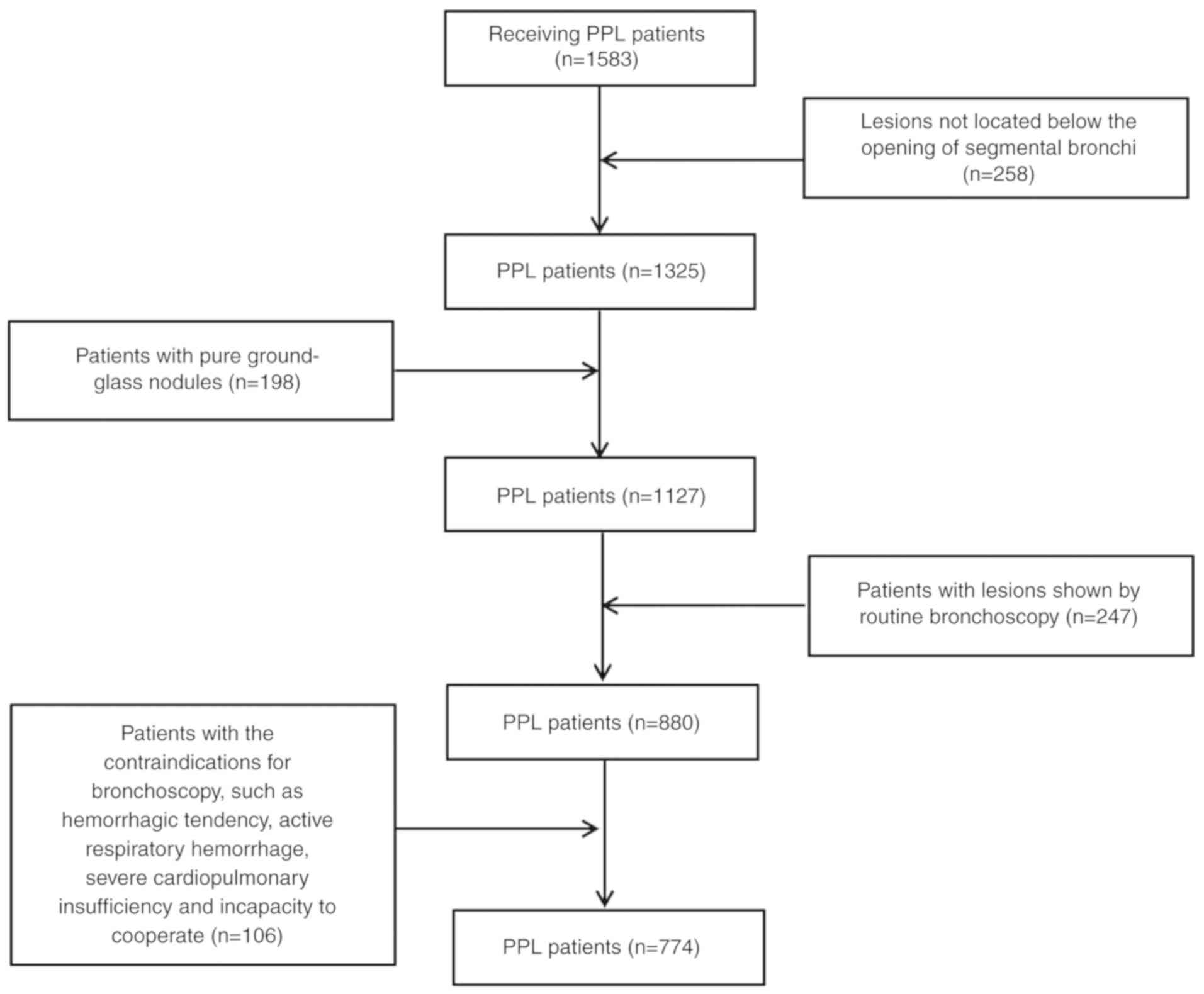
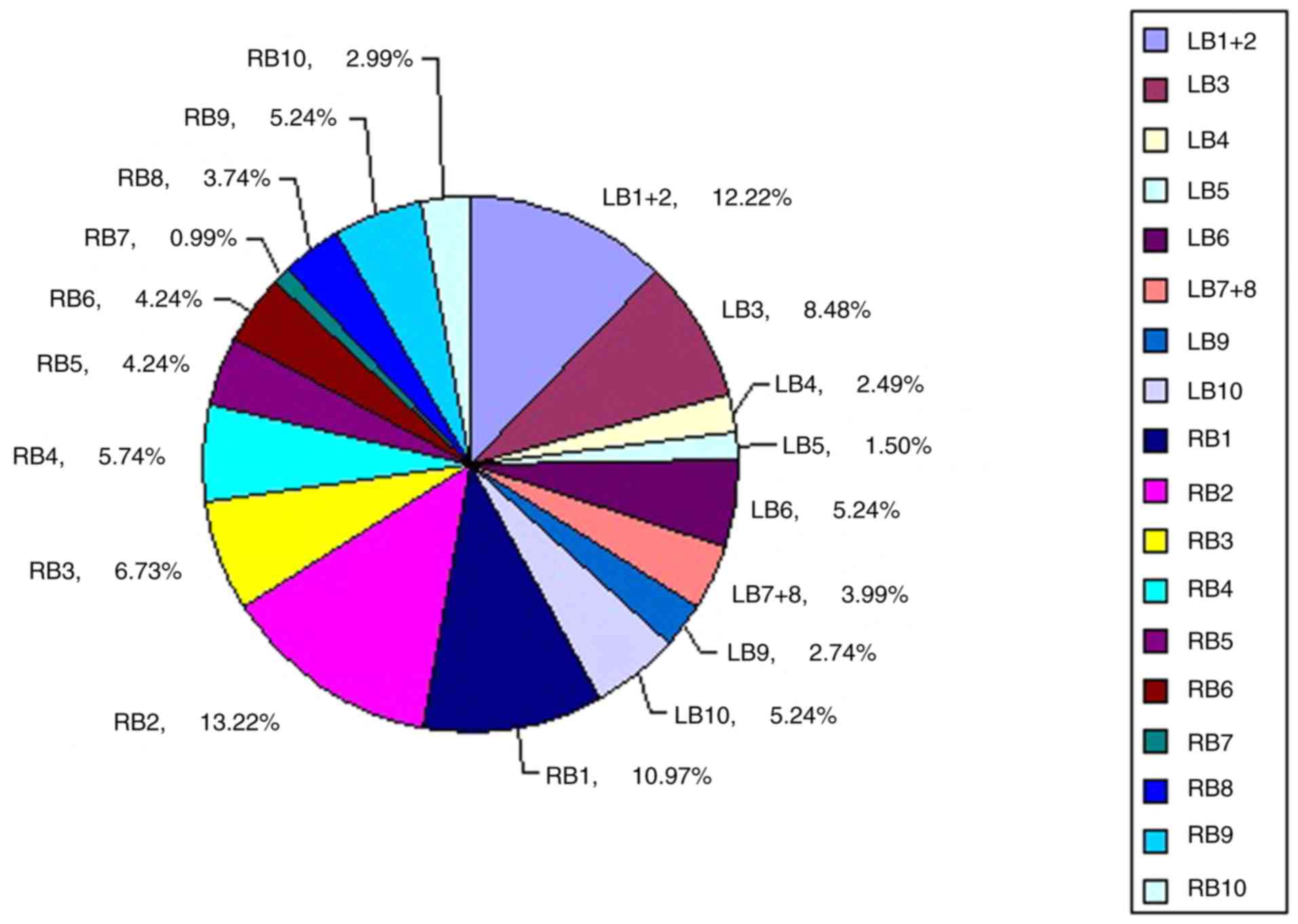
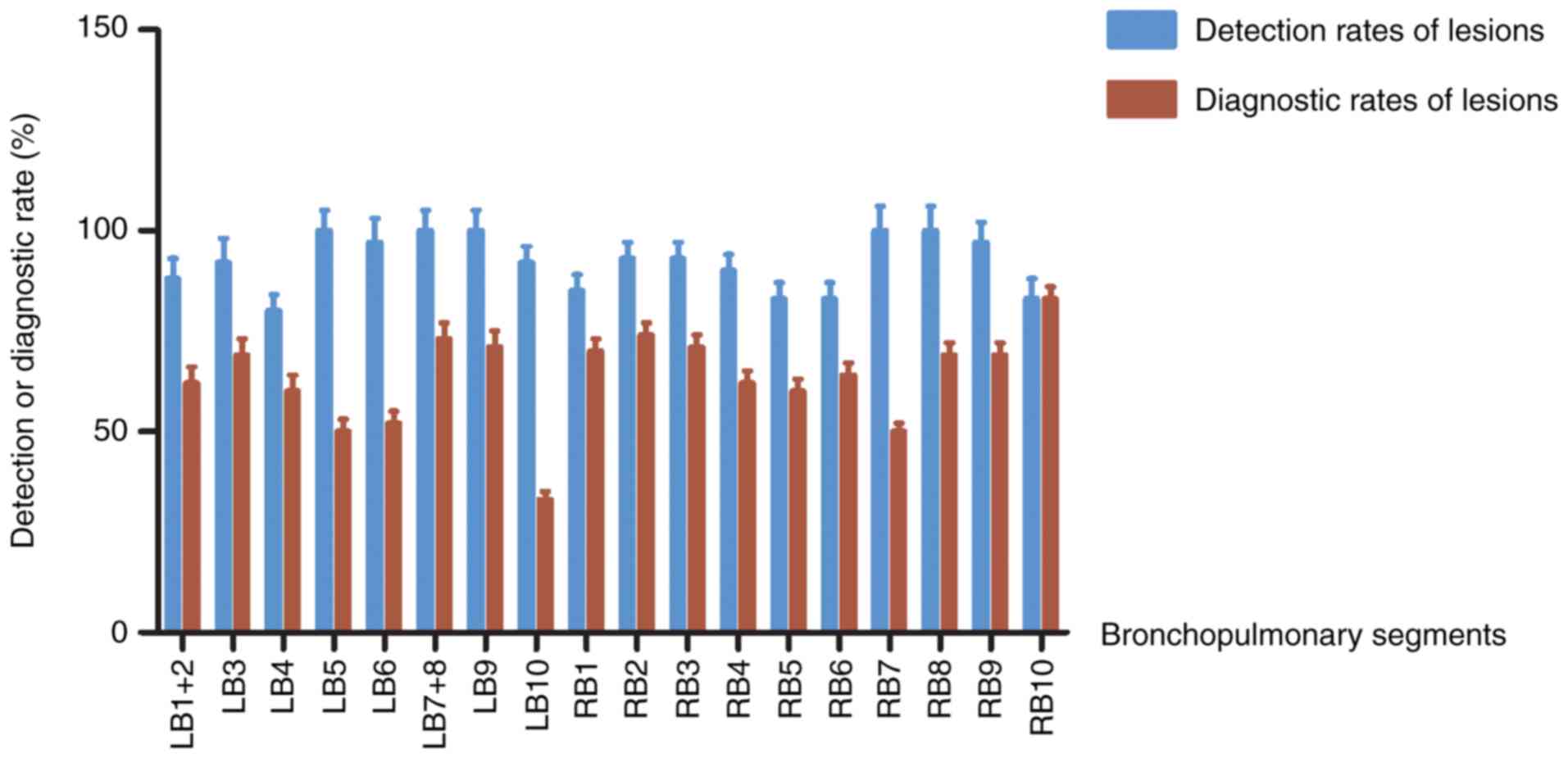
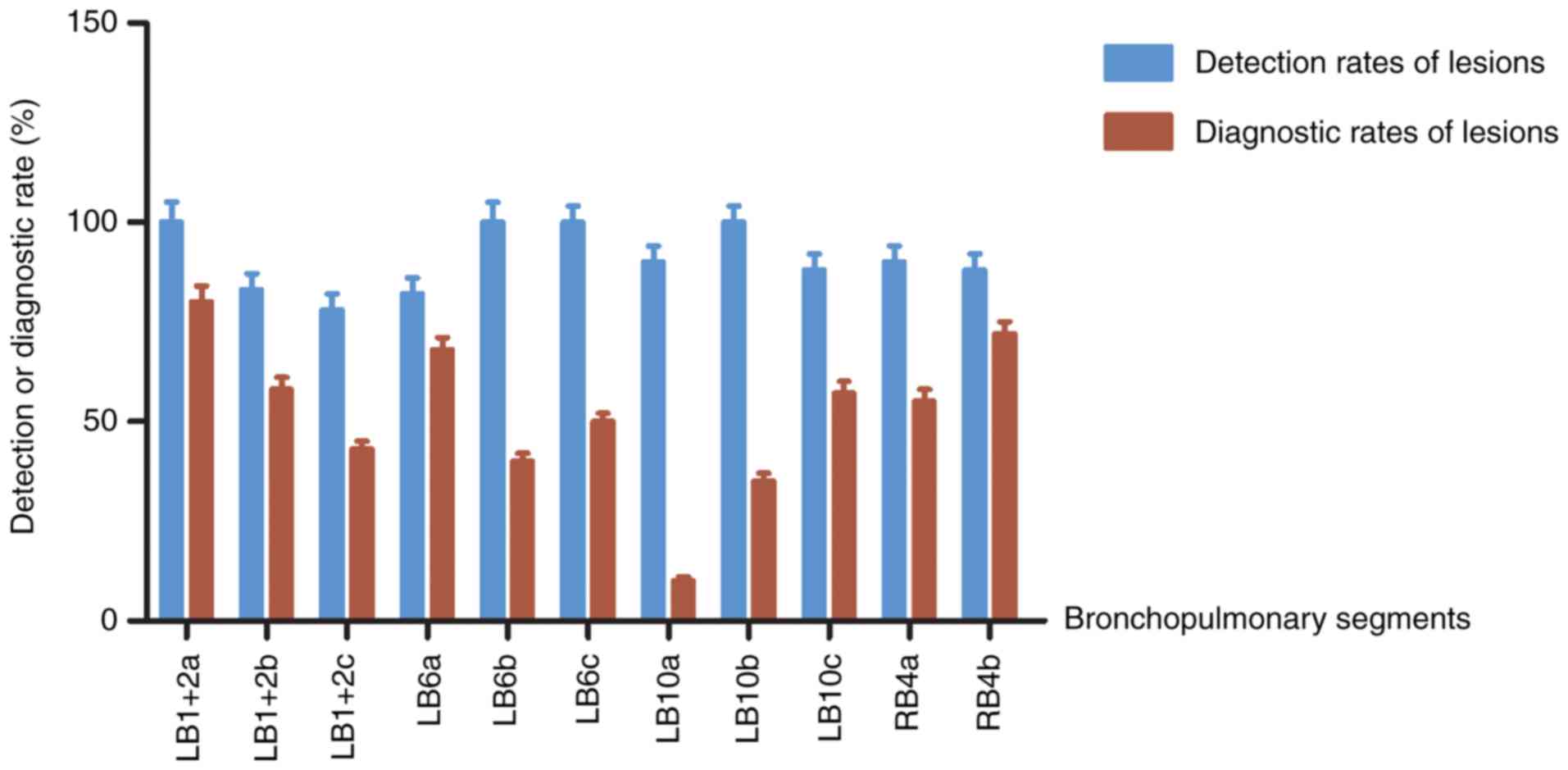
|
1
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Zheng R, Zeng H, Zhang S and Chen W:
Estimates of cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2013. Chin J
Cancer. 36(66)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wong MCS, Lao XQ, Ho KF, Goggins WB and
Tse SLA: Incidence and mortality of lung cancer: Global trends and
association with socioeconomic status. Sci Rep.
7(14300)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Zeng H, Zheng R, Guo Y, Zhang S, Zou X,
Wang N, Zhang L, Tang J, Chen J, Wei K, et al: Cancer survival in
China, 2003-2005: A population-based study. Int J Cancer.
136:1921–1930. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Wang T, Luo L and Zhou Q: Risk of pleural
recurrence in early stage lung cancer patients after percutaneous
transthoracic needle biopsy: A meta-analysis. Sci Rep.
7(42762)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Luo K, Lin Y, Lin X, Yu X, Wen J, Xi K,
Lin P and Zhang L: Localization of peripheral pulmonary lesions to
aid surgical resection: A novel approach for electromagnetic
navigation bronchoscopic dye marking. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg.
52:516–521. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Han Y, Kim HJ, Kong KA, Kim SJ, Lee SH,
Ryu YJ, Lee JH, Kim Y, Shim SS and Chang JH: Diagnosis of small
pulmonary lesions by transbronchial lung biopsy with radial
endobronchial ultrasound and virtual bronchoscopic navigation
versus CT-guided transthoracic needle biopsy: A systematic review
and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 13(e0191590)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Durakovic A, Andersen H, Christiansen A
and Hammen I: Retrospective analysis of radial EBUS outcome for the
diagnosis of peripheral pulmonary lesion: Sensitivity and
complications. Eur Clin Respir J. 2(28947)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Kurimoto N, Miyazawa T, Okimasa S, Maeda
A, Oiwa H, Miyazu Y and Murayama M: Endobronchial ultrasonography
using a guide sheath increases the ability to diagnose peripheral
pulmonary lesions endoscopically. Chest. 126:959–965.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Liu J, Han J, Lv H and Li B: An ultrasonic
sensor system based on a two-dimensional state method for highway
vehicle violation detection applications. Sensors (Basel).
15:9000–9021. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Park J, Je Y, Lee H and Moon W: Design of
an ultrasonic sensor for measuring distance and detecting
obstacles. Ultrasonics. 50:340–346. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Paradis TJ, Dixon J and Tieu BH: The role
of bronchoscopy in the diagnosis of airway disease. J Thorac Dis.
8:3826–3837. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Durheim MT, Kim S, Gulack BC, Burfeind WR,
Gaissert HA, Kosinski AS and Hartwig MG: Mortality and respiratory
failure after thoracoscopic lung biopsy for interstitial lung
disease. Ann Thorac Surg. 104:465–470. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Lieberman S, Gleason JB, Ilyas MIM,
Martinez F, Mehta JP and Savage EB: Assessing the safety and
clinical impact of thoracoscopic lung biopsy in patients with
interstitial lung disease. J Clin Diagn Res. 11:OC57–OC59.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Jo Y, Han DH, Beck KS, Park JS and Kim TJ:
Practice pattern of transthoracic needle biopsy: 2016 survey in the
members of Korean society of thoracic radiology. Korean J Radiol.
18:1005–1011. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Anzidei M, Porfiri A, Andrani F, Di
Martino M, Saba L, Catalano C and Bezzi M: Imaging-guided chest
biopsies: Techniques and clinical results. Insights Imaging.
8:419–428. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Heerink WJ, de Bock GH, de Jonge GJ, Groen
HJ, Vliegenthart R and Oudkerk M: Complication rates of CT-guided
transthoracic lung biopsy: Meta-analysis. Eur Radiol. 27:138–148.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Accordino MK, Wright JD, Buono D, Neugut
AI and Hershman DL: Trends in use and safety of image-guided
transthoracic needle biopsies in patients with cancer. J Oncol
Pract. 11:e351–e359. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kim EJ and Kim KC: Utility of radial probe
endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial lung biopsy in
diffuse lung lesions. Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul). 82:201–210.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zhan P, Zhu QQ, Miu YY, Liu YF, Wang XX,
Zhou ZJ, Jin JJ and Li Q: Comparison between endobronchial
ultrasound-guided transbronchial biopsy and CT-guided transthoracic
lung biopsy for the diagnosis of peripheral lung cancer: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Transl Lung Cancer Res.
6:23–34. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Dhooria S, Sehgal IS, Gupta N, Aggarwal
AN, Behera D and Agarwal R: Role of radial endobronchial
ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration in the diagnosis
of pulmonary nodules: Case report and literature review. Lung
India. 34:61–64. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Steinfort DP, Khor YH, Manser RL and
Irving LB: Radial probe endobronchial ultrasound for the diagnosis
of peripheral lung cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur
Respir J. 37:902–910. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Hayama M, Izumo T, Chavez C, Matsumoto Y,
Tsuchida T and Sasada S: Additional transbronchial needle
aspiration through a guide sheath for peripheral pulmonary lesions
that cannot be detected by radial EBUS. Clin Respir J. 11:757–764.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Boonsarngsuk V, Kanoksil W and
Laungdamerongchai S: Diagnosis of peripheral pulmonary lesions with
radial probe endobronchial ultrasound-guided bronchoscopy. Arch
Bronconeumol. 50:379–383. 2014.(In English, Spanish). PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Zhang Q, Zhang S, Xu X, Xu Q and Zhou J:
Value of radial probe endobronchial ultrasound-guided
transbronchial biopsy and computer tomography-guided transthoracic
needle aspiration in the diagnosis of peripheral pulmonary lesions.
Medicine (Baltimore). 96(e7843)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zhang S, Zhou J, Zhang Q, Xu Q and Xu X:
Diagnosis of peripheral lung diseases by combined measurement with
ultrasound guidance under bronchoscope. Chin J Tuberc Respir.
38:566–569. 2015.(In Chinese).
|
|
27
|
Fukusumi M, Ichinose Y, Arimoto Y, Takeoka
S, Homma C, Matsuoka H, Mouri A, Hamamoto Y, Matsumoto J and
Kamimura M: Bronchoscopy for pulmonary peripheral lesions with
virtual fluoroscopic preprocedural planning combined with EBUS-GS:
A pilot study. J Bronchology Interv Pulmonol. 23:92–97.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Hsia DW, Jensen KW, Curran-Everett D and
Musani AI: Diagnosis of lung nodules with peripheral/radial
endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial biopsy. J
Bronchology Interv Pulmonol. 19:5–11. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Eberhardt R, Anantham D, Ernst A,
Feller-Kopman D and Herth F: Multimodality bronchoscopic diagnosis
of peripheral lung lesions: A randomized controlled trial. Am J
Respir Crit Care Med. 176:36–41. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|