisms of S-allyl mercaptocysteine for breast cancer
therapy. BMC Complement Altern Med. 14:2702014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ng KT, Guo DY, Cheng Q, Geng W, Ling CC,
Li CX, Liu XB, Ma YY, Lo CM, Poon RT, et al: A garlic derivative,
S-allylcysteine (SAC), suppresses proliferation and metastasis of
hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One. 7:e316552012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu Z, Li M, Chen K, Yang J, Chen R, Wang
T, Liu J, Yang W and Ye Z: S-allylcysteine induces cell cycle
arrest and apoptosis in androgen-independent human prostate cancer
cells. Mol Med Rep. 5:439–443. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chung LY: The antioxidant properties of
garlic compounds: Allyl cysteine, alliin, allicin, and allyl
disulfide. J Med Food. 9:205–213. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
García E, Santana-Martínez R, Silva-Islas
CA, Colín-González AL, Galván-Arzate S, Heras Y, Maldonado PD,
Sotelo J and Santamaría A: S-allyl cysteine protects against
MPTP-induced striatal and nigral oxidative neurotoxicity in mice:
Participation of Nrf2. Free Radic Res. 48:159–167. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xu YS, Feng JG, Zhang D, Zhang B, Luo M,
Su D and Lin NM: S-allylcysteine, a garlic derivative, suppresses
proliferation and induces apoptosis in human ovarian cancer cells
in vitro. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 35:267–274. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Compston A and Coles A: Multiple
sclerosis. Lancet. 372:1502–1517. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lassmann H: Pathophysiology of
inflammation and tissue injury in multiple sclerosis: What are the
targets for therapy. J Neurol Sci. 306:167–169. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zeinali H, Baluchnejadmojarad T, Fallah S,
Sedighi M, Moradi N and Roghani M: S-allyl cysteine improves
clinical and neuropathological features of experimental autoimmune
encephalomyelitis in C57BL/6 mice. Biomed Pharmacother. 97:557–563.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kyo E, Uda N, Kasuga S and Itakura Y:
Immunomodulatory effects of aged garlic extract. J Nutr.
131:1075S–1079S. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Morihara N, Sumioka I, Moriguchi T, Uda N
and Kyo E: Aged garlic extract enhances production of nitric oxide.
Life Sci. 71:509–517. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Imai J, Ide N, Nagae S, Moriguchi T,
Matsuura H and Itakura Y: Antioxidant and radical scavenging
effects of aged garlic extract and its constituents. Planta Med.
60:417–420. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Timeus F, Crescenzio N, Doria A, Foglia L,
Pagliano S, Ricotti E, Fagioli F, Tovo PA and Cordero di
Montezemolo L: In vitro anti-neuroblastoma activity of
saquinavir and its association with imatinib. Oncol Rep.
27:734–740. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
van Engeland M, Nieland LJ, Ramaekers FC,
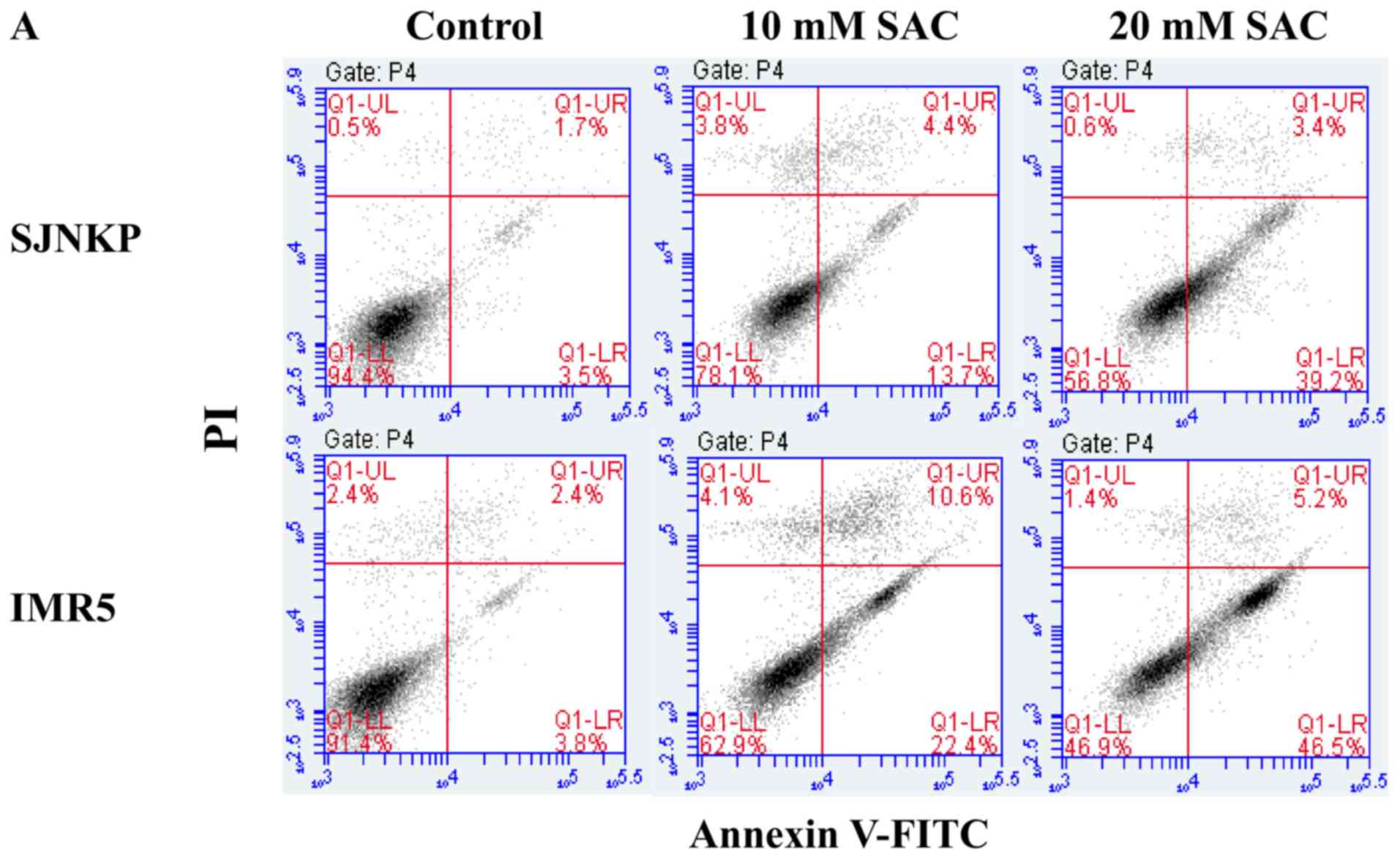
Schutte B and Reutelingsperger CP: Annexin V-affinity assay: A
review on an apoptosis detection system based on phosphatidylserine
exposure. Cytometry. 31:1–9. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
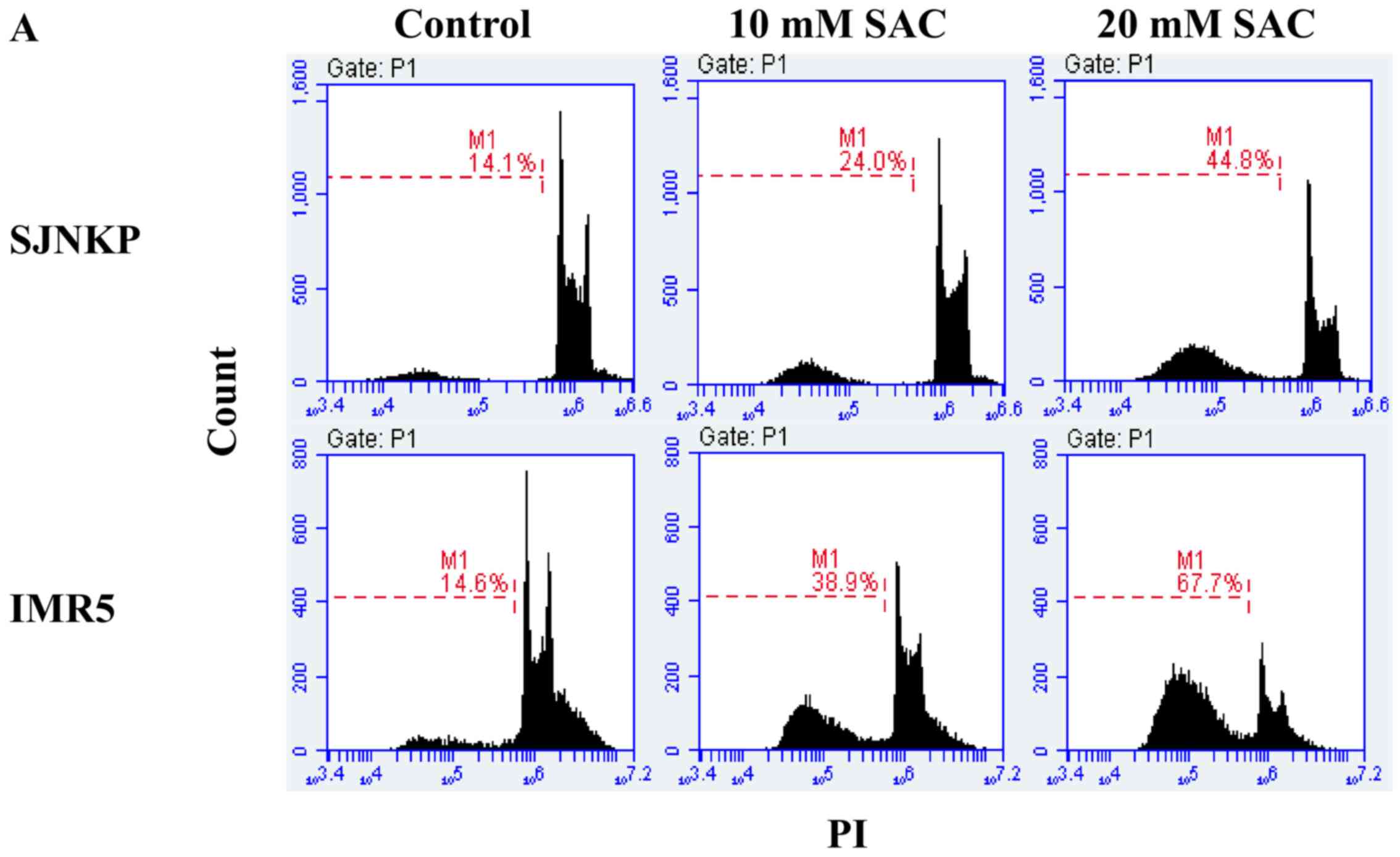
Nicoletti I, Migliorati G, Pagliacci MC,
Grignani F and Riccardi C: A rapid and simple method for measuring
thymocyte apoptosis by propidium iodide staining and flow
cytometry. J Immunol Methods. 139:271–279. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
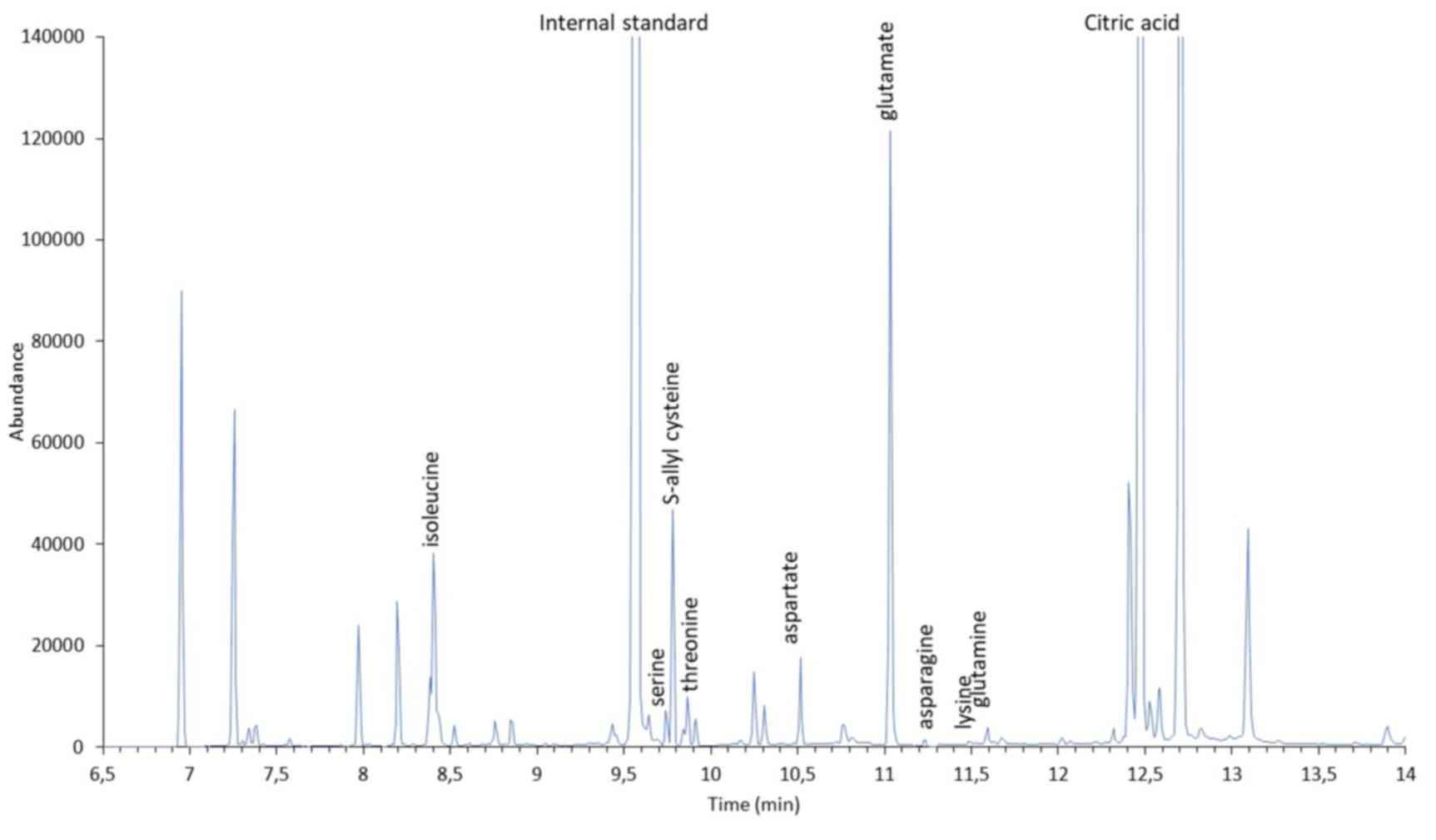
Jiménez-Martín E, Ruiz J, Pérez-Palacios
T, Silva A and Antequera T: Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
method for the determination of free amino acids as their
dimethyl-tert-butylsilyl (TBDMS) derivatives in animal source food.
J Agric Food Chem. 60:2456–2463. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Frezza C, Cipolat S and Scorrano L:
Organelle isolation: Functional mitochondria from mouse liver,
muscle and cultured fibroblasts. Nat Protoc. 2:287–295. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gornall AG, Bardawill CJ and David MM:
Determination of serum proteins by means of the biuret reaction. J
Biol Chem. 177:751–766. 1949.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kamo N, Muratsugu M, Hongoh R and Kobatake
Y: Membrane potential of mitochondria measured with an electrode
sensitive to tetraphenyl phosphonium and relationship between
proton electrochemical potential and phosphorylation potential in
steady state. J Membr Biol. 49:105–121. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Rottenberg H: Non-equilibrium
thermodynamics of energy conversion in bioenergetics. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 549:225–253. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tietze F: Enzymic method for quantitative
determination of nanogram amounts of total and oxidized
glutathione: Applications to mammalian blood and other tissues.
Anal Biochem. 27:502–522. 1969. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kanda Y: Investigation of the freely
available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone
Marrow Transplant. 48:452–458. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ho JN, Kang M, Lee S, Oh JJ, Hong SK, Lee
SE and Byun SS: Anticancer effect of S-allyl-L-cysteine via
induction of apoptosis in human bladder cancer cells. Oncol Lett.
15:623–629. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hoehner JC, Gestblom C, Hedborg F,
Sandstedt B, Olsen L and Påhlman S: A developmental model of
neuroblastoma: Differentiating stromapoor tumors' progress along an
extra-adrenal chromaffin lineage. Lab Invest. 75:659–675.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Huang M and Weiss WA: Neuroblastoma and
MYCN. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 3:a0144152013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Fonseka P, Liem M, Ozcitti C, Adda CG, Ang
CS and Mathivanan S: Exosomes from N-Myc amplified neuroblastoma
cells induce migration and confer chemoresistance to non-N-Myc
amplified cells: Implications of intratumour heterogeneity. J
Extracell Vesicles. 8:15976142019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lawson LD: Garlic: A review of its
medicinal effects and indicated active compounds. Phytomedicines of
Europe: Chemistry and biological activity. Lawson LD and Bauer R;
ACS symposium series, : 691. American Chemical Society; Washington,
DC, USA: pp. 176–209. 1998, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Kodera Y, Suzuki A, Imada O, Kasuga S,
Sumioka I, Kanezawa A, Taru N, Fujikawa M, Nagae S, Masamoto K, et
al: Physical, chemical, and biological properties of
S-allylcysteine, an amino acid derived from garlic. J Agric Food
Chem. 50:622–632. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Colín-González AL, Santana RA, Silva-Islas
CA, Chánez-Cárdenas ME, Santamaría A and Maldonado PD: The
antioxidant mechanisms underlying the aged garlic extract- and
S-allylcysteine-induced protection. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2012:9071622012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Maldonado PD, Alvarez-Idaboy JR,
Aguilar-González A, Lira-Rocha A, Jung-Cook H, Medina-Campos OM,
Pedraza-Chaverri J and Galano A: Role of allyl group in the
hydroxyl and peroxylradical scavenging activity of S-allylcysteine.
J Phys Chem B. 115:13408–13417. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Dairam A, Fogel R, Daya S and Limson JL:
Antioxidant and iron-binding properties of curcumin, capsaicin, and
S-allylcysteine reduce oxidative stress in rat brain homogenate. J
Agric Food Chem. 56:3350–3356. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Pinto JT, Qiao C, Xing J, Rivlin RS,
Protomastro ML, Weisler ML, Tao Y, Thaler H and Heston WD: Effects
of garlic thioallyl derivatives on growth, glutathione
concentration, and polyamine formation of human prostate carcinoma
cells in culture. Am J Clin Nutr. 66:398–405. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Kim KM, Chun SB, Koo MS, Choi WJ, Kim TW,
Kwon YG, Chung HT, Billiar TR and Kim YM: Differential regulation
of NO availability from macrophages and endothelial cells by the
garlic component S-allyl cysteine. Free Radic Biol Med. 30:747–756.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kim SR, Jung YR, An HJ, Kim DH, Jang EJ,
Choi YJ, Moon KM, Park MH, Park CH, Chung KW, et al: Anti-wrinkle
and anti-inflammatory effects of active garlic components and the
inhibition of MMPs via NF-κB signaling. PLoS One. 8:e738772013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Mong MC and Yin MC: Nuclear factor
κB-dependent anti-inflammatory effects of S-allyl cysteine and
S-propyl cysteine in kidney of diabetic mice. J Agric Food Chem.
60:3158–3165. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Grancara S, Zonta F, Ohkubo S, Brunati AM,
Agostinelli E and Toninello A: Pathophysiological implications of
mitochondrial oxidative stress mediated by mitochondriotropic
agents and polyamines: The role of tyrosine phosphorylation. Amino
Acids. 47:869–883. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|