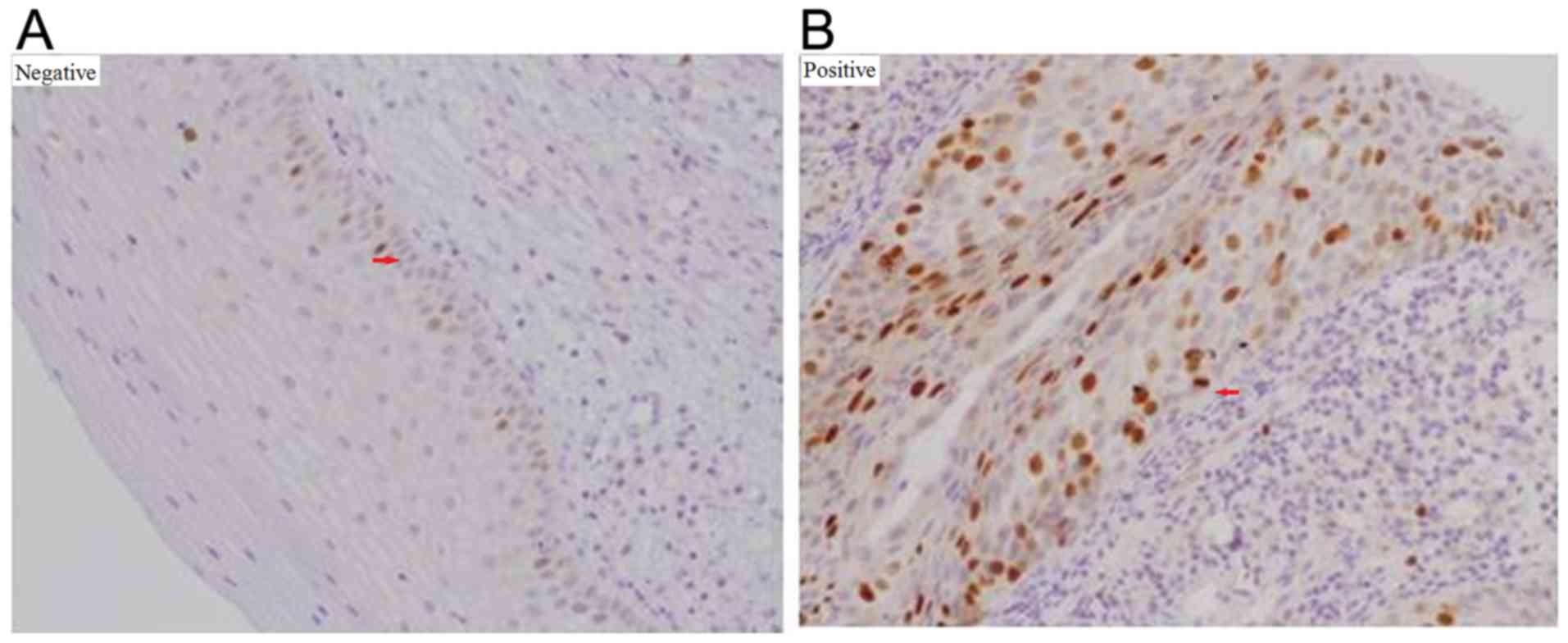
|
1
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Wang Z, Wang J, Fan J, Zhao W, Yang X, Wu
L, Li D, Ding L, Wang W, Xu J, et al: Risk factors for cervical
intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical cancer in Chinese women:
Large study in Jiexiu, Shanxi Province, China. J Cancer. 8:924–932.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Zhang S, Zhao P, Zeng H,
Zou X and He J: Annual report on status of cancer in China, 2010.
Chin J Cancer Res. 26:48–58. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Schlecht NF, Platt RW, Duarte-Franco E,
Costa MC, Sobrinho JP, Prado JC, Ferenczy A, Rohan TE, Villa LL and
Franco EL: Human papillomavirus infection and time to progression
and regression of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 95:1336–1343. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Pretet JL, Jacquard AC, Saunier M, Clavel
C, Dachez R, Gondry J, Pradat P, Soubeyrand B, Leocmach Y, Mougin
C, et al: Human papillomavirus genotype distribution in low-grade
squamous intraepithelial lesions in France and comparison with
CIN2-3 and invasive cervical cancer: The EDiTH III study. Gynecol
Oncol. 110:179–184. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Koeneman MM, Kruitwagen RF, Nijman HW,
Slangen BF, Van Gorp T and Kruse AJ: Natural history of high-grade
cervical intraepithelial neoplasia: A review of prognostic
biomarkers. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 15:527–546. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Zhao WH, Hao M, Cheng XT, Yang X, Wang ZL,
Cheng KY, Liu FL and Bai YX: c-myc gene copy number variation in
cervical exfoliated cells detected on fluorescence in situ
hybridization for cervical cancer screening. Gynecol Obstet Invest.
81:416–423. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Choi YJ and Park JS: Clinical significance
of human papillomavirus genotyping. J Gynecol Oncol.
27(e21)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Rodriguez AC, Schiffman M, Herrero R,
Wacholder S, Hildesheim A, Castle PE, Solomon D and Burk R:
Proyecto Epidemiologico Guanacaste G. Rapid clearance of human
papillomavirus and implications for clinical focus on persistent
infections. J Natl Cancer Inst. 100:513–517. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Egawa N, Egawa K, Griffin H and Doorbar J:
Human papillomaviruses; epithelial tropisms, and the development of
neoplasia. Viruses. 7:3863–3890. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zhao W, Hao M, Wang Y, Feng N, Wang Z,
Wang W, Wang J and Ding L: Association between folate status and
cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. Eur J Clin Nutr. 70:837–842.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Walts AE and Bose S: p16, Ki-67, and BD
ProExC immunostaining: A practical approach for diagnosis of
cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. Hum Pathol. 40:957–964.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ortega S, Malumbres M and Barbacid M:
Cyclin D-dependent kinases INK4 inhibitors and cancer. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1602:73–87. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Takagi M, Sueishi M, Saiwaki T, Kametaka A
and Yoneda Y: A novel nucleolar protein, NIFK, interacts with the
forkhead associated domain of Ki-67 antigen in mitosis. J Biol
Chem. 276:25386–25391. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Leone G, DeGregori J, Yan Z, Jakoi L,
Ishida S, Williams RS and Nevins JR: E2F3 activity is regulated
during the cell cycle and is required for the induction of S phase.
Genes Dev. 12:2120–2130. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Goodwin EC and DiMaio D: Repression of
human papillomavirus oncogenes in HeLa cervical carcinoma cells
causes the orderly reactivation of dormant tumor suppressor
pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:12513–125138. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Halloush RA, Akpolat I, Jim Zhai Q,
Schwartz MR and Mody DR: Comparison of ProEx C with p16INK4a and
Ki-67 immunohistochemical staining of cell blocks prepared from
residual liquid-based cervicovaginal material: A pilot study.
Cancer. 114:474–480. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Badr RE, Walts AE, Chung F and Bose S: BD
ProEx C: A sensitive and specific marker of HPV-associated squamous
lesions of the cervix. Am J Surg Pathol. 32:899–906.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Liao GD, Sellors JW, Sun HK, Zhang X, Bao
YP, Jeronimo J, Chen W, Zhao FH, Song Y, Cao Z, et al: p16 INK4A
immunohistochemical staining and predictive value for progression
of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 1: A prospective study
in China. Int J Cancer. 134:1715–1724. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Sagasta A, Castillo P, Saco A, Torné A,
Esteve R, Marimon L, Ordi J and Del PM: p16 staining has limited
value in predicting the outcome of histological low-grade squamous
intraepithelial lesions of the cervix. Mod Pathol. 29:51–59.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Silva DC, Goncalves AK, Cobucci RN,
Mendonca RC, Lima PH and Júnior GC: Immunohistochemical expression
of P16, KI67 and P53 in cervical lesions-A systematic review.
Pathol Res Pract. 213:723–729. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Solomon D, Davey D, Kurman R, Moriarty A,
O'connor D, Prey M, Raab S, Sherman M, Wilbur D, Wright T Jr, et
al: The 2001 bethesda system: Terminology for reporting results of
cervical cytology. JAMA. 287:2114–2119. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Tao P, Zheng W, Wang Y and Bian ML:
Sensitive HPV genotyping based on the flow-through hybridization
and gene chip. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012(938780)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Bornstein J, Bentley J, Bösze P, Girardi
F, Haefner H, Menton M, Perrotta M, Prendiville W, Russell P,
Sideri M, et al: 2011 colposcopic terminology of the international
federation for cervical pathology and colposcopy. Obstet Gynecol.
120:166–172. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Darragh TM, Colgan TJ, Thomas Cox J,
Heller DS, Henry MR, Luff RD, McCalmont T, Nayar R, Palefsky JM,
Stoler MH, et al: The Lower Anogenital Squamous Terminology
Standardization project for HPV-associated lesions: Background and
consensus recommendations from the College of American Pathologists
and the American Society for Colposcopy and Cervical Pathology. Int
J Gynecol Pathol. 32:76–115. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wang WC, Wu TT, Chandan VS, Lohse CM and
Zhang L: Ki-67 and ProExC are useful immnohistochemical markers in
esophageal squamous intraepithelial neoplasia. Hum Pathol.
42:1430–1437. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Shi J, Liu H, Wilkerson M, Huang Y,
Meschter S, Dupree W, Schuerch C and Lin F: Evaluation of p16INK4a,
minichromosome maintenance protein 2, DNA topoisomerase IIalpha,
ProEX C, and p16INK4a-ProEX C in cervical squamous intraepithelial
lesions. Hum Pathol. 38:1335–1344. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Pinto AP, Schlecht NF, Woo TY, Crum CP and
Cibas ES: Biomarker (ProEx C, p16(INK4A), and MiB-1) distinction of
high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion from its mimics. Mod
Pathol. 21:1067–1074. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Liu C, Ding L, Bai L, Chen X, Kang H, Hou
L and Wang J: Folate receptor alpha is associated with cervical
carcinogenesis and regulates cervical cancer cells growth by
activating ERK1-2-c-Fos-c-Jun. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
491:1083–1089. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Galen RS and Gambino SR: Beyond Normality:
The Predictive Value and Efficiency of Medical Diagnoses. John
Wiley, Sons, New York, NY, pp1-237, 1975.
|
|
31
|
Youden WJ: Index for rating diagnostic
tests. Cancer. 3:32–35. 1950.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Khleif SN, DeGregori J, Yee CL, Otterson
GA, Kaye FJ, Nevins JR and Howley PM: Inhibition of cyclin
D-CDK4-CDK6 activity is associated with an E2F-mediated induction
of cyclin kinase inhibitor activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
93:4350–4354. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Liu HQ, Wang YH, Wang LL and Hao M:
P16INK4A and survivin: Diagnostic and prognostic markers in
cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical squamous cell
carcinoma. Exp Mol Pathol. 99:44–49. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Branca M, Ciotti M, Santini D, Di Bonito
L, Giorgi C, Benedetto A, Paba P, Favalli C, Costa S, Agarossi A,
et al: p16(INK4A) Expression is related to grade of cin and
high-risk human papillomavirus but does not predict virus clearance
after conization or disease outcome. Int J Gynecol Pathol.
23:354–365. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Darragh TM, Colgan TJ, Cox JT, Heller DS,
Henry MR, Luff RD, McCalmont T, Nayar R, Palefsky JM, Stoler MH, et
al: The lower anogenital squamous terminology standardization
project for HPV associated lesions: Background and consensus
recommendations from the College of American Pathologists and the
American society for colposcopy and cervical pathology. J Low Genit
Tract Dis. 16:205–242. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Cortecchia S, Galanti G, Sgadari C, Costa
S, De Lillo M, Caprara L, Barillari G, Monini P, Nannini R, Ensoli
B and Bucchi L: Follow-up study of patients with cervical
intraepithelial neoplasia grade 1 overexpressing p16Ink4a. Int J
Gynecol Cancer. 23:1663–1669. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
del Pino M, Garcia S, Fuste V, Alonso I,
Fuste P, Torne A and Ordi J: Value of p16(INK4a) as a marker of
progression-regression in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade
1. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 201:488.e1–7. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Hariri J and Oster A: The negative
predictive value of p16INK4a to assess the outcome of cervical
intraepithelial neoplasia 1 in the uterine cervix. Int J Gynecol
Pathol. 26:223–228. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Ozaki S, Zen Y and Inoue M: Biomarker
expression in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia: Potential
progression predictive factors for low-grade lesions. Hum Pathol.
42:1007–1012. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Hanprasertpong J, Tungsinmunkong K,
Chichareon S, Wootipoom V, Geater A, Buhachat R and Boonyapipat S:
Correlation of p53 and Ki-67 (MIB-1) expressions with
clinicopathological features and prognosis of early stage cervical
squamous cell carcinomas. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 36:572–580.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Mitildzans A, Arechvo A, Rezeberga D and
Isajevs S: Expression of p63, p53 and Ki-67 in patients with
cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. Turk Patoloji Derg. 33:9–16.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Nayar R and Wilbur DC: The Bethesda System
for Reporting Cervical Cytology Definitions, Criteria, and
Explanatory Note, 3rd (ed). Switzerland: Springer International
Publishing, 103-134, 2015.
|
|
43
|
Šekoranja D and Repše Fokter A: Triaging
atypical squamous cells-cannot exclude high-grade squamous
intraepithelial lesion With p16-Ki67 dual stain. J Low Genit Tract
Dis. 21:108–111. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Tornesello ML, Buonaguro L, Giorgi-Rossi P
and Buonaguro FM: Viral and cellular biomarkers in the diagnosis of
cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cancer. Biomed Res Int.
2013:519–619. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Kanthiya K, Khunnarong J, Tangjitgamol S,
Puripat N and Tanvanich S: Expression of the p16 and Ki67 in
cervical squamous intraepithelial lesions and cancer. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 17:3201–3202. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kruse AJ, Baak JP, Janssen EA, Kjellevold
KH, Fiane B, Lovslett K, Bergh J and Robboy S: Ki67 predicts
progression in early CIN: Validation of a multivariate
progression-risk model. Cell Oncol. 26:13–20. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Osaki M, Osaki M, Yamashita H, Shomori K,
Yoshida H and Ito H: Expression of minichromosome maintenance-2 in
human malignant fibrous histiocytomas: Correlations with Ki-67 and
P53 expression, and apoptosis. Int J Mol Med. 10:161–168.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Gibbons D, Fogt F, Kasznica J, Holden J
and Nikulasson S: Comparison of topoisomerase II alpha and MIB-1
expression in uterine cervical squamous lesions. Mod Pathol.
10:409–413. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ishimi Y, Okayasu I, Kato C, Kwon HJ,
Kimura H, Yamada K and Song SY: Enhanced expression of Mcm proteins
in cancer cells derived from uterine cervix. Eur J Biochem.
270:1089–1101. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|