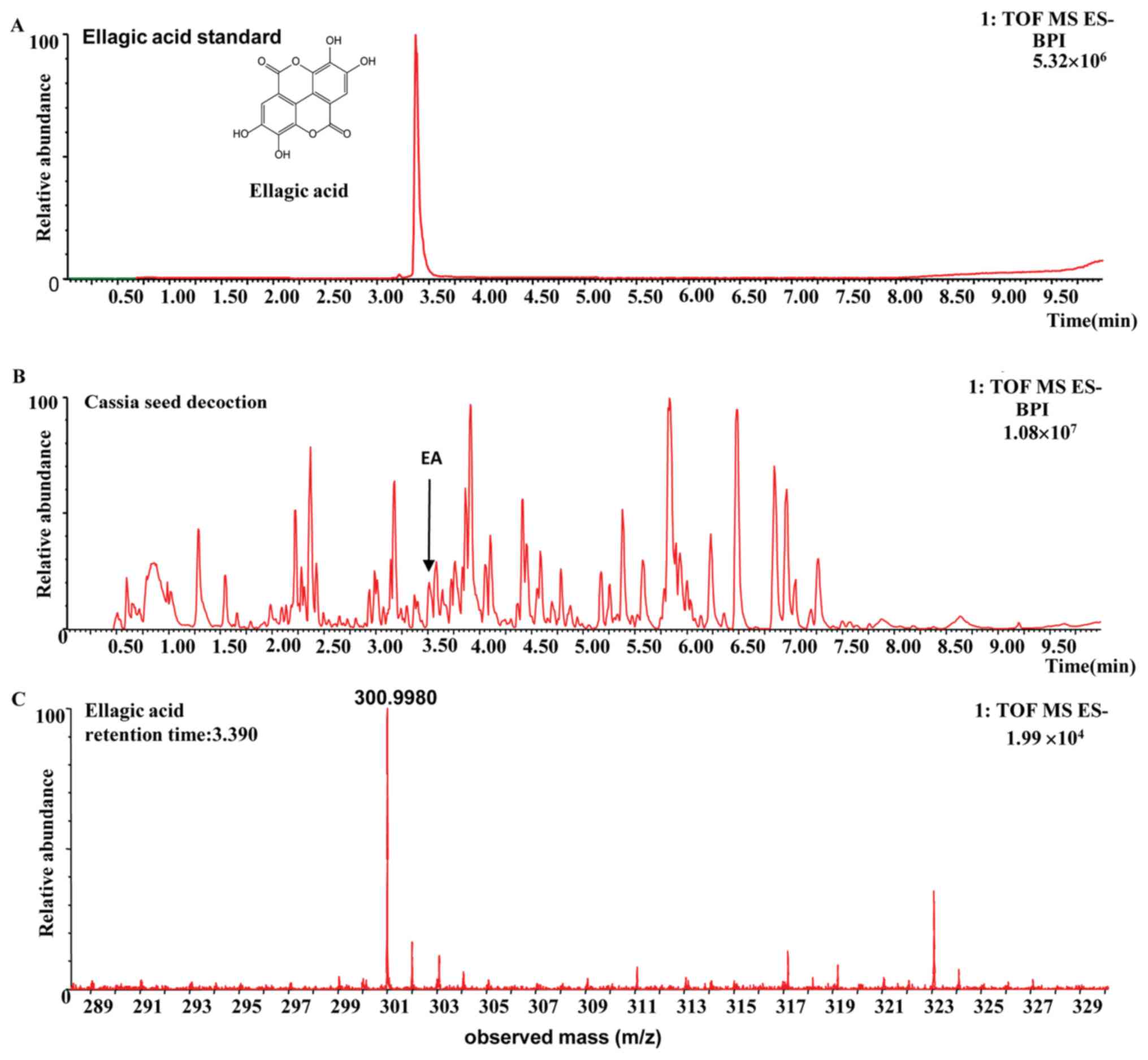
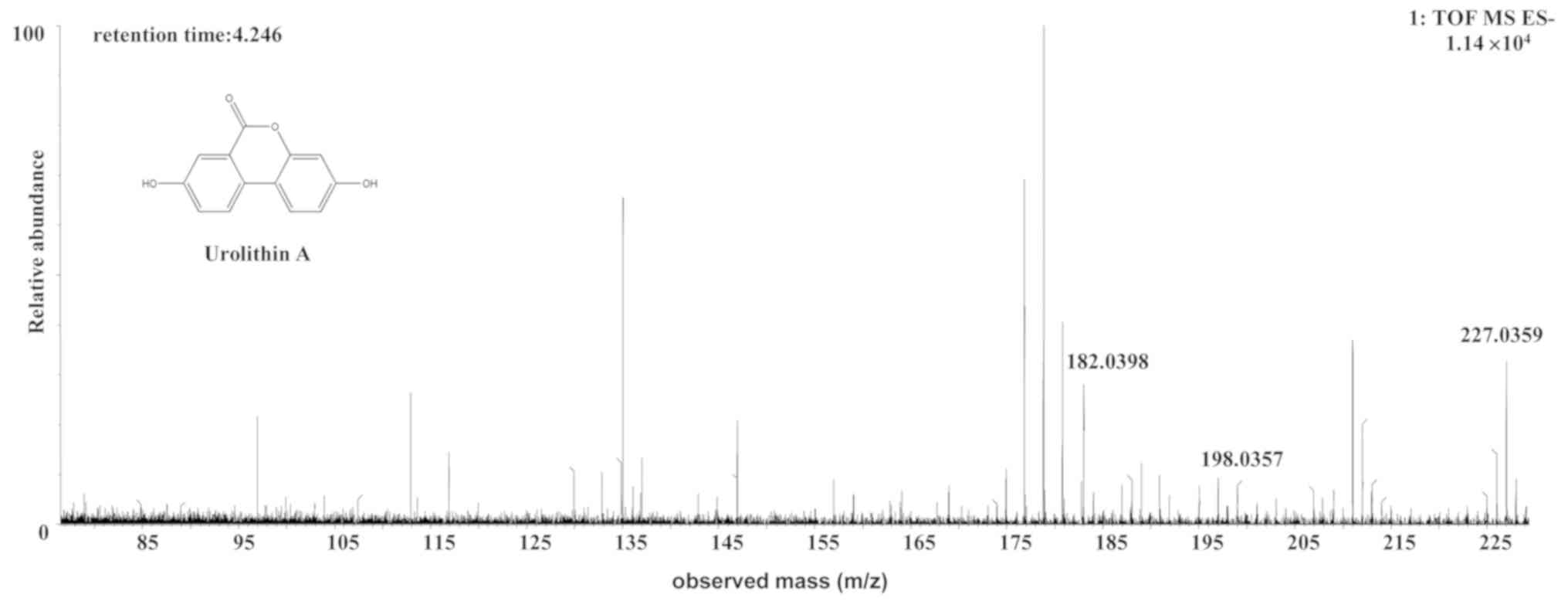
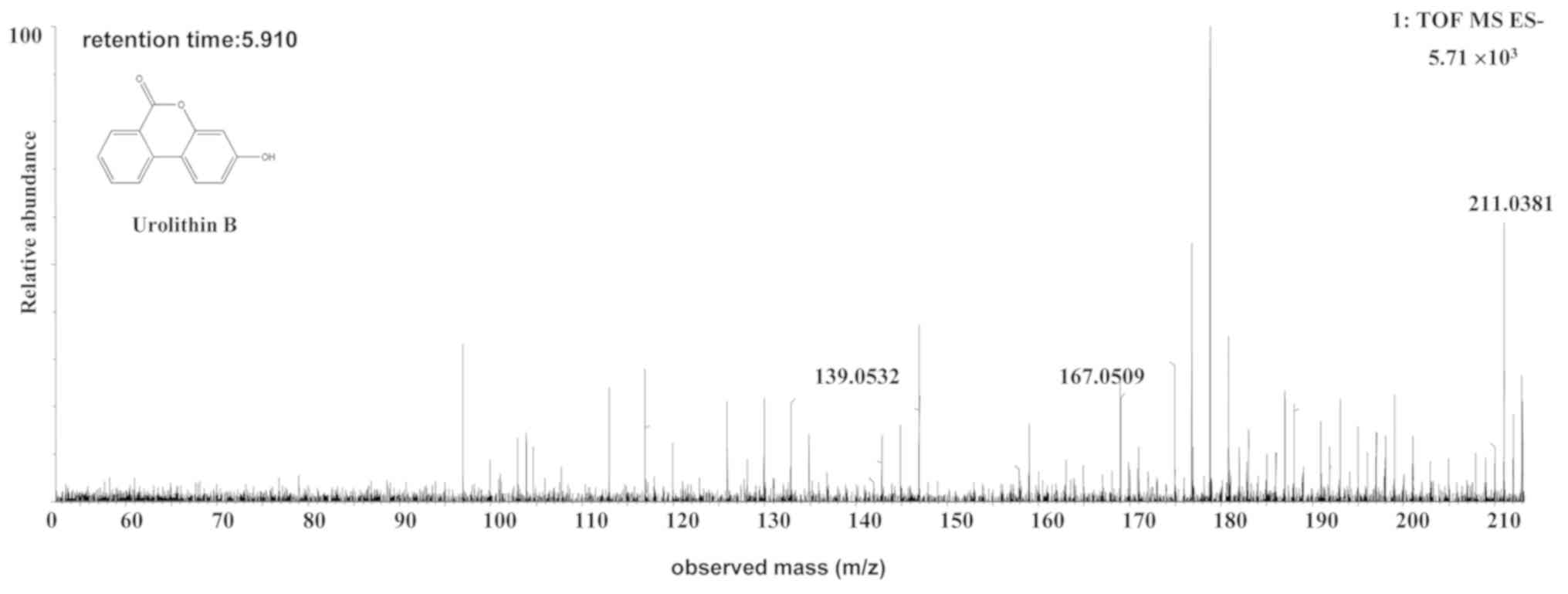
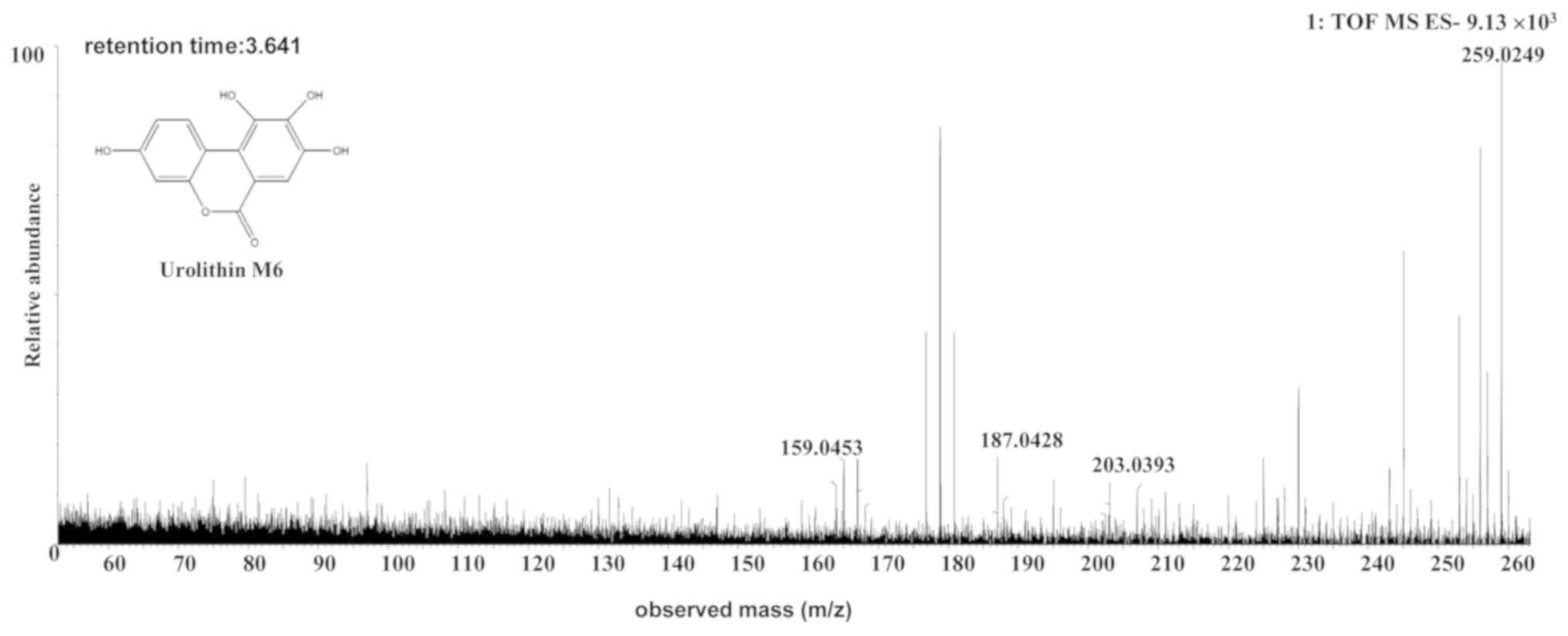
|
1
|
Yang C, Yin X, Dong X Zhang X, You L, Wang
W, Wang J, Chen Q and Ni J: Determination of the phytochemical
composition of Jingning fang and the in vivo pharmacokinetics of
its metabolites in rat plasma by UPLC-MS/MS. J Chromatogr B Analyt
Technol Biomed Life Sci. 1067:71–88. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Wu S, Xu W, Wang FR and Yang XW: Study of
the biotransformation of tongmai formula by human intestinal flora
and its intestinal permeability across the caco-2 cell monolayer.
Molecules. 20:18704–18716. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Feng W, Ao H, Peng C and Yan D: Gut
microbiota, a new frontier to understand traditional Chinese
medicines. Pharmacol Res. 142:176–191. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Goodman AL and Gordon JI: Our unindicted
coconspirators: Human metabolism from a microbial perspective. Cell
Metab. 12:111–116. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Wang RF, Yuan M, Yang XB, Xu W and Yang
XW: Intestinal bacterial transformation-a nonnegligible part of
Chinese medicine research. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 15:532–549.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Koeth RA, Wang Z, Levison BS, Buffa JA,
Org E, Sheehy BT, Britt EB, Fu X, Wu Y, Li L, et al: Intestinal
microbiota metabolism of L-carnitine, a nutrient in red meat,
promotes atherosclerosis. Nat Med. 19:576–585. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Cohen LJ, Esterhazy D, Kim SH, Lemetre C,
Aguilar RR, Gordon EA, Pickard AJ, Cross JR, Emiliano AB, Han SM,
et al: Commensal bacteria make GPCR ligands that mimic human
signalling molecules. Nature. 549:48–53. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
State Pharmacopoeia Commission of the PRC:
Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China. Vol. Ⅰ. Beijing.
People's Medical Publishing House, 2015.
|
|
9
|
Xin T, Zhang Y, Pu X, Gao R, Xu Z and Song
J: Trends in herbgenomics. Sci China Life Sci. 62:288–308.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Huang YL, Chow CJ and Tsai YH:
Composition, characteristics, and in-vitro physiological effects of
the water-soluble polysaccharides from Cassia seed. Food Chem.
134:1967–1972. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Sahu J, Koley KM and Sahu BD: Attribution
of antibacterial and antioxidant activity of Cassia tora extract
toward its growth promoting effect in broiler birds. Vet World.
10:221–226. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Dong X, Fu J, Yin X, Yang C, Zhang X, Wang
W, Du X, Wang Q and Ni J: Cassiae semen: A review of its
phytochemistry and pharmacology (Review). Mol Med Rep.
16:2331–2346. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Xie Q, Guo FF and Zhou W: Protective
effects of cassia seed ethanol extract against carbon
tetrachloride-induced liver injury in mice. Acta Biochim Pol.
59:265–270. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim M, Lim SJ, Lee HJ and Nho CW: Cassia
tora seed extract and its active compound aurantio-obtusin inhibit
allergic responses in IgE-mediated mast cells and anaphylactic
models. J Agric Food Chem. 63:9037–9046. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Yi JH, Park HJ, Lee S, Jung JW, Kim BC,
Lee YC, Ryu JH and Kim DH: Cassia obtusifolia seed ameliorates
amyloid β-induced synaptic dysfunction through anti-inflammatory
and Akt/GSK-3β pathways. J Ethnopharmacol. 178:50–57.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ju MS, Kim HG, Choi JG, Ryu JH, Hur J, Kim
YJ and Oh MS: Cassiae semen, a seed of Cassia obtusifolia, has
neuroprotective effects in Parkinson's disease models. Food Chem
Toxicol. 48:2037–2044. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Drever BD, Anderson WG, Riedel G, Kim DH,
Ryu JH, Choi DY and Platt B: The seed extract of Cassia obtusifolia
offers neuroprotection to mouse hippocampal cultures. J Pharmacol
Sci. 107:380–392. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Shi BJ, Zhang WD, Jiang HF, Zhu YY, Chen
L, Zha XM, Lu YY and Zhang WM: A new anthraquinone from seed of
Cassia obtusifolia. Nat Prod Res. 30:35–41. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Xu YL, Tang LY, Zhou XD, Zhou GH and Wang
ZJ: Five new anthraquinones from the seed of Cassia obtusifolia.
Arch Pharm Res. 38:1054–1058. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
García-Villalba R, Beltrán D, Espín JC,
Selma MV and Tomás-Barberán FA: Time course production of
urolithins from ellagic acid by human gut microbiota. J Agric Food
Chem. 61:8797–8806. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Koppel N, Maini Rekdal V and Balskus EP:
Chemical transformation of xenobiotics by the human gut microbiota.
Science. 356:2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Mullen W, Yokota T, Lean ME and Crozier A:
Analysis of ellagitannins and conjugates of ellagic acid and
quercetin in raspberry fruits by LC-MSn. Phytochemistry.
64:617–624. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Lee JH, Johnson JV and Talcott ST:
Identification of ellagic acid conjugates and other polyphenolics
in muscadine grapes by HPLC-ESI-MS. J Agric Food Chem.
53:6003–6010. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Cerdá B, Periago P, Espín JC and
Tomás-Barberán FA: Identification of urolithin a as a metabolite
produced by human colon microflora from ellagic acid and related
compounds. J Agric Food Chem. 53:5571–5576. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Lucas R, Alcantara D and Morales JC: A
concise synthesis of glucuronide metabolites of urolithin-B,
resveratrol, and hydroxytyrosol. Carbohydr Res. 344:1340–1346.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Rupiani S, Guidotti L, Manerba M, Di Ianni
L, Giacomini E, Falchi F, Di Stefano G, Roberti M and Recanatini M:
Synthesis of natural urolithin M6, a galloflavin mimetic, as a
potential inhibitor of lactate dehydrogenase A. Org Biomol Chem.
14:10981–10987. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Nuñez-Sánchez MA, García-Villalba R,
Monedero-Saiz T, García-Talavera NV, Gómez-Sánchez MB,
Sánchez-Álvarez C, García-Albert AM, Rodríguez-Gil FJ, Ruiz-Marín
M, Pastor-Quirante FA, et al: Targeted metabolic profiling of
pomegranate polyphenols and urolithins in plasma, urine and colon
tissues from colorectal cancer patients. Mol Nutr Food Res.
58:1199–1211. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
González-Barrio R, Truchado P, Ito H,
Espin JC and Tomás-Barberán FA: UV and MS identification of
Urolithins and Nasutins, the bioavailable metabolites of
ellagitannins and ellagic acid in different mammals. J Agric Food
Chem. 59:1152–1162. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Seeram NP, Henning SM, Zhang Y, Suchard M,
Li Z and Heber D: Pomegranate juice ellagitannin metabolites are
present in human plasma and some persist in urine for up to 48
hours. J Nutr. 136:2481–2485. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
García-Villalba R, Espín JC and
Tomás-Barberán FA: Chromatographic and spectroscopic
characterization of urolithins for their determination in
biological samples after the intake of foods containing
ellagitannins and ellagic acid. J Chromatogr A. 1428:162–175.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Giorgio C, Mena P, Del Rio D, Brighenti F,
Barocelli E, Hassan-Mohamed I, Callegari D, Lodola A and Tognolini
M: The ellagitannin colonic metabolite urolithin D selectively
inhibits EphA2 phosphorylation in prostate cancer cells. Mol Nutr
Food Res. 59:2155–2167. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Fan M, Qin K, Ding F, Huang Y, Wang X and
Cai B: Identification and differentiation of major components in
three different ‘Sheng-ma’ crude drug species by UPLC/Q-TOF-MS.
Acta Pharm Sin B. 7:185–192. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Vattem DA and Shetty K: Biological
functionality of ellagic acid: A review. J Food Biochem.
29:234–266. 2005.
|
|
34
|
Jadhav PD and Laddha KS: Synthesis of new
ellagic acid derivatives. Indian J Chem B. 45:1551–1553. 2006.
|
|
35
|
Huang ZH, Xu Y, Wang Q and Gao XY:
Metabolism and mutual biotransformations of anthraquinones and
anthrones in rhubarb by human intestinal flora using UPLC-Q-TOF/MS.
J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 1104:59–66.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Piwowarski JP, Granica S, Zwierzyńska M,
Stefańska J, Schopohl P, Melzig MF and Kiss AK: Role of human gut
microbiota metabolism in the anti-inflammatory effect of
traditionally used ellagitannin-rich plant materials. J
Ethnopharmacol. 155:801–809. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Stolarczyk M, Piwowarski JP, Granica S,
Stefanska J, Naruszewicz M and Kiss AK: Extracts from
Epilobium sp. herbs, their components and gut microbiota
metabolites of Epilobium ellagitannins, urolithins, inhibit
hormone-dependent prostate cancer cells-(LNCaP) proliferation and
PSA secretion. Phytother Res. 27:1842–1848. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Haddad EH, Gaban-Chong N, Oda K and Sabaté
J: Effect of a walnut meal on postprandial oxidative stress and
antioxidants in healthy individuals. Nutr J. 13(4)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Han QA, Yan C, Wang L, Li G, Xu Y and Xia
X: Urolithin A attenuates ox-LDL-induced endothelial dysfunction
partly by modulating microRNA-27 and ERK/PPAR-γ pathway. Mol Nutr
Food Res. 60:1933–1943. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Ryu D, Mouchiroud L, Andreux PA, Katsyuba
E, Moullan N, Nicolet-Dit-Félix AA, Williams EG, Jha P, Lo Sasso G,
Huzard D, et al: Urolithin A induces mitophagy and prolongs
lifespan in C. elegans and increases muscle function in rodents.
Nat Med. 22:879–893. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Chen P, Chen F, Lei J, Li Q and Zhou B:
Activation of the miR-34a-mediated SIRT1/mTOR signaling pathway by
urolithin A attenuates D-galactose-induced brain aging in mice.
Neurotherapeutics. 16:1269–1282. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Kumar RS, Narasingappa RB, Joshi CG,
Girish TK, Prasada Rao UJ and Danagoudar A: Evaluation of Cassia
tora Linn. against oxidative stress-induced DNA and cell membrane
damage. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 9:33–43. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
David LA, Maurice CF, Carmody RN,
Gootenberg DB, Button JE, Wolfe BE, Ling AV, Devlin AS, Varma Y,
Fischbach MA, et al: Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human
gut microbiome. Nature. 505:559–563. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Ezenwa VO, Gerardo NM, Inouye DW, Medina M
and Xavier JB: Microbiology. Animal behavior and the microbiome.
Science. 338:198–199. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Espín JC, Larrosa M, García-Conesa MT and
Tomás-Barberán F: Biological significance of urolithins, the gut
microbial ellagic Acid-derived metabolites: The evidence so far.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013(270418)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Selma MV, Beltrán D, García-Villalba R,
Espín JC and Tomás-Barberán FA: Description of urolithin production
capacity from ellagic acid of two human intestinal Gordonibacter
species. Food Funct. 5:1779–1784. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Clarke G, Sandhu KV, Griffin BT, Dinan TG,
Cryan JF and Hyland NP: Gut reactions: Breaking down
xenobiotic-microbiome interactions. Pharmacol Rev. 71:198–224.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|