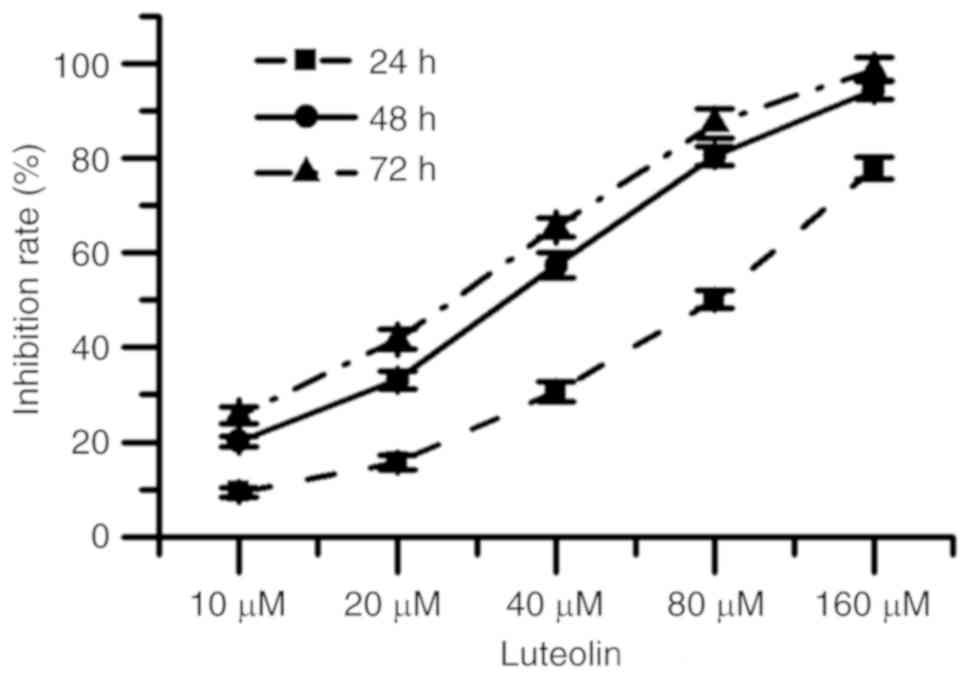
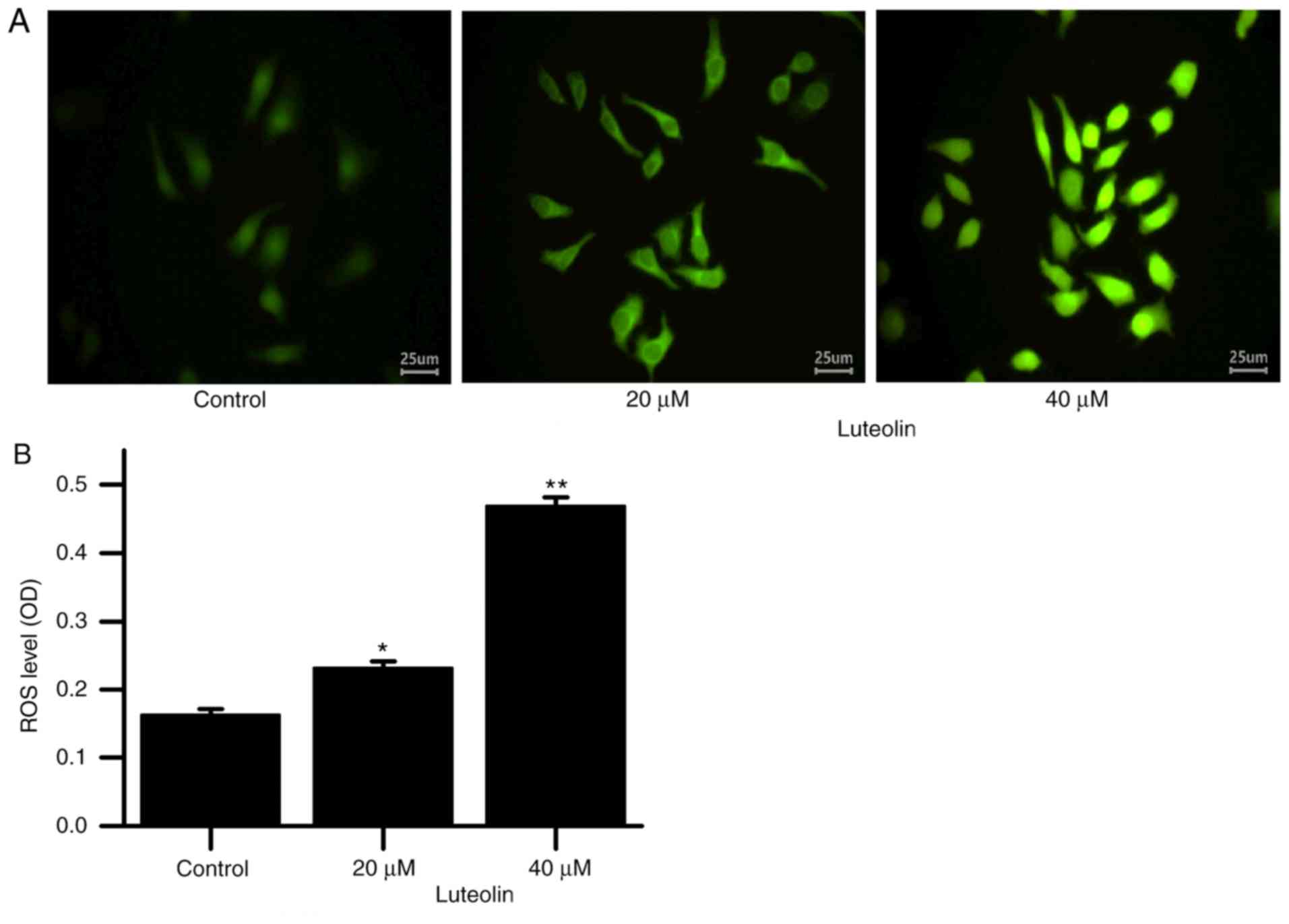
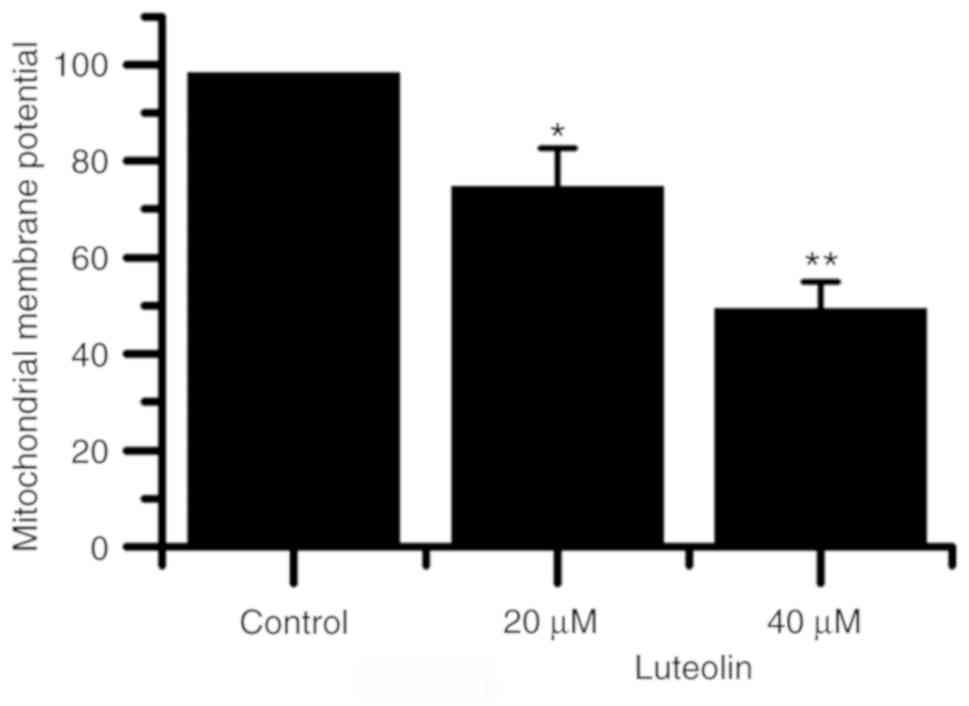
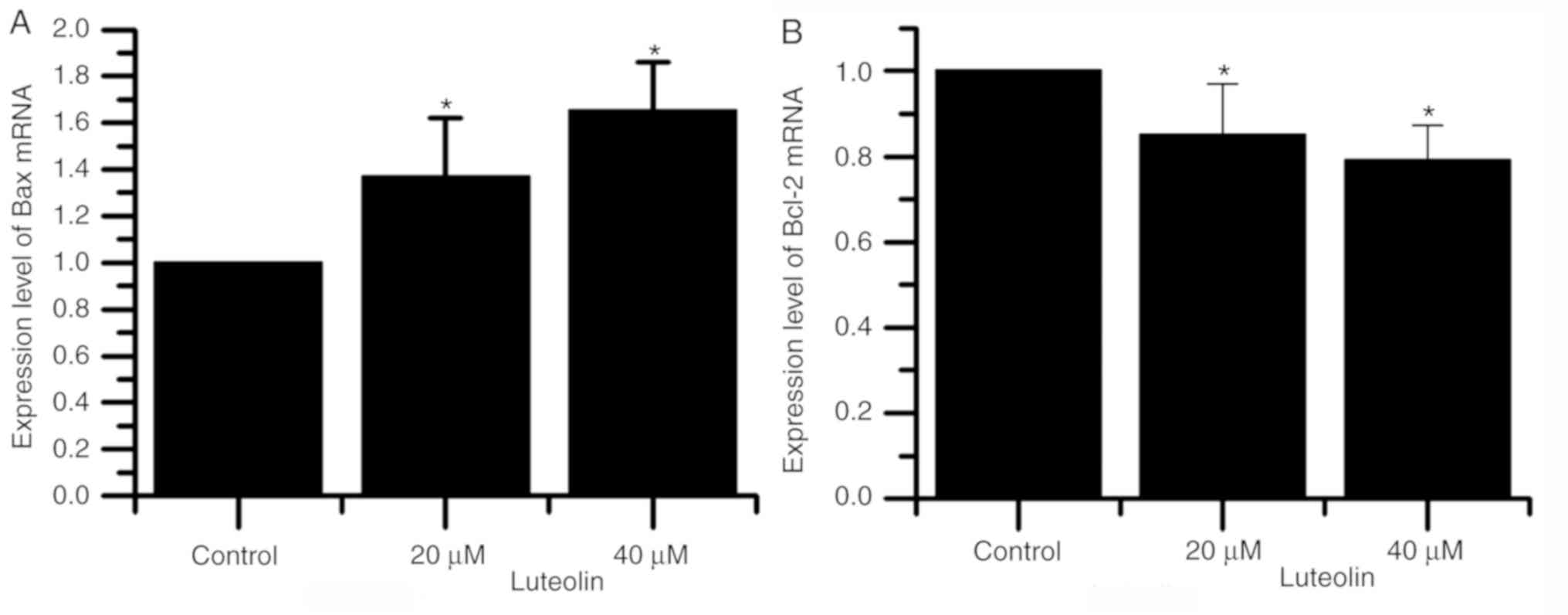
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and JEMAL A: Cancer
statistics, 2019. Ca Cancer J Clin. 69:7–34. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bailey CE, Hu CY, You YN, Bednarski BK,
Rodriguez-Bigas MA, Skibber JM, Cantor SB and Chang GJ: Increasing
disparities in the age-related incidences of colon and rectal
cancers in the united states, 1975–2010. JAMA Surg. 150:17–22.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Reddy BS: Metabolic epidemiology of colon
cancer. Oncology. 1991:88–98. 2015.
|
|
4
|
Aran V, Victorino AP, Thuler LC and
Ferreira CG: Colorectal cancer: Epidemiology, disease mechanisms
and interventions to reduce onset and mortality. Clin Colorectal
Cancer. 15:195–203. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cunningham D, Atkin W, Lenz HJ, Lynch HT,
Minsky B, Nordlinger B and Starling N: Colorectal cancer. Lancet.
375:1030–1047. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chang HF and Yang LL: Gamma-mangostin, a
micronutrient of mangosteen fruit, induces apoptosis in human colon
cancer cells. Molecules. 17:8010–8021. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Scagliarini L, Anania G, Marino S,
Marchitelli I and Resta G: Treatment of colorectal cancer:
Multidisciplinay approach. Eur J Surg Oncol. 44:5552018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Lin Y, Shi R, Wang X and Shen HM:
Luteolin, a flavonoid with potential for cancer prevention and
therapy. Current Cancer Drug Targets. 8:634–646. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lopez-Lazaro M: Distribution and
biological activities of the flavonoid luteolin. Mini Rev Med Chem.
9:31–59. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xu T, Li D and Jiang D: Targeting cell
signaling and apoptotic pathways by luteolin: Cardioprotective role
in rat cardiomyocytes following ischemia/reperfusion. Nutrients.
4:2008–2019. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lim DY, Jeong Y, Tyner AL and Park JH:
Induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in HT-29 human colon
cancer cells by the dietary compound luteolin. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 292:G66–G75. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wu G, Li J, Yue J, Zhang S and Yunusi K:
Liposome encapsulated luteolin showed enhanced antitumor efficacy
to colorectal carcinoma. Mol Med Rep. 17:2456–2464. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen Z, Zhang B, Gao F and Shi R:
Modulation of G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by
luteolin in human colon cancer cells and xenografts. Oncol Lett.
15:1559–1565. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Meng X, Zhong WQ and Zhang XR: Luteolin
inhibits the colon cancer HT-29 cell proliferation, migration and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition: An experimental study. J Hainan
Med University. 23:5–8. 2017.
|
|
15
|
Chulenbayeva LE, Shaiken TE and Opekun AR:
Sa1967 The effect of flavonoids luteolin and quercetin upon colon
cancer cells in vitro; ‘So What's in Your Fiber’? Gastroenterology.
148:S–370. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Pandurangan AK, Dharmalingam P, Sadagopan
SK, Ramar M, Munusamy A and Ganapasam S: Luteolin induces growth
arrest in colon cancer cells through involvement of
Wnt/β-catenin/GSK-3β signaling. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol.
32:131–139. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lim DY, Cho HJ, Kim J, Nho CW, Lee KW and
Park JH: Luteolin decreases IGF-II production and downregulates
insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signaling in HT-29 human
colon cancer cells. BMC Gastroenterol. 12:92012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Abdelhadi L, Vito CD, Giussani P, Viani P
and Riboni L: Luteolin induces an alteration of the
Ceramide/Sphingosine-1-phosphate ratio leading to apoptosis in
human colon cancer cells. 2013.
|
|
19
|
Molavian HR, Goldman A, Phipps CJ,
Kohandel M, Wouters BG, Sengupta S and Sivaloganathan S:
Drug-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) rely on cell membrane
properties to exert anticancer effects. Sci Rep. 6:274392016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen M, Zhou B, Zhong P, Rajamanickam V,
Dai X, Karvannan K, Zhou H, Zhang X and Liang G: Increased
intracellular reactive oxygen species mediates the anti-cancer
effects of WZ35 via activating mitochondrial apoptosis pathway in
prostate cancer cells. Prostate. 77:489–504. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kobayashi M and Yamamoto M: Molecular
mechanisms activating the Nrf2-Keap1 pathway of antioxidant gene
regulation. Antioxid Redox Signal. 7:385–394. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kundu JK and Surh Y: Nrf2-Keap1 signaling
as a potential target for chemoprevention of
inflammation-associated carcinogenesis. Pharm Res. 27:999–1013.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lee MH, Hong SH, Park C, Kim GY, Leem SH,
Choi SH, Keum YS, Hyun JW, Kwon TK, Hong SH and Choi YH:
Hwang-Heuk-San induces apoptosis in HCT116 human colorectal cancer
cells through the ROS-mediated activation of caspases and the
inactivation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Oncol Rep.
36:205–214. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hoshyar R, Bathaie SZ and Sadeghizadeh M:
Crocin triggers the apoptosis through increasing the Bax/Bcl-2
ratio and caspase activation in human gastric adenocarcinoma, AGS,
cells. DNA Cell Biol. 32:50–57. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wood PA, Du-Quiton J, You S and Hrushesky
WJ: Circadian clock coordinates cancer cell cycle progression,
thymidylate synthase, and 5-fluorouracil therapeutic index. Mol
Cancer Ther. 5:2023–2033. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sun Y, Liu P and Chen J: Traditional
Chinese Medicine constitution analysis as predictors for Breast
Cancer: A cross-sectional and case control study. Langmuir.
12:4404–4410. 2015.
|
|
28
|
Parekh HS, Liu G and Wei MQ: A new dawn
for the use of traditional Chinese medicine in cancer therapy. Mol
Cancer. 8:212009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Konkimalla VB and Efferth T: Anti-cancer
natural product library from Traditional Chinese medicine. Comb
Chem High Throughput Screen. 11:7–15. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kang KA, Piao MJ, Ryu YS, Hyun YJ, Park
JE, Shilnikova K, Zhen AX, Kang HK, Koh YS, Jeong YJ and Hyun JW:
Luteolin induces apoptotic cell death via antioxidant activity in
human colon cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 51:1169–1178. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xuemin C, Yi L, Wunier, et al: The diverse
roles of small Rho GTPases in cancer cell biology. Chinese J Cell
Biol. 2015.
|
|
32
|
Xu Y, So C, Lam HM, Fung MC and Tsang SY:
Apoptosis reversal promotes cancer stem cell-like cell formation.
Neoplasia. 20:295–303. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lowe SW and Lin AW: Apoptosis in cancer.
Carcinogenesis. 21:485–495. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dobrzycka B, Terlikowski SJ, Bernaczyk PS,
Garbowicz M, Niklinski J, Chyczewski L and Kulikowski M: Prognostic
significance of Smac/DIABLO in endometrioid endometrial cancer.
Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 48:678–681. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhao Y, Qu T, Wang P, Li X, Qiang J, Xia
Z, Duan H, Huang J and Zhu L: Unravelling the relationship between
macroautophagy and mitochondrial ROS in cancer therapy. Apoptosis.
21:517–531. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu Y, Yang B, Zhang L, Cong X, Liu Z, Hu
Y, Zhang J and Hu H: Ginkgolic acid induces interplay between
apoptosis and autophagy regulated by ROS generation in colon
cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 498:246–253. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pavithra PS, Mehta A and Verma RS:
Aromadendrene oxide 2, induces apoptosis in skin epidermoid cancer
cells through ROS mediated mitochondrial pathway. Life Sci.
197:19–29. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Babayev E, Wang T, Szigeti-buck K, Lowther
K, Taylor HS, Horvath T and Seli E: Reproductive aging is
associated with changes in oocyte mitochondrial dynamics, function,
and mtDNA quantity. Maturitas. 93:121–130. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zorov DB, Juhaszova M and Sollott SJ:
Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) and ROS-induced ROS
release. Physiol Rev. 94:909–950. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Cho HD, Lee JH, Moon KD, Park KH, Lee MK
and Seo KI: Auriculasin-induced ROS causes prostate cancer cell
death via induction of apoptosis. Food Chem Toxicol. 111:660–669.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Opferman JT and Kothari A: Anti-apoptotic
BCL-2 family members in development. Cell Death Differ. 25:37–45.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Heidelberg SB: Mitochondria Apoptosis
Pathway (M). Springer; Berlin Heidelberg: 2008
|
|
43
|
Huang X, Lu Q, Shen N and Wang Y:
Inhibitory effects of Alkaline S. Chinenis polysaccharides on
proliferation and invasion abilities of colon cancer HT-29 cells in
vitro. J Jilin University Medicine Edition. 41:287–290. 2015.
|
|
44
|
Jeong DW, Kim TS, Cho IT and Kim IY:
Modification of glycolysis affects cell sensitivity to apoptosis
induced by oxidative stress and mediated by mitochondria. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 313:984–991. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Rowe LA, Degtyareva N and Doetsch PW: DNA
damage-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) stress response in
Saccharomyces cerevisiae. 45:1167–1177. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Nauseef WM: Nox enzymes in immune cells.
Semin Immunopathol. 30:195–208. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Nauseef WM: Assembly of the phagocyte
NADPH oxidase. Histochem Cell Biol. 122:277–291. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Spencer NY and Engelhardt JF: The basic
biology of redoxosomes in cytokine-mediated signal transduction and
implications for disease-specific therapies. Biochemistry.
53:1551–1564. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Brandes RP, Weissmann N and Schröder K:
Nox family NADPH oxidases: Molecular mechanisms of activation. Free
Radic Biol Med. 76:208–226. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Kang SW, Lee S and Lee EK: ROS and energy
metabolism in cancer cells: Alliance for fast growth. Arch Pharm
Res. 38:338–345. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Cao LJ, Gong H, Yan M, Li HD and Sun L:
Research progress on Nrf2-ARE signaling pathway involved in liver
disease pathological mechanism. Chinese Pharmacological Bulletin.
31:1057–1061. 2015.
|
|
52
|
Kang KA, Piao MJ, Hyun YJ, Zhen AX, Cho
SJ, Ahn MJ, Yi JM and Hyun JW: Luteolin promotes apoptotic cell
death via upregulation of Nrf2 expression by DNA demethylase and
the interaction of Nrf2 with p53 in human colon cancer cells. Exp
Ther Med. 51:402019.
|
|
53
|
Zuo Q, Wu R, Xiao X, Yang C, Yang Y, Wang
C, Lin L and Kong AN: The dietary flavone luteolin epigenetically
activates the Nrf2 pathway and blocks cell transformation in human
colorectal cancer HCT116 cells. J Cell Biochem. 119:9573–9582.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|