|
1
|
Deyo RA and Mirza SK: Clinical practice.
Herniated lumbar intervertebral disk. N Engl J Med. 374:1763–1772.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Kepler CK, Ponnappan RK, Tannoury CA,
Risbud MV and Anderson DG: The molecular basis of intervertebral
disc degeneration. Spine J. 13:318–330. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Kallewaard JW, Geurts JW, Kessels A,
Willems P, van Santbrink H and van Kleef M: Efficacy, safety, and
predictors of intradiscal methylene blue injection for discogenic
low back pain: Results of a multicenter prospective clinical
series. Pain Pract. 16:405–412. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Cunha C, Silva AJ, Pereira P, Vaz R,
Goncalves RM and Barbosa MA: The inflammatory response in the
regression of lumbar disc herniation. Arthritis Res Ther.
20(251)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
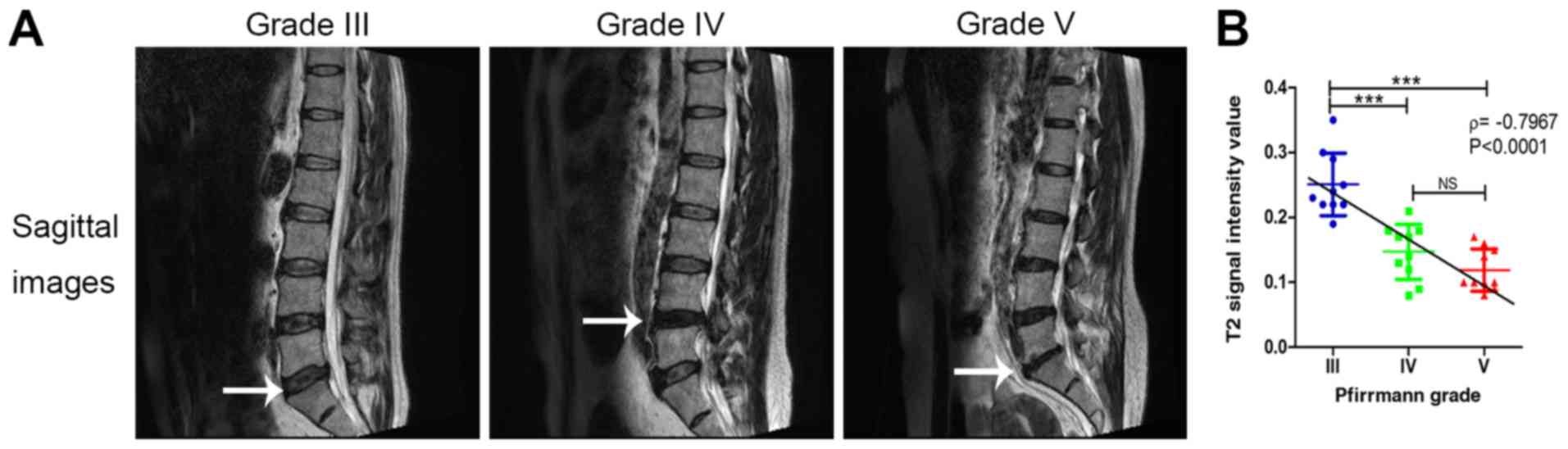
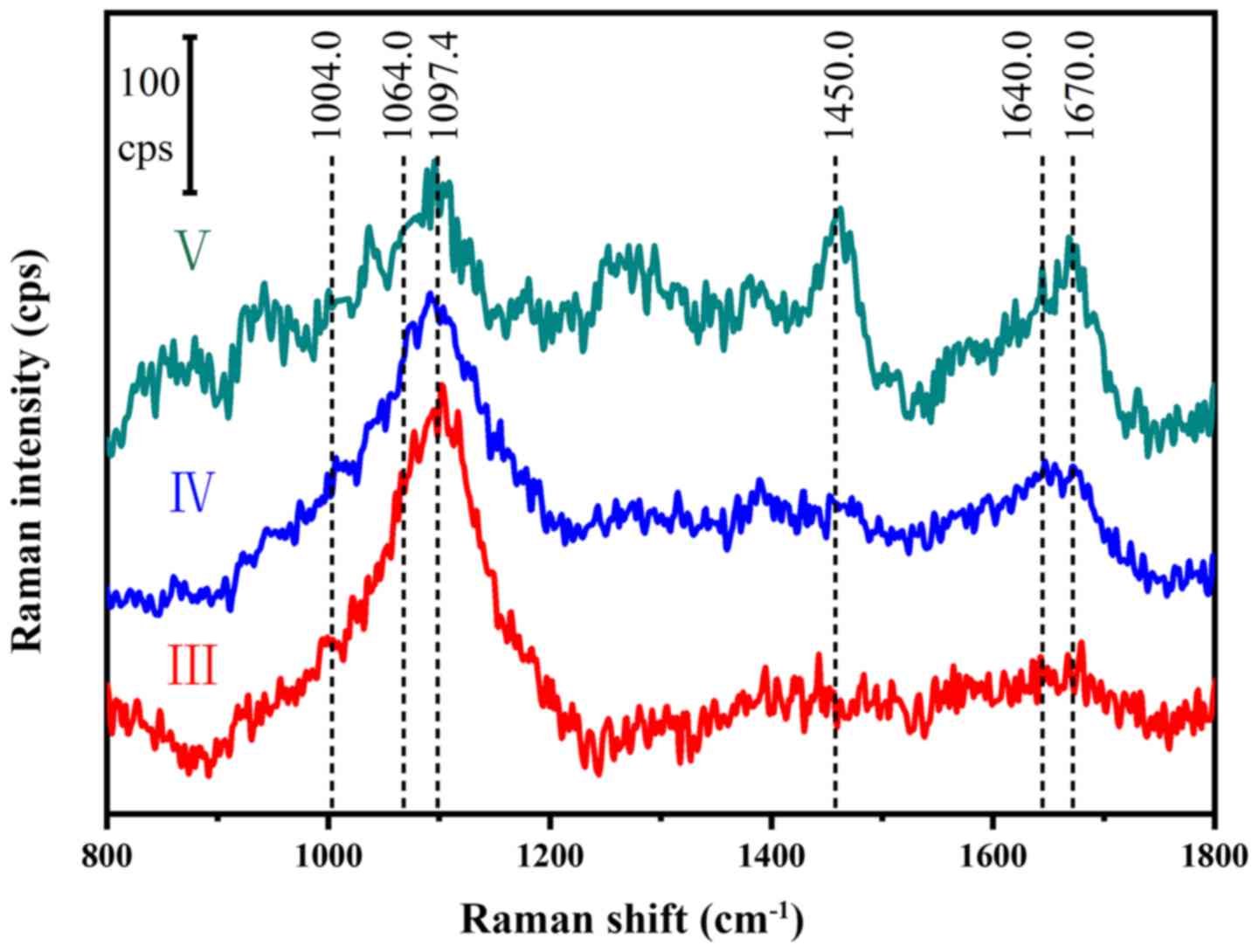
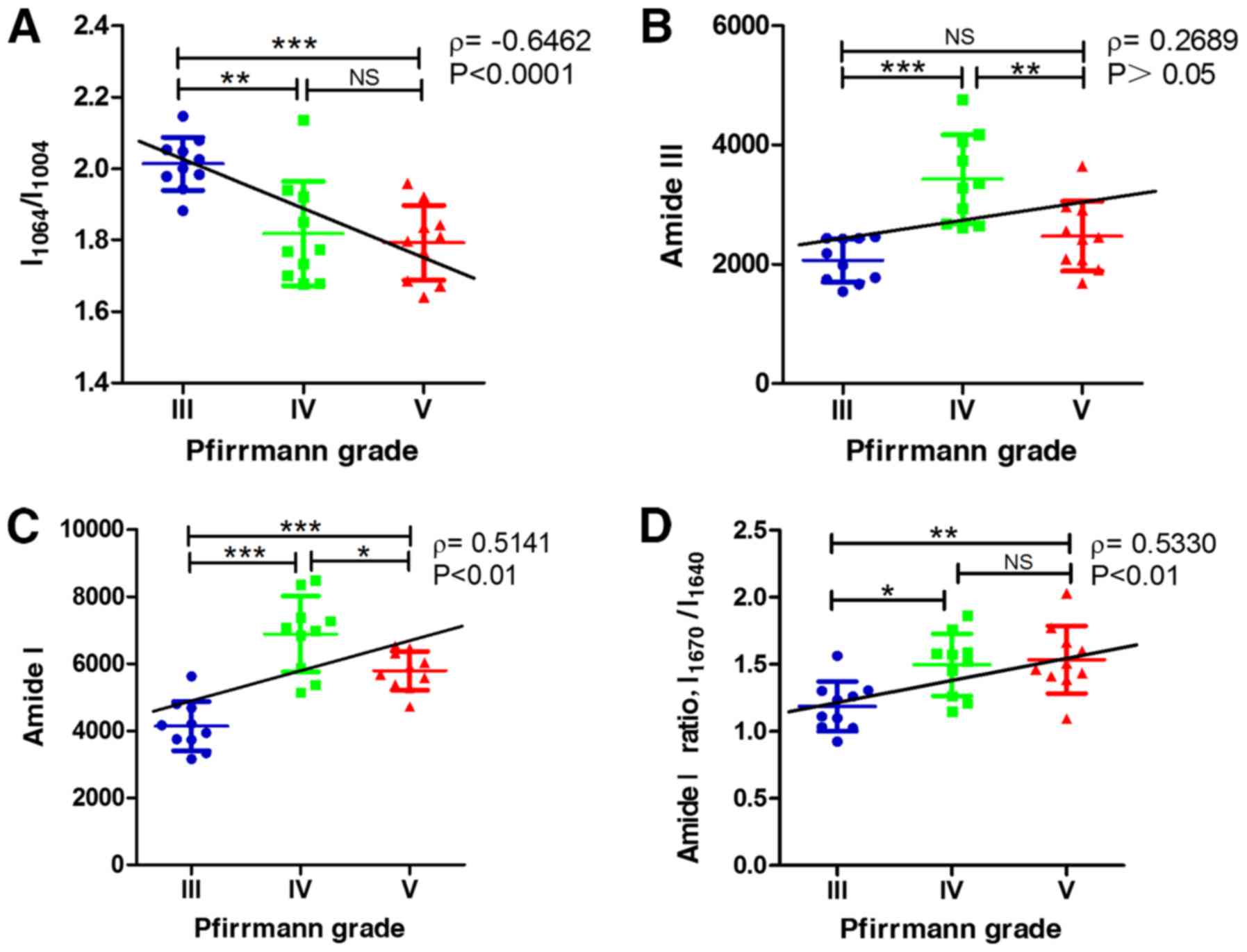
|
|
5
|
Cheung KM, Karppinen J, Chan D, Ho DW,
Song YQ, Sham P, Cheah KS, Leong JC and Luk KD: Prevalence and
pattern of lumbar magnetic resonance imaging changes in a
population study of one thousand forty-three individuals. Spine
(Phila Pa 1976). 34:934–940. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wang Y, Wang H, Lv F, Ma X, Xia X and
Jiang J: Asymmetry between the superior and inferior endplates is a
risk factor for lumbar disc degeneration. J Orthop Res.
36:2469–2475. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
He A, Wang WZ, Qiao PF, Qiao GY, Cheng H
and Feng PY: Quantitative evaluation of compressed l4-5 and s1
nerve roots of lumbar disc herniation patients by diffusion tensor
imaging and fiber tractography. World Neurosurg. 115:e45–e52.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zhang W, Ma X, Wang Y, Zhao J, Zhang X,
Gao Y and Li S: Assessment of apparent diffusion coefficient in
lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Eur Spine J. 23:1830–1836.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Radek M, Pacholczyk-Sienicka B, Jankowski
S, Albrecht Ł, Grodzka M, Depta A and Radek A: Assessing the
correlation between the degree of disc degeneration on the
Pfirrmann scale and the metabolites identified in HR-MAS NMR
spectroscopy. Magn Reson Imaging. 34:376–380. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Xiong X, Zhou Z, Figini M, Shangguan J,
Zhang Z and Chen W: Multi-parameter evaluation of lumbar
intervertebral disc degeneration using quantitative magnetic
resonance imaging techniques. Am J Transl Res. 10:444–454.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pudlas M, Brauchle E, Klein TJ, Hutmacher
DW and Schenke-Layland K: Non-invasive identification of
proteoglycans and chondrocyte differentiation state by Raman
microspectroscopy. J Biophotonics. 6:205–211. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Kong K, Kendall C, Stone N and Notingher
I: Raman spectroscopy for medical diagnostics-from in-vitro
biofluid assays to in-vivo cancer detection. Adv Drug Deliv Rev.
89:121–134. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kumar R, Singh GP, Gronhaug KM, Afseth NK,
de Lange Davies C, Drogset JO and Lilledahl MB: Single cell
confocal Raman spectroscopy of human osteoarthritic chondrocytes: A
preliminary study. Int J Mol Sci. 16:9341–9353. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Keating ME and Byrne HJ: Raman
spectroscopy in nanomedicine: Current status and future
perspective. Nanomedicine (Lond). 8:1335–1351. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Nima ZA, Biswas A, Bayer IS, Hardcastle
FD, Perry D, Ghosh A, Dervishi E and Biris AS: Applications of
surface-enhanced Raman scattering in advanced bio-medical
technologies and diagnostics. Drug Metab Rev. 46:155–175.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Gong B, Oest ME, Mann KA, Damron TA and
Morris MD: Raman spectroscopy demonstrates prolonged alteration of
bone chemical composition following extremity localized
irradiation. Bone. 57:252–258. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Lu FK, Calligaris D, Olubiyi OI, Norton I,
Yang W, Santagata S, Xie XS, Golby AJ and Agar NY: Label-free
neurosurgical pathology with stimulated Raman imaging. Cancer Res.
76:3451–3462. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Pence I and Mahadevan-Jansen A: Clinical
instrumentation and applications of Raman spectroscopy. Chem Soc
Rev. 45:1958–1979. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Wang WJ, Yang W, Ouyang ZH, Xue JB, Li XL,
Zhang J, He WS, Chen WK, Yan YG and Wang C: MiR-21 promotes ECM
degradation through inhibiting autophagy via the PTEN/akt/mTOR
signaling pathway in human degenerated NP cells. Biomed
Pharmacother. 99:725–734. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Luoma EK, Raininko R, Nummi PJ, Luukkonen
R, Manninen HI and Riihimäki HA: Suitability of cerebrospinal fluid
as a signal-intensity reference on MRI: Evaluation of
signal-intensity variations in the lumbosacral dural sac.
Neuroradiology. 39:728–732. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Tsao YT, Huang YJ, Wu HH, Liu YA, Liu YS
and Lee OK: Osteocalcin mediates biomineralization during
osteogenic maturation in human mesenchymal stromal cells. Int J Mol
Sci. 18(pii: E159)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Takahashi Y, Sugano N, Takao M, Sakai T,
Nishii T and Pezzotti G: Raman spectroscopy investigation of
load-assisted microstructural alterations in human knee cartilage:
Preliminary study into diagnostic potential for osteoarthritis. J
Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 31:77–85. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Buchwald T, Niciejewski K, Kozielski M,
Szybowicz M, Siatkowski M and Krauss H: Identifying compositional
and structural changes in spongy and subchondral bone from the hip
joints of patients with osteoarthritis using Raman spectroscopy. J
Biomed Opt. 17(017007)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Caraher MC, Sophocleous A, Beattie JR,
O'Driscoll O, Cummins NM, Brennan O, O'Brien FJ, Ralston SH, Bell
SEJ, Towler M and Idris AI: Raman spectroscopy predicts the link
between claw keratin and bone collagen structure in a rodent model
of oestrogen deficiency. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis.
1864:398–406. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Quade M, Schumacher M, Bernhardt A, Lode
A, Kampschulte M, Voß A, Simon P, Uckermann O, Kirsch M and
Gelinsky M: Strontium-modification of porous scaffolds from
mineralized collagen for potential use in bone defect therapy.
Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 84:159–167. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Murab S and Ghosh S: Impact of
osmoregulatory agents on the recovery of collagen conformation in
decellularized corneas. Biomed Mater. 11(065005)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Masic A, Bertinetti L, Schuetz R, Galvis
L, Timofeeva N, Dunlop JW, Seto J, Hartmann MA and Fratzl P:
Observations of multiscale, stress-induced changes of collagen
orientation in tendon by polarized Raman spectroscopy.
Biomacromolecules. 12:3989–3996. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Unal M, Jung H and Akkus O: Novel Raman
spectroscopic biomarkers indicate that postyield damage denatures
bone's collagen. J Bone Miner Res. 31:1015–1025. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Lurie JD, Moses RA, Tosteson AN, Tosteson
TD, Carragee EJ, Carrino JA, Kaiser JA and Herzog RJ: Magnetic
resonance imaging predictors of surgical outcome in patients with
lumbar intervertebral disc herniation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
38:1216–1225. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Yang SH, Espinoza Orias AA, Pan CC, Senoo
I, Andersson GBJ, An HS and Inoue N: Spatial geometric and magnetic
resonance signal intensity changes with advancing stages of nucleus
pulposus degeneration. BMC Musculoskelet Disord.
18(473)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Benneker LM, Heini PF, Anderson SE, Alini
M and Ito K: Correlation of radiographic and MRI parameters to
morphological and biochemical assessment of intervertebral disc
degeneration. Eur Spine J. 14:27–35. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Cassinelli EH, Hall RA and Kang JD:
Biochemistry of intervertebral disc degeneration and the potential
for gene therapy applications. Spine J. 1:205–214. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Tertti M, Paajanen H, Laato M, Aho H, Komu
M and Kormano M: Disc degeneration in magnetic resonance imaging. A
comparative biochemical, histologic, and radiologic study in
cadaver spines. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 16:629–634. 1991.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Kalb S, Martirosyan NL, Kalani MY, Broc GG
and Theodore N: Genetics of the degenerated intervertebral disc.
World Neurosurg. 77:491–501. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Shi C, Wu H, Du D, Im HJ, Zhang Y, Hu B,
Chen H, Wang X, Liu Y, Cao P, et al: Nicotinamide
phosphoribosyltransferase inhibitor APO866 prevents IL-1β-induced
human nucleus pulposus cell degeneration via autophagy. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 49:2463–2482. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Dehring KA, Smukler AR, Roessler BJ and
Morris MD: Correlating changes in collagen secondary structure with
aging and defective type II collagen by Raman spectroscopy. Appl
Spectrosc. 60:366–372. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|