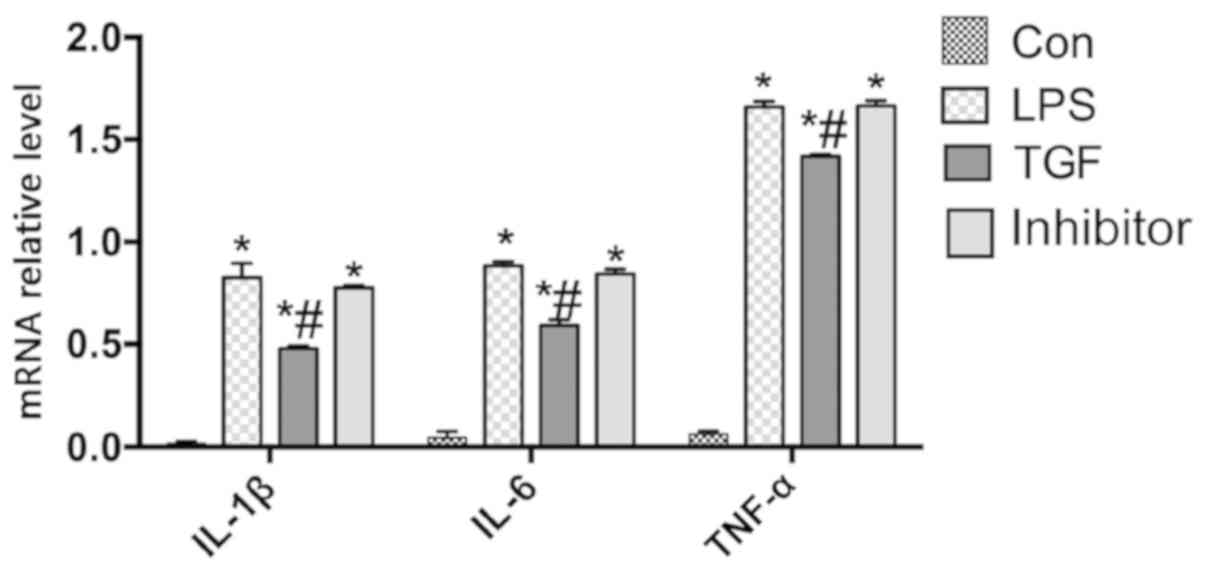
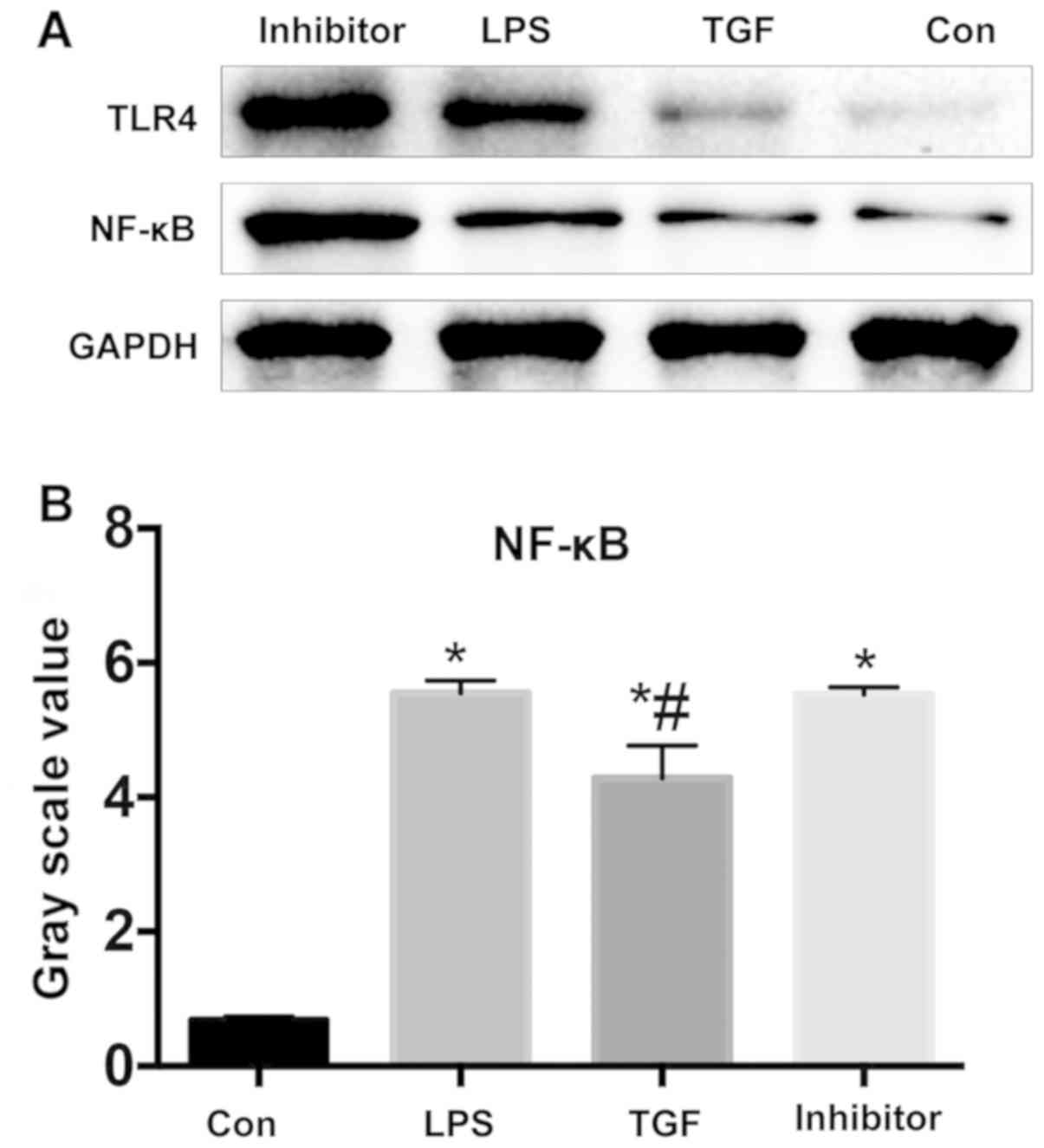
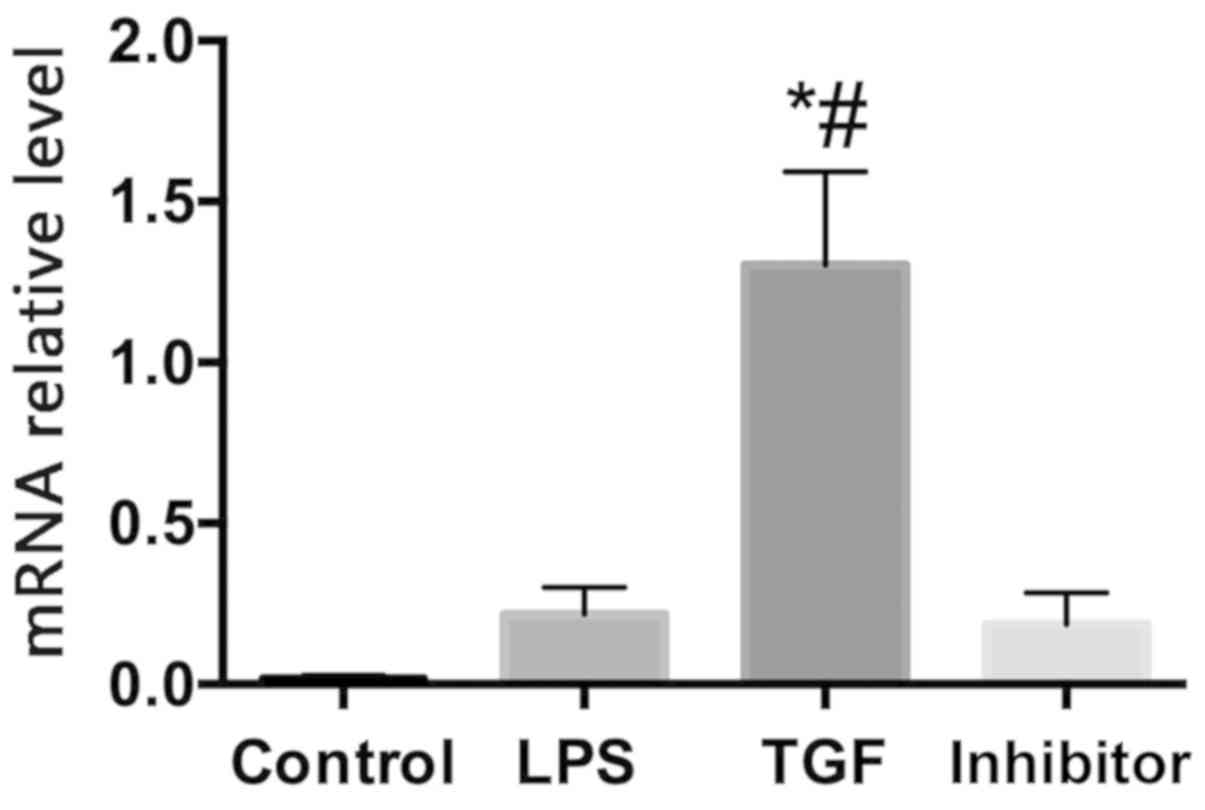
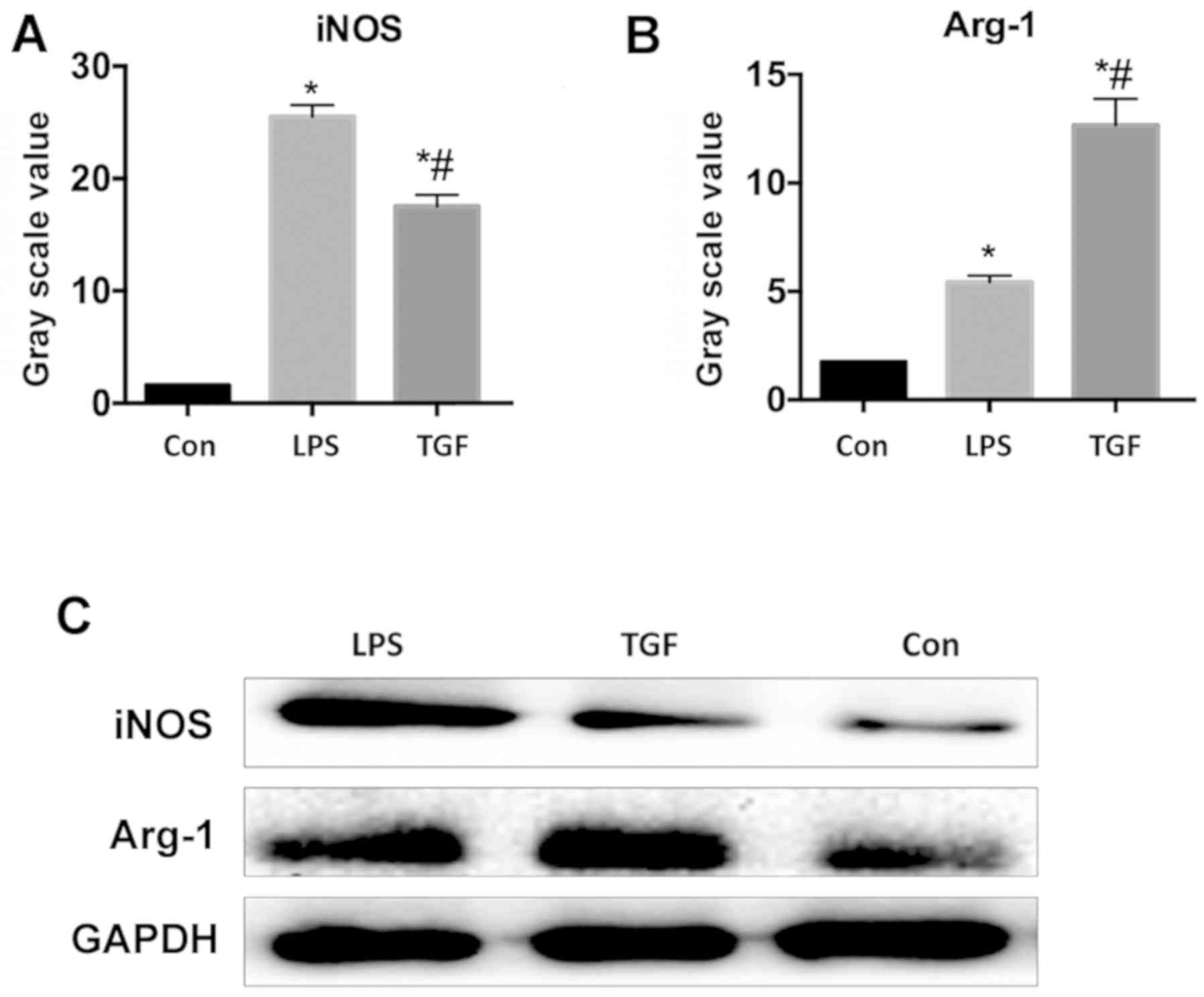
|
1
|
Zakharia K, Tabibian A, Lindor KD and
Tabibian JH: Complications, symptoms, quality of life and pregnancy
in cholestatic liver disease. Liver Int. 38:399–411.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Zhao S, Li N, Zhen Y, Ge M, Li Y, Yu B, He
H and Shao RG: Protective effect of gastrodin on bile duct
ligation-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats. Food Chem Toxicol.
86:202–207. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Seca AM and Pinto DC: Plant secondary
metabolites as anticancer agents: Successes in clinical trials and
therapeutic application. Int J Mol Sci. 19(19)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Miyaguchi S, Ebinuma H, Imaeda H, Nitta Y,
Watanabe T, Saito H and Ishii H: A novel treatment for refractory
primary biliary cirrhosis? Hepatogastroenterology. 47:1518–1521.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Drivdal M, Holven KB, Retterstøl K,
Aagenaes Ø and Kase BF: A nine year follow-up study of patients
with lymphoedema cholestasis syndrome 1 (LCS1/Aagenaes syndrome).
Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 78:566–574. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Paquissi FC: Immunity and fibrogenesis:
The role of Th17/IL-17 axis in HBV and HCV-induced chronic
hepatitis and progression to cirrhosis. Front Immunol.
8(1195)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Burnevich ES, Popova EN, Ponomarev AB,
Nekrasova TP, Lebedeva MV, Filatova AL, Shchanitcyna EM, Ponomareva
LA, Beketov VD, Bondarenko IB, et al: Autoimmune liver disease
(primary biliary cholangitis/autoimmune hepatitis-overlap)
associated with sarcoidosis (clinical cases and literature review).
Ter Arkh. 91:89–94. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zhu J, Wang R, Xu T, Zhang S, Zhao Y, Li
Z, Wang C, Zhou J, Gao D, Hu Y, et al: Salvianolic acid a
attenuates endoplasmic reticulum stress and protects against
cholestasis-induced liver fibrosis via the SIRT1/HSF1 pathway.
Front Pharmacol. 9(1277)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Mohammadi A, Blesso CN, Barreto GE, Banach
M, Majeed M and Sahebkar A: Macrophage plasticity, polarization and
function in response to curcumin, a diet-derived polyphenol, as an
immunomodulatory agent. J Nutr Biochem. 66:1–16. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Cheng Z, Zhou YZ, Wu Y, Wu QY, Liao XB, Fu
XM and Zhou XM: Diverse roles of macrophage polarization in aortic
aneurysm: Destruction and repair. J Transl Med.
16(354)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Sica A, Erreni M, Allavena P and Porta C:
Macrophage polarization in pathology. Cell Mol Life Sci.
72:4111–4126. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Gong W, Huang F, Sun L, Yu A, Zhang X, Xu
Y, Shen Y and Cao J: Toll-like receptor-2 regulates macrophage
polarization induced by excretory-secretory antigens from
Schistosoma japonicum eggs and promotes liver pathology in
murine schistosomiasis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis: Dec 27, 2018 (Epub
ahead of print). doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007000..
|
|
13
|
Cho U, Kim B, Kim S, Han Y and Song YS:
Pro-inflammatory M1 macrophage enhances metastatic potential of
ovarian cancer cells through NF-κB activation. Mol Carcinog.
57:235–242. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Wang Y, Smith W, Hao D, He B and Kong L:
M1 and M2 macrophage polarization and potentially therapeutic
naturally occurring compounds. Int Immunopharmacol. 70:459–466.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Qing L, Fu J, Wu P, Zhou Z, Yu F and Tang
J: Metformin induces the M2 macrophage polarization to accelerate
the wound healing via regulating AMPK/mTOR/NLRP3 inflammasome
singling pathway. Am J Transl Res. 11:655–668. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang Y, Guo X, Jiao G, Luo L, Zhou L,
Zhang J and Wang B: Splenectomy promotes macrophage polarization in
a mouse model of concanavalin A- (ConA-) induced liver fibrosis.
BioMed Res Int. 2019(5756189)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Lu CH, Lai CY, Yeh DW, Liu YL, Su YW, Hsu
LC, Chang CH, Catherine Jin SL and Chuang TH: Involvement of M1
macrophage polarization in endosomal Toll-like receptors activated
psoriatic inflammation. Mediators Inflamm: Dec 16, 2018 (Epub ahead
of print). doi: 10.1155/2018/3523642.
|
|
18
|
Tsuneyama K, Harada K, Kono N, Hiramatsu
K, Zen Y, Sudo Y, Gershwin ME, Ikemoto M, Arai H and Nakanuma Y:
Scavenger cells with gram-positive bacterial lipoteichoic acid
infiltrate around the damaged interlobular bile ducts of primary
biliary cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 35:156–163. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Prunier C, Baker D, Ten Dijke P and Ritsma
L: TGF-β family signaling pathways in cellular dormancy. Trends
Cancer. 5:66–78. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Dragotto J, Canterini S, Del Porto P,
Bevilacqua A and Fiorenza MT: The interplay between
TGF-β-stimulated TSC22 domain family proteins regulates cell-cycle
dynamics in medulloblastoma cells. J Cell Physiol. 234:18349–18360.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Derynck R and Budi EH: Specificity,
versatility, and control of TGF-β family signaling. Sci Signal.
12(12)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Dropmann A, Dediulia T, Breitkopf-Heinlein
K, Korhonen H, Janicot M, Weber SN, Thomas M, Piiper A, Bertran E,
Fabregat I, et al: TGF-β1 and TGF-β2 abundance in liver diseases of
mice and men. Oncotarget. 7:19499–19518. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Li MO, Wan YY, Sanjabi S, Robertson AK and
Flavell RA: Transforming growth factor-beta regulation of immune
responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 24:99–146. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kim KK, Sheppard D and Chapman HA: TGF-β1
signaling and tissue fibrosis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
10(10)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Tang J, Gifford CC, Samarakoon R and
Higgins PJ: Deregulation of negative controls on TGF-β1 signaling
in tumor progression. Cancers (Basel). 10(10)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zeng WQ, Zhang JQ, Li Y, Yang K, Chen YP
and Liu ZJ: A new method to isolate and culture rat kupffer cells.
PLoS One. 8(e70832)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Mishra B, Tang Y, Katuri V, Fleury T, Said
AH, Rashid A, Jogunoori W and Mishra L: Loss of cooperative
function of transforming growth factor-beta signaling proteins,
smad3 with embryonic liver fodrin, a beta-spectrin, in primary
biliary cirrhosis. Liver Int. 24:637–645. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Neuman M, Angulo P, Malkiewicz I,
Jorgensen R, Shear N, Dickson ER, Haber J, Katz G and Lindor K:
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and transforming growth factor-beta
reflect severity of liver damage in primary biliary cirrhosis. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 17:196–202. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Martinez OM, Villanueva JC, Gershwin ME
and Krams SM: Cytokine patterns and cytotoxic mediators in primary
biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology. 21:113–119. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu B, Zhang X, Zhang FC, Zong JB, Zhang W
and Zhao Y: Aberrant TGF-β1 signaling contributes to the
development of primary biliary cirrhosis in murine model. World J
Gastroenterol. 19:5828–5836. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Hasan MS, Karim AB, Rukunuzzaman M, Haque
A, Akhter MA, Shoma UK, Yasmin F and Rahman MA and Rahman MA: Role
of liver biopsy in the diagnosis of neonatal cholestasis due to
biliary atresia. Mymensingh Med J. 27:826–833. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Houwen R: Chapter 6.4. Diagnostic Progress
in Cholestasis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 66 (Suppl
1):S134–S136. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Trauner M, Meier PJ and Boyer JL:
Molecular pathogenesis of cholestasis. N Engl J Med. 339:1217–1227.
1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Virani S, Akers A, Stephenson K, Smith S,
Kennedy L, Alpini G and Francis H: Comprehensive review of
molecular mechanisms during cholestatic liver injury and
cholangiocarcinoma. J Liver. 7(7)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Cies JJ and Giamalis JN: Treatment of
cholestatic pruritus in children. Am J Health Syst Pharm.
64:1157–1162. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Hirschfield GM and Heathcote EJ:
Cholestasis and cholestatic syndromes. Curr Opin Gastroenterol.
25:175–179. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Sun X, Xie Z, Ma Y, Pan X, Wang J, Chen Z
and Shi P: TGF-β inhibits osteogenesis by upregulating the
expression of ubiquitin ligase SMURF1 via MAPK-ERK signaling. J
Cell Physiol. 233:596–606. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Hu B, Xu C, Cao P, Tian Y, Zhang Y, Shi C,
Xu J, Yuan W and Chen H: TGF-β stimulates expression of chondroitin
polymerizing factor in nucleus pulposus cells through the Smad3,
RhoA/ROCK1, and MAPK signaling pathways. J Cell Biochem.
119:566–579. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Du M, Chen W, Zhang W, Tian XK, Wang T, Wu
J, Gu J, Zhang N, Lu ZW, Qian LX, et al: TGF-β1 regulates the
ERK/MAPK pathway independent of the SMAD pathway by repressing
miRNA-124 to increase MALAT1 expression in nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Biomed Pharmacother. 99:688–696. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Coppola N, Zampino R, Sagnelli C, Bellini
G, Marrone A, Stanzione M, Capoluongo N, Boemio A, Minichini C,
Adinolfi LE, et al: Cannabinoid receptor 2-63 QQ variant is
associated with persistently normal aminotransferase serum levels
in chronic hepatitis C. PLoS One. 9(e99450)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Mazzella G, Salzetta A, Casanova S,
Morelli MC, Villanova N, Miniero R, Sottili S, Novelli V, Cipolla
A, Festi D, et al: Treatment of chronic sporadic-type non-A, non-B
hepatitis with lymphoblastoid interferon: Gamma GT levels
predictive for response. Dig Dis Sci. 39:866–870. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Van Campenhout S, Van Vlierberghe H and
Devisscher L: Common bile duct ligation as model for secondary
biliary cirrhosis. Methods Mol Biol. 1981:237–247. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Lotowska JM, Sobaniec-Lotowska ME,
Lebensztejn DM, Daniluk U, Sobaniec P, Sendrowski K, Daniluk J,
Reszec J, Debek W, Festi D, et al: Ultrastructural characteristics
of rat hepatic oval cells and their intercellular contacts in the
model of biliary fibrosis: New insights into experimental liver
fibrogenesis. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2017(2721547)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Liu TZ, Lee KT, Chern CL, Cheng JT, Stern
A and Tsai LY: Free radical-triggered hepatic injury of
experimental obstructive jaundice of rats involves overproduction
of proinflammatory cytokines and enhanced activation of nuclear
factor kappaB. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 31:383–390. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Huang ZH, Huang X and Li Y: Changes and
significance of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6 level
in plasma and bile during the formation of acute intrahepatic
cholestasis in New Zealand white rabbits. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za
Zhi. 11(313)2003.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Sen R and Baltimore D: Inducibility of
kappa immunoglobulin enhancer-binding protein NF-kappaB by a
posttranslational mechanism. Cell. 47:921–928. 1986.
|
|
47
|
Ghosh S and Hayden MS: New regulators of
NF-kappaB in inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 8:837–848.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Editors PO: PLOS ONE Editors: Expression
of Concern: The interplay between NF-kappaB and E2F1 coordinately
regulates inflammation and metabolism in human cardiac cells. PLoS
One. 14(e0216434)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Park J, Ha SH, Abekura F, Lim H, Magae J,
Ha KT, Chung TW, Chang YC, Lee YC, Chung E, et al:
4-O-carboxymethyl ascochlorin inhibits expression levels of on
inflammation-related cytokines and matrix metalloproteinase-9
through NF-κB/MAPK/TLR4 signaling pathway in LPS-activated RAW264.7
cells. Front Pharmacol. 10(304)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
van der Tuin SJ, Li Z, Berbée JF,
Verkouter I, Ringnalda LE, Neele AE, van Klinken JB, Rensen SS, Fu
J, de Winther MP, et al: Lipopolysaccharide lowers cholesteryl
ester transfer protein by activating F4/80+Clec4f+Vsig4+Ly6C-
Kupffer cell subsets. J Am Heart Assoc. 7(7)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Feng P, Zhu W, Chen N, Li P, He K and Gong
J: Cathepsin B in hepatic Kupffer cells regulates activation of
TLR4-independent inflammatory pathways in mice with
lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao.
38:1465–1471. 2018.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Zhang WJ, Fang ZM and Liu WQ: NLRP3
inflammasome activation from Kupffer cells is involved in liver
fibrosis of Schistosoma japonicum-infected mice via NF-κB.
Parasit Vectors. 12(29)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Ohtani N and Kawada N: Role of the
gut-liver axis in liver inflammation, fibrosis, and cancer: A
special focus on the gut microbiota relationship. Hepatol Commun.
3:456–470. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|