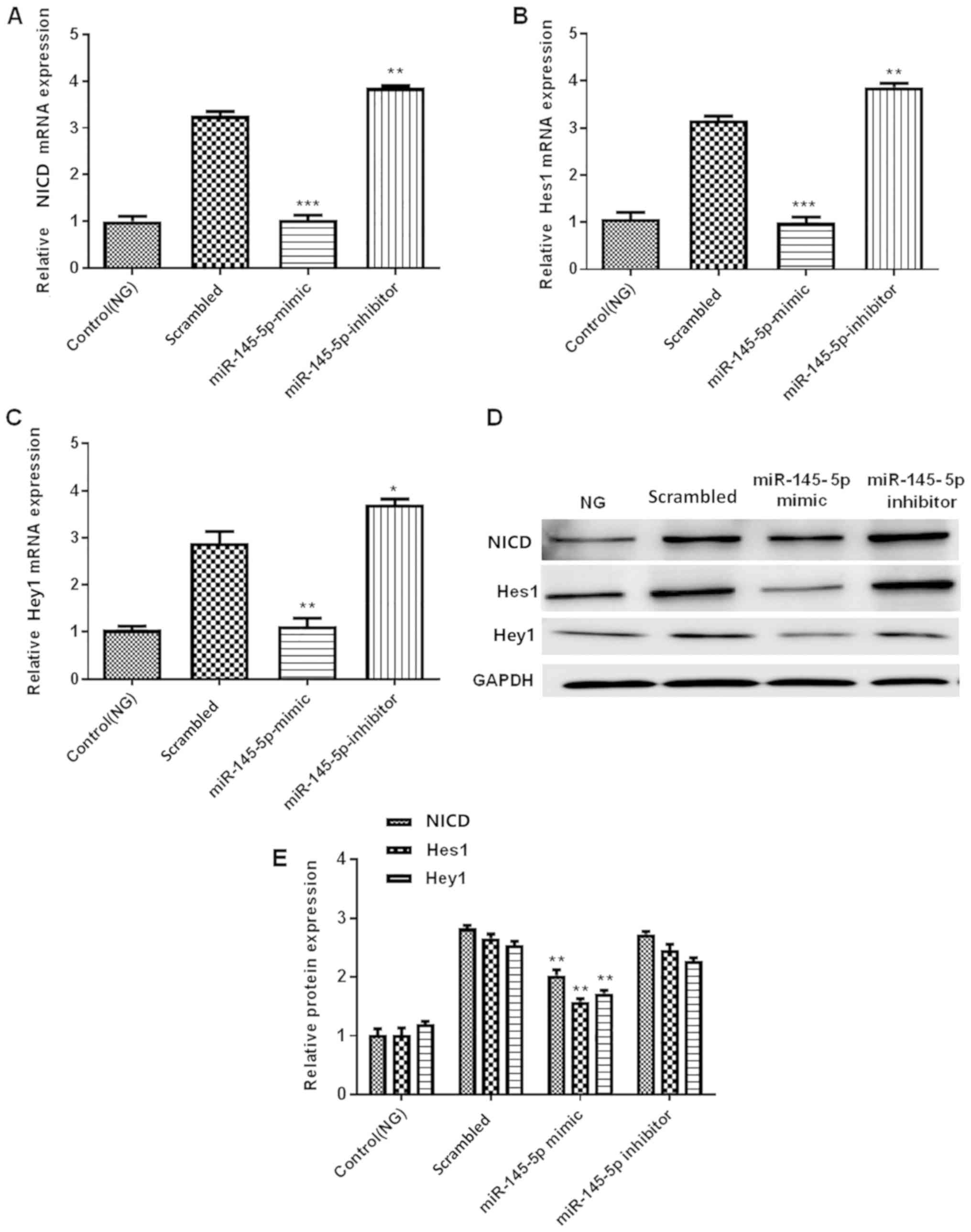
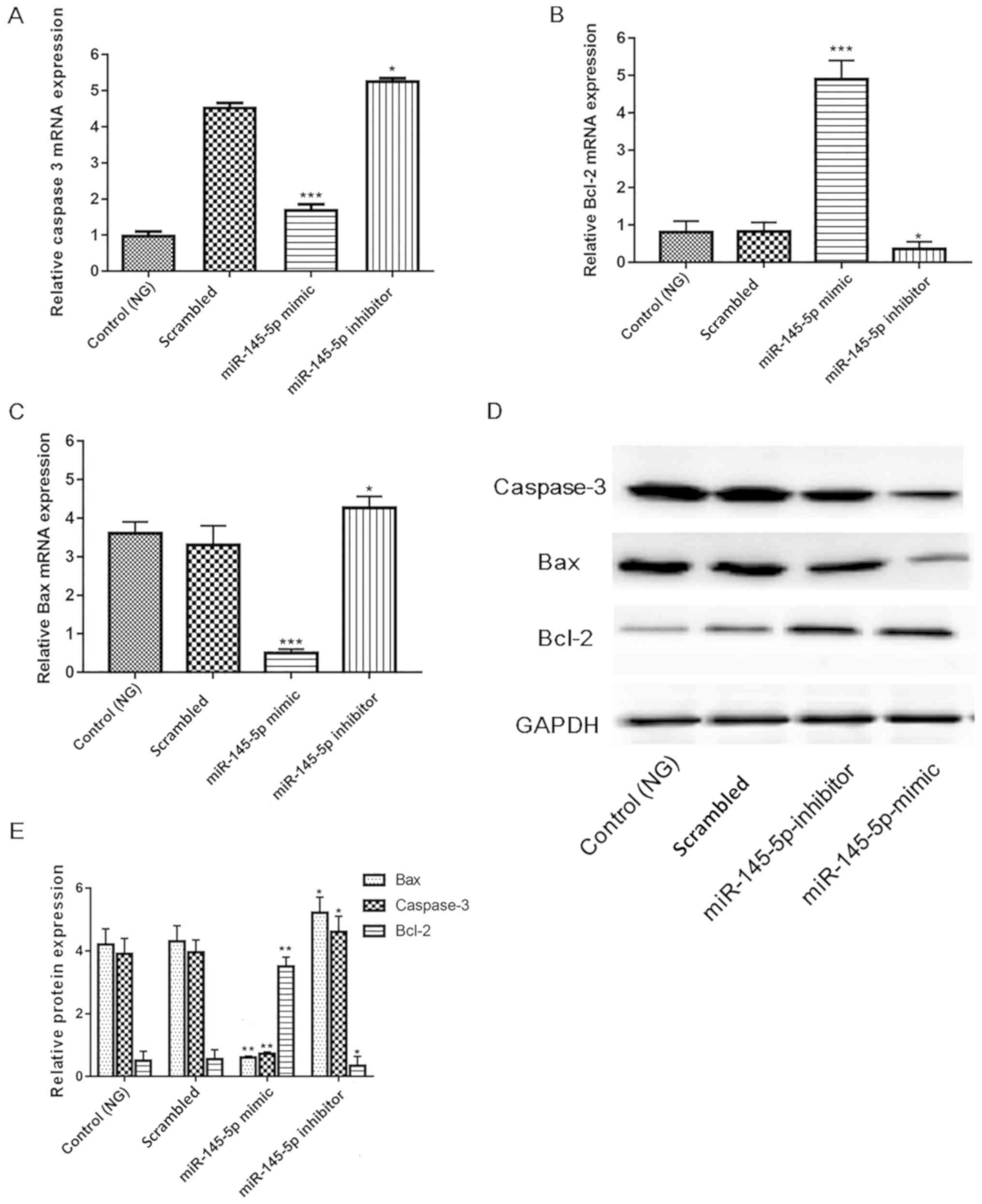
|
1
|
Tong L and Adler SG: Diabetic kidney
disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 13:335–338. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ying Q and Wu G: Molecular mechanisms
involved in podocyte EMT and concomitant diabetic kidney diseases:
An update. Ren Fail. 39:474–483. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Asanuma K: The role of podocyte injury in
chronic kidney disease. Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi.
38:26–36. 2015.(In Japanese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Brosius FC and Coward RJ: Podocytes,
signaling pathways and vascular factors in diabetic kidney disease.
Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 21:304–310. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Armelloni S, Corbelli A, Giardino L, Li M,
Ikehata M, Mattinzoli D, Messa P, Pignatari C, Watanabe S and
Rastaldi MP: Podocytes: Recent biomolecular developments. Biomol
Concepts. 5:319–330. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tetreault N and De Guire V: miRNAs: Their
discovery, biogenesis and mechanism of action. Clin Biochem.
46:842–845. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Duarte FV, Palmeira CM and Rolo AP: The
role of microRNAs in mitochondria: Small players acting wide. Genes
(Basel). 5:865–886. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–354. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li T and Cho WC: MicroRNAs: Mechanisms,
functions and progress. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics.
10:237–238. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Graves P and Zeng Y: Biogenesis of
mammalian microRNAs: A global view. Genomics Proteomics
Bioinformatics. 10:239–245. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fu Y, Wang C, Zhang D, Chu X, Zhang Y and
Li J: miR-15b-5p ameliorated high glucose-induced podocyte injury
through repressing apoptosis, oxidative stress, and inflammatory
responses by targeting Sema3A. J Cell Physiol. 234:20869–20878.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ma J, Li YT, Zhang SX, Fu SZ and Ye XZ:
miR-590-3p attenuates acute kidney injury by inhibiting tumor
necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 in septic mice.
Inflammation. 42:637–649. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li H, Zhu X, Zhang J and Shi J:
MicroRNA-25 inhibits high glucose-induced apoptosis in renal
tubular epithelial cells via PTEN/AKT pathway. Biomed Pharmacother.
96:471–479. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Peng J, Wu Y, Deng Z, Zhou Y, Song T, Yang
Y, Zhang X, Xu T, Xia M, Cai A, et al: miR-377 promotes white
adipose tissue inflammation and decreases insulin sensitivity in
obesity via suppression of sirtuin-1 (SIRT1). Oncotarget.
8:70550–70563. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Barutta F, Tricarico M, Corbelli A,
Annaratone L, Pinach S, Grimaldi S, Bruno G, Cimino D, Taverna D,
Deregibus MC, et al: Urinary exosomal microRNAs in incipient
diabetic nephropathy. PLoS One. 8:e737982013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yamamoto S, Schulze KL and Bellen HJ:
Introduction to Notch signaling. Methods Mol Biol. 1187:1–14. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hori K, Sen A and Artavanis-Tsakonas S:
Notch signaling at a glance. J Cell Sci. 126:2135–2140. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Penton AL, Leonard LD and Spinner NB:
Notch signaling in human development and disease. Semin Cell Dev
Biol. 23:450–457. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Braune EB and Lendahl U: Notch-a
goldilocks signaling pathway in disease and cancer therapy. Discov
Med. 21:189–196. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Voelkel JE, Harvey JA, Adams JS, Lassiter
RN and Stark MR: FGF and Notch signaling in sensory neuron
formation: A multifactorial approach to understanding signaling
pathway hierarchy. Mech Dev. 134:55–66. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Saleem MA, O'Hare MJ, Reiser J, Coward RJ,
Inward CD, Farren T, Xing CY, Ni L, Mathieson PW and Mundel P: A
conditionally immortalized human podocyte cell line demonstrating
nephrin and podocin expression. J Am Soc Nephrol. 13:630–638.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shepard BD, Natarajan N, Protzko RJ, Acres
OW and Pluznick JL: A cleavable N-terminal signal peptide promotes
widespread olfactory receptor surface expression in HEK293T cells.
PLoS One. 8:e687582013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Loo DT: In situ detection of apoptosis by
the TUNEL assay: An overview of techniques. Methods Mol Biol.
682:3–13. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shan H, Zhang Y, Lu Y, Zhang Y, Pan Z, Cai
B, Wang N, Li X, Feng T, Hong Y and Yang B: Downregulation of
miR-133 and miR-590 contributes to nicotine-induced atrial
remodelling in canines. Cardiovasc Res. 83:465–472. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pockley AG, Foulds GA, Oughton JA,
Kerkvliet NI and Multhoff G: Immune cell phenotyping using flow
cytometry. Curr Protoc Toxicol. 66:18.8.1–34. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam J and Bartel DP:
Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs.
eLife. 4:e050052015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Liu W and Wang X: Prediction of functional
microRNA targets by integrative modeling of microRNA binding and
target expression data. Genome Biol. 20:182019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zheng R, Pan L, Gao J, Ye X, Chen L, Zhang
X, Tang W and Zheng W: Prognostic value of miR-106b expression in
breast cancer patients. J Surg Res. 195:158–165. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu ZH, Dai XM and Du B: Hes1: A key role
in stemness, metastasis and multidrug resistance. Cancer Biol Ther.
16:353–359. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lopez-Mateo I, Arruabarrena-Aristorena A,
Artaza-Irigaray C, Lopez JA, Calvo E and Belandia B: HEY1 functions
are regulated by its phosphorylation at Ser-68. Biosci Rep.
36(pii): e003432016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Choudhary GS, Al-Harbi S and Almasan A:
Caspase-3 activation is a critical determinant of genotoxic
stress-induced apoptosis. Methods Mol Biol. 1219:1–9. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Laulier C and Lopez BS: The secret life of
Bcl-2: Apoptosis- independent inhibition of DNA repair by Bcl-2
family members. Mutat Res. 751:247–257. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhu S, Li T, Tan J, Yan X, Zhang D, Zheng
C, Chen Y, Xiang Z and Cui H: Bax is essential for death
receptor-mediated apoptosis in human colon cancer cells. Cancer
Biother Radiopharm. 27:577–581. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kim D, Lim S, Park M, Choi J, Kim J, Han
H, Yoon K, Kim K, Lim J and Park S: Ubiquitination-dependent CARM1
degradation facilitates Notch1-mediated podocyte apoptosis in
diabetic nephropathy. Cell Signal. 26:1774–1782. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Matoba K, Kawanami D, Nagai Y, Takeda Y,
Akamine T, Ishizawa S, Kanazawa Y, Yokota T and Utsunomiya K:
Rho-kinase blockade attenuates podocyte apoptosis by inhibiting the
notch signaling pathway in diabetic nephropathy. Int J Mol Sci.
18(pii): E17952017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gao F, Yao M, Cao Y, Liu S, Liu Q and Duan
H: Valsartan ameliorates podocyte loss in diabetic mice through the
Notch pathway. Int J Mol Med. 37:1328–1336. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yamamoto S, Schulze KL and Bellen HJ:
Introduction to Notch signaling. Notch Signaling: Methods and
Protocols. Bellen HJ and Yamamoto S: Springer; New York, NY: pp.
1–14. 2014
|
|
40
|
Sun J, Zhao F, Zhang W, Lv J, Lv J and Yin
A: BMSCs and miR-124a ameliorated diabetic nephropathy via
inhibiting notch signalling pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 22:4840–4855.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhang X, Song S and Luo H: Regulation of
podocyte lesions in diabetic nephropathy via miR-34a in the Notch
signaling pathway. Medicine (Baltimore). 95:e50502016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Liu XD, Zhang LY, Zhu TC, Zhang RF, Wang
SL and Bao Y: Overexpression of miR-34c inhibits high
glucose-induced apoptosis in podocytes by targeting Notch signaling
pathways. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:4525–4534. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chen M, Zhang Y, Li W and Yang J:
MicroRNA-145 alleviates high glucose-induced proliferation and
migration of vascular smooth muscle cells through targeting ROCK1.
Biomed Pharmacother. 99:81–86. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hui Y and Yin Y: MicroRNA-145 attenuates
high glucose-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in retinal
endothelial cells through regulating TLR4/NF-κB signaling. Life
Sci. 207:212–218. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lim JH, Youn DY, Yoo HJ, Yoon HH, Kim MY,
Chung S, Kim YS, Chang YS, Park CW and Lee JH: Aggravation of
diabetic nephropathy in BCL-2 interacting cell death suppressor
(BIS)-haploinsufficient mice together with impaired induction of
superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity. Diabetologia. 57:214–223.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Deshpande SD, Putta S, Wang M, Lai JY,
Bitzer M, Nelson RG, Lanting LL, Kato M and Natarajan R:
Transforming growth factor-β-induced cross talk between p53 and a
microRNA in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes.
62:3151–3162. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kolati SR, Kasala ER, Bodduluru LN,
Mahareddy JR, Uppulapu SK, Gogoi R, Barua CC and Lahkar M: BAY
11–7082 ameliorates diabetic nephropathy by attenuating
hyperglycemia-mediated oxidative stress and renal inflammation via
NF-κB pathway. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 39:690–699. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Gao F, Yao M, Shi Y, Hao J, Ren Y, Liu Q,
Wang X and Duan H: Notch pathway is involved in high
glucose-induced apoptosis in podocytes via Bcl-2 and p53 pathways.
J Cell Biochem. 114:1029–1038. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|