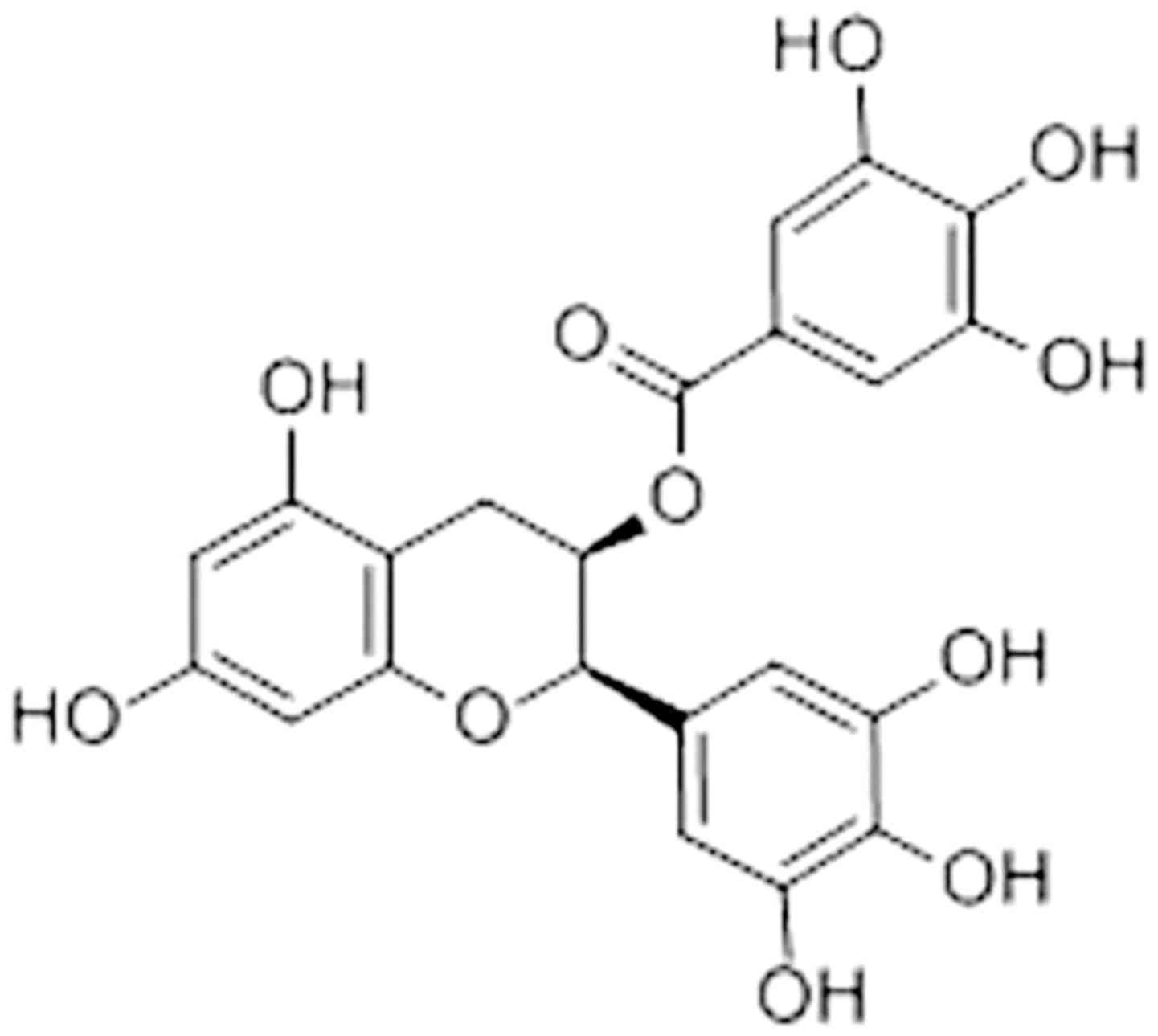
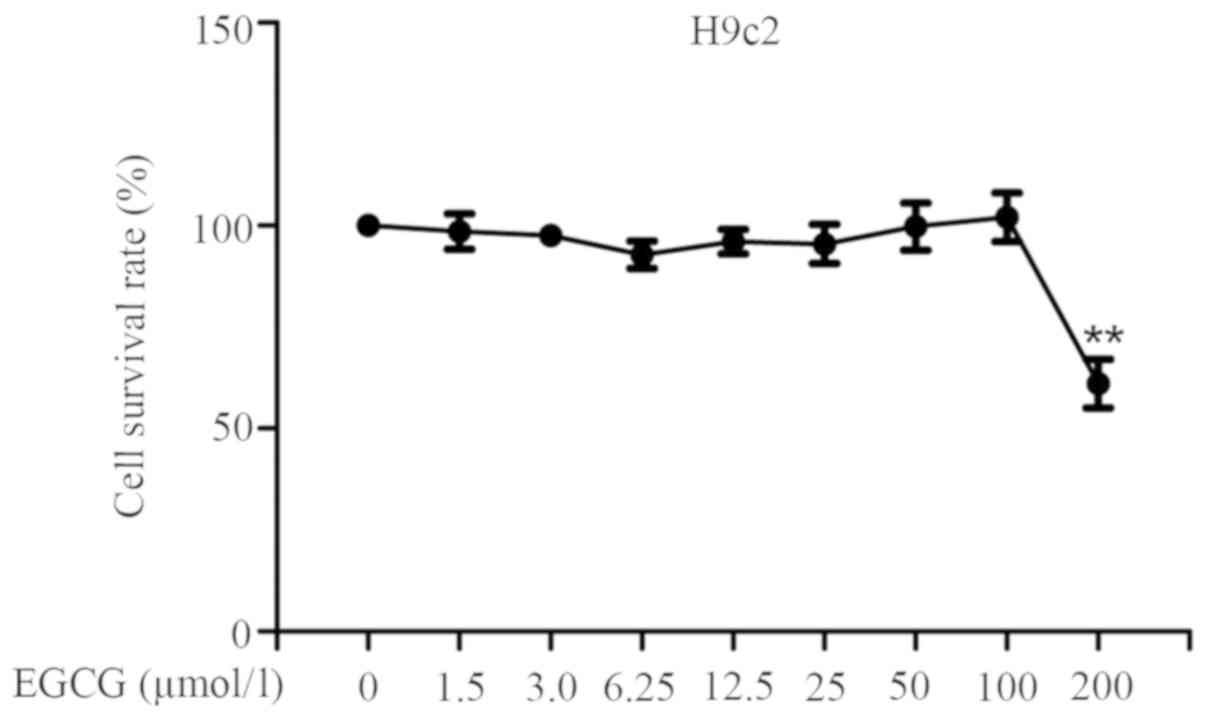
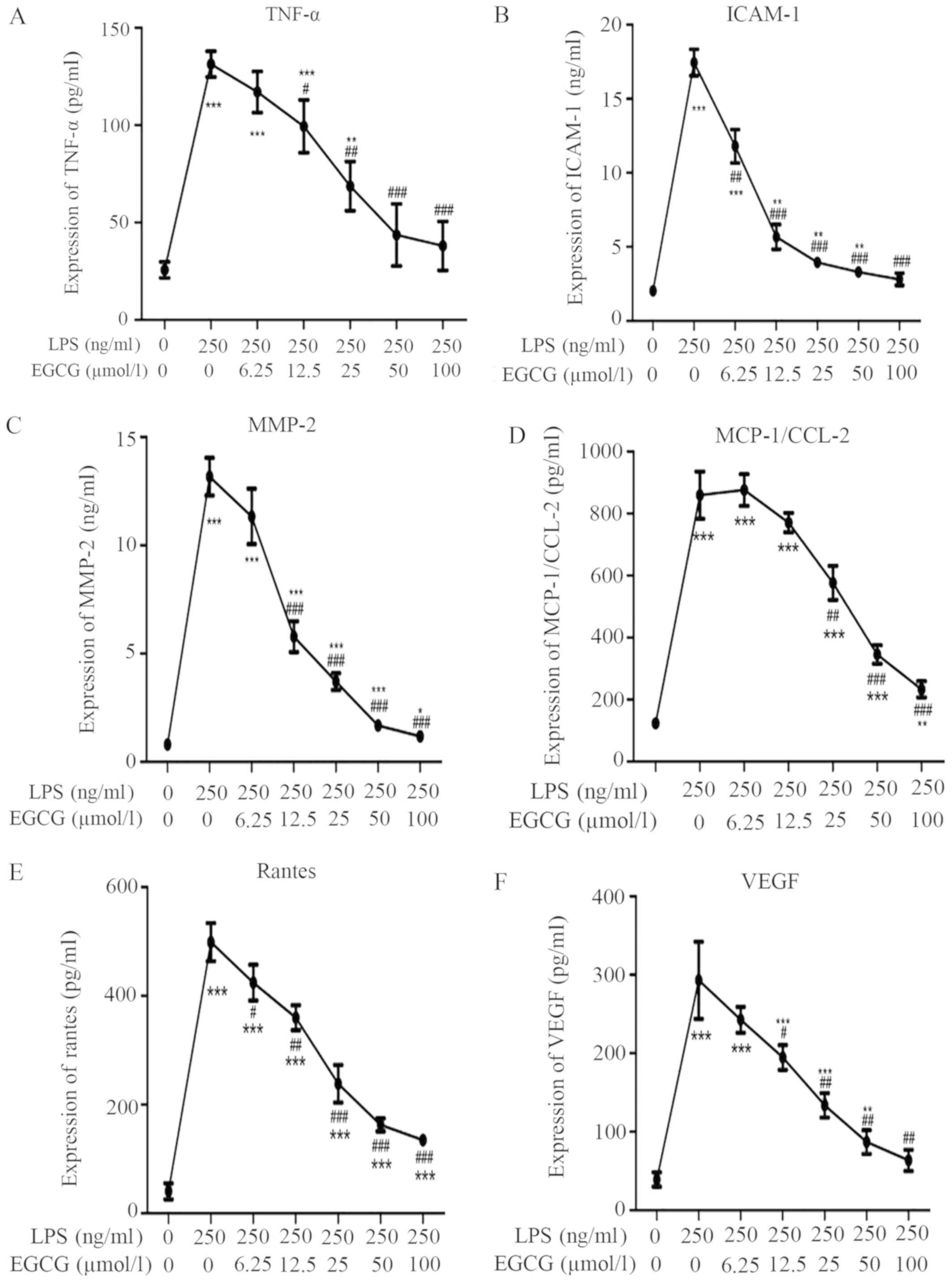
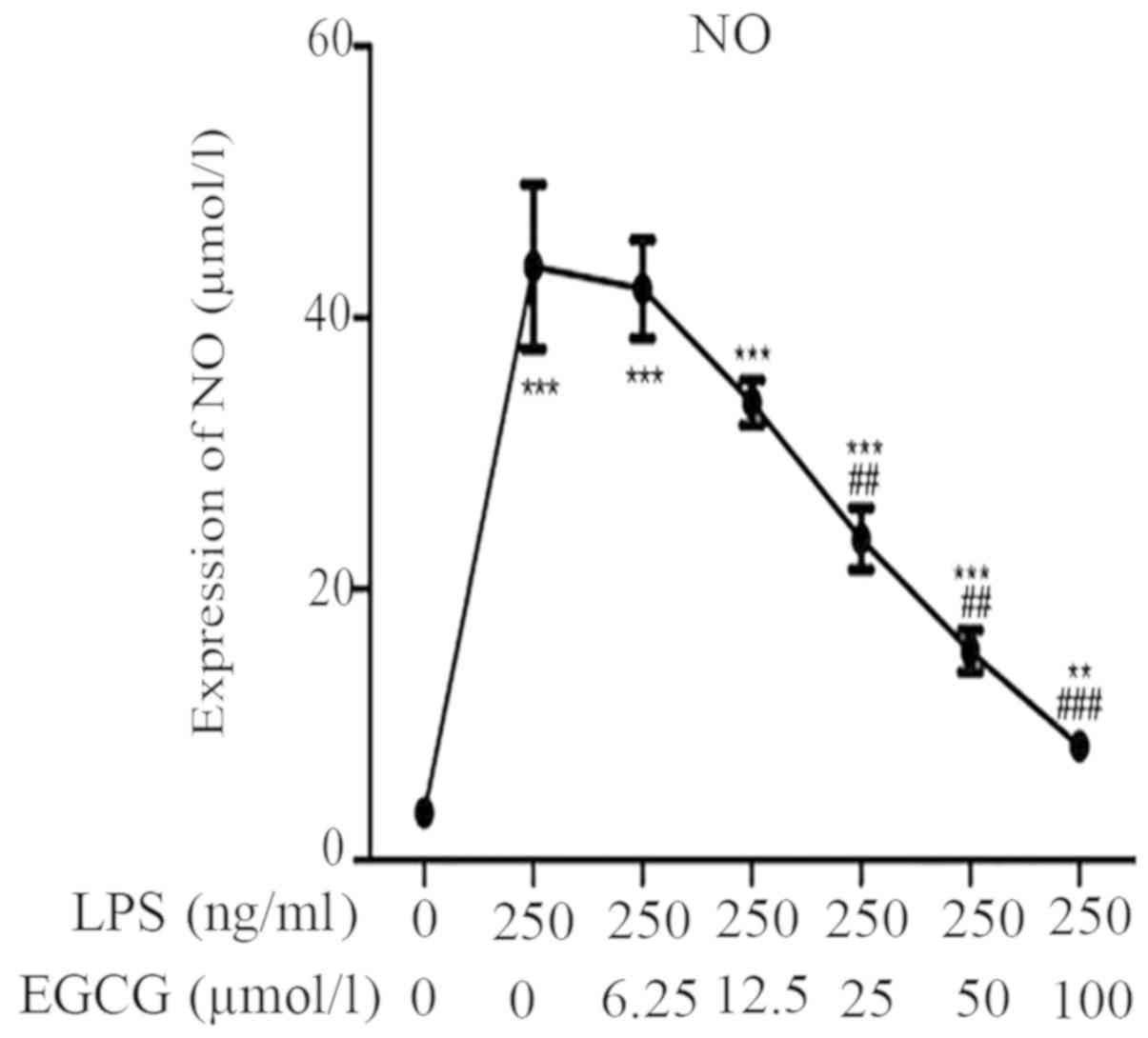
|
1
|
Coggins M and Rosenzweig A: The fire
within: Cardiac inflammatory signaling in health and disease. Circ
Res. 110:116–25. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Marchant DJ, Boyd JH, Lin DC, Granville
DJ, Garmaroudi FS and McManus BM: Inflammation in myocardial
diseases. Circ Res. 110:126–144. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Płóciennikowska A, Hromada-Judycka A,
Borzęcka K and Kwiatkowska K: Co-operation of TLR4 and raft
proteins in LPS-induced pro-inflammatory signaling. Cell Mol Life
Sci. 72:557–581. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Wan QQ, Wu D and Ye QF: The expression
profiles of circRNAs in lung tissues from rats with
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome: A
microarray study. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 493:684–689.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Zhang J, Yang S, Chen F, Li H and Chen B:
Ginkgetin aglycone ameliorates LPS-induced acute kidney injury by
activating SIRT1 via inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway. Cell
Biosci. 7(44)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Frazier WJ, Xue J, Luce WA and Liu Y: MAPK
signaling drives inflammation in LPS-stimulated cardiomyocytes: The
route of crosstalk to G-protein-coupled receptors. PLoS One.
7(e50071)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Goldberg RB: Cytokine and cytokine-like
inflammation markers, endothelial dysfunction, and imbalanced
coagulation in development of diabetes and its complications. J
Clin Endocrinol Metab. 94:3171–3182. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Cocco G, Jerie P, Amiet P and Pandolfi S:
Inflammation in heart failure: Known knowns and unknown unknowns.
Expert Opin Pharmacother. 18:1225–1233. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Tschöpe C, Walther T, Escher F, Spillmann
F, Du J, Altmann C, Schimke I, Bader M, Sanchez-Ferrer CF,
Schultheiss HP and Noutsias M: Transgenic activation of the
kallikrein-kinin system inhibits intramyocardial inflammation,
endothelial dysfunction and oxidative stress in experimental
diabetic cardiomyopathy. FASEB J. 19:2057–2059. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Ma XL, Kumar S, Gao F, Louden CS, Lopez
BL, Christopher TA, Wang C, Lee JC, Feuerstein GZ and Yue TL:
Inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase decreases
cardiomyocyte apoptosis and improves cardiac function after
myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. Circulation. 99:1685–1691.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Sun TL, Liu Z, Qi ZJ, Huang YP, Gao XQ and
Zhang YY: (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) attenuates
arsenic-induced cardiotoxicity in rats. Food Chem Toxicol.
93:102–110. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Yang CS, Lambert JD, Ju J, Lu G and Sang
S: Tea and cancer prevention: Molecular mechanisms and human
relevance. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 224:265–273. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Khan N, Afaq F, Saleem M, Ahmad N and
Mukhtar H: Targeting multiple signaling pathways by green tea
polyphenol (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Cancer Res.
66:2500–2505. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kuriyama S, Shimazu T, Ohmori K, Kikuchi
N, Nakaya N, Nishino Y, Tsubono Y and Tsuji I: Green tea
consumption and mortality due to cardiovascular disease, cancer,
and all causes in Japan: The Ohsaki study. JAMA. 296:1255–1265.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Tseng CL, Hung YJ, Chen ZY, Fang HW and
Chen KH: Synergistic effect of artificial tears containing
epigallocatechin gallate and hyaluronic acid for the treatment of
rabbits with dry eye syndrome. PLoS One.
11(e0157982)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Hammad FT and Lubbad L: The effect of
epigallocatechin-3-gallate on the renal dysfunction in the
obstructed kidney in the rat. Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol.
9:119–126. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bliksoen M, Kaljusto ML, Vaage J and
Stensløkken KO: Effects of hydrogen sulphide on
ischaemia-reperfusion injury and ischaemic preconditioning in the
isolated, perfused rat heart. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 34:344–349.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zhang W, Suo M, Yu G and Zhang M:
Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects of cryptotanshinone
through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in a rat model of neuropathic
pain. Chem Biol Interact. 305:127–133. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Franceschelli S, Pesce M, Ferrone A, Gatta
DM, Patruno A, Lutiis MA, Quiles JL, Grilli A, Felaco M and
Speranza L: Biological effect of licochalcone C on the regulation
of PI3K/Akt/eNOS and NF-kappaB/iNOS/NO signaling pathways in H9c2
cells in response to LPS stimulation. Int J Mol Sci. 18:
pii(E690)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Li X, Jiang L, Lin S, He Y, Shen G, Cai Z,
Ling M, Ni J, Zhang H and Zhang M: Inhibition of mTORC1 renders
cardiac protection against lipopolysaccharide. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 7:8432–8442. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sah JF, Balasubramanian S, Eckert RL and
Rorke EA: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits epidermal growth
factor receptor signaling pathway. Evidence for direct inhibition
of ERK1/2 and AKT kinases. J Biol Chem. 279:12755–12762.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Yang CS, Wang X, Lu G and Picinich SC:
Cancer prevention by tea: Animal studies, molecular mechanisms and
human relevance. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:429–439. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Ou HC, Song TY, Yeh YC, Huang CY, Yang SF,
Chiu TH, Tsai KL, Chen KL, Wu YJ, Tsai CS, et al: EGCG protects
against oxidized LDL-induced endothelial dysfunction by inhibiting
LOX-1-mediated signaling. J Appl Physiol (1985). 108:1745–1756.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Xu H, Lui WT, Chu CY, Ng PS, Wang CC and
Rogers MS: Anti-angiogenic effects of green tea catechin on an
experimental endometriosis mouse model. Hum Reprod. 24:608–618.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kim IB, Kim DY, Lee SJ, Sun MJ, Lee MS, Li
H, Cho JJ and Park CS: Inhibition of IL-8 production by green tea
polyphenols in human nasal fibroblasts and A549 epithelial cells.
Biol Pharm Bull. 29:1120–1125. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Ge M, Xiao Y, Chen H, Luo F, Du G and Zeng
F: Multiple antiviral approaches of (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate
(EGCG) against porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus
infection in vitro. Antiviral Res. 158:52–62. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Liang Y, Liu KWK, Yeung SC, Li X, Ip MSM
and Mak JCW: (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate reduces cigarette
smoke-induced airway neutrophilic inflammation and mucin
hypersecretion in rats. Front Pharmacol. 8(618)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Saeed NM, El-Naga RN, El-Bakly WM,
Abdel-Rahman HM, Salah ElDin RA and El-Demerdash E:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate pretreatment attenuates
doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats: A mechanistic study.
Biochem Pharmacol. 95:145–155. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Othman AI, Elkomy MM, El-Missiry MA and
Dardor M: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate prevents cardiac apoptosis by
modulating the intrinsic apoptotic pathway in isoproterenol-induced
myocardial infarction. Eur J Pharmacol. 794:27–36. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Peter B, Bosze S and Horvath R:
Biophysical characteristics of proteins and living cells exposed to
the green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCg): Review
of recent advances from molecular mechanisms to nanomedicine and
clinical trials. Eur Biophys J. 46:1–24. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Liu C, Li P, Qu Z, Xiong W, Liu A and
Zhang S: Advances in the antagonism of Epigallocatechin-3-gallate
in the treatment of digestive tract tumors. Molecules. 24:
pii(E1726)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zhu W, Mei H, Jia L, Zhao H, Li X, Meng X,
Zhao X, Xing L and Yu J: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate mouthwash
protects mucosa from radiation-induced mucositis in head and neck
cancer patients: A prospective, non-randomised, phase 1 trial.
Invest New Drugs: Nov 7, 2019 (Epub ahead of print).
|
|
33
|
Seok JK, Lee JW, Kim YM and Boo YC:
Punicalagin and (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate rescue cell
viability and attenuate inflammatory responses of human epidermal
keratinocytes exposed to airborne particulate matter PM10. Skin
Pharmacol Physiol. 31:134–143. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Holczer M, Besze B, Zámbó V, Csala M,
Bánhegyi G and Kapuy O: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) promotes
autophagy-dependent survival via influencing the balance of
mTOR-AMPK pathways upon endoplasmic reticulum stress. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2018(6721530)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Ma Y, Hu Y, Wu J, Wen J, Li S, Zhang L,
Zhang J, Li Y and Li J: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits
angiotensin II-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy via regulating
Hippo signaling pathway in H9c2 rat cardiomyocytes. Acta Biochim
Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 51:422–430. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Zhang C, Liao P, Liang R, Zheng X and Jian
J: Epigallocatechin gallate prevents mitochondrial impairment and
cell apoptosis by regulating miR-30a/p53 axis. Phytomedicine.
61(152845)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Magi S, Nasti AA, Gratteri S, Castaldo P,
Bompadre S, Amoroso S and Lariccia V: Gram-negative endotoxin
lipopolysaccharide induces cardiac hypertrophy: Detrimental role of
Na(+)-Ca(2+) exchanger. Eur J Pharmacol. 746:31–40. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Li Y, Liu X, Du A, Zhu X and Yu B: miR-203
accelerates apoptosis and inflammation induced by LPS via targeting
NFIL3 in cardiomyocytes. J Cell Biochem. 120:6605–6613.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Su Q, Yao J and Sheng C: Geniposide
Attenuates LPS-induced injury via Up-regulation of miR-145 in H9c2
cells. Inflammation. 41:1229–1237. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Massion PB, Feron O, Dessy C and Balligand
JL: Nitric oxide and cardiac function: Ten years after, and
continuing. Circ Res. 93:388–398. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Franceschelli S, Pesce M, Ferrone A,
Patruno A, Pasqualone L, Carlucci G, Ferrone V, Carlucci M, de
Lutiis MA, Grilli A, et al: A Novel biological role of α-mangostin
in modulating inflammatory response through the activation of
sirt-1 signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol. 231:2439–2451.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Franceschelli S, Pesce M, Ferrone A, De
Lutiis MA, Patruno A, Grilli A, Felaco M and Speranza L:
Astaxanthin treatment confers protection against oxidative stress
in U937 cells stimulated with lipopolysaccharide reducing
O2-production. PLoS One. 9(e88359)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Hori M and Yamaguchi O: Is tumor necrosis
factor-alpha friend or foe for chronic heart failure? Circ Res.
113:492–494. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Khodadadi I, Vahedi MS, Abdi M, Daneshkhah
N, Rahbari R, Menbari S, Ahmadi D, Ahmadi A, Lahoorpour F,
Hakhamaneshi MS, et al: Evaluation of adenosine deaminase (ADA)
isoenzymes activity and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNFα)
concentration in chronic heart failure. EXCLI J. 13:58–66.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Eskandari V, Amirzargar AA, Mahmoudi MJ,
Rahnemoon Z, Rahmani F, Sadati S, Rahmati Z, Gorzin F, Hedayat M
and Rezaei N: Gene expression and levels of IL-6 and TNFα in PBMCs
correlate with severity and functional class in patients with
chronic heart failure. Ir J Med Sci. 187:359–368. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Parish RC and Evans JD: Inflammation in
chronic heart failure. Ann Pharmacother. 42:1002–1016.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Everett BM, Cornel JH, Lainscak M, Anker
SD, Abbate A, Thuren T, Libby P, Glynn RJ and Ridker PM:
Anti-Inflammatory therapy with canakinumab for the prevention of
hospitalization for heart failure. Circulation. 139:1289–1299.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Zhang H, Li H, Ge A, Guo E, Liu S and
Zhang L: Long non-coding RNA TUG1 inhibits apoptosis and
inflammatory response in LPS-treated H9c2 cells by down-regulation
of miR-29b. Biomed Pharmacother. 101:663–669. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Hao R and Su G, Sun X, Kong X, Zhu C and
Su G: Adiponectin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced cell injury
of H9c2 cells by regulating AMPK pathway. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin
(Shanghai). 51:168–177. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Gonzalez A, Ravassa S, Beaumont J, López B
and Díez J: New targets to treat the structural remodeling of the
myocardium. J Am Coll Cardiol. 58:1833–1843. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Wu Y, Xia ZY, Meng QT, Zhu J, Lei S, Xu J
and Dou J: Shen-Fu injection preconditioning inhibits myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury in diabetic rats: Activation of eNOS
via the PI3K/Akt pathway. J Biomed Biotechnol.
2011(384627)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Li Q, Shen L, Wang Z, Jiang HP and Liu LX:
Tanshinone IIA protects against myocardial ischemia reperfusion
injury by activating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Biomed
Pharmacother. 84:106–114. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Ibrahim AS, El-Remessy AB, Matragoon S,
Zhang W, Patel Y, Khan S, Al-Gayyar MM, El-Shishtawy MM and Liou
GI: Retinal microglial activation and inflammation induced by
amadori-glycated albumin in a rat model of diabetes. Diabetes.
60:1122–1133. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|