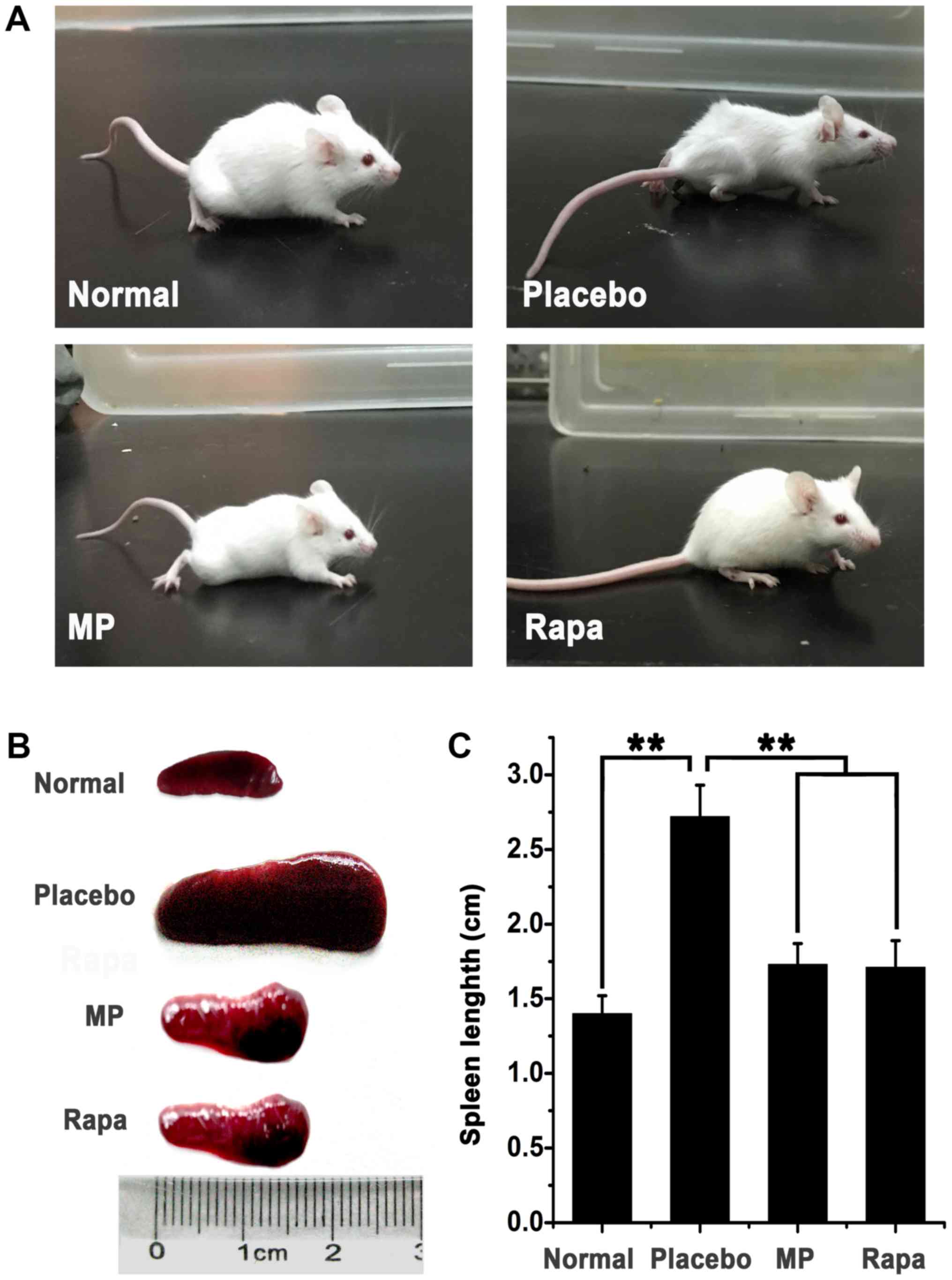
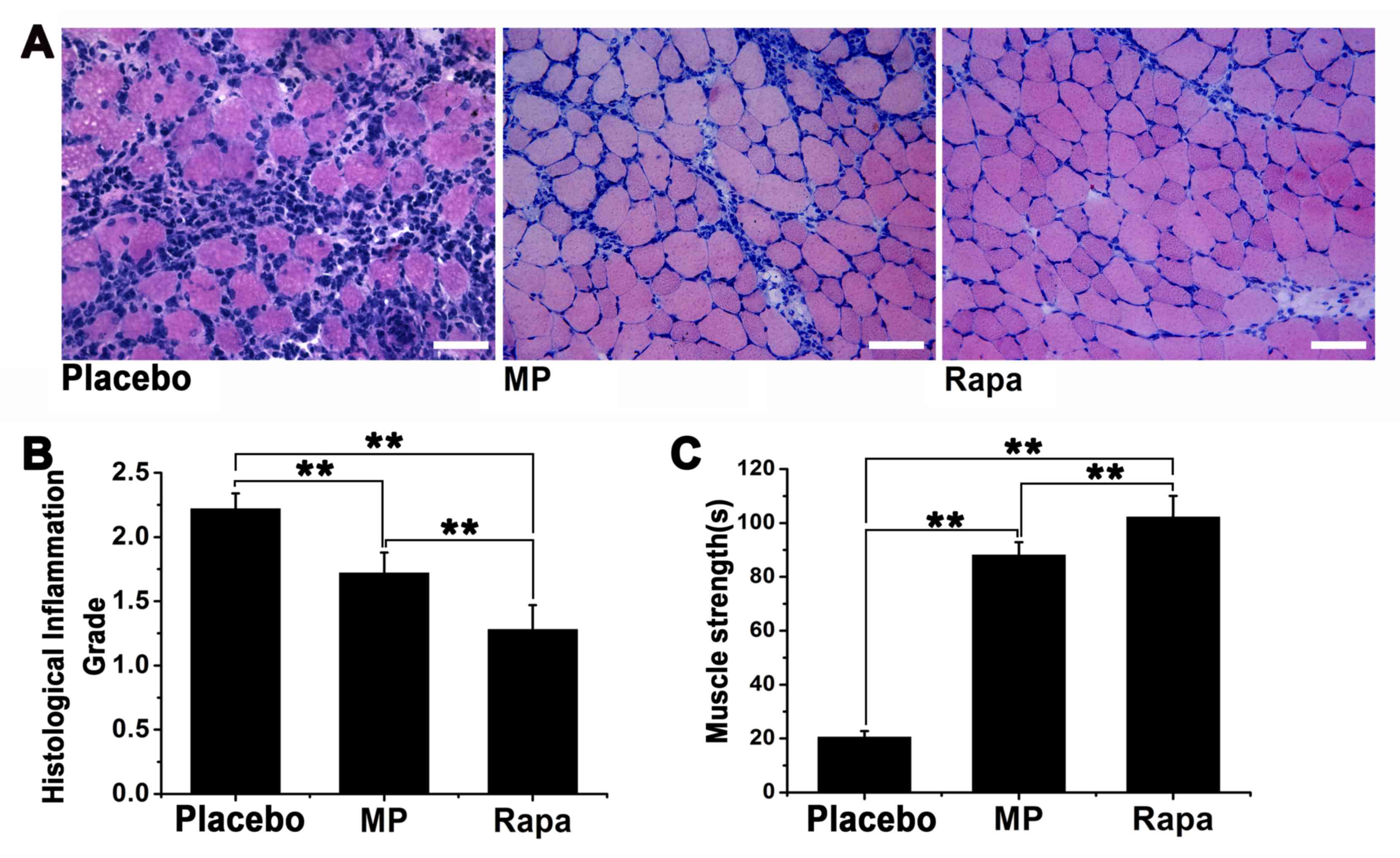
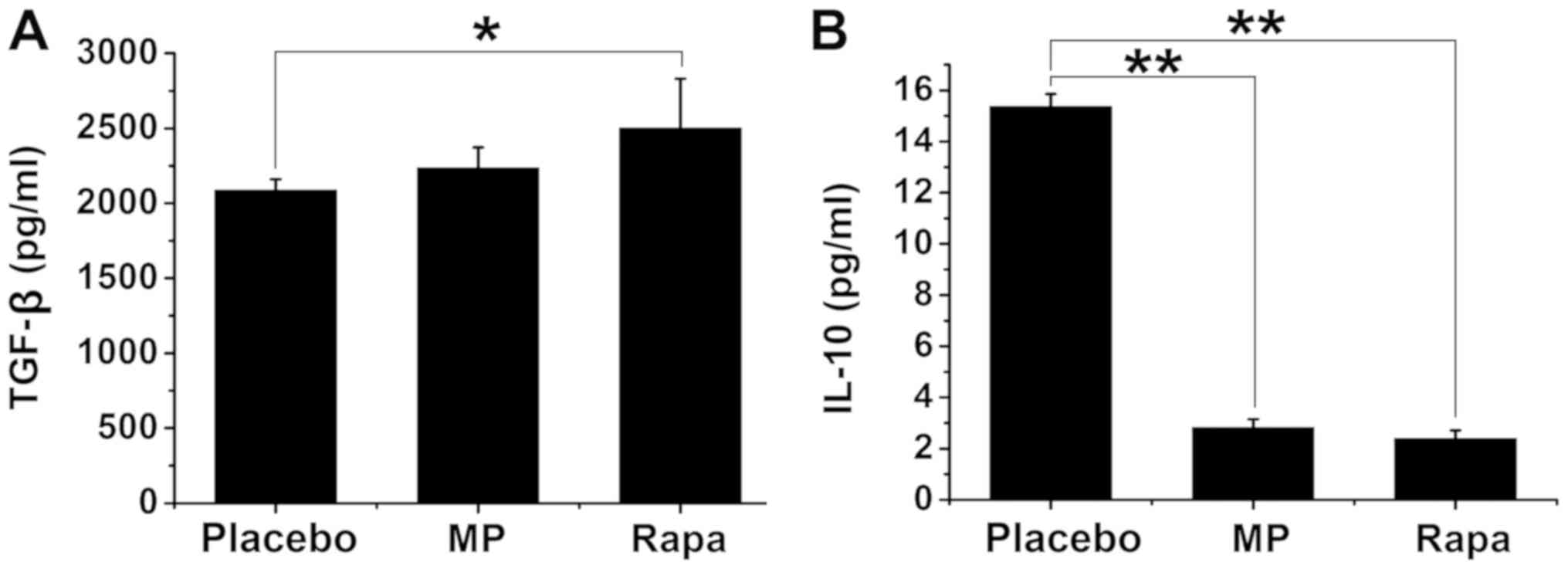
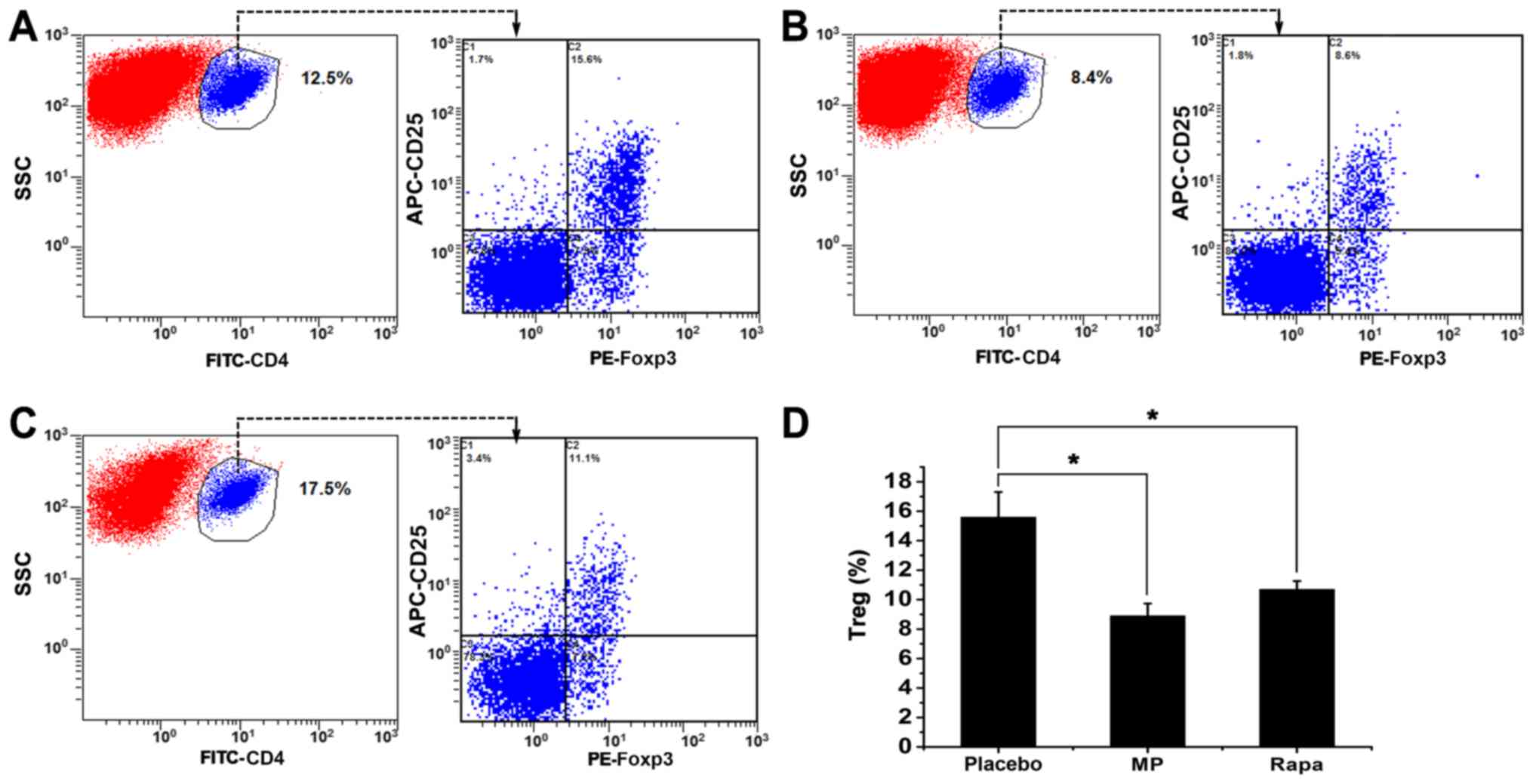
|
1
|
Dalakas MC: Therapeutic advances and
future prospects in immune-mediated inflammatory myopathies. Ther
Adv Neurol Disord. 1:157–166. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Dalakas MC and Hohlfeld R: Polymyositis
and dermatomyositis. Lancet. 362:971–982. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Hilton-Jones D: Inflammatory muscle
diseases. Curr Opin Neurol. 14:591–596. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Mastaglia FL and Phillips BA: Idiopathic
inflammatory myopathies: Epidemiology, classification, and
diagnostic criteria. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 28:723–741.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Zeng L, Maruyama S, Nakamura K,
Parker-Duffen JL, Adham IM, Zhong X, Lee HK, Querfurth H and Walsh
K: The injury-induced myokine insulin-like 6 is protective in
experimental autoimmune myositis. Skelet Muscle.
4(16)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kojima T, Tanuma N, Aikawa Y, Shin T,
Sasaki A and Matsumoto Y: Myosin-Induced autoimmune polymyositis in
the rat. J Neurol Sci. 151:141–148. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Gunawardena H: The clinical features of
myositis-associated autoantibodies: A review. Clin Rev Allergy
Immunol. 52:45–57. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Mozaffar T and Pestronk A: Myopathy with
anti-Jo-1 antibodies: Pathology in perimysium and neighbouring
muscle fibres. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 68:472–478.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Gelardi C, Paolini L and Danieli MG:
Subcutaneous immunoglobulin G in idiopathic inflammatory
myopathies: Therapeutic implications. Isr Med Assoc J. 16:646–647.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tournadre A: Therapeutic strategy in
inflammatory myopathies (polymyositis, dermatomyositis, overlap
myositis, and immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy). Rev Med
Interne. 35:466–471. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Donia M, Mangano K, Amoroso A, Mazzarino
MC, Imbesi R, Castrogiovanni P, Coco M, Meroni P and Nicoletti F:
Treatment with rapamycin ameliorates clinical and histological
signs of protracted relapsing experimental allergic
encephalomyelitis in dark agouti rats and induces expansion of
peripheral CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells. J Autoimmun.
33:135–140. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Gu L, Deng WS, Sun XF, Zhou H and Xu Q:
Rapamycin ameliorates CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in mice through
reciprocal regulation of the Th17/Treg cell balance. Mol Med Rep.
14:1153–1161. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Li WW, Sun P, Chen DD, Wang WQ, Jiao GH,
Wang YJ, Zhou L, Wang BM and Zhang J: Preventive and therapeutic
effects of rapamycin against autoimmune hepatitis and liver
fibrosis and possible mechanisms. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi.
24:368–374. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
14
|
Liu CF, Liu H, Fang Y, Jiang SH, Zhu JM
and Ding XQ: Rapamycin reduces renal hypoxia, interstitial
inflammation and fibrosis in a rat model of unilateral ureteral
obstruction. Clin Invest Med. 37(E142)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Salehi M, Bagherpour B, Shayghannejad V,
Mohebi F and Jafari R: Th1, Th2 and Th17 cytokine profile in
patients with multiple sclerosis following treatment with
rapamycin. Iran J Immunol. 13:141–147. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang B, Ding W, Zhang M, Li H and Gu Y:
Rapamycin attenuates aldosterone-induced tubulointerstitial
inflammation and fibrosis. Cell Physiol Biochem. 35:116–125.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wang GY, Zhang Q, Yang Y, Chen WJ, Liu W,
Jiang N and Chen GH: Rapamycin combined with allogenic immature
dendritic cells selectively expands CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T
cells in rats. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 11:203–208.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Gambineri E, Torgerson TR and Ochs HD:
Immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, and X-linked
inheritance (IPEX), a syndrome of systemic autoimmunity caused by
mutations of FOXP3, a critical regulator of T-cell homeostasis.
Curr Opin Rheumatol. 15:430–435. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Li X, Liang Y, LeBlanc M, Benner C and
Zheng Y: Function of a Foxp3 cis-element in protecting regulatory T
cell identity. Cell. 158:734–748. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Shevach EM: Regulatory T cells in
autoimmmunity. Ann Rev Immunol. 18:423–449. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Cohen JL, Trenado A, Vasey D, Klatzmann D
and Salomon BL: CD4(+)CD25(+) immunoregulatory T cells: New
therapeutics for graft-versus-host disease. J Exp Med. 196:401–406.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Allenbach Y, Solly S, Grégoire S, Dubourg
O, Salomon B, Butler-Browne G, Musset L, Herson S, Klatzmann D and
Benveniste O: Role of regulatory T cells in a new mouse model of
experimental autoimmune myositis. Am J Pathol. 174:989–998.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Prevel N, Allenbach Y, Klatzmann D,
Salomon B and Benveniste O: Beneficial role of rapamycin in
experimental autoimmune myositis. PLoS One.
8(e74450)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kang J, Zhang HY, Feng GD, Feng DY and Jia
HG: Development of an improved animal model of experimental
autoimmune myositis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:14457–14464.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Contet C, Rawlins JN and Deacon RM: A
comparison of 129S2/SvHsd and C57BL/6JOlaHsd mice on a test battery
assessing sensorimotor, affective and cognitive behaviours:
Implications for the study of genetically modified mice. Behav
Brain Res. 124:33–46. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kohyama K and Matsumoto Y: C-Protein in
the skeletal muscle induces severe autoimmune polymyositis in lewis
rats. J Neuroimmunol. 98:130–135. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Matsumoto Y, Kohyama K, Park IK, Nakajima
M and Hiraki K: Characterization of pathogenic T cells and
autoantibodies in C-protein-induced autoimmune polymyositis. J
Neuroimmunol. 190:90–100. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Okiyama N, Hasegawa H, Oida T, Hirata S,
Yokozeki H, Fujimoto M, Miyasaka N and Kohsaka H: Experimental
myositis inducible with transfer of dendritic cells presenting a
skeletal muscle C protein-derived CD8 epitope peptide. Int Immunol.
27:327–332. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Taylor A, Verhagen J, Blaser K, Akdis M
and Akdis CA: Mechanisms of immune suppression by interleukin-10
and transforming growth factor-beta: The role of T regulatory
cells. Immunology. 117:433–442. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Yamane T, Muramatsu A, Yoshino S, Matsui
S, Shimura M, Tsujii Y, Iwatsuki K, Kobayashi-Hattori K and Oishi
Y: MTOR inhibition by rapamycin increases ceramide synthesis by
promoting transforming growth factor-β1/Smad signaling in the skin.
FEBS Open Bio. 6:317–325. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Borkowski TA, Letterio JJ, Farr AG and
Udey MC: A role for endogenous transforming growth factor beta 1 in
langerhans cell biology: The skin of transforming growth factor
beta 1 null mice is devoid of epidermal langerhans cells. J Exp
Med. 184:2417–2422. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Horwitz DA, Zheng SG and Gray JD: The role
of the combination of IL-2 and TGF-beta or IL-10 in the generation
and function of CD4+ CD25+ and CD8+ regulatory T cell subsets. J
Leukoc Biol. 74:471–478. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Yagi H, Nomura T, Nakamura K, Yamazaki S,
Kitawaki T, Hori S, Maeda M, Onodera M, Uchiyama T, Fujii S and
Sakaguchi S: Crucial role of FOXP3 in the development and function
of human CD25+CD4+ regulatory T cells. Int Immunol. 16:1643–1656.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Waschbisch A, Schwab N, Ruck T, Stenner MP
and Wiendl H: FOXP3+ T regulatory cells in idiopathic inflammatory
myopathies. J Neuroimmunol. 225:137–142. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Banica L, Besliu A, Pistol G, Stavaru C,
Ionescu R, Forsea AM, Tanaseanu C, Dumitrache S, Otelea D, Tamsulea
I, et al: Quantification and molecular characterization of
regulatory T cells in connective tissue diseases. Autoimmunity.
42:41–49. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Mai J, Wang H and Yang XF: Th 17 cells
interplay with Foxp3+ Tregs in regulation of inflammation and
autoimmunity. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 15:986–1006.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Mammana S, Bramanti P, Mazzon E, Cavalli
E, Basile MS, Fagone P, Petralia MC, McCubrey JA, Nicoletti F and
Mangano K: Preclinical evaluation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in
animal models of multiple sclerosis. Oncotarget. 9:8263–8277.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Evangelisti C, Evangelisti C, Chiarini F,
Lonetti A, Buontempo F, Bressanin D, Cappellini A, Orsini E,
McCubrey JA and Martelli AM: Therapeutic potential of targeting
mTOR in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (review). Int J Oncol.
45:909–918. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Matsushima M, Kikuchi E, Matsumoto K,
Hattori S, Takeda T, Kosaka T, Miyajima A and Oya M: Intravesical
dual PI3K/mTOR complex 1/2 inhibitor NVP-BEZ235 therapy in an
orthotopic bladder cancer model. Int J Oncol. 47:377–383.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Pai C, Walsh CM and Fruman DA:
Context-specific function of S6K2 in th cell differentiation. J
Immunol. 197:3049–3058. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Babchia N, Calipel A, Mouriaux F, Faussat
AM and Mascarelli F: The PI3K/Akt and mTOR/P70S6K signaling
pathways in human uveal melanoma cells: Interaction with B-Raf/ERK.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 51:421–429. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Paskas S, Mazzon E, Basile MS, Cavalli E,
Al-Abed Y, He M, Rakocevic S, Nicoletti F, Mijatovic S and
Maksimovic-Ivanic D: Lopinavir-NO, a nitric oxide-releasing HIV
protease inhibitor, suppresses the growth of melanoma cells in
vitro and in vivo. Invest New Drugs. 37:1014–1028. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Basile MS, Mazzon E, Krajnovic T, Draca D,
Cavalli E, Al-Abed Y, Bramanti P, Nicoletti F, Mijatovic S and
Maksimovic-Ivanic D: Anticancer and differentiation properties of
the nitric oxide derivative of lopinavir in human glioblastoma
cells. Molecules. 23(E2463)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Maksimovic-Ivanic D, Fagone P, McCubrey J,
Bendtzen K, Mijatovic S and Nicoletti F: HIV-Protease inhibitors
for the treatment of cancer: Repositioning HIV protease inhibitors
while developing more potent NO-hybridized derivatives? Int J
Cancer. 140:1713–1726. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Nicoletti F, Di Marco R, Patti F, Reggio
E, Nicoletti A, Zaccone P, Stivala F, Meroni PL and Reggio A: Blood
levels of transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-beta1) are
elevated in both relapsing remitting and chronic progressive
multiple sclerosis (MS) patients and are further augmented by
treatment with interferon-beta 1b (IFN-beta1b). Clin Exp Immunol.
113:96–99. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Cui J, Zhang F, Wang Y, Liu J, Ming X, Hou
J, Lv B, Fang S and Yu B: Macrophage migration inhibitory factor
promotes cardiac stem cell proliferation and endothelial
differentiation through the activation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR and
AMPK pathways. Int J Mol Med. 37:1299–1309. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Gunther S, Fagone P, Jalce G, Atanasov AG,
Guignabert C and Nicoletti F: Role of MIF and D-DT in
immune-inflammatory, autoimmune, and chronic respiratory diseases:
From pathogenic factors to therapeutic targets. Drug Discov Today.
24:428–439. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Richard V, Kindt N and Saussez S:
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor involvement in breast cancer
(Review). Int J Oncol. 47:1627–1633. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Mangano K, Mazzon E, Basile MS, Di Marco
R, Bramanti P, Mammana S, Petralia MC, Fagone P and Nicoletti F:
Pathogenic role for macrophage migration inhibitory factor in
glioblastoma and its targeting with specific inhibitors as novel
tailored therapeutic approach. Oncotarget. 9:17951–17970.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|