|
1
|
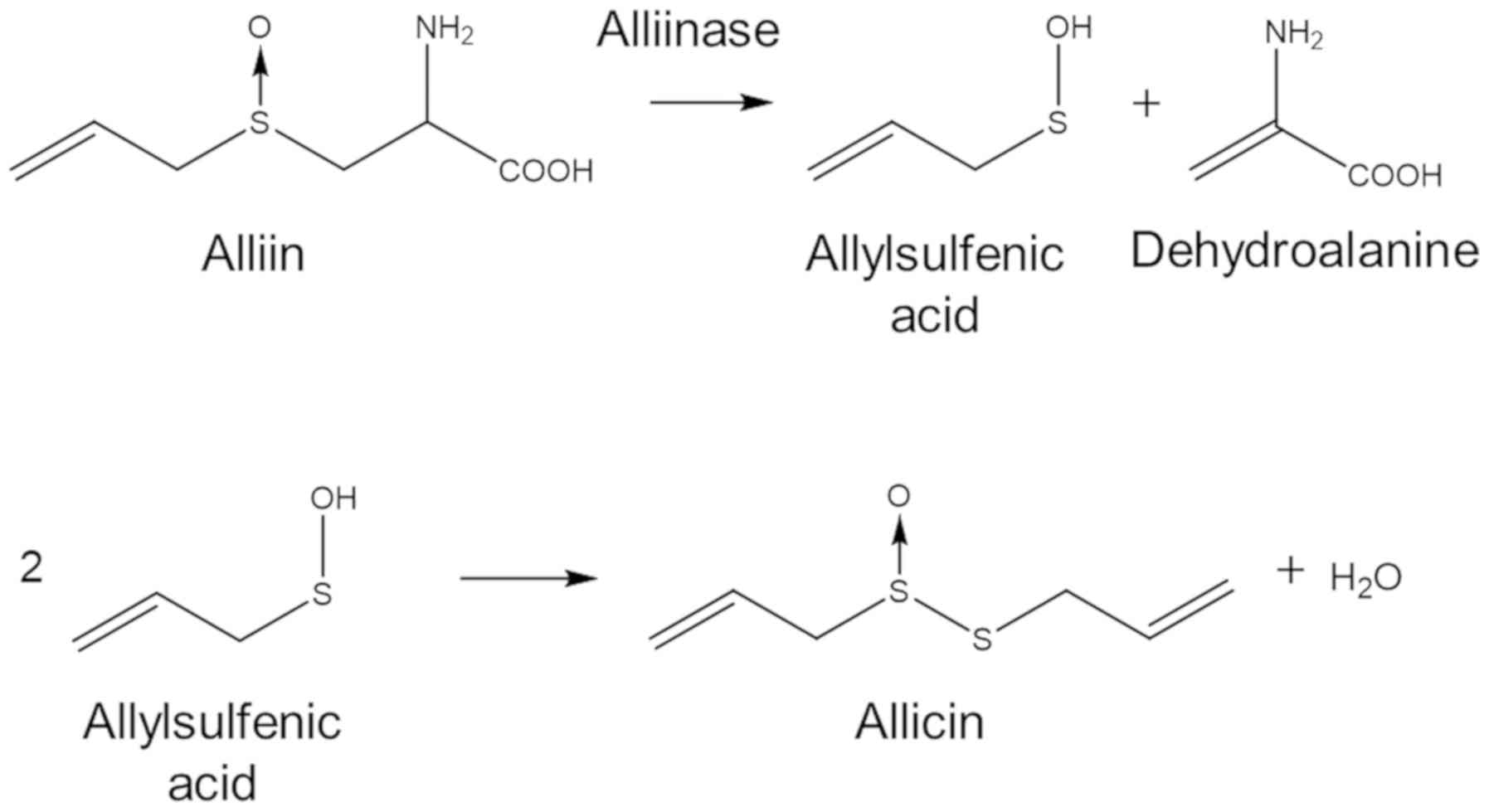
Cavallito CJ and Bailey JH: Allicin, the
antibacterial principle of Allium sativum. I. Isolation, physical
properties and antibacterial action. J Am Chem Soc. 66:1950–1951.
1944. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Block E: Garlic and the other Alliums. The
Lore and the Science (RSC Publishing); 2010
|
|
3
|
Borlinghaus J, Albrecht F, Gruhlke MC,
Nwachukwu ID and Slusarenko AJ: Allicin: Chemistry and biological
properties. Molecules. 19:12591–12618. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Albrecht F, Leontiev R, Jacob C and
Slusarenko AJ: An optimized facile procedure to synthesize and
purify allicin. Molecules. 22(pii): E7702017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cavallito CJ, Bailey JH and Buch J:
Allicin, the antibacterial principle of Allium sativum. III. Its
precursor and ‘essential oil of garlic’. J Am Chem Soc.
67:1032–1033. 1945. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Rabinkov A, Miron T, Konstantinovski L,
Wilchek M, Mirelman D and Weiner L: The mode of action of allicin:
Trapping of radicals and interaction with thiol containing
proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1379:233–244. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rabinkov A, Miron T, Mirelman D, Wilchek
M, Glozman S, Yavin E and Weiner L: S-allylmercaptoglutathione: The
reaction product of allicin with glutathione possesses SH-modifying
and antioxidant properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1499:144–153.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Miron T, Rabinkov A, Mirelman D, Wilchek M
and Weiner L: The mode of action of allicin: Its ready permeability
through phospholipid membranes may contribute to its biological
activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1463:20–30. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gruhlke MC, Hemmis B, Noll U, Wagner R,
Luehring H and Slusarenko AJ: The defense substance allicin from
garlic permeabilizes membranes of Beta vulgaris, Rhoeo discolor,
Chara corallina and artificial lipid bilayers. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1850:602–611. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Müller A, Eller J, Albrecht F, Prochnow P,
Kuhlmann K, Bandow JE, Slusarenko AJ and Leichert LI: Allicin
induces thiol stress in bacteria through S-Allylmercapto
modification of protein cysteines. J Biol Chem. 291:11477–11490.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Reiter J, Levina N, van der Linden M,
Gruhlke M, Martin C and Slusarenko AJ: Diallylthiosulfinate
(Allicin), a volatile antimicrobial from garlic (Allium sativum),
kills human lung pathogenic bacteria, including MDR strains, as a
vapor. Molecules. 22(pii): E17112017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Loi VV, Huyen NTT, Busche T, Tung QN,
Gruhlke MCH, Kalinowski J, Bernhardt J, Slusarenko A and Antelmann
H: Staphylococcus aureus responds to allicin by global
S-thioallylation-role of the Brx/BSH/YpdA pathway and the
disulfide reductase MerA to overcome allicin stress. Free Radic
Biol Med. 139:55–59. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gruhlke MCH, Antelmann H, Bernhardt J,
Kloubert V, Rink L and Slusarenko AJ: The human allicin-proteome:
S-thioallylation of proteins by the garlic defence substance
allicin and its biological effects. Free Radic Biol Med.
131:144–153. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lawson LD and Hunsaker SM: Allicin
bioavailability and bioequivalence from garlic supplements and
garlic foods. Nutrients. 10(pii): E8122018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bjarnsholt T, Jensen PØ, Rasmussen TB,
Christophersen L, Calum H, Hentzer M, Hougen HP, Rygaard J, Moser
C, Eberl L, et al: Garlic blocks quorum sensing and promotes rapid
clearing of pulmonary Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections.
Microbiology. 151:3873–3880. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Smyth AR, Cifelli PM, Ortori CA, Righetti
K, Lewis S, Erskine P, Holland ED, Givskov M, Williams P, Camara M,
et al: Garlic as an inhibitor of Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum
sensing in cystic fibrosis-a pilot randomized controlled trial.
Pediatr Pulmonol. 45:356–362. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Minchin WC: A study in tubercle virus,
polymorphism and the treatment of tuberculosis and lupus with Oleum
alii. 3rd. Bailliere, Tindall & Cox; London: pp. 1101927
|
|
18
|
Sheppard JG and Long TE: Allicin-inspired
fluoroquinolones as antibacterials against ESKAPE pathogens. Bioorg
Medic Chem Lett. 26:5545–5549. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Högberg LD, Heddini A and Cars O: The
global need for effective antibiotics: Challenges and recent
advances. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 31:509–515. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ventola CL: The antibiotic resistance
crisis: Part 1: Causes and threats. P T. 40:277–283.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Powers JH: Antimicrobial drug
development-the past, the present, and the future. Clin Microbiol
Infect. 10 (Suppl 4):S23–S31. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Silver LL: Challenges of antibacterial
discovery. Clin Microbiol Rev. 24:71–109. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Muto CA, Jernigan JA, Ostrowsky BE, Richet
HM, Jarvis WR, Boyce JM and Farr BM: SHEA guideline for preventing
nosocomial transmission of multidrug-resistant strains of
Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus. Infect Control Hosp
Epidemiol. 24:362–386. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Georg AM, Jones PM and Middleton PG:
Cystic fibrosis infections: Treatment strategies and prospects.
FEMS Microbiol Lett. 300:153–164. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Davies J and Davies D: Origins and
evolution of antibiotic resistance. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev.
74:417–433. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Croucher NJ, Harris SR, Fraser C, Quail
MA, Burton J, van der Linden M, McGee L, von Gottberg A, Song JH,
Ko KS, et al: Rapid pneumococcal evolution in response to clinical
interventions. Science. 331:430–435. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dini C, Fabbri A and Geraci A: The
potential role of garlic (Allium sativum) against the multi-drug
resistant tuberculosis pandemic: A review. Ann Ist Super Sanita.
47:465–473. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Dörner P, Müller PM, Reiter J, Gruhlke MC,
Slusarenko AJ, Schröder W and Klaas M: Feasibility of a
surface-coated lung model for the quantification of active agent
deposition for preclinical studies. bioRxiv. doi:
10.1101/639245.
|
|
29
|
Borlinghaus J, Bolger A, Schier C, Vogel
A, Gruhlke MCH and Slusarenko AJ: Plant-microbe co-evolution:
allicin resistance in a Pseudomonas fluorescens strain
(PfAR-1) isolated from garlic. bioRxiv. 769265doi:
https://doi.org/10.1101/769265.
|
|
30
|
Karunakaran R, Mauchline TH, Hosie AH and
Poole PS: A family of promoter probe vectors incorporating
autofluorescent and chromogenic reporter proteins for studying gene
expression in Gram-negative bacteria. Microbiology. 151:3249–3256.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Leontiev R, Hohaus N, Jacob C, Gruhlke MCH
and Slusarenko AJ: A comparison of the antibacterial and antifungal
activities of thiosulfinate analogues of allicin. Sci Rep.
8:67632018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Horn T, Bettray W, Slusarenko AJ and
Gruhlke MCH: S-allylmercaptoglutathione is a substrate for
glutathione reductase (E.C. 1.8.1.7) from Yeast (Saccharomyces
cerevisiae). Antioxidants. 7(pii): E862018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Koch HP and Lawson LD: Garlic: The science
and therapeutic application of Allium sativum L. and related
species. Williams & Wilkins; Baltimore, MD: 1996
|
|
34
|
Gruhlke MC, Nicco C, Batteux F and
Slusarenko AJ: The effects of allicin, a reactive sulfur species
from garlic, on a selection of mammalian cell lines. Antioxidants.
6(pii): E12016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cantin AM, North SL, Hubbard RC and
Crystal RG: Normal alveolar epithelial lining fluid contains high
levels of glutathione. J Appl Physiol. 63:152–157. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Rahman I: Inflammation and the regulation
of glutathione level in lung epithelial cells. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 1:425–447. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
van der Poll T and Opal SM: Pathogenesis,
treatment, and prevention of pneumococcal pneumonia. Lancet.
374:1543–1556. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lüngen AE, Bezela S, Kniebs C, Cornelissen
CG, Jockenhoevel S and Thiebes AL: Differentiation and evaluation
of respiratory epithelial cells on polycarbonate urethane
nonwovens. Pneumologie. 73:1172019.
|