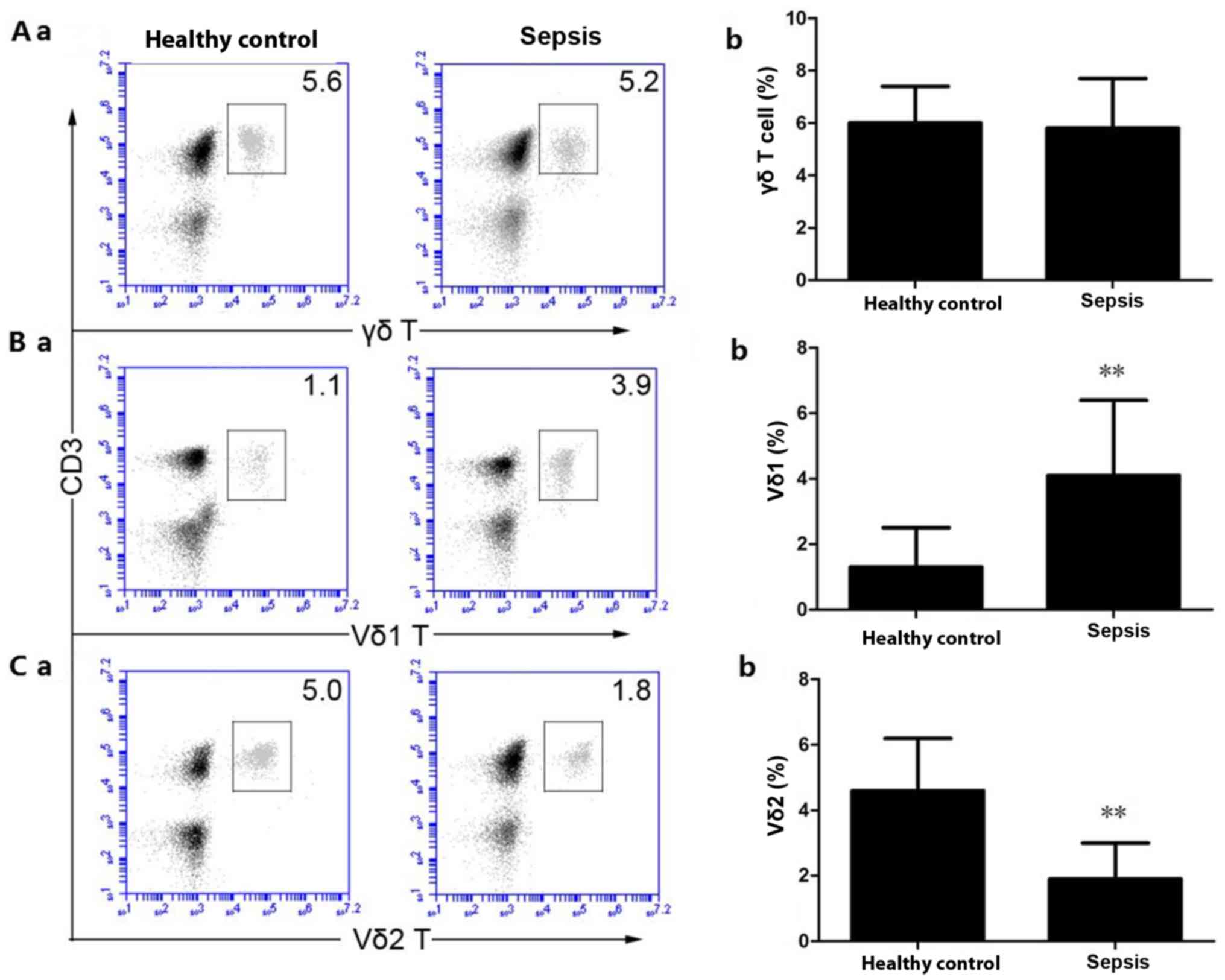
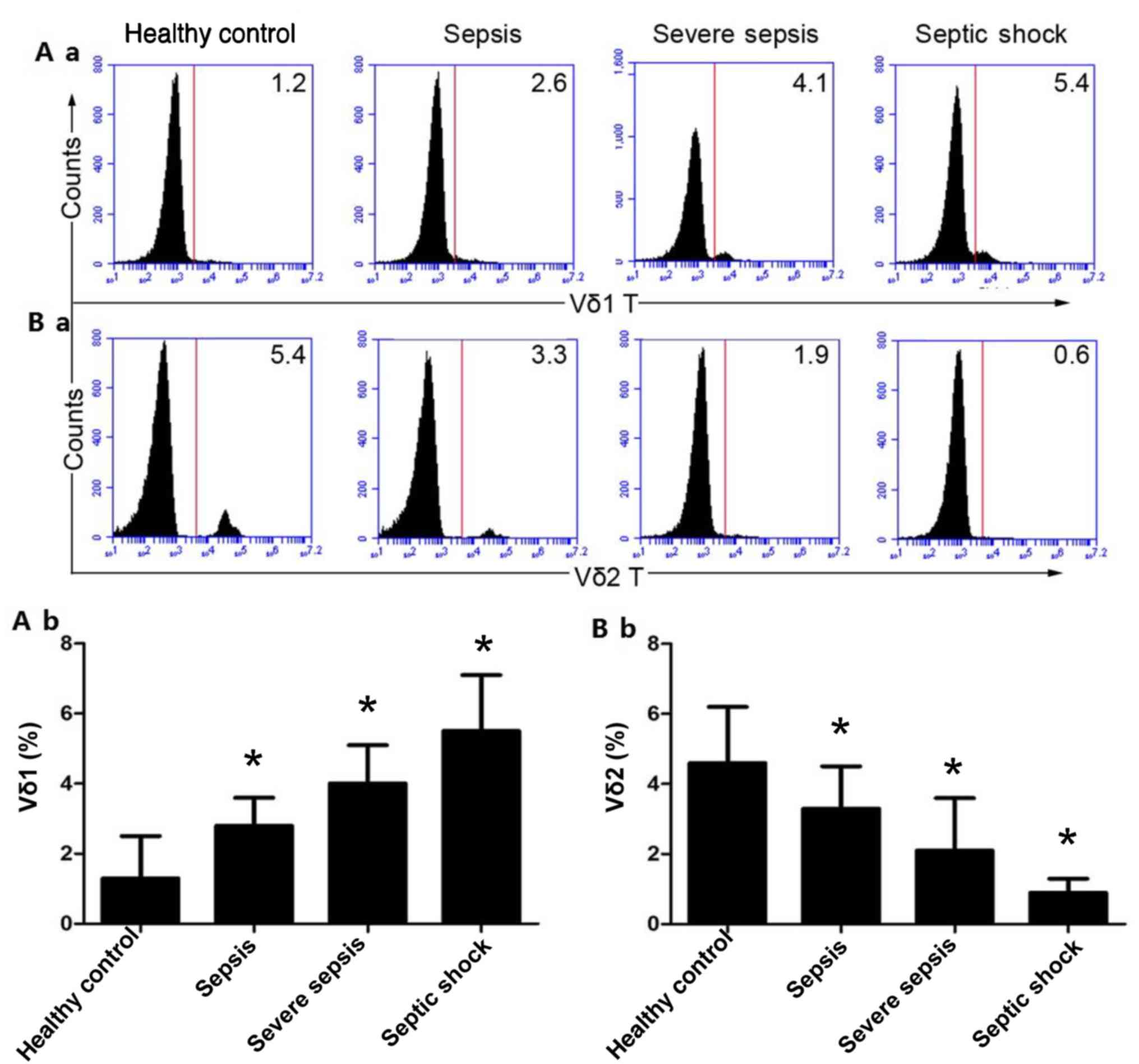
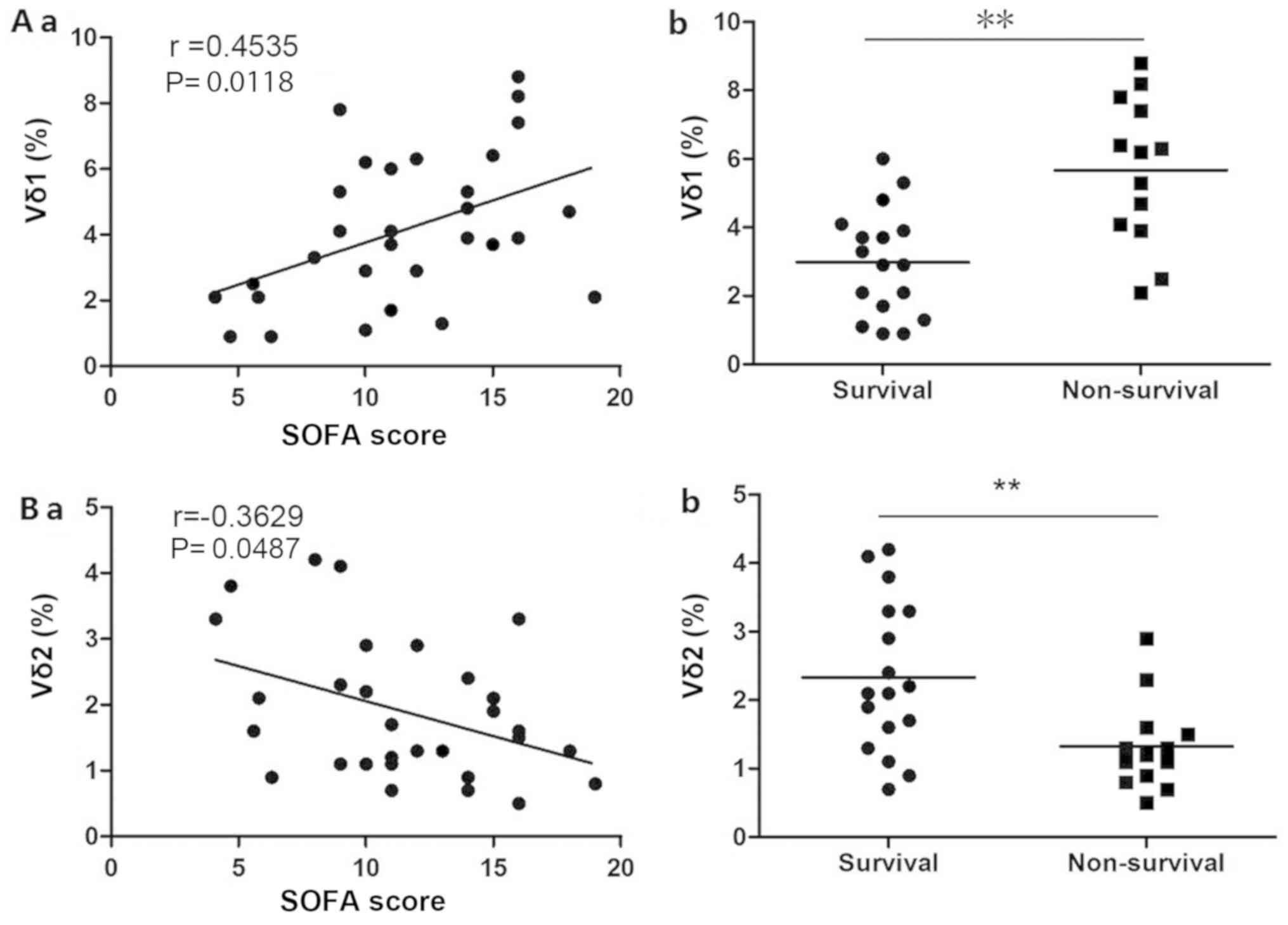
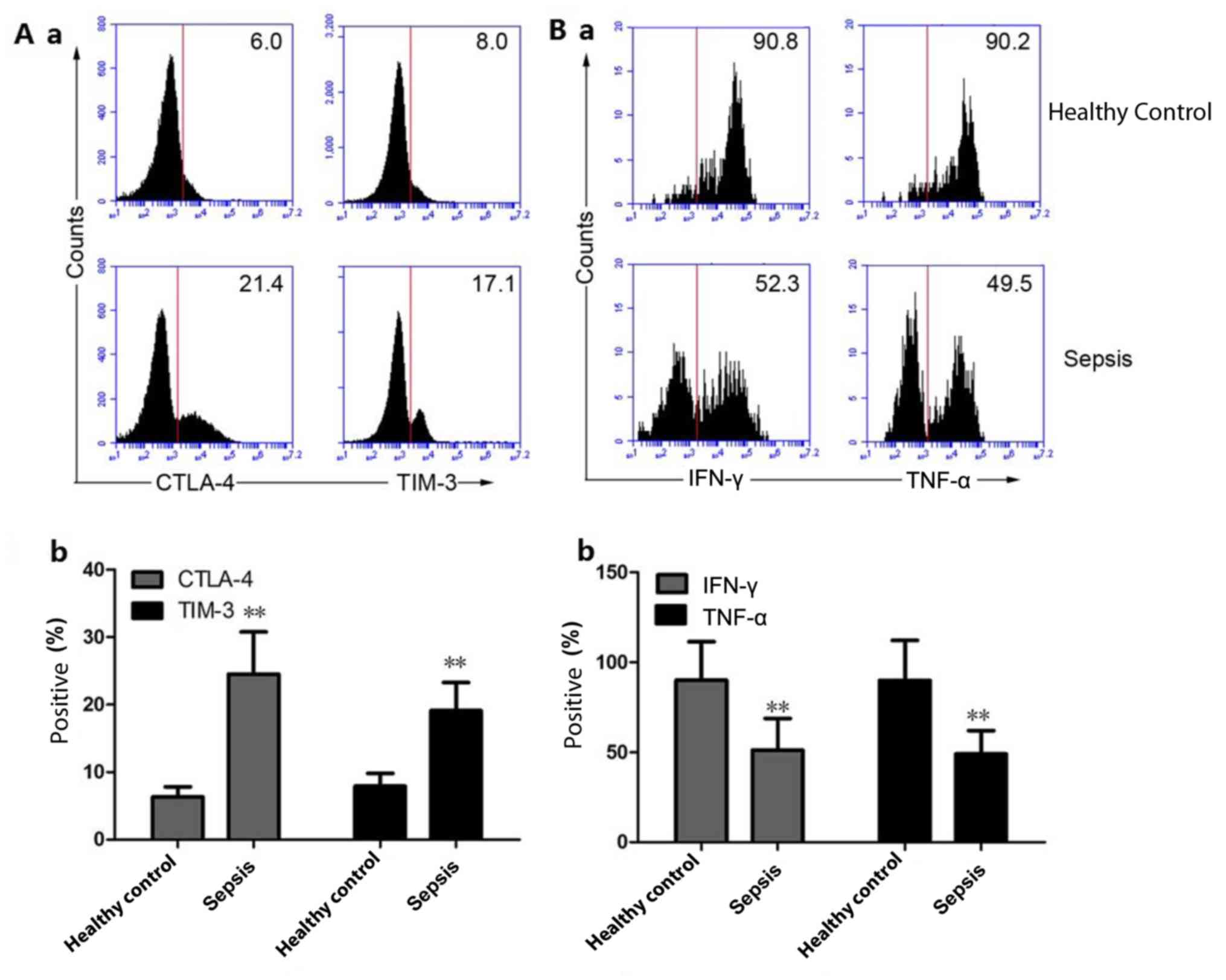
|
1
|
Nam M, Son BH, Seo JE, Kim IR, Park CK and
Kim HK: Improved diagnostic and prognostic power of combined delta
neutrophil index and mean platelet volume in pediatric sepsis. Ann
Clin Lab Sci. 48:223–230. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jones BL and Smith SM: Choice of
crystalloid and mortality in sepsis-all in the timing? Crit Care
Med. 42(e796)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Barochia AV, Cui X and Eichacker PQ: The
surviving sepsis campaign's revised sepsis bundles. Curr Infect Dis
Rep. 15:385–393. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Hotchkiss RS, Monneret G and Payen D:
Sepsis-induced immunosuppression: From cellular dysfunctions to
immunotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol. 13:862–874. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Otto GP, Sossdorf M, Claus RA, Rödel J,
Menge K, Reinhart K, Bauer M and Riedemann NC: The late phase of
sepsis is characterized by an increased microbiological burden and
death rate. Crit Care. 15(R183)2011.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Limaye AP, Kirby KA, Rubenfeld GD,
Leisenring WM, Bulger EM, Neff MJ, Gibran NS, Huang ML, Santo Hayes
TK, Corey L and Boeckh M: Cytomegalovirus reactivation in
critically ill immunocompetent patients. JAMA. 300:413–422.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Shevach EM, DiPaolo RA, Andersson J, Zhao
DM, Stephens GL and Thornton AM: The lifestyle of naturally
occurring CD4+ CD25+ Foxp3+
regulatory T cells. Immunol Rev. 212:60–73. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Sakaguchi S, Ono M, Setoguchi R, Yagi H,
Hori S, Fehervari Z, Shimizu J, Takahashi T and Nomura T:
Foxp3+ CD25+ CD4+ natural
regulatory T cells in dominant self-tolerance and autoimmune
disease. Immunol Rev. 212:8–27. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wan YY: Regulatory T cells: Immune
suppression and beyond. Cell Mol Immunol. 7:204–210.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Pan X, Ji Z and Xue J: Percentage of
peripheral CD19+CD24hiCD38hi regulatory B cells in neonatal sepsis
patients and its functional implication. Med Sci Monit.
22:2374–2378. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Huang H, Xu R, Lin F, Bao C, Wang S, Ji C,
Li K, Jin L, Mu J, Wang , et al: High circulating CD39(+)
regulatory T cells predict poor survival for sepsis patients. Int J
Infect Dis. 30:57–63. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Shao M, Liu B, Wang JQ, Tao XG, Zhou SS,
Jin K and Zhang CP: Clinical significance of
CD4+CD25+ T cell examination in sepsis
patients. J Hunan Chin Med Univ. 31:8–10. 2011.
|
|
13
|
Raga S, Julià MR, Crespí C, Figuerola J,
Martínez N, Milà J and Matamoros N: Gammadelta T lymphocytes from
cystic fibrosis patients and healthy donors are high TNF-alpha and
IFN-gamma-producers in response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Respir Res. 4(9)2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Gao L, Lu Q, Huang LJ, Ruan LH, Yang JJ,
Huang WL, ZhuGe WS, Zhang YL, Fu B, Jin KL and ZhuGe QC:
Transplanted neural stem cells modulate regulatory T, γδ T cells
and corresponding cytokines after intracerebral hemorrhage in rats.
Int J Mol Sci. 15:4431–4441. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Andreu-Ballester JC, Zamora V,
Garcia-Ballesteros C, Benet-Campos C, Lopez-Chuliá F,
Tormo-Calandín C and Cuéllar C: Anti-Anisakis sp. antibodies in
serum of patients with sepsis and their relationship with γδ T
cells and disease severity. Int J Parasitol. 48:483–491.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Hayday AC: [gamma][delta] cells: A right
time and a right place for a conserved third way of protection.
Annu Rev Immunol. 18:975–1026. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Triebel F and Hercend T: Subpopulations of
human peripheral T gamma delta lymphocytes. Immunol Today.
10:186–188. 1989.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Haas W, Pereira P and Tonegawa S:
Gamma/delta cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 11:637–685. 1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kabelitz D, Wesch D and He W: Perspectives
of gammadelta T cells in tumor immunology. Cancer Res. 67:5–8.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Levy MM, Fink MP, Marshall JC, Abraham E,
Angus D, Cook D, Cohen J, Opal SM, Vincent JL and Ramsay G:
SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS: 2001 SCCM /ESICM /ACCP/ATS/SIS
international sepsis definitions conference. Crit Care Med.
31:1250–1256. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Soyocak A, Kurt H, Ozgen M, Turgut Cosan
D, Colak E and Gunes HV: MiRNA-146a, miRNA-155 and JNK expression
levels in peripheral blood mononuclear cells according to grade of
knee osteoarthritis. Gene. 627:207–211. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Kumar V: T cells and their
immunometabolism: A novel way to understanding sepsis
immunopathogenesis and future therapeutics. Eur J Cell Biol.
97:379–392. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Ichinohe T, Ichimiya S, Kishi A, Tamura Y,
Kondo N, Ueda G, Torigoe T, Yamaguchi A, Hiratsuka H, Hirai I, et
al: T-cell receptor variable gamma chain gene expression in the
interaction between rat gammadelta-type T cells and heat-shock
protein 70-like molecule. Microbiol Immunol. 47:351–357.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Andreu-Ballester JC, Tormo-Calandín C,
Garcia-Ballesteros C, Pérez-Griera J, Amigó V, Almela-Quilis A,
Ruiz del Castillo J, Peñarroja-Otero C and Ballester F: Association
of γδ T cells with disease severity and mortality in septic
patients. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 20:738–746. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Andreu-Ballester JC, García-Ballesteros C,
Benet-Campos C, Amigó V, Almela-Quilis A, Mayans J and Ballester F:
Values for αβ and γδ T-lymphocytes and CD4+,
CD8+, and CD56+ subsets in healthy adult
subjects: Assessment by age and gender. Cytometry B Clin Cytom.
82:238–244. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Sabbagh P, Karkhah A, Nouri HR, Javanian M
and Ebrahimpour S: The significance role of regulatory T cells in
the persistence of infections by intracellular bacteria. Infect
Genet Evol. 62:270–274. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Cuende J, Liénart S, Dedobbeleer O, van
der Woning B, De Boeck G, Stockis J, Huygens C, Colau D, Somja J,
Delvenne P, et al: Monoclonal antibodies against GARP/TGF-β1
complexes inhibit the immunosuppressive activity of human
regulatory T cells in vivo. Sci Transl Med.
7(284ra56)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Li X, Kang N, Zhang X, Dong X, Wei W, Cui
L, Ba D and He W: Generation of human regulatory gammadelta T cells
by TCRgammadelta stimulation in the presence of TGF-beta and their
involvement in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. J
Immunol. 186:6693–6700. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Jain N, Nguyen H, Chambers C and Kang J:
Dual function of CTLA-4 in regulatory T cells and conventional T
cells to prevent multiorgan autoimmunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
107:1524–1528. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Wang F, Hou H, Xu L, Jane M, Peng J, Lu Y,
Zhu Y and Sun Z: Tim-3 signaling pathway as a novel negative
mediator in lipopolysaccharide-induced endotoxic shock. Hum
Immunol. 75:470–478. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Lafont V, Liautard J, Sable-Teychene M,
Sainte-Marie Y and Favero J: Isopentenyl pyrophosphate, a
mycobacterial non-peptidic antigen, triggers delayed and highly
sustained signaling in human gamma delta T lymphocytes without
inducing eown-modulation of T cell antigen receptor. J Biol Chem.
276:15961–15967. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|